
17/06/2013
1
The cause related phase of
p.d. therapy
( Initial phase)
The p.d. treatment runs in 3 phases ;
Initial
Corrective
Maintenance

17/06/2013
2
Goals of ph. 1
Go beyond control of inflam & Plaque reduction by
mechanical means as its also involves ;
1- Evaluate & alter pt.sysemic risk as systemic disease,
smoking, substance abuse ,medication…consultation
2- pl+.control by pt.
3- Removal of pl+ & ca+
4- Antimicrobial agents & devices as pl+ sampling
& AB sensitivity test
5- control or elimination of local
factors including;
1. Treat.of poorly fitting restoration
2. Correction of poorly fitting prosthetic devices
3. Restoration of carious lesion
4. Odontoplasty
5. Tooth movement
6. Treat.of food impaction area
7. Treat.of occlusal trauma
8. Exo.of hopeless teeth

17/06/2013
3
A no.of conditions need to be considered in
formulating treatment plan for each pt.
1. General health & tolerance of treatment
2. no. of teeth present
3. Amount of supra G.ca+
4. Amount of sub G.ca+
5. P.P.D.
6. Furcation involvement
A no.of conditions need to be
considered in formulating
treatment plan for each pt.
6- Alignment of teeth
7- Margin of restoration
8- Developmental anomalies
9- Limited opening or tendency to gag
( physical barrier)
11- Pt.cooperation
12- Pt..sensitivity (requiring anasthesia)

17/06/2013
4
Pt.information
Recognition of BOP.,PPD. with the assistance of handy
mirror
Dental plaque , also D.p.with associated G.infl.
Tooth brushing technique is demonstrated ,then
takeover by pt.with correction of the technique if
required
Repeat the demonstration & instruction process with
I.D. aids
D.P. is the cause of the problem its
elimination will prevent G.disease
this is easier said than done

17/06/2013
5
Pt.motivation
Continuous encouraging the pt.to perform good oral
hygiene measures to control p+ & regular return
visits for maintenance & reinforcement
Pt. non-compliance with both
prescribed oral hygiene regimen &
regular return visits are common
occurrence in dental practice
So the pt.should has a willing & able
to make behavior's changes
Self performed p.control methods
P+control
removal of p+on a regular basis & prevention of
its accumulation on teeth & adjacent G.t.
Daily removal of p+ lead to
resolution of G.inflammation in few days &
retard ca+formation & reduce the no.of
subgingival sites with p.gingivalis

17/06/2013
6
Teeth cleaning every 24-48H is sufficient
It has been found that most of people
brushing of their teeth Last only 2min. &
remove only 40% p+
So its advisable to increase frequency to
twice/day
3 or more times brushing/day has
no additional advantage
Self performed p+control
methods
So
cleaning once a day with all necessary tools is sufficient if its
performed meticulously
If p+control not adequate,a second brushing will be helpful
P+ growth occur within hours ,so should completely removed
at the very least every 48h.in p.d. healthy subjects to
prevent inflammation
In p.d.pt.
there are a lot of defects in G.arch with long exposed roots
so need brushing Every 24 hr.
for 30min.instead of 5-10min.

17/06/2013
7
Toothbrush alone is not sufficient
P.d. lesion predominantly found I.D.
P+ begins on the interproximal surfaces
P+ develops first in the interproximal surfaces of
7,6 & 5,4.
Followed by proximal Surfaces of anterior teeth
then facial surfaces of 7,6,5,4,
& least amount seen in the lingual Surfaces
Different types, the best is the one which works for that
pt.that detected where there are no p. & no harm to
tooth or G.
so
Efficiency of brushing is of value than the technique of
brushing that performed
Many subjects leave p+ post. & interproximally
Tooth brushing
17/06/2013
8
Characteristic of ideal brush;
soft to medium,
contra-angle,
short head,
uniform rows,
no more than 3-4 rows,
6 evenly spaced tufts
/row,
rounded end ,
synthetic bristle
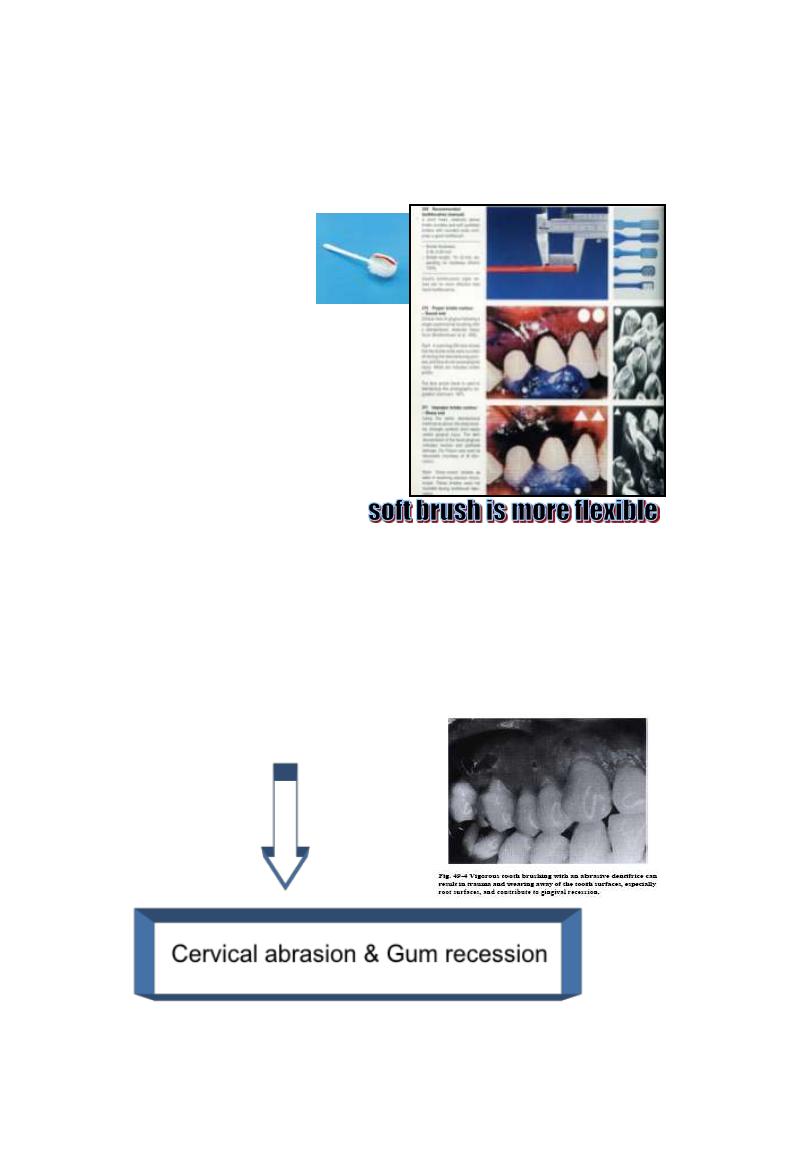
Hard brush +
vigorous horizontal brushing + course abrasive
dentifrice
Cervical abrasion & Gum recession
17/06/2013
9
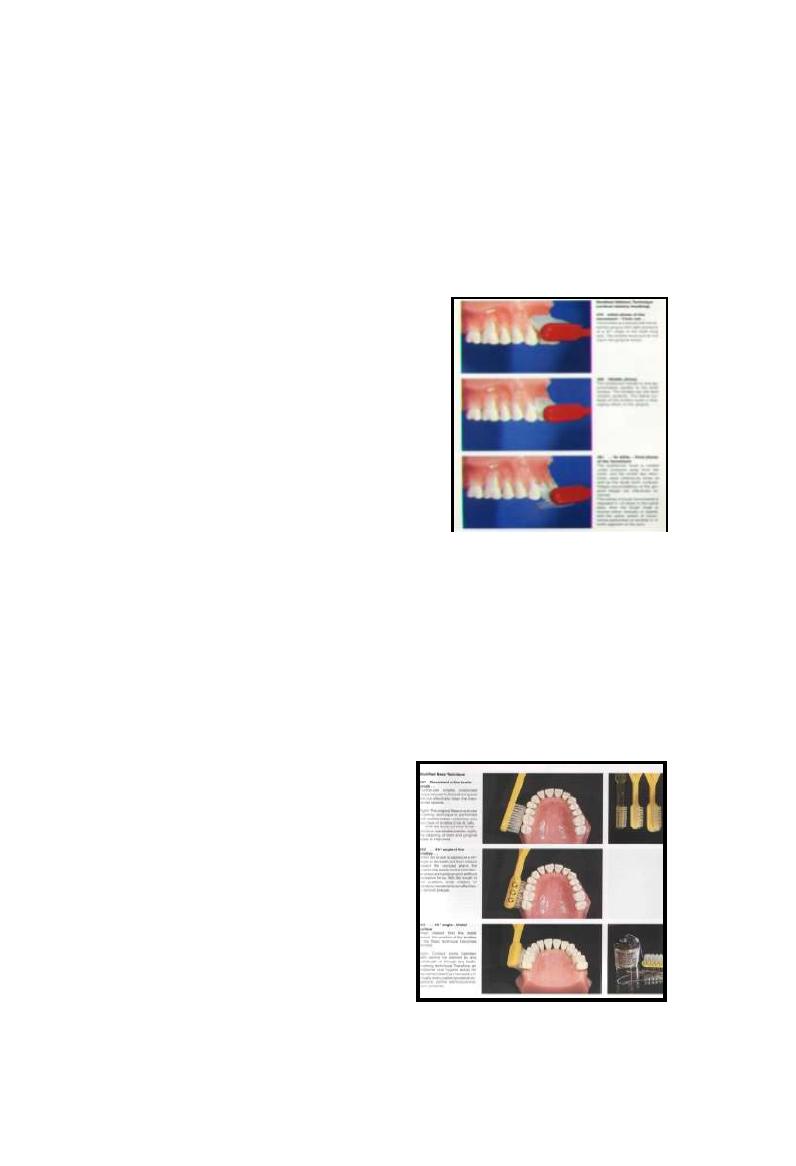
Roll technique
Indicated when there is p.dontitis with receded papillae &
spaced teeth Called
modified stillman technique
Bristle ends resting partly on adjacent G. & partly on
cervical portion of teeth at oblique angle then move in
occlusal direction
(5-8 times for each site)
Incorrect technique lead to GR that
Depend on;
frequency
Force
brush type ?
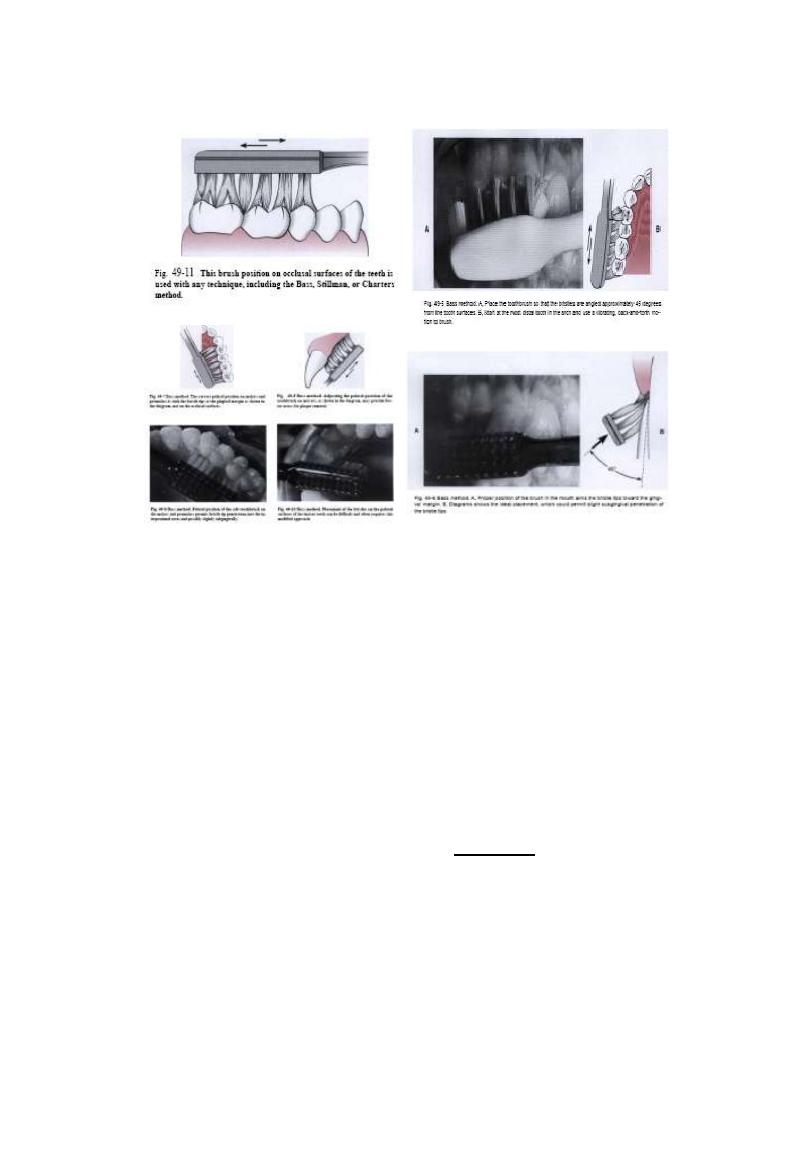
Vibratory technique
Modified bass method
5-6 times at each sites
For pt.with p.d.disease as
it provide access to
clean the G.area
It permit bristle tip
penetrate into p.d. area
& possibly slightly
subgingivally
17/06/2013
10
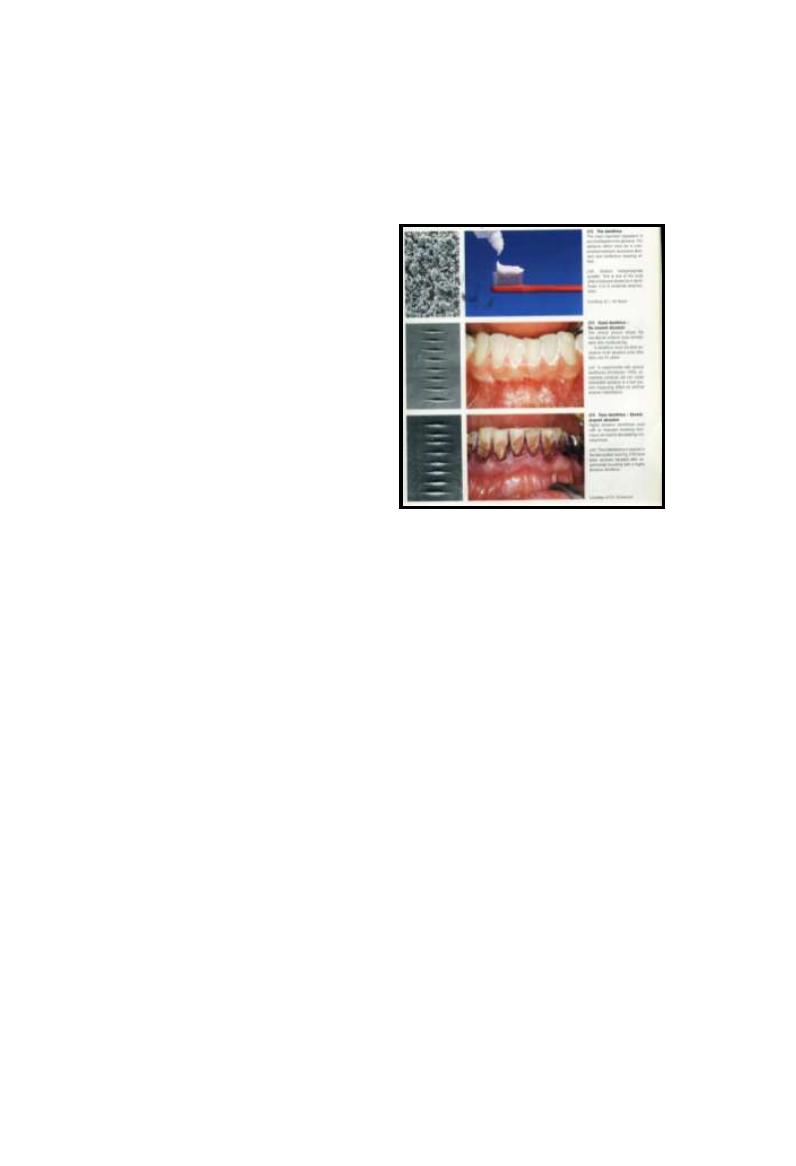
Dentifrice
Facilitate removal of p+ & stain by increase mechanical
friction due to presence of abrasive particles
Contain active substance as fluoride, chx or others
Appropriate size of abrasive particles; neither large nor small
Made of abrasive particles (Insoluble inorganic salts) such as
silicone oxide or aluminum oxide (20-40%) in toothpaste
& (95%) in toothpowder
Also have
H2O
soap
flavoring
sweetening
therapeutic
coloring
preservatives agents
17/06/2013
11
Hard lesion (tooth
abrasion) caused by large
abrasive contained
dentifrice
Soft lesion (Gum recession)
caused by incorrect
toothbrushing
• Pyrophosphate
• induces reduction of
supragingival tarter? to
about 30% by interfere with
crystal formation
Overzealous brushing lead to
G.R.
Bacteremia
Wedge-shaped defect
Painful ulceration of G.
indicated in ;
Children & adolescence
Children with physical or mental disabilitis ,
Hospitalized pt.
Pt. with fixed ortho. appliance
Powered tooth brush
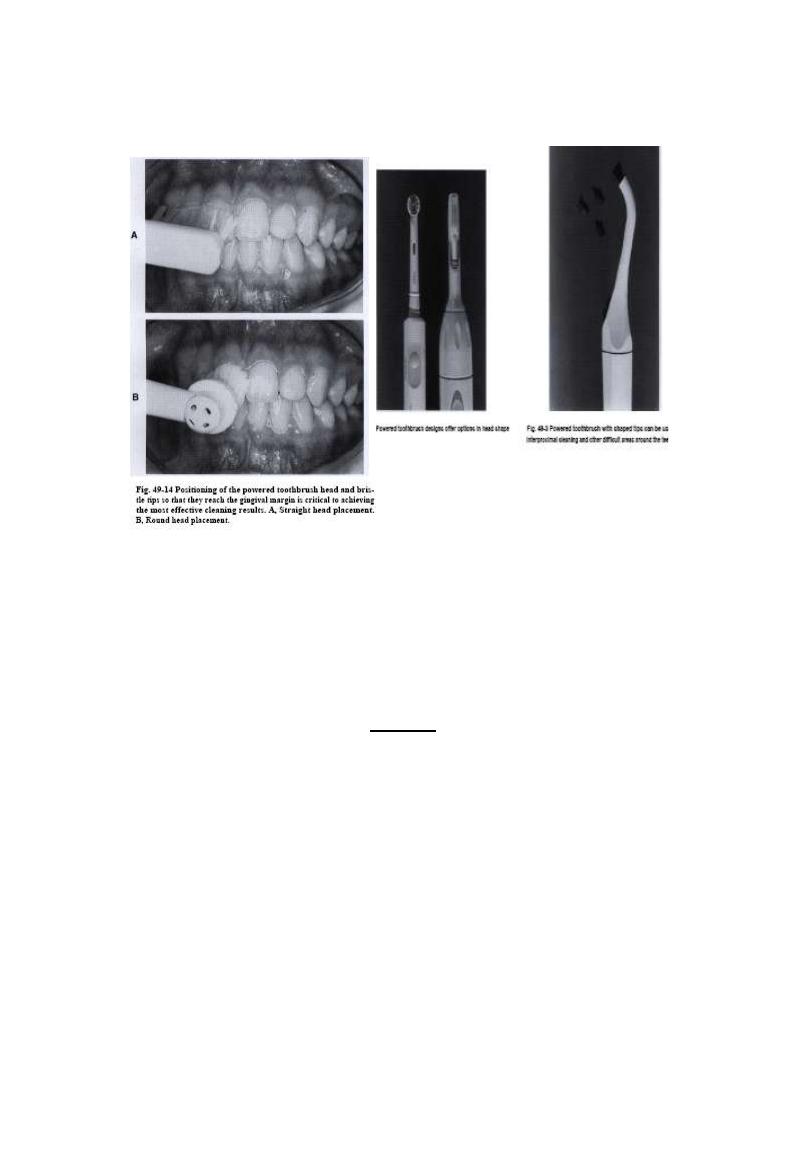
17/06/2013
12
Interdental aids
For removal of p+ not for food debris ?
D.Floss ;
Used when the papillae filled I.D.space
Waxed floss used when there is proximal filling
Must contact the entire proximal surfaces of each tooth
Abuse leads to loss of papillae
Proximal groove in G.papillae may be seen due to Snap floss
past contact area injuring G.
Floss holder used for
Handicapped pt.,
Pt. lack manual dexterity
Hospitalized pt. nursing
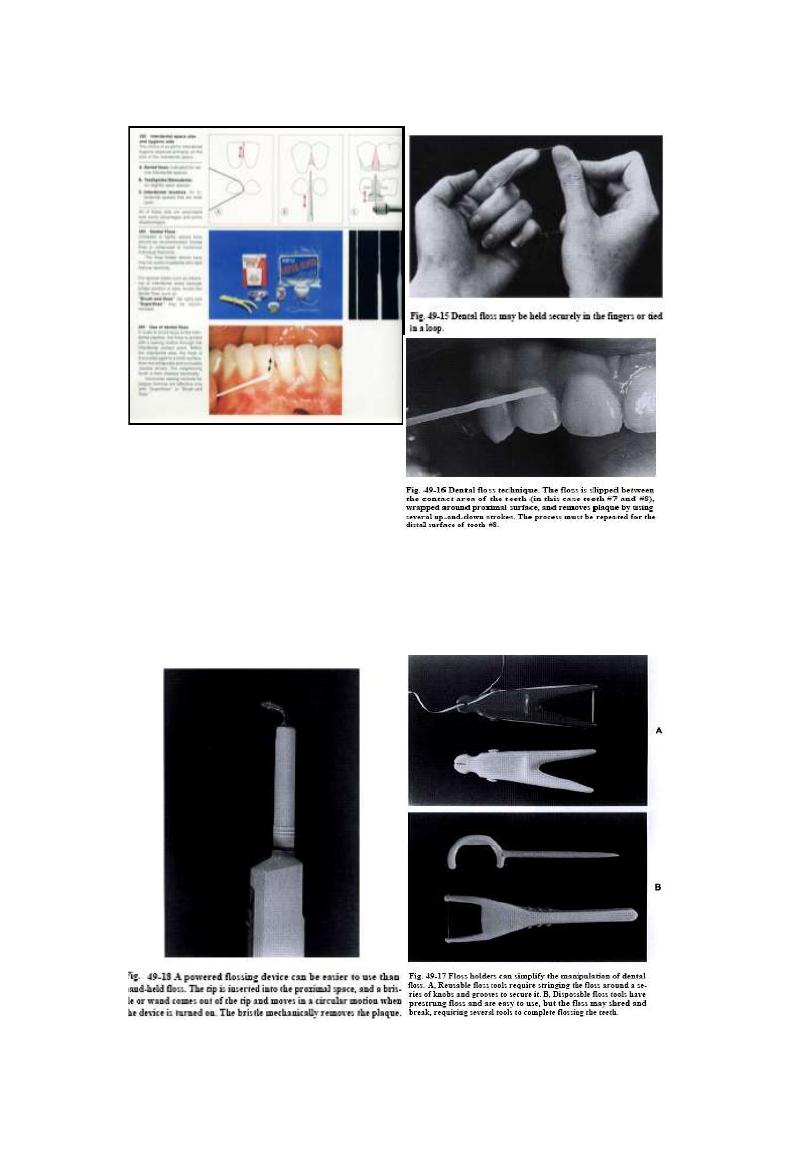
17/06/2013
13
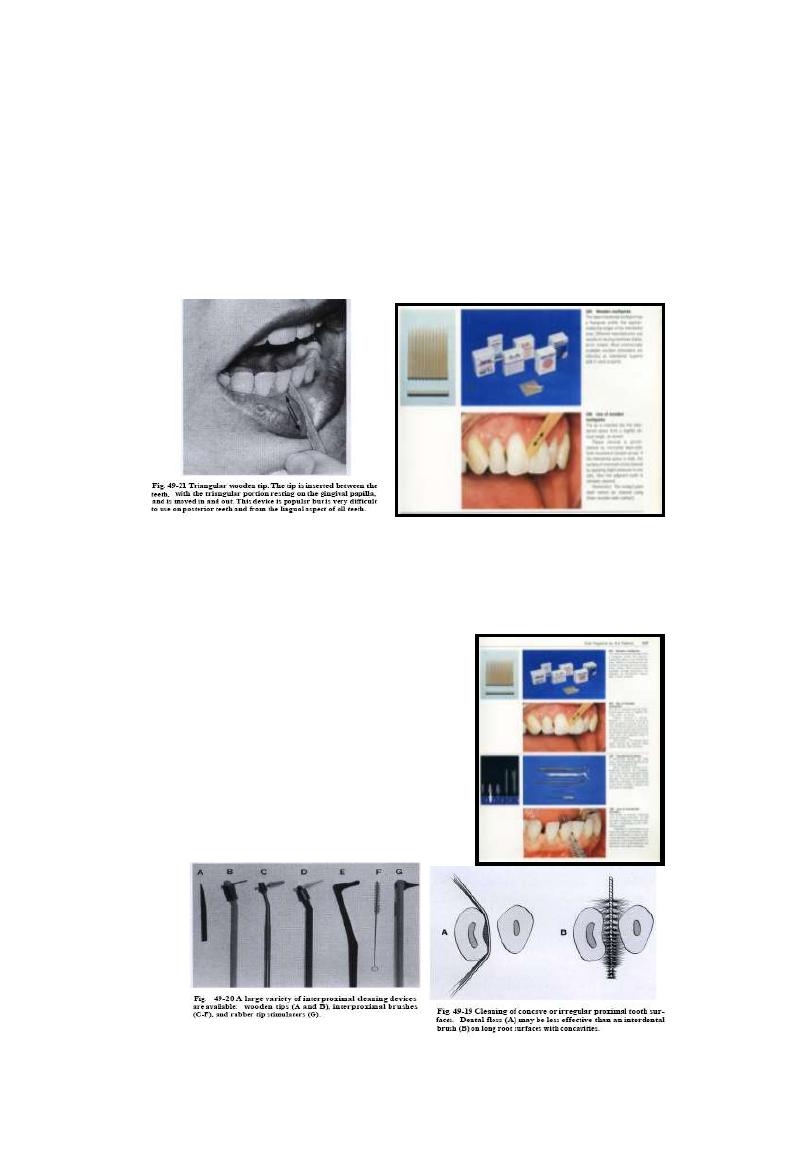
17/06/2013
14
Toothpick (stimudent)
Used in proximal area of receded papillae
It induces no trauma to G.because of resiliency of G.T.
Interproximal brush
Used in ;
Large I.D.space
Concave tooth surface
Furcation involvement
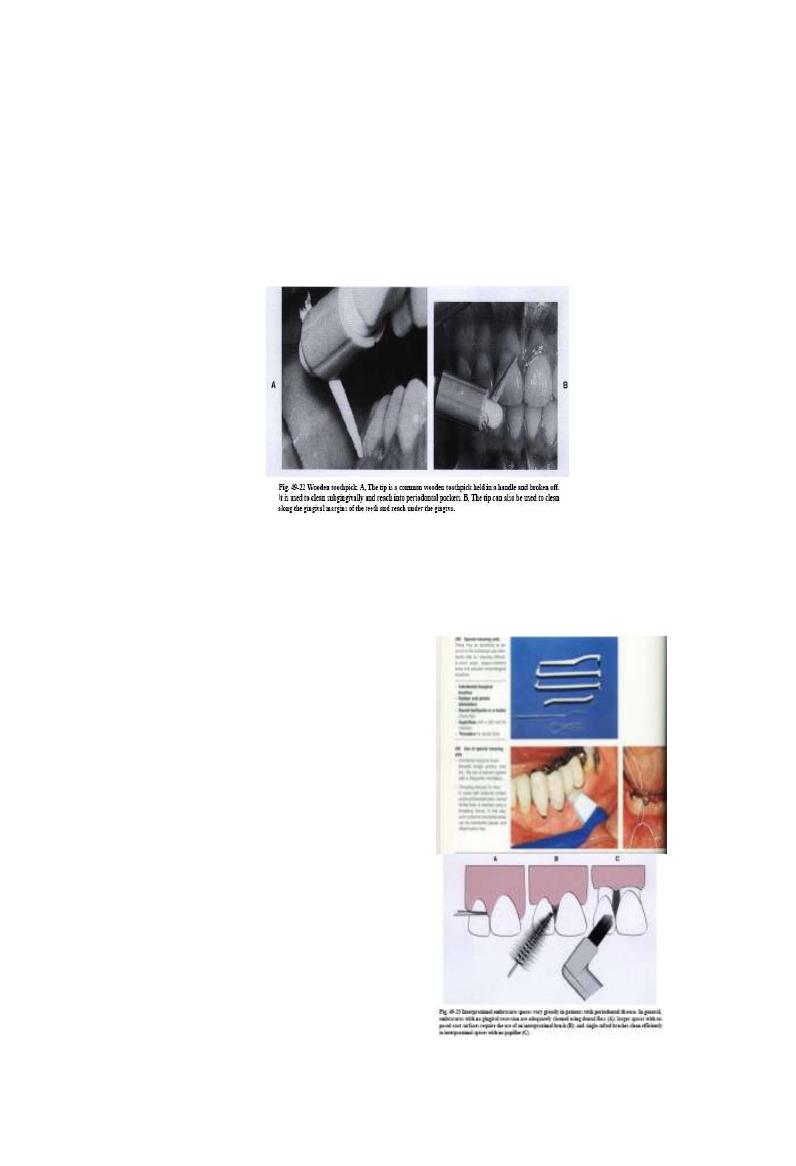
17/06/2013
15
perio-Aid
Used for cleaning G.margin, G.sulcus & p.d.
Single-tufted brush
Used in ;
furcation area,
B.or L.surfaces with irregular
margin,
Isolated area of deep recession,
L.Surface of lower posterior
teeth where tongue impedes
tooth brush
Inter proximal surfaces with no
papillae

17/06/2013
16
Disclosing agent
Adjunctive aid used by pt. to evaluate
efficacy of home care
Provide pt.with an educational &
motivational root to improve
efficiency of p+ control
Erythrocin,fuchsin,food coloring agent
Supplied as Solution (wafer) or tablet
that crushed b/w teeth & moved
around mouth for few seconds then
spit out
Oral irrigators
Apply high pressure steady
or pulsating water
Clean around
ortho.appliance & fixed
prosthesis
Retard accumulation of
P+& ca+& disturb
subgingival p+
Could be used by Delivering
antibacterial agent to
P.D.pocket
