Blood types
Abdulqadir Kh.HamadAbdulqadir.bio@raparinuni.org
University of Ishik
Faculty of dentistryPractical Medical Physiology
2th stage
Ab-Ag Reactions
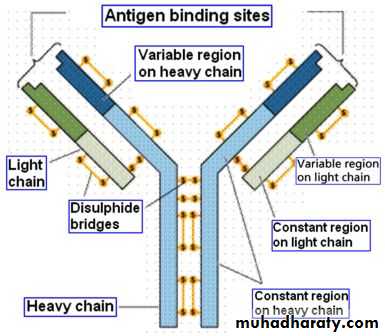
ANTIBODY - is a glycoprotein molecule made by Blymphocytes, present in serum and other body fluids which mediates humoral immunity. Antibodies are shaped like a "Y" with the two "arms" of the Y being the regions that bind antigens and the "tail" of the Y being a constant region that is recognized by Fc receptors
ANTIGEN - A molecule that binds to antibodies . Antigens come in many forms: for example, small molecules in the environment and a huge array of bacterial and viral surface proteins, lipids and carbohydrates.
Ab-Ag Reactions
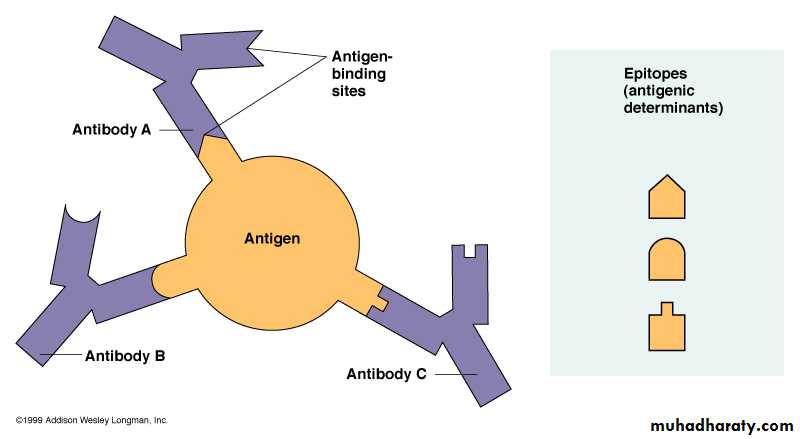
EPITOPE (= “antigenic determinant” ) - a site on the surface of an antigen molecule to which a single antibody molecule binds; generally an antigen has (and generally does) several or many different epitopes and reacts with many different antibodies.
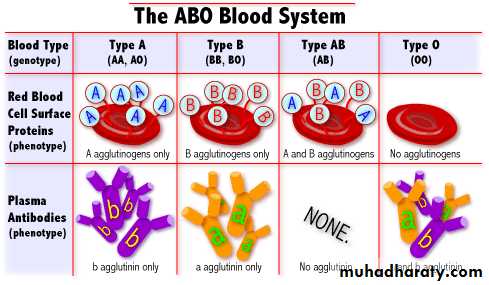
The ABO System
Blood Types ( Antibodies and antigens will agglutinate)Antigens on RBCs (A, B, AB or none = O)
Antibodies in plasma (anti A, anti B, anti AB)Rh antigens & antibodies
Four blood groups based on presence or absence of blood antigens (agglutinogens) on surface of RBCs
• A - A antigen
• B - B antigen
• AB - both AB antigens
• O - no AB antigens
•
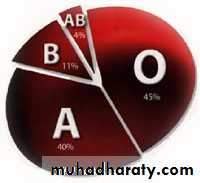
• 45%
• Common Blood groups are the 4 blood types?
• 4%
• 40%
• 11%
• Rh (D) positive 85%
• Rh (D) negative 15%
ABO Blood Grouping System
ABO Blood Grouping System
There are four major blood groups determined by the presence or absence of two antigens – A and B – on the surface of red blood cells:• Group A – has only the A antigen on red cells (and B antibody in the plasma)
• Group B – has only the B antigen on red cells (and A antibody in the plasma)
• Group AB – has both A and B antigens on red cells (but neither A nor B antibody in the plasma)
• Group O – has neither A nor B antigens on red cells (but both A and B antibody are in the plasma)
• Summary
• • 11
Rh Factors (Rhesus monkeys )The presence of the protein, or lack of it, is referred to as the Rh (for Rhesus) factor.
If your blood does contain the protein, your blood is said to be Rh positive (Rh+). If your blood does not contain the protein, your blood is said to be Rh negative (Rh-).
A+ A-B+ B-AB+ AB-O+ O-
• RH is the most complex system, with over 45 antigens
• Discovered in 1940 after work on Rhesus monkeysABO & Rh Blood Grouping System
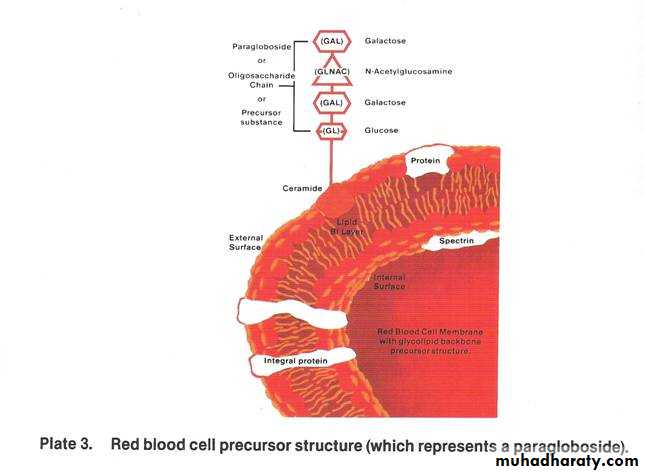
A red blood cell (RBC) with three different antigens on the surface of its membrane. The antigens are glycolipids.ABO & Rh Blood Grouping System
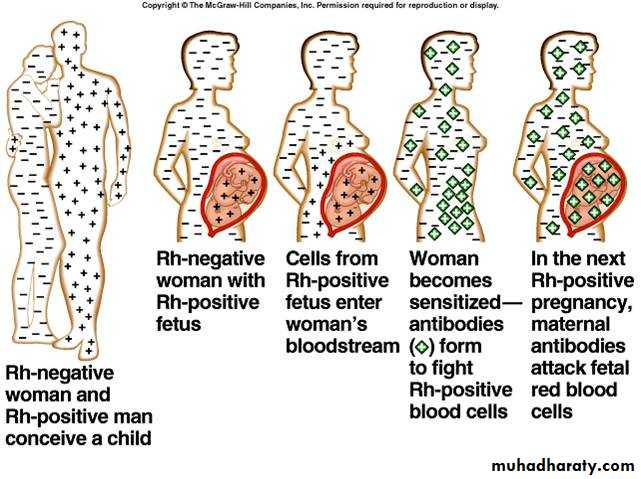
Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn (HDN)
Usually related to D antigen exposure and the
formation of anti-D
• Resulted from D negative female and D positive male producing and offspring.
– The baby will probably be D positive.
• 1st pregnancy not effected, the 2nd pregnancy and on will be effected.
• To prevent this occurrence the female is injected with anti RH antibodies.
Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn – How it Occurs
A. child is Rh positiveB. during pregnancy fetal Rh + RBC escape into maternal circulation
C. Mother produces antibodies to Rh (D) antigen
D. Second pregnancy with Rh (D) positive child results in destruction of fetal D positive RBC
A
B
C
D
Reference
http://anthro.palomar.edu/blood/ABO_system.htmhttp://www.biology.arizona.edu/human_bio/
problem_sets/blood_types/genotypes.html
http://www.redcrossblood.org/learn-about-blood/bloodtypes
http://www.icr.org/article/3647/