Orientation
Medicine college / Iraqia universityPractical biology
Huda ayad
Lab / 320/12/2015
Orientation
Objectives:-1- Define of direction terms.
2- What types of sections .
3- Recognize the bones that make up the skull frog.
Orientation
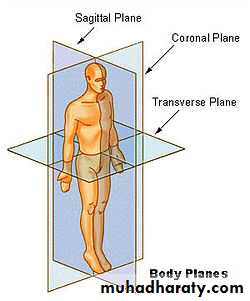
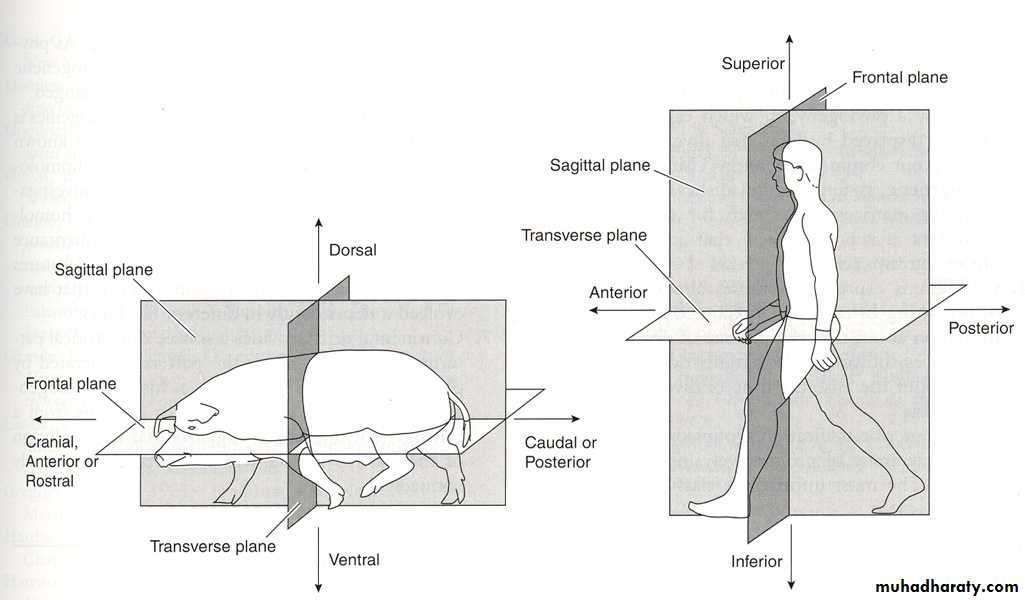
There are certain terms (Direction terms) are common use to determine the position of certain organs or part in relation to the body or another part of the body, It follows:-1- Anterior: - pertaining to the front or head end of the body.
2- Posterior: - pertaining to the tail or hind end of the body.
3- Ventral: - The belly or the lower side of the body, away from the back.
4- Dorsal: - The back or the upper surface of the body, opposite of ventral.
5- Lateral: - Towards the side of body, at each side of the midline.
6- Median: - The middle of the body.
7- Proximal: - Near the point of articulation.
8- Distal: - Away from the point articulation.
9- Superior: - The upper, higher in position
10- Inferior: - The lower in position.
11-Pre- axial: - The nearer to the main longitudinal axis of the body.
12- Post- axial: - The away from the main longitudinal axis of the body.
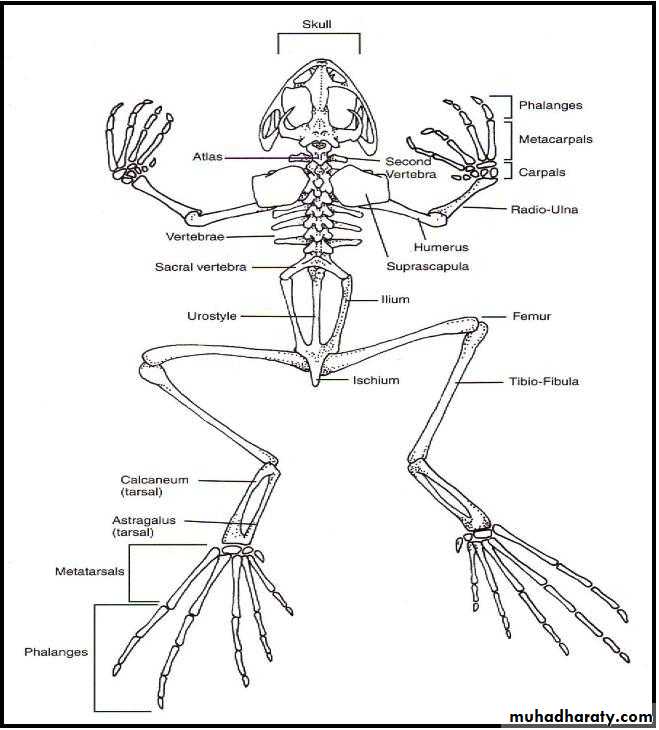
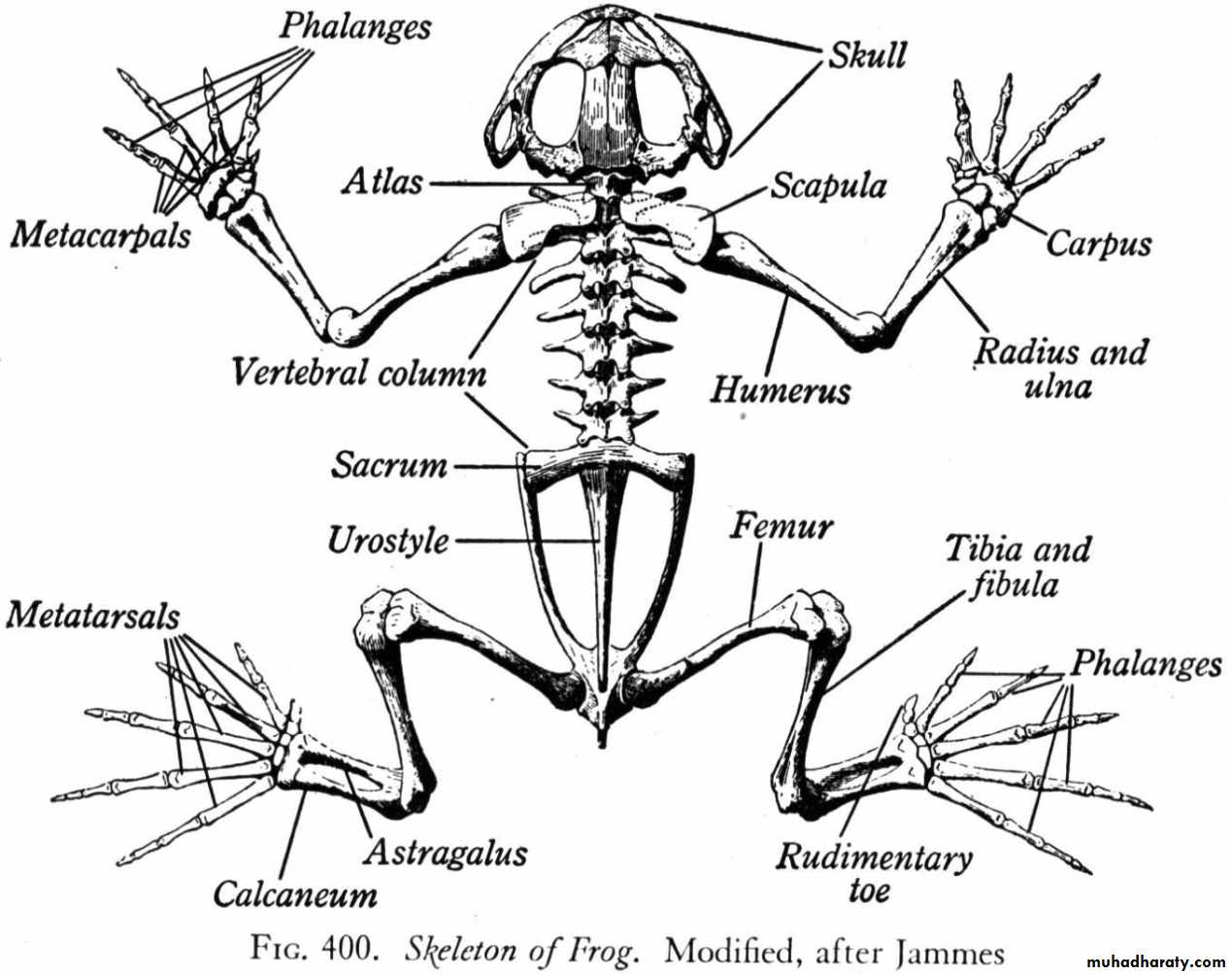
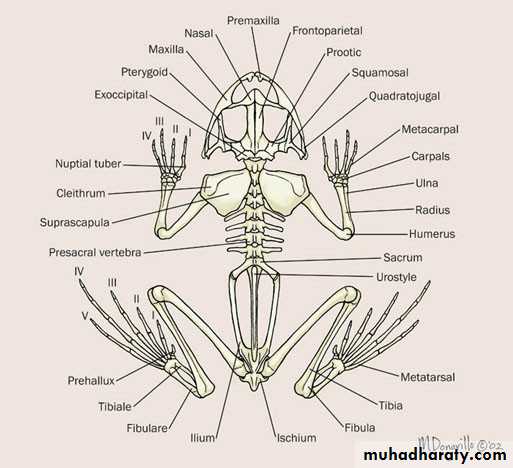
Skeleton of frog
Ventral view) )Dorsal view ) )
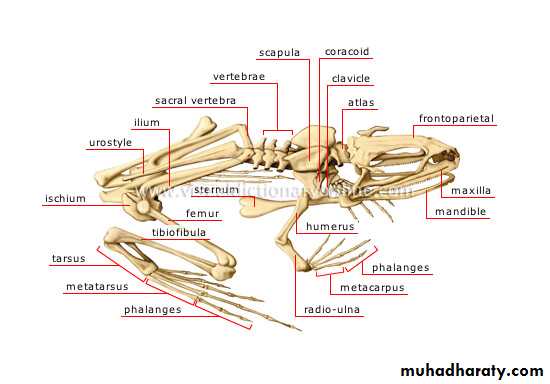
Skeleton of frog( Lateral view)
Skeleton of frogSections :-
cuts are made through the various objects to produce thin slices for detailed study of the structure , at the level of light microscope and fine structure or ultra structure at the electron microscope .There are many levels sections, We will take the following it :-
1- Transverse section (T.S) or cross section (C.S) :-
a transverse cut through a structure or tissue or
Is one line made horizontally through object , hence its place lies at right angles to the main longitudinal axis of the body .
Longitudinal section (L.S ) :- 2-
Is one line made Parallel to the main longitudinal axis of the body , or a section that is cut along the long axis of a structure. the opposite is a cross-section
3- sagittal section (S.S) :-
Pertaining to the median , vertical longitudinal plane , or is a vertical plane which passes from ventral (front) to dorsal (rear) dividing the body into right and left halves.
A ( Cross section) B (Longitudinal section)
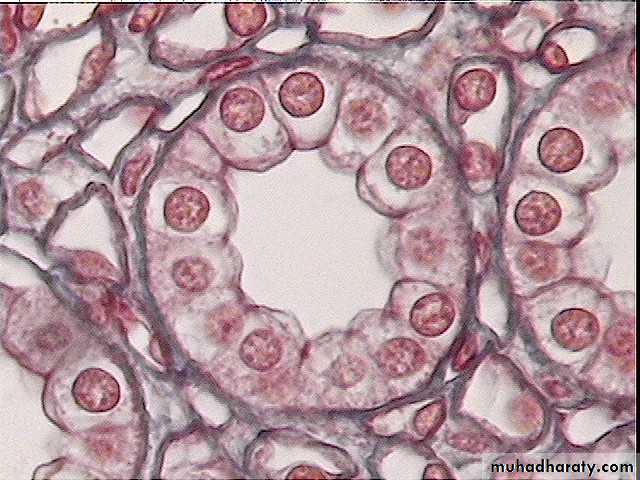
Epitheial cell and their neighbors( Cross section )
Simple cuboidal epithelium tissuesagittal section
sagittal section
Skeleton of frog
The endoskeletal of the frog is composed of two main divisions ; the axial and the perpendicular skeleton . The axial skeleton includes the skull , sternum and vertebral column. The appendicular skeleton consists of the pectoral and pelvis girdles and the bones of the limbs , The functions of a skeleton include providing support for the body, protection of delicate internal organs.
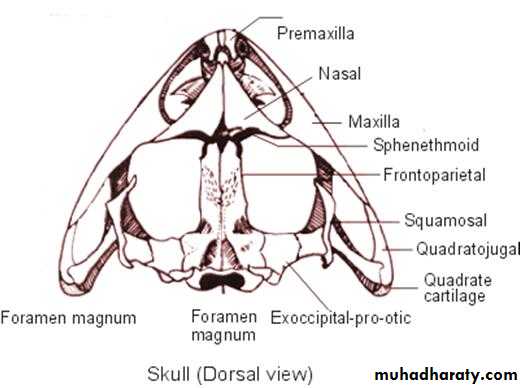
(Dorsal view )
Skeleton of frog- We can see some the bones skull the frog from dorsal view including :-
1-Premaxilla
2- Maxilla
3- Quadratojugal
4-Quadrate cartilage
5- Squamosal
6- Frontoparietal
7- Exoccipital
8- Foramen magnum
9- Nasal
(Dorsal view) Skull (cranium ) of frog
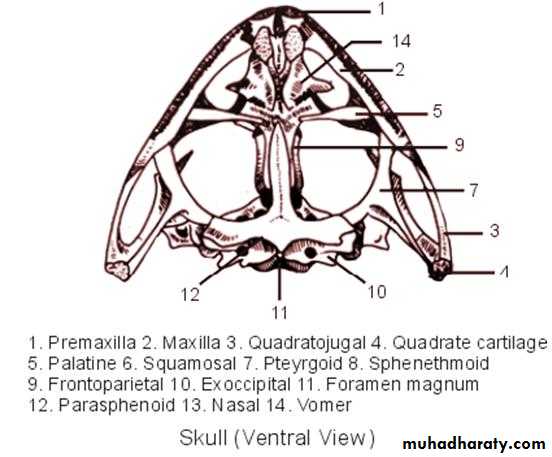
- We can see some the bones skull the frog from ventral view including :-1-Premaxilla
2- Maxilla
3- Quadratojugal
4- Quadrate cartilage
5- Squamosal
6- Frontoparietal
7-Exoccipital
8- Foramen magnum
9- Nasal
10-Palatine
11- Pteyrgoid
Skull (cranium ) of frog
( ventral view)