
Dr. Taqey Ali AlMosawey
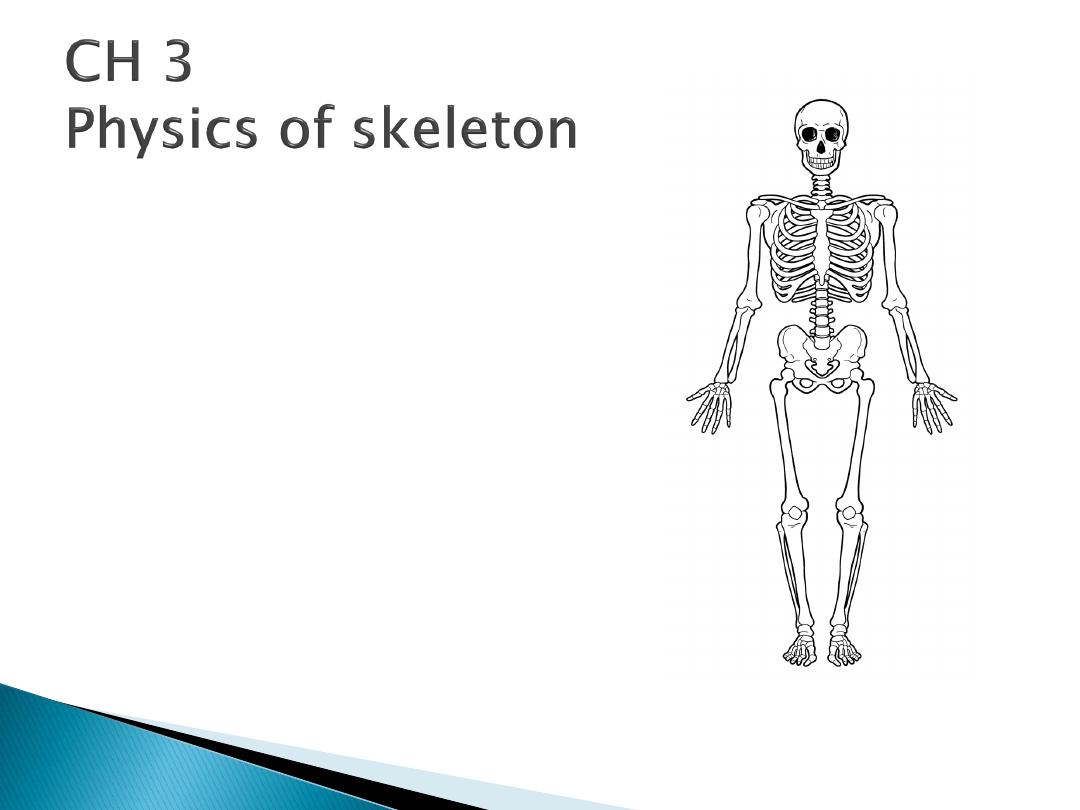
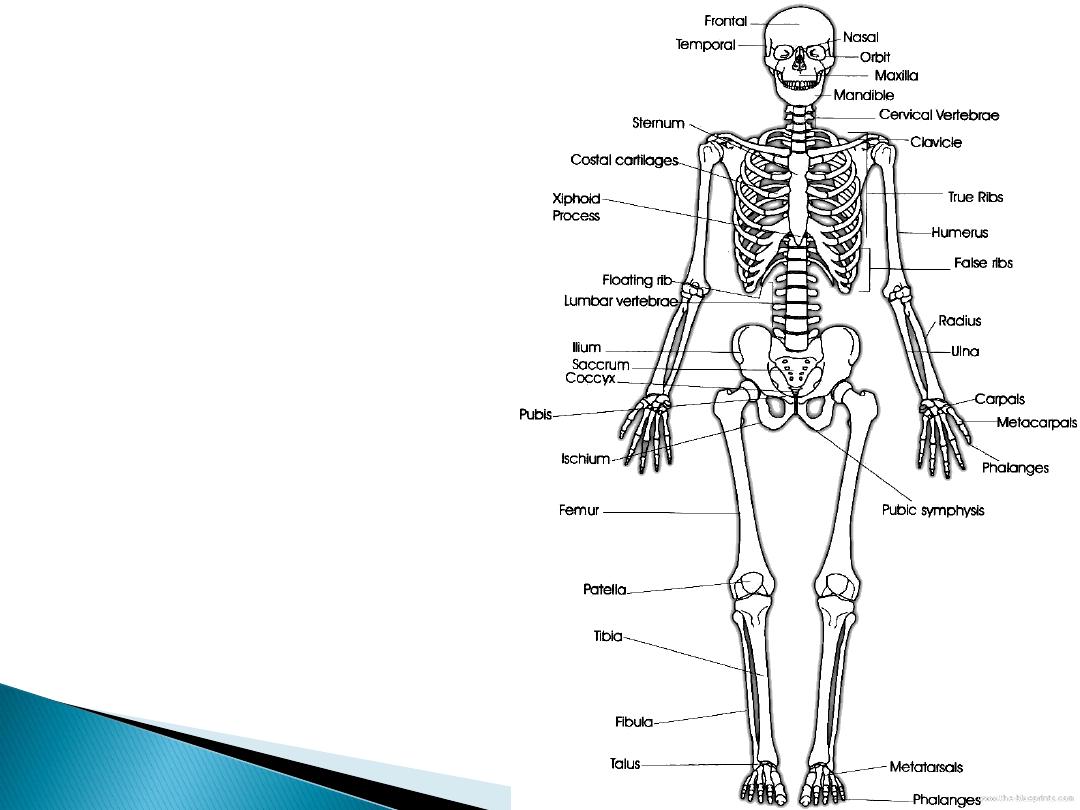
There are 206
bones in the body
(fig.1)
Fig1 skeleton

They are designed and oriented to suit their
functions. The bones has at lest six functions
which are:
1- supporting: e.g. legs support the body, Neck
vertebrae support the head, the back bone
vertebrae support the track and the body.
2- locomotion: legs and knee, joints.
3- protection and organs: the skull protects the
brain, chest ribs and sternum protect the heart
and lungs, and the back bone protects the Spinal
cord.

4- storage of chemical: bones are Ca
++
bank
of the body i.e. absorber lease Ca
++
sensor →
parathyroid gated → paratherome → bones →
Ca
++
.
5- nourishment: the teeth in the upper and
lower jaws used for cutting and chewing the
food. Cut (incisors, tear (canines) grand
(molars)). 2 kind of teeth: deciduous (baby)
permanent.
6- sound transmission: the ossicles in the
middle ear transmit the sound vibrations to
the sound.

7- breathing: ribs and nuseles
forwocagewhich increase or decrease the
chest volume to maintain breath i.e.
inspiration (inhalation and expirations)
muscle are attached to the bone, by tendons
and ligaments to support the body and for
locomotion and some other function of the
bones.
Bones are living tissues has a bloods supply
and nerves. Most of the bone tissue is inert
but about of 2% of the bone cells maintain
the bone in a healthy condition which is
called osteocytes it is distributed through the
bone.

The bone of the body contains about 1000 gm of
calcium. The body destroys about 0.5 gm of Ca
++
each day (this process is called osteoclast) and
built up about the same amount of Ca
++
(osteoblast. This process is called bone
remodeling. In youth; osteoblast
<
osteoclast. In
eldery: osteoblast
>
osteoclast which reduce
mass and volume of the bone which is called
osteoporosis (porons bones) (fig.2) which results
in bone fracture (mainly in the hips of old
women). The osteopotic bone is weaker than the
normal bone.
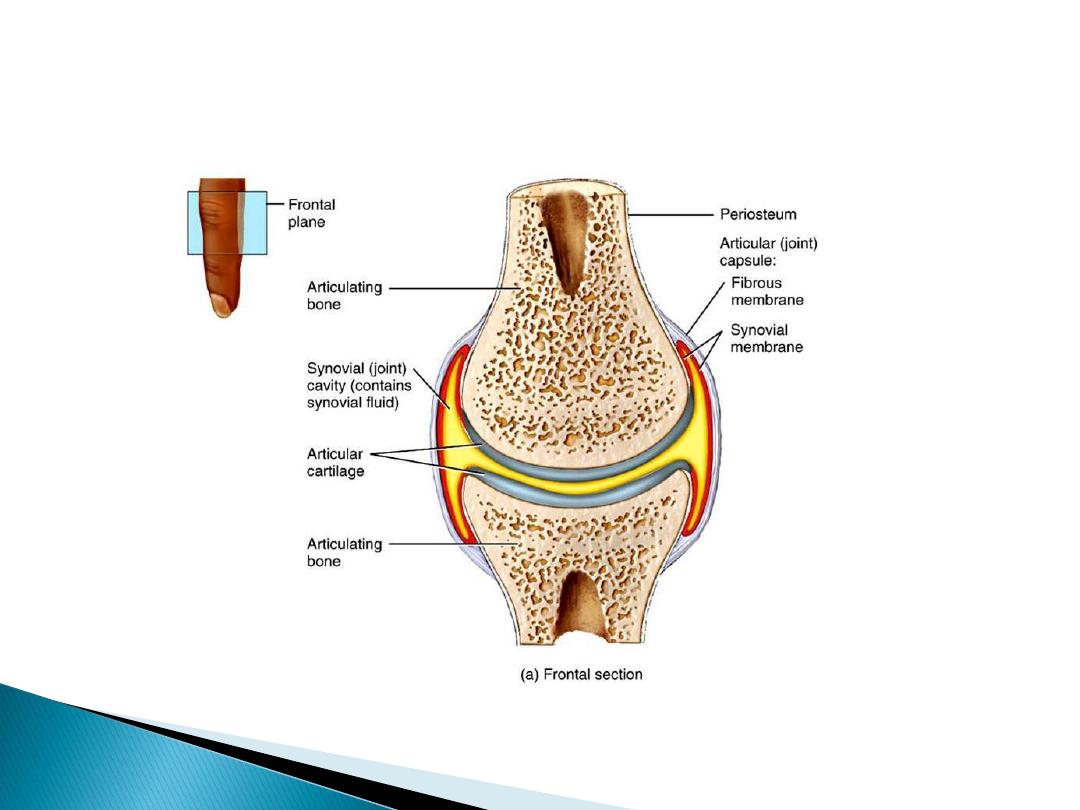
Fig2 joint

Question: calculate the time required for your
bones to be completely remodel?
Composition of the bone: the bone is
composed from two quite different malerials
plus wates:
Collagen: it is organic material forms about
40% of the weight of solid bone and 60% of it
volume. Its different from the other collagen
in the skin and other parts of the body.
Bone minerals: it is the inorganic parts of the
bone. Forms about 60% of the weight of solid
bone and 40% of its volume. It is made of
caliciume hydroxyapetite Ca
10
(PO
4
)
6
(OH)
2
.

When the collagen is separated from bone
minerals it is flexible like rubber while bone
manirals are fragile and can be crushed with
the fingers bones are formed from very small
crystals which are made from minerals and
fited in the template of collagen. The crystals
are rod shaped of diameters of 20 to 70 Aº
and lengths of 50 to 100 Aº these crystals
has very large area of 400000 m
2
(about 100
acres). These crystals are surrounded by a
layer of water contains many nutrients and
chemical needed by the bone which are
normally supplied to the body by the blood.
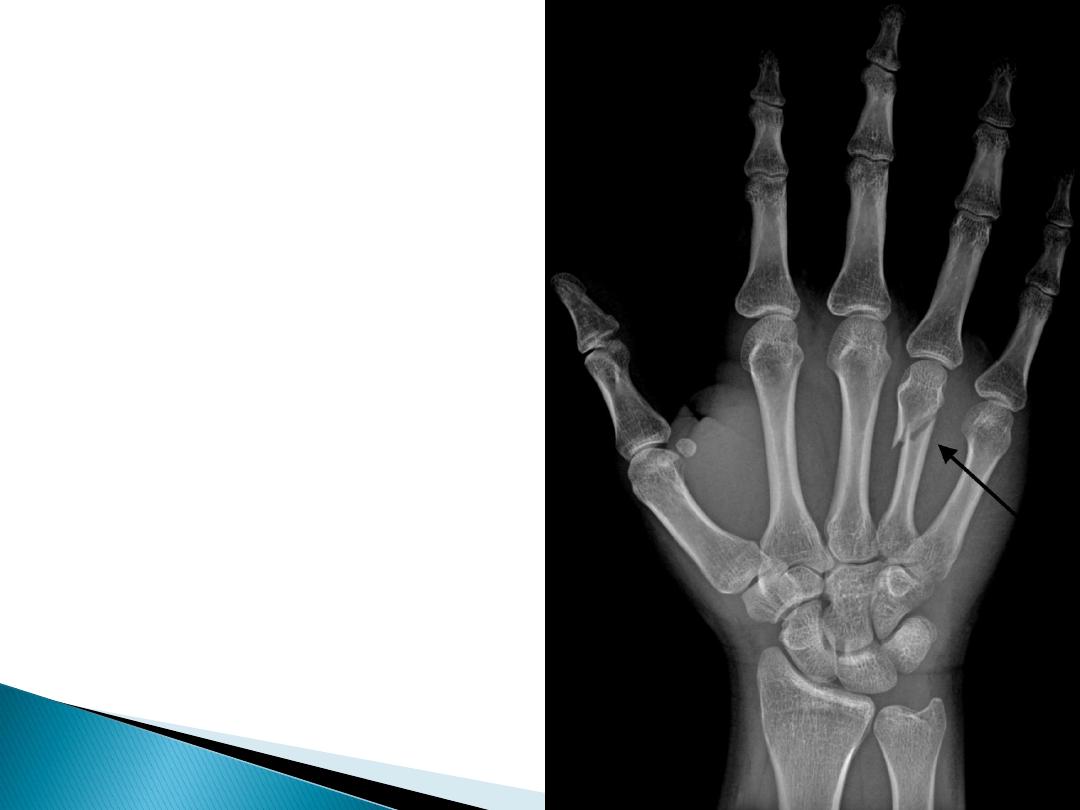
The bone containts a
large amount of Ca
and because Ca is a
heavy material
(atomic mass=40)
therfore it normally
absorbs X-ray when
the bone irradiated
by this radiation the
colure of X-ray film
will be more whiter
after irradiation.
(fig.3)

The bones are composed by one or two types
which are:
Compact bone: it is solid bone which normally
formed the shaft of the bone and it is thicker at
the middle of the bone and thinner at the two
ends.
Trabecular bone: it is a spongy or cancellons
bone made up of thin thread – like trabeculae.
Trabecular bone is considreably weaker than
compact bone due to the reduced to the amount
of bone in a given volume.

The osteoporotic boneis also weaker: the
density of the bone 1.9 gm/cm
3
which
remains constant through all the life. It also
remains nearly 1.9 in the osteoporotic bone
even when the bone becomes more porous
and disappears from inside (endosteal) and it
strength is reduced because it become
thinner the length of the bone L in charged
when it placed under a tension or
compression like any other material.

According to Hooke’s low the strain is acselas
is linearly with stress (where F is the applied
force and A is the cross sectional area of the
bone) (fig.4). as the force increases, the
lengthily of the increases more rapidly and
the bone breaks at stress of about 120
N/mm
2
. We can measure young’s modulus
from the liner portion of the curve only:-

This equation is valid for both tension and
compression. The bones don’t normally break
due to compression, they usually break due
to shear or under tension. The shear is
happened by catching the foot and twisting
the bone while falling. A shear fracture often
results in spiral break in which the bone
puncture the skin. This kind of fracture is
called compound fracture and it is become
more infected than simple fracture. The body
can repair bone fracture rapidly if the fracture
reason is immobilized. At eldery the feeling
process is affected.

Fracture in eldery or in the back bone
requires long time to repair and the patient
stay tying on the body for few months which
results in bed ulcers. The patient should
stand as soon as he can. Bed ulcers can be
treated by ultra violet rays.
Metal prosthetic chip joints, pins, nails and so
forth are often used to repair such damaged
bones. Local electrical fields in the bone may
play a role in growth and repair of the bone
because the bone generates electric charged
when bent bones joints.

Rheumatoid arthritis which result in over
production of synovial fluid in the joint and
causes swollen joints
Osteoarthritis a disease of the joint it self.
Threads squeeze synovial fluid from the
porosi, of bone low viscosity means good
lubrication the coefficient of friction reduced
between the bones in the knee by synovial
fluid to less than 0.01 where that of steel
blade on ice is about 0.03 .
