
1-Generation stations
1-1 What is Power Plant?
A power plant or a power generating station, is basically an industrial
location that is utilized for the generation and distribution of electric power in mass
scale, usually in the order of several 1000 Watts. These are generally located at the
sub-urban regions or several kilometers away from the cities or the load centers,
because of its requisites like huge land and water demand, along with several
operating constraints like the waste disposal etc. For this reason, a power
generating station has to not only take care of efficient generation but also the fact
that the power is transmitted efficiently over the entire distance. And that’s why,
the transformer switch yard to regulate transmission voltage also becomes an
integral part of the power plant.
At the center of it, however, nearly all power generating stations has an A.C.
generator or an alternator, which is basically a rotating machine that is equipped to
convert energy from the mechanical domain (rotating turbine) into electrical
domain by creating relative motion between a magnetic field and the conductors.
The energy source harnessed to turn the generator shaft varies widely, and is
chiefly dependent on the type of fuel used.
1-2Types of Power Station:
A power plant can be of several types depending mainly on the type of fuel
used. Since for the purpose of bulk power generation, only thermal, nuclear and
hydro power comes handy, Let us have a look in these types of power stations in
details.

1-2-1 Steam Power Station:
A thermal power station or a coal fired thermal power plant is by far, the
most conventional method of generating electric power with reasonably high
efficiency. It uses coal as the primary fuel to boil the water available to
superheated steam for driving the steam turbine. The steam turbine is then
mechanically coupled to an alternator rotor, the rotation of which results in the
generation of electric power.
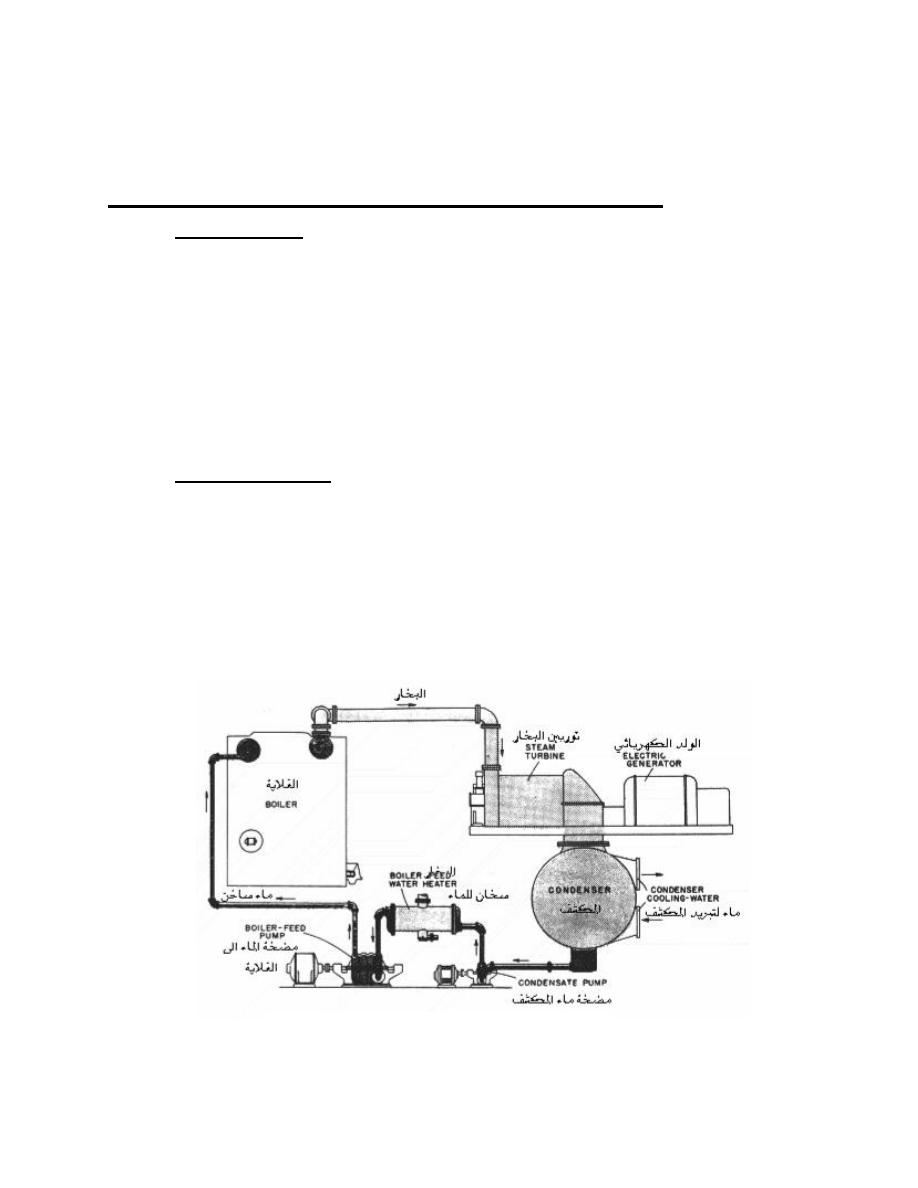
Theory of Steam Power Station:
The theory of thermal power station or working of thermal power station is
very simple. A power generation plant mainly consists of alternator runs with help
of steam turbine. The steam is obtained from high pressure boilers.
In coal thermal power plant, the steam is produced in high pressure in the
steam boiler due to burning of fuel (pulverized coal) in boiler furnaces. This steam
is further supper heated in a super heater. This supper heated steam then enters into
the turbine and rotates the turbine blades. The turbine is mechanically so coupled
with alternator that its rotor will rotate with the rotation of turbine blades. After
entering in turbine the steam pressure suddenly falls and corresponding volume of
the steam increases. After imparting energy to the turbine rotor the steam passes
out of the turbine blades into the condenser. In the condenser the cold water is
circulated with the help of pump which condenses the low pressure wet steam.
This condensed water is further supplied to low pressure water heater where the
low pressure steam increases the temperature of this feed water, it is again heated
in high pressure.
For better understanding we furnish every step of function of a thermal
power station as follows:-
1) First the pulverized coal is burnt into the furnace of steam boiler.
2) High pressure steam is produced in the boiler.
3) This steam is then passed through the super heater, where it further heated
up.
4) This supper heated steam is then entered into a turbine at high speed.
5) In turbine this steam force rotates the turbine blades that means here in
the turbine the stored potential energy of the high pressured steam is converted into
mechanical energy.
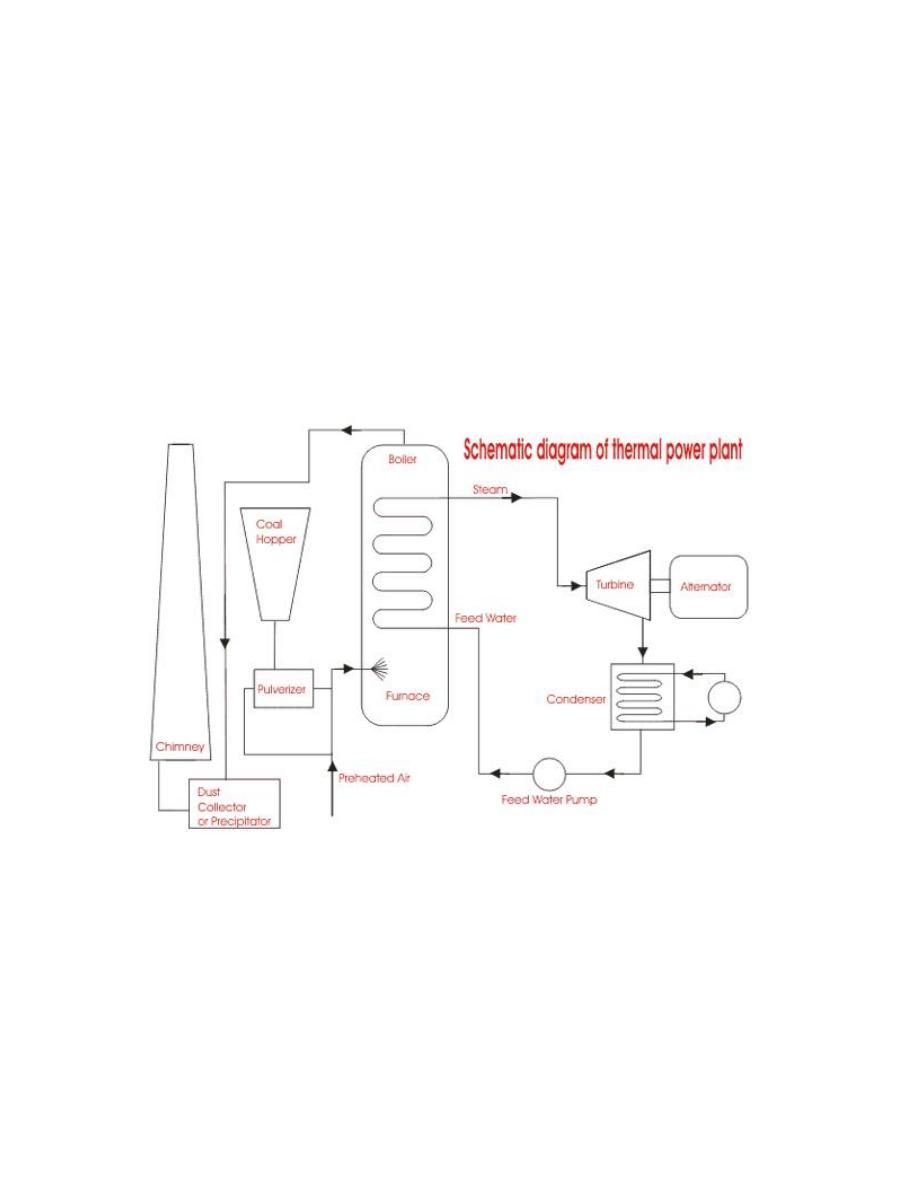
6) After rotating the turbine blades, the steam has lost its high pressure,
passes out of turbine blades and enters into a condenser.
7) In the condenser the cold water is circulated with help of pump which
condenses the low pressure wet steam.
8) This condensed water is then further supplied to low pressure water heater
where the low pressure steam increases the temperature of this feed water, it is then
again heated in a high pressure heater where the high pressure of steam is used for
heating.
9) The turbine in thermal power station acts as a prime mover of the
alternator.
Figure(1)
Line Diagram of Power Plant

Efficiency of Steam Power Station or Plant:
The overall efficiency of a thermal power station or plant varies from 20% to
26% and it depends upon plant capacity.
Installed plant capacity
Average overall thermal efficiency
upto 1MW
4%
1MW to 10MW
12%
10MW to 50MW
16%
50MW to 100MW
24%
above 100MW
27%
Steam Power Plant Location:
Many points to be considered to decide the best optimized location of the
power plant .
1) The electric power generation plant must be constructed at such a place
where the cost of land is quite reasonable.
2) The land should be such that the acquisition of private property must be
minimum .
3) A large quantity of cooling water is required for the condensers etc of
thermal power generation plant, hence the plant should preferably situated beside
big source of natural water source such as big river.
4) Availability of huge amount of fuel at reasonable cost is one of the major
criterion for choosing plant location.
5) The plant should be established on plane land.
6) The soil should be such that it should provide good and firm foundation
of plant and buildings.
7) The thermal power plant location should not be very nearer to dense
locality as there are smoke, noise steam, water vapors etc.
8) There must be ample scope of development of future demand.
9) Place for ash handling plant for thermal power station should also be
available very nearby.
10) Very tall chimney of power station should not obstruct the traffics of air
ships.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Steam Power Station:
a)
Advantages:
1) Economical for low initial cost other than any generating plant.
2) Land required less than hydro power plant.
3) Since coal is main fuel & its cost is quite cheap than petrol/diesel so
generation cost is economical.
4) There are easier maintenance.
5) Thermal power plant can be installed in any location where transportation
& bulk of water are available.
b) Disadvantages:
1) The running cost for a thermal power station is comparatively high due
to fuel , maintenance etc.
2) Large amount of smoke causes air pollution .The thermal power station is
responsible for Global warming.
3) The heated water that comes from thermal power plant has an adverse
effect on the lives in the water and disturbs the ecology.
4) Overall efficiency of thermal power plant is low like less 30%.
Figure(2)
Steam Power Plant

1-2-2 Gas Power Station:
Gas turbine engines derive their power from burning fuel in a combustion
chamber and using the fast flowing combustion gases to drive a turbine in much
the same way as the high pressure steam drives a steam turbine.
One major difference however is that the gas turbine has a second turbine
acting as an air compressor mounted on the same shaft. The air turbine
(compressor) draws in air, compresses it and feeds it at high pressure into the
combustion chamber increasing the intensity of the burning flame.
It is a positive feedback mechanism. As the gas turbine speeds up, it also
causes the compressor to speed up forcing more air through the combustion
chamber which in turn increases the burn rate of the fuel sending more high
pressure hot gases into the gas turbine increasing its speed even more.
Uncontrolled runaway is prevented by controls on the fuel supply line which limit
the amount of fuel fed to the turbine thus limiting its speed.
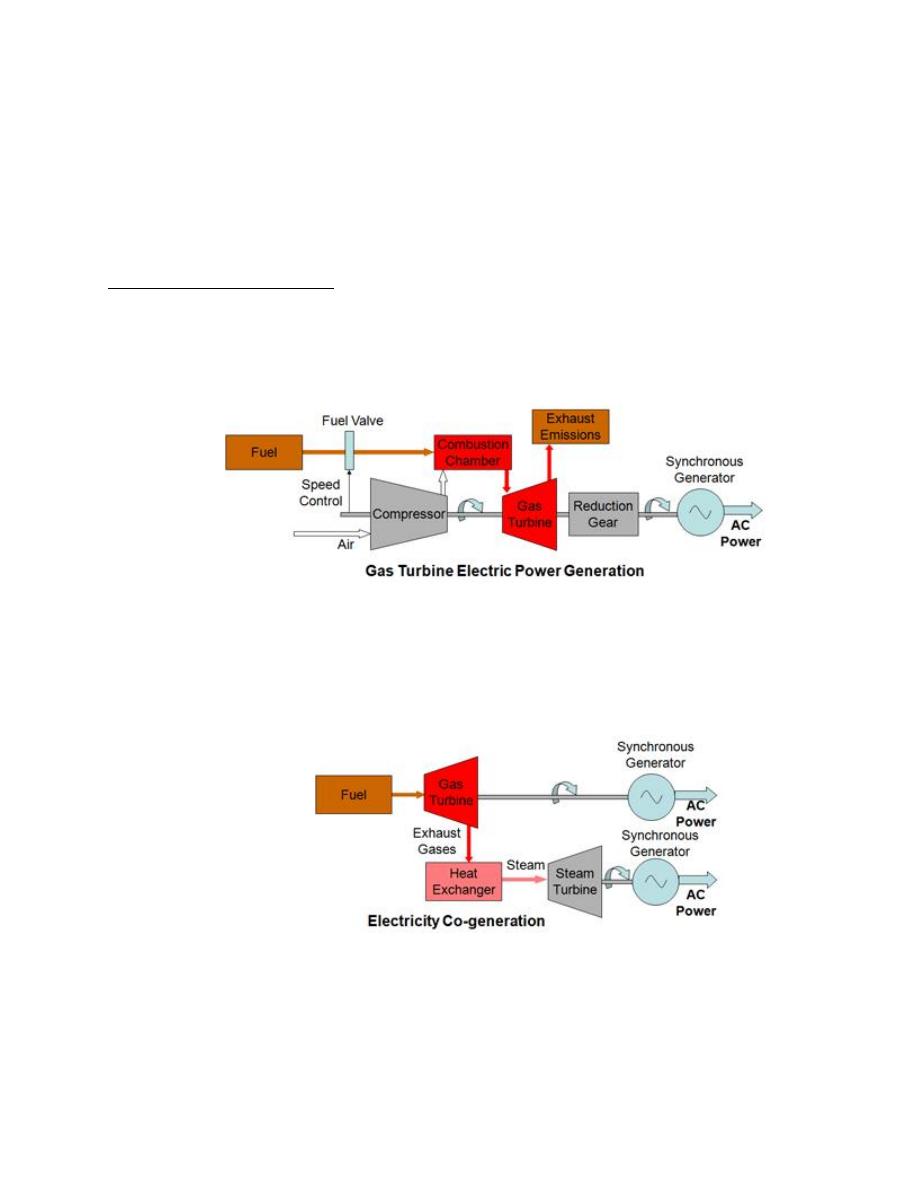
Figure(3)
Gas Power Plant
The thermodynamic process used by the gas turbine is known as the Brayton
cycle. Analogous to the Carnot cycle in which the efficiency is maximised by
increasing the temperature difference of the working fluid between the input and
output of the machine, the Brayton cycle efficiency is maximised by increasing the
pressure difference across the machine. The gas turbine is comprised of three main
components: a compressor, a combustor, and a turbine. The working fluid, air, is
compressed in the compressor (adiabatic compression - no heat gain or loss), then
mixed with fuel and burned by the combustor under constant pressure conditions in
the combustion chamber (constant pressure heat addition). The resulting hot gas
expands through the turbine to perform work (adiabatic expansion). Much of
the power produced in the turbine is used to run the compressor and the rest is
available to run auxiliary equipment and do useful work. The system is an open
system because the air is not reused so that the fourth step in the cycle, cooling the
working fluid, is omitted .
Gas turbines have a very high power to weight ratio and are lighter and
smaller than internal combustion engines of the same power. Though they are
mechanically simpler than reciprocating engines, their characteristics of high speed
and high temperature operation require high precision components and exotic
materials making them more expensive to manufacture
Turbine Configurations
Gas turbine power generators are used in two basic configurations
Simple Systems
consisting of the gas turbine driving an
electrical power generator.
Combined Cycle Systems
which are designed for maximum
efficiency in which the hot exhaust gases from the gas turbine are
used to raise steam to power a steam turbine with both turbines being
connected to electricity generators.

Advantages & Disadvantages Of Gas Turbine Plants:
a) Advantages
1. They are more compact, since fuel is burnt directly in the small
combustion Chamber in the gas turbine rather than in a bulky boiler.
2. Gas Turbine has no condenser.
3. They can be started and take more load quickly (i.e.15 - 30 min).
4. They are simpler in design and easy to maintain.
5. They consume less metal and other materials for the same capacity.
6. They cost less.
7.
Unlike steam turbines , they require very less water for cooling.
8. Gas Turbine is more suitable for power generation, where water
scarcity exists or the water is more precious.
b) Disadvantages:
1. They have a lower specific power .
2. They have lower efficiency at the modern state of progress.
3. They have a shorter service life .
4. They are more sensitive to fuel quality .
1-2-3 Hydro Power Plant :
Power system mainly contains three parts namely generation, transmission
and distribution. Generation means how to generate electricity from the available
source and there are various methods to generate electricity but in this article we
only focused on generation of electricity by the means of hydro or water (hydro
power plant). As we know that the power plant is defined as the place where power
is generated from a given source, so here the source is hydro that’s why we called
it hydro power plant.
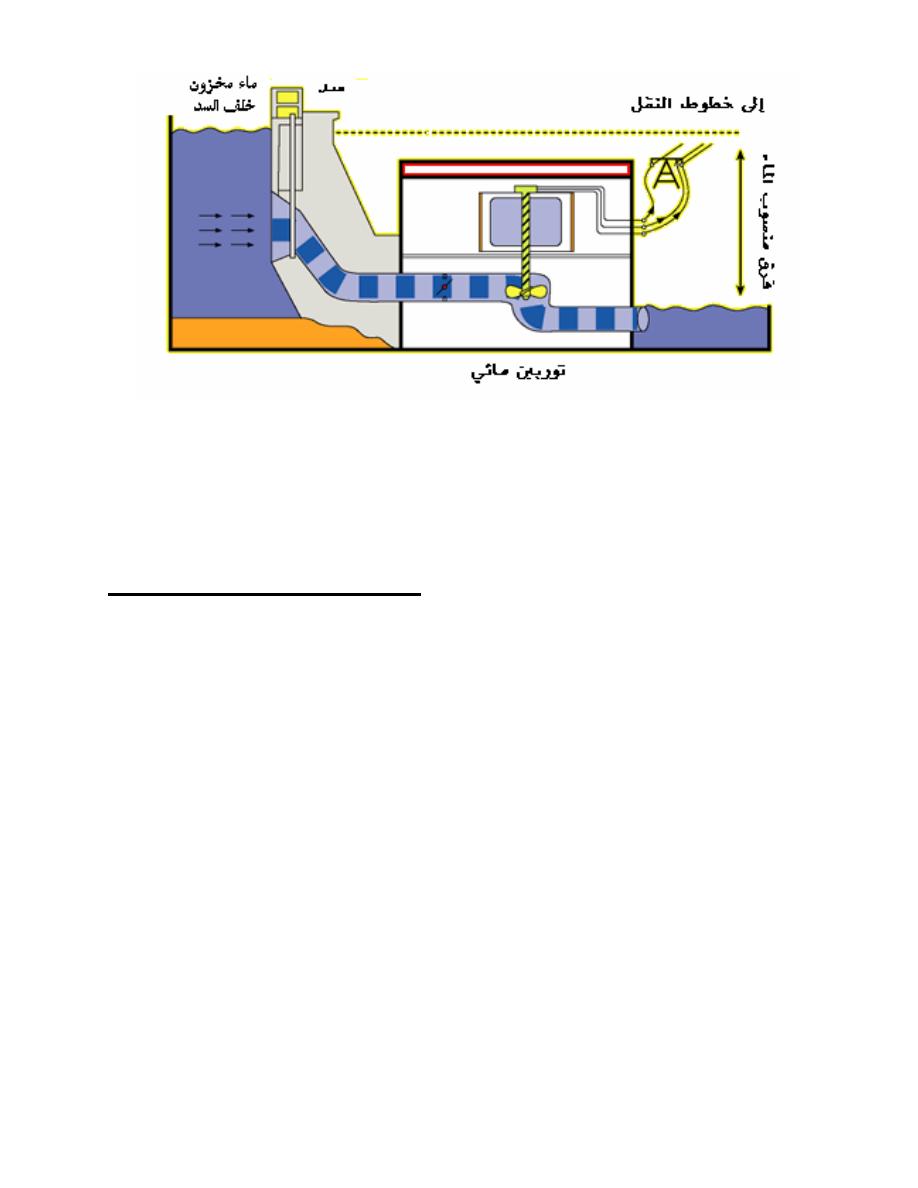
Figure(4)
Hydro Power Plant

In hydro power plant we use gravitational force of fluid water to run the
turbine which is coupled with electric generator to produce electricity. This power
plant plays an important role to protect our fossil fuel which is limited, because the
generated electricity in hydro power station is the use of water which is renewable
source of energy and available in lots of amount without any cost. The big
advantage of hydro power is the water which the main stuff to produce electricity
in hydro power plant is free, it not contain any type of pollution and after generated
electricity the price of electricity is average not too much high.
Construction and Working of Hydro Power Plant:
Fundamental parts of hydro power plant are
a) Area.
b) Dam.
c) Reservoir.
d) Penstock.
e) Storage tank.
f) Turbines and generators.
g) Switchgear and protection.
For construction of hydro power plant first we choose the area where the
water is sufficient to reserve and no any crisis of water and suitable to build a dam,
then we construct the dam. The main function of dam is to stop the flow of water
and reserve the water in reservoir. Mainly dam is situated at a good height to
increase the force of water. Reservoir stocks up lots of water which is employed to
generate power by means of turbines . After that Penstock, the pipe which is
connected between dam and turbine blades and most important purpose of the
penstock is to enlarge the kinetic energy of water that’s why this pipe is made up
of extremely well-built material which carry on the pressure of water. To control
the pressure of water means increase or decrease water pressure whenever
required, we use a valve. Storage tank comes in picture when the some reason the
pressure of water in reservoir is decreases then we use storage tank it is directly
connected to penstock and use only in emergency condition. After that we employ
turbine and generator. Turbine is the main stuff, when water comes through the
penstock with high kinetic energy and falls on turbine blades, turbine rotates at
high speed. As we know that the turbine is an engine that transfers energy of fluid
into mechanical energy which is coupled with generator and generator converts
mechanical energy into electrical energy which we utilize at the end. In hydro
power plant we also add switchgears and protections which control and protect the
whole process inside the plant. The control equipments consists control circuits,
control devices, warning, instrumentation etc and connect to main control board.
After generating electricity at low voltage, we use step up transformer to enlarge
the level of voltage (generally 132KV, 220KV, 400KV and above) as per our

requirement. After that we transmit the electric power to the load center, and then
we step down the voltage for industrial and large consumer and then again we step
down the voltage to distribute electricity at domestic level which we used at home.
This is the whole process of generating electricity by the means of hydro
(hydro power plant) and then transmitting and distributing electricity.
History of Hydro Power Plant
First hydro power is used by the Greekins to spin water wheels for crushing
wheat into flour before more than 2000 years ago. In the 1700's, hydropower was
generally used for pumping irrigation (non-natural use of water on the way to the
land) water. We start to generate electricity from hydro power in 1882 when
United States (U S) establishes a first hydro power station which generate 12.5
kilowatts (KW) of power. The rapid growth of hydro power comes in 1900’s when
hydraulic reaction turbine comes in picture as a result in 1900’s hydro power plants
fulfill the requirement of 40% of total United States' electricity. In between 1905-
1911 largest hydro power station (Roosevelt Dam) is built by the united state and
its generated capacity is increased from 4500kW to 36,000kW.In 1914 S.J. Zowski
developed the high specific speed reaction (Francis) turbine runner for low head
applications. 1922 the first time a hydroelectric plant was built specifically for
crest power. In 1933 Hoover Dam, Arizona generated electricity first time. In 1940
over 1500 hydro power plants generate about one third of the United States'
electrical energy.
If we compare the countries on the basis of generated electricity by the
means of hydro power, Canada on the top after that United State then Brazil then
Russia then China then Norway and at 7th number India is present. India fulfills
the 3.5% power to the total world power through hydro power plants.
In India scope of hydro power is very good, first hydro power station,
capacity of 130kW establishes in Asia at mounts of Darjeeling in 1898 and after
that in 1902 Shimsh (Shivanasamudra) is established and both located in India.
Now a day in India the leading hydro power plant is located of river Naptha Jhakri
hydro project of 1500MW in Himachal Pradesh. In India main boost come in the
field of hydro power in august 1998 when the Government of India publicized a
plan on ‘Hydro Power Development’ after that in November 2008 once again
Indian government announced this plan and as a result India become leading
country list to produce hydro power.
This a general idea about hydro power plant.
1-2-4 Diesel Power Station:
For generating electrical power, it is essential to rotate the rotor of an
alternator by means of a prime mover. The prime mover can be driven by different
methods. Using diesel engine as prime mover is one of the popular methods of
generating power. When prime mover of the alternators is diesel engine, the power
station is called diesel power station.
The mechanical power required for driving alternator comes from
combustion of diesel. As the diesel costs high, this type of power station is not
suitable for producing power in large scale in our country.
But for small scale production of electric power, and where, there is no other
easily available alternatives of producing electric power, diesel power station are
used.
Steam power stations and hydro power plants are mainly used to produce
maximum portion of the electrical load demands. But for steam power station,
sufficient supply of coal and water are required.
Figure(5)
Diagram of Hydro Power Plant

For hydro power station, plenty source of water and big dams are required.
But where all these facilities are not available, such as no easy way of coal
transportation and no scope of constructing dam, there it is established.
Diesel power plants are also popularly used as standby supply of different
industries, commercial complexes, hospitals, etc. During power cut, these diesel
power generators are run to fulfil required demand.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Diesel Power Station:
a. Advantages
1. This is simple in design point of view.
2. Required very small space.
3. It can also be designed for portable use.
4. It has quick starting facility, the small diesel generator set can be started
within few seconds.
5. It can also be stopped as when required stopping small size diesel power
station, even easier than it’s starting
6. As these machines can easily be started and stopped as when required,
there may not be any standby loss in the system.
7. Cooling is easy and required smaller quantity of water in this type power
station.
8. Initial cost is less than other types of power station.
9. Thermal efficiency of diesel is quite higher than of coal.
10.Small involvement is less than steam power station.
b. Disadvantages:
1. As we have already mentioned, the cost of diesel is very high compared
to coal. This is the main reason for which a diesel power plant is not
getting popularity over other means of generating power. In other words
the running cost of this plant is higher compared to steam and hydro
power plants.
2. The plant generally used to produce small power requirement.
3. Cost of lubricants is high.
4. Maintenance is quite complex and costs high.
Different Components of Diesel Power Station

In addition to diesel generator set or DG set there are many other auxiliaries
attached to at diesel power station. Let’s discuss one by one.
a) Fuel Supply System:
In fuel supply system there are one storage tank, where oil in stored.
Strainer : This oil then pump to dry tank, by means of transfer pump.
During transferring from main tank to smaller dry tank, the oil passes
through strainer to remove solid impurities. From dry tank to main tank, there is
another pipe connection. This is over flow pipe. This pipe connection is used to
return the oil from dry tank to main tank in the event of over flowing.
From dry tank the oil is injected in the diesel engine by means of fuel
injection pump.
b) Air Intake System:
This system supplies necessary air to the engine for fuel combustion. It
consists of a pipe for supplying of fresh air to the engine. Filters are provided to
remove dust particles from air.
c) Exhaust System:
The exhaust gas is removed from engine, to the atmosphere by means of an
exhaust system. A silencer is normally used in this system to reduce noise level of
the engine.
d) Cooling System:
The heat produced due to internal combustion, drives the engine. But some
parts of this heat raise the temperature of different parts of the engine. High
temperature may cause permanent damage to the machine. Hence, it is essential to
maintain the overall temperature of the engine to a tolerable level. Cooling system
of diesel power station does exactly so. The cooling system requires a water
source, water source, water pump and cooling towers. The pump circulates water
through cylinder and head jacket. The water takes away heat from the engine and it
becomes hot. The hot water is cooled by cooling towers and is re-circulated for
cooling.

e) Lubricating System:
This system minimises the water of rubbing surface of the engine. Here
lubricating oil is stored in main lubricating oil tank. This lubricating oil is drawn
from the tank by means of oil pump. Then the oil is passed through the oil filter for
removing impurities. From the filtering point, this clean lubricating oil is delivered
to the different points of the machine where lubrication is required the oil cooler is
provided in the system to keep the temperature of the lubricating oil as low as
possible.
f) Starting System:
For starting a diesel engine, initial rotation of the engine shaft is required.
Until the firing start and the unit runs with its own power. For small DG set, the
initial rotation of the shaft is provided by handles but for large diesel power station.
Compressed air is made for starting.
Figure(6)
Diesel Power Plant

1-2-5 Nuclear Power Station or Nuclear Power Plant
Electrical power can be generated by means of nuclear power. In nuclear
power station, electrical power is generated by nuclear reaction.
Here, heavy radioactive elements such as Uranium (U235) or Thorium
(Th232) are subjected to nuclear fission. This fission is done in a special apparatus
called as reactor. Before going to details of nuclear power station, let’s try to
understand what is fission? In fission process, the nuclei of heavy radioactive
atoms are broken into two nearly equal parts. During this breaking of nuclei, huge
quantity of energy is released. This release of energy is due to mass defect. That
mean, the total mass of initial product would be reduced during fission. This loss
of mass during fission is converted into heat energy as per famous equation E =
mc2, established by Albert Einstein.
The basic principle of nuclear power station is same as steam power station.
Only difference is that, instead of using heat generated due to coal combustion,
here in nuclear power plant, heat generated due to nuclear fission is used to
produce steam from water in the boiler. This steam is used to drive a steam turbine.
This turbine is the prime mover of the alternator. This alternator generates
electrical energy. Although, the availability of nuclear fuel is not plenty but very
less amount of nuclear fuel can generate huge amount of electrical energy. This is
the unique feature of a nuclear power plant. One kg of uranium is equivalent to
4500 metric tons of high grade coal. That means complete fission of 1 kg uranium
can produce as much heat as can be produced by complete combustion of 4500
metric tons high grade coal. This is why, although nuclear fuel is much costlier, but
nuclear fuel cost per unit electrical energy is still lower than that cost of energy
generated by means of other fuel like coal and diesel. To meet up conventional fuel
crisis in present era, nuclear power station can be the most suitable alternatives.

Advantages & Disadvantages of Nuclear Power Station:
a) Advantages
1) As we said, the fuel consumption in this power station is quite low and
hence, cost for generating single unit is quite less than other conventional
power generation method.
2) A nuclear power station occupies much smaller space compared to other
conventional power station of same capacity.
3) This station does not require plenty of water, hence it is not essential to
construct plant near natural source of water. This also does not required
huge quantity of fuel; hence it is also not essential to construct the plant
near coal mine, or the place where good transport facilities are available.
Because of this, the nuclear power station can be established very near to
the load centre.
b) Disadvantages :
1) The fuel is not easily available and it is very costly.
2) Initial cost for constructing nuclear power station is quite high.
3) Erection and commissioning of this plant is much complicated and
sophisticated than other conventional power station.
4) The fission by products are radioactive in nature, and it may cause high
radioactive pollution.
5) The maintenance cost is higher and the man power required to run a
nuclear power plant is quite higher since speciality trained people are
required.
6) Sudden fluctuation of load cannot be met up efficiently by nuclear
plant.
7) As the by products of nuclear reaction is high radioactive, it is very big
problem for disposal of this by products. It can only be disposed deep
inside ground or in a sea away from sea share.

Different Components of Nuclear Power Station:
A nuclear power station has mainly four components.
1) Nuclear reactor.
2) Heat exchanger.
3) Steam turbine.
4) Alternator.
Let’s discuss these components one by one:
1) Nuclear Reactor:
In nuclear reactor, Uranium 235 is subjected to nuclear fission. It controls the chain
reaction that starts when the fission is done. The chain reaction must be controlled
otherwise rate of energy release will be fast, there may be a high chance of
explosion. In nuclear fission, the nuclei of nuclear fuel, such as U235 are
bombarded by slow flow of neutrons. Due to this bombarding, the nuclei of
Figure(7)
Nuclear Power Plant

Uranium is broken, which causes release of huge heat energy and during breaking
of nuclei, number of neutrons are also emitted.
These emitted neutrons are called fission neutrons. These fission neutrons cause
further fission. Further fission creates more fission neutrons which again accelerate
the speed of fission. This is cumulative process. If the process is not controlled, in
very short time the rate of fission becomes so high, it will release so huge amount
of energy, there may be dangerous explosion. This cumulative reaction is called
chain reaction. This chain reaction can only be controlled by removing fission
neutrons from nuclear reactor. The speed of the fission can be controlled by
changing the rate of removing fission neutrons from reactors.
A nuclear reactor is a cylindrical shaped stunt pressure vessel. The fuel rods are
made of nuclear fuel i.e. Uranium moderates, which is generally made of graphite
cover the fuel rods. The moderates slow down the neutrons before collision with
uranium nuclei. The controls rods are made of cadmium because cadmium is a
strong absorber of neutrons.
The control rods are inserted in the fission chamber. These cadmium controls rods
can be pushed down and pull up as per requirement. When these rods are pushed
down enough, most of the fission neutrons are absorbed by these rods, hence the
chain reaction stops. Again, while the controls rods are pulled up, the availability
of fission neutrons becomes more which increases the rates of chain reaction.
Hence, it is clear that by adjusting the position of the control rods, the rate of
nuclear reaction can be controlled and consequently the generation of electrical
power can be controlled as per load demand. In actual practice, the pushing and
pulling of control rods are controlled by automatic feedback system as per
requirement of the load. It is not controlled manually. The heat released during
nuclear reaction, are carried to the heat exchanger by means of coolant consist of
sodium metal.
2) Heat Exchanger:
In heat exchanger, the heat carried by sodium metal, is dissipated in water and
water is converted to high pressure steam here. After releasing heat in water the
sodium metal coolant comes back to the reactor by means of coolant circulating
pump.
3) Steam Turbine:
In nuclear power plant, the steam turbine plays the same role as coal power plant.
The steam drives the turbine in same way. After doing its job, the exhaust steam
comes into steam condenser where it is condensed to provide space to the steam
behind it.
4) Alternator:
An alternator, coupled with turbine, rotates and generates electrical power, for
utilization.
Site Selection of Nuclear Power Station
1)
Availability of water :
Although very large quantity of water is not
regulated as hydro-electric power plant, but still sufficient supply of neutral
water is obvious for cooling purposes in nuclear power station. That is why
it is always preferable to locate this plant near a river or sea side.
2)
Disposal of Water :
The by products or wastes of nuclear power station
are radioactive and may cause severe health hazards. Because of this, special
care to be taken during disposal of wastes of nuclear power plant. The
wastes must be buried in sufficient deep from earth level or these must be
disposed off in sea quite away from the sea share. Hence, during selecting
the location of nuclear plant, these factor must be taken into consideration.
3)
Distance from Populated Area :
As there is always a probability of
radioactivity, it is always preferable to locate a nuclear station sufficiently
away from populated area.
4)
Transportation Facilities :
During commissioning period, heavy
equipments to be erected, which to be transported from manufacturer site. So
good railways and road ways availabilities are required. For availability of
skilled manpower good public transport should also be present at the site.

Renewable energy sources
1) Solar Energy:
Now a day’s solar energy system play an important role in the field of
producing electricity or other domestic uses like water heating, cooking etc. As we
know that major part of generated electricity or electricity depends upon coal
which is used in thermal power plant (in In India 65% of total power is generated
by the thermal power plant). But the main problem is here that the fuel used in
thermal power plant is coal which is in limited amount and may be not available in
future to produce or generate electricity. That is the main reason to solar energy
system comes to the picture.
2)
Wind energy:
Or wind power is extracted from air flow using wind turbines or sails to
produce mechanical or electrical energy. Windmills are used for their mechanical
power, wind pumps for water pumping, and sails to propel ships. Wind power as
an alternative to fossil fuels, is plentiful, renewable, widely distributed, clean,
produces no greenhouse gas emissions during operation, and uses little land.
3) Geothermal Earth Energy:
Geothermal energy is thermal energy generated and stored in the Earth.
Thermal energy is the energy that determines the temperature of matter. The
geothermal energy of the Earth's crust originates from the original formation of
the planet and from radioactive decay of materials.
Geothermal power is cost effective, reliable, sustainable, and environmentally
friendly,[8] but has historically been limited to areas near tectonic plate
boundaries. Recent technological advances have dramatically expanded the range
and size of viable resources, especially for applications such as home heating,
opening a potential for widespread exploitation. Geothermal wells release
greenhouse gases trapped deep within the earth, but these emissions are much
lower per energy unit than those of fossil fuels. As a result, geothermal power has
the potential to help mitigate global warming if widely deployed in place of fossil
fuels.

4) Tidal Energy:
Tidal energy is produced by the surge of ocean waters during the rise and fall
of tides.
Tidal energy production is still in its infancy. The amount of power produced
so far has been small. There are very few commercial-sized tidal power plants
operating in the world.
Placing turbines in tidal streams is complex, because the machines are large
and disrupt the tide they are trying toharness. The environmental impact could be
severe, depending on the size of the turbine and the site of the tidal stream.
Turbines are most effective in shallow water. This produces more energy and
allows ships to navigatearound the turbines. A tidal generator's turbine blades also
turn slowly, which helps marine life avoid getting caught in the system.
