
University of Mosul
college of Dentistry
Oral and Maxillofacial dept.
periodontics unit
Treatment plan

The aim of the treatment plan is…
the coordination of all
treatment procedures for
the purpose of creating a
well-functioning dentition
in a healthy periodontal
environment

Except for emergencies,
No treatment should be started
until the treatment plan has been established.

The primary goals are
• elimination of gingival inflammation
(elimination of root irritants, pocket eradication/
reduction)
• correction of the conditions that cause and/or
perpetuate it
.
(establishment of gingival contours and
mucogingival relationships conducive to the
preservation of periodontal health, restoration
of carious areas, and correction of existing
restorations)

Treatment plan should includes..
• Teeth to be retained or extracted
• Pocket therapy, by means of surgical or nonsurgical
methods, and the techniques to be used
• The need for occlusal correction, prior, during, or after
pocket therapy
• The use of implant therapy
• The need for temporary restorations
• Final restorations that will be needed after therapy and
which teeth will be abutments if fixed prosthesis is used
• The need for orthodontic consultation
• Endodontic therapy
• Regarding esthetic considerations in periodontal therapy
• On sequence of therapy
Extracting
or
Preserving a Tooth
?
1. It is so mobile that function becomes painful.
2. It can cause acute abscesses during therapy.
3. There is no use for it in the overall treatment plan.

• Consideration of occlusal relationship.
• Systemic conditions should be carefully
evaluated.
• Supportive periodontal care

Explaining the treatment plan to the patient

Be specific
قل
...
انت تعاني من التهاب اللثة أو التهاب األنسجة المحيطة باألسنان
المزمن او الحاد
و ال تقل
...
عندك مشاكل باللثة أو يحتاج نعالج اللثة مالتك

Begin your discussion on
a positive note
ـأبدأ حديثك ب
...
يوجد أسنان نكدر نحافظ عليها
ـو ال تبدأ ب
...
عندك أسنان الزم نقلعها

Present the entire treatment plan
as a unit
أخبرالمريض ان عالج األسنان المنخورة وتعويض الصناعي
لألسنان هو جزء مهم ألتمام عالج التهابات اللثة بشكل صحيح
و ال تقل
...
راح نكمل عالج اللثة هسة و بعدين عود اذا
كدرت اقلع هذه األسنان و كمل الحشوات
و الطخم

• Periodontal disease is a microbial infection.
• It is not feasible to place restorations or
bridges on teeth with untreated periodontal
disease.
• Failure to eliminate periodontal disease not
only results in the loss of teeth already
severely involved but also shortens the life
span of other teeth that.


Phase I therapy
• initial therapy,
• nonsurgical periodontal therapy,
• cause related therapy,
• the etiotropic phase of therapy.

The objective of Phase I therapy
• is to alter or eliminate the microbial etiology
and contributing factors for gingival and
periodontal diseases.
• The result is the arresting of the progression
of disease and preservation of the dentition in
a state of health, comfort, and function with
appropriate esthetics.

It includes:
• complete removal of calculus,
• correction of defective restorations,
• treatment of carious lesions,
• a comprehensive daily plaque control
regimen.

• General health and tolerance of treatment
• Number of teeth present
• Amount of supragingival calculus
• Amount of subgingival calculus
• Probing pocket depths (amount of attachment
loss is less significant than depth of pockets
for determining the treatment plan)

• Furcation involvement
• Alignment of teeth
• Margins of restorations
• Developmental anomalies
• Physical barriers to access (i.e., limited opening or
tendency to gag)
• Patient cooperation
• Patient sensitivity (requiring use of anesthesia or
analgesia)

Reevaluation
of the periodontal case should occur
about
4
weeks
after the completion of the
scaling and root planing
procedures.

• epithelial and connective tissue
healing,
• correction of conditions such as
overhanging margins,
• sufficient practice with oral hygiene
skills
4
weeks period will be enough for…
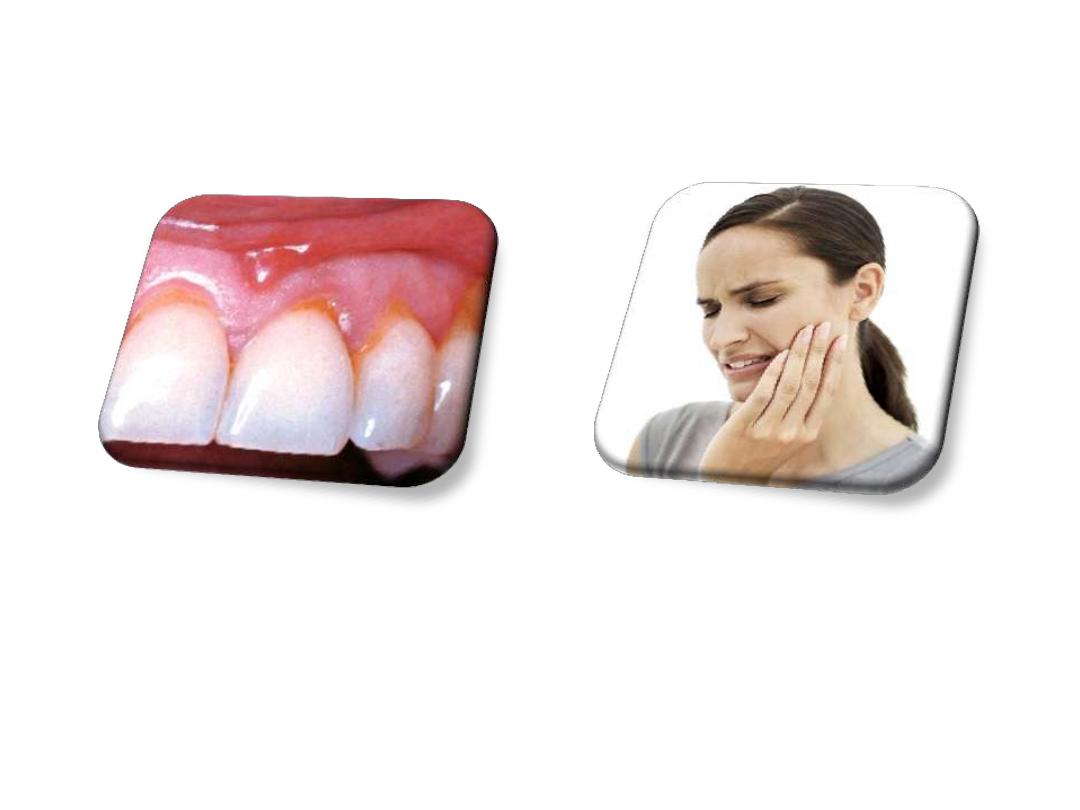
• Transient root hypersensitivity
• recession of the gingival margins
Patients should be warned
at the outset of
treatment that these results may happen;
otherwise
it may come as an
unpleasant
surprise.

candidate for referral
• Apical migration of the epithelial attachment,
probing depths of greater than 5 mm
• Extent of disease:
• Root length:
• Hypermobility,
• Difficulty of scaling and root planing:
• Restorative work:
• Age of the patient:
• Resolution by shrinkage
