first stage
Medical Physics
Lec-5
4/1/2016
د.تيماء
pressure
pressure is define as the force per unit area in a gas or a liquid .
for a solid the quantity of force per unit area is referred as stress .
P = F N
A m²
Or
dynes/cm ²
5
atmospheric pressure 1= 10 N /m²
5
1 atm = 10 N/m²
The unit of pressure is Pascal (Pa )
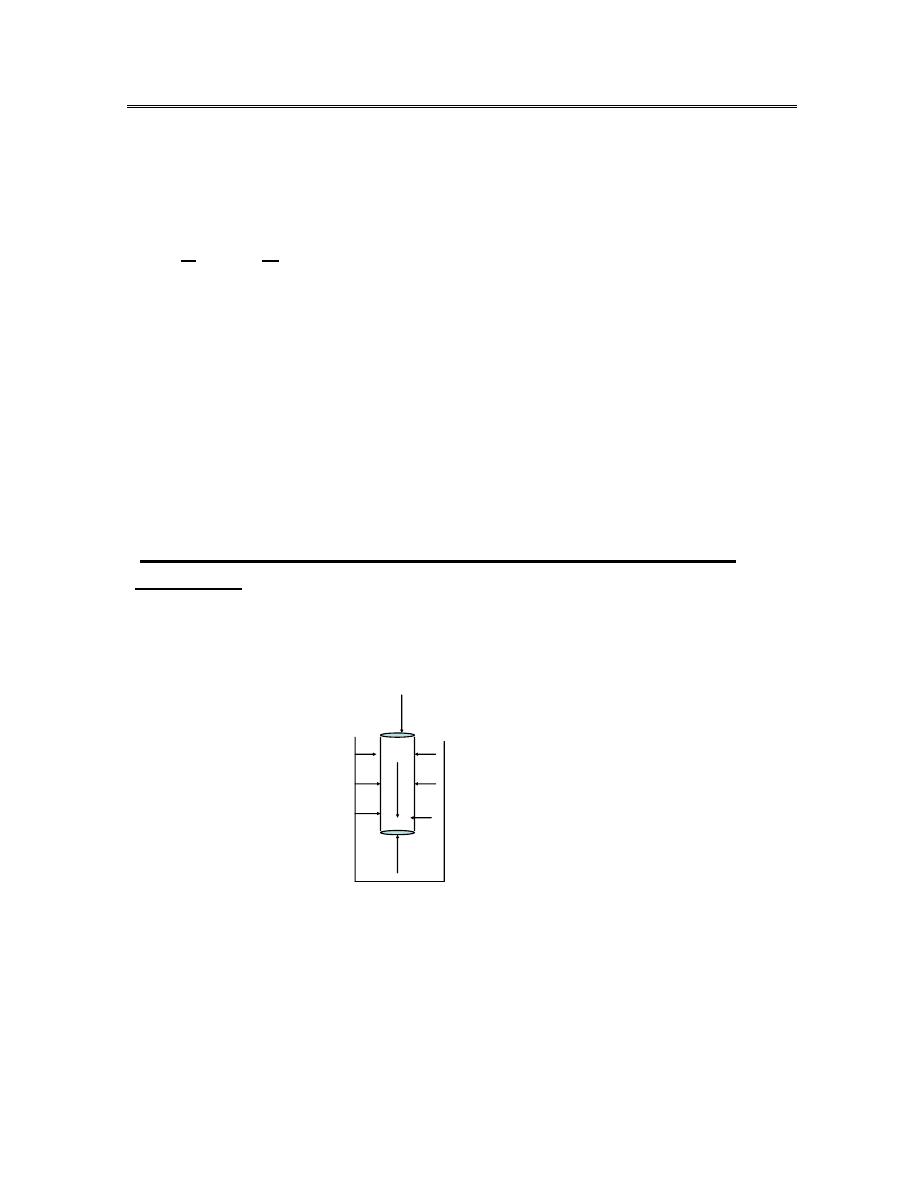
In medicine , the unit of pressure is measured by the height of a column of
mercury .The pressure in a liquid depends on the depth at which we measure
it .
The pressure in a liquid depends on the depth at which we
measure it
.
The pressure in a liquid depends on
the depth at which we measure it
Po
P
water
h
A
mg
ρ
figure (1)
Po = atmospheric pressure

2
P = pressure in the liquid
A = cross sectional area of the cylinder .
h = height of the cylinder
ρ = the density of the liquid
The pressure in the liquid at depth h exerts on the cylinder an
up ward force = PA
The atmospheric pressure exerts a down ward force on the top of the cylinder
of amount = Po A.
The volume of the cylinder is = h A
The mass of the liquid in the cylinder = ρ h A
The weight of this mass of liquid is =ρ h Ag which gives an down ward
force (figure 1)
at balance
PA = Po A + ρ g h A
or
P = ρ g h + Po absolute pressure
absolute pressure = gauge pressure + atmospheric pressure
gauge pressure = ρ g h
The pressure at a point in a liquid due to its own weight is proportional to the
density of the liquid and to the depth of the point below the surface of the
liquid .
Example
What height of water will produce the same pressure as 120 mmHg ?
gauge pressure= ρ g h
P = (13.6 gm/cm³ )(980 g/sec²) (12 cm )
5
= 1.6 x 10 dynes / cm²
for water
5
1.6 x 10 = (1g/cm³ )( 980 cm /sec²)( h cm H2O)
h = 163 cm H2O
There are a number of places in the body where the pressures are lower than
3
atmospheric , or negative. For example , when we breath in (inspire) the
pressure in the lungs must be somewhat lower than atmospheric pressure or
the air would not flow in .When a person drinks through a straw the pressure
in his mouth must be negative by an amount equal to the height of his mouth
above the level of the liquid he drinking . The heart acts as a pump ,
producing quit high pressure to force the blood through the arteries .The
returning venous blood is at quite low pressure and needs help to get from the
legs to the heart . The failure of this return system in the legs often results in
varicose veins .
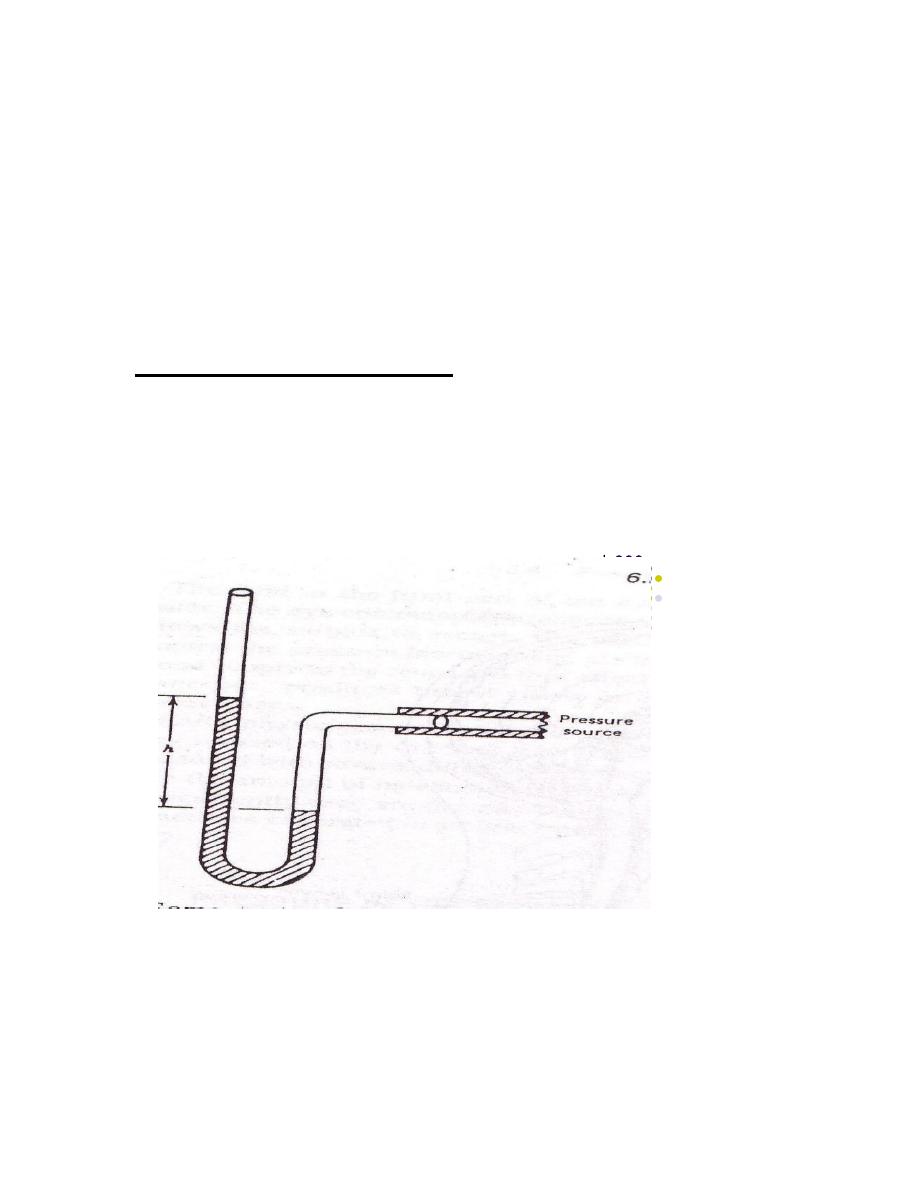
Measurement of body pressure
The classical method of measuring pressure is to determine the height of a
column of liquid that produces a pressure equal to the pressure being
measured . An instrument that measures pressure by this method is called a
manometer. Manometer is a U-shaped tube containing a fluid that is
connected to the pressure to be measured .The levels in the arms change until
the difference in the levels is equal to the pressure .This types of manometer
can measure both positive and negative pressure (figure 2).
manometer
figure (2)
The most common clinical instrument used in measuring pressure is the
sphygmomanometer , which measures blood pressure . In a mercury
manometer the pressure is indicated by the height of a column of mercury

4
inside a glass tube . In an aneroid type the pressure changes the shape of a
sealed flexible container which causes a needle to move on a dial .
Pressure in the digestive system.
The pressure is greater than atmospheric in most of the gastrointestinal
system however ,in the esophagus , the pressure between the lungs and chest
wall and usually less than atmospheric.
Pressure in the skeleton
The highest pressures in the body are found in the weight in on one leg ,such
as when walking , the pressure in the knee joint may be more than 10 atm.
The finger bones are flat rather cylindrical on the gripping side , and the
force is over a larger surface ; this reduces the pressure in the tissues over
the bones.
Pressure effects while diving
Boyle s law state that for a fixed quantity of gas at a fixed temperature
the product of the absolute pressure and volume is constant (PV= constant ).
If the absolute pressure is doubled , the volume is halved.
Example
What volume of air at atmospheric pressure
5
of 1.01x 10 N/ m² is needed to fill a
14.2 liter scuba tank to a pressure
7
of 1.45 x10 N/ m² ?
P1v1 = P2V2
5 7
(1.01 x 10 ) (v1 ) = ( 1.45 x 10 ) (14.2 )
V1 = 2 x 10³ liters

5
Solution
Q 6.6 Positive pressure is used in blood transfusion suppose a container is
placed 1m above a vein with a venous pressure of 2 mm Hg ; if the
density of the blood is 1.04 g/cm³ , what is the net pressure acting to
transfer the blood into the vein ?
The gauge pressure of 1 m blood above a vein is = 100 x 1.04 x 980
The gauge pressure of this height 1m in mercury is = 13.6 x 980 x h
100 x 1.04 x 980 =13.6 x 980 x h
OR ρ
1
h
1
=ρ
2
h
2
100 x 1.04 = 13.6 x h
2
h
2 =
7.65 cm
h
2 =
76.5mm Hg
The venous pressure = 2 mmHg
The net pressure = 76.5 – 2 = 74.5 mmHg
Q.6.7 Suppose you are a deep – diver preparing for a dive to 30m .
a. what absolute pressure and gauge pressure will you experience ?
gauge pressure = ρ g h
= 1000 x 10 x 30
5
=3 x 10 N/m²
gauge pressure = 3 atm
absolute pressure= gauge pressure + atmospheric pressure
absolute pressure= 3 atm + 1atm =4 atm
Q 6.8 Negative pressure or suction is often used to drain body cavities .In
the drainage arrangement for the gastrointestinal region ,the
negative pressure supplied to the collection bottle is 100 mmHg
and the top end of the tube is 37 cm above the end of the tube in the
body. Find the negative pressure at the lower end
of the tube .
p1 =p2
p1 = is the pressure of 37 cm of water
p1= ρ
1
h
1
p2 pressure of 37cm in mercury
p2= ρ
2
h
2
ρ
1
h
1
=ρ
2
h
2
1 x 37 = 13.6 x h2
h2 = 2.7 cm Hg(the height of mercury correspond
to 37cm of water)
The negative pressure = 100 -27 = 73 mm Hg
The negative pressure = 7.3 cm Hg

6
Q6.9 Atmospheric pressure is due to weight of the air above us .The
density of air is 1.3 x 10ˉ³g/ cm³ what is the weight in dynes of 1 cm³
of air ?If this weight were spread over 1 cm³ what would be the
pressure ? what fraction of 1 atm would it be ?
a .The weight of air in dynes of 1 cm³ is
Density = mass
Volume
ρ = m
v
1.3 x 10ˉ³ g/ cm³ =mass
1 cm³
Mass = 1.3 x 10ˉ³ gm
W = mg
W = 1.3 x 10ˉ³ x 980
W = 1.27 dyne
b. pressure = Force
area
p = 1.27 dyne = 1.27 dyne /cm²
1cm²
C .The pressure of air = ρ g h
The pressure of air = 1.3 x 10ˉ³ x 980 x 1
=1.3 x 10ˉ³ x 980 dyne /cm²
Pressure of mercury of 1 cm height of air is
Pressure of mercury = 13.6 x 980 x`1
P(air) =1.3 x 10ˉ³ x 980 x 1
P(Hg) 13.6 x 980 x`1
-5
P(air) =9.6x10
P(Hg)
-5
1 atm = 760 mm Hg, 1cm of air = 9.6x10 cm Hg
-4
1cm of air =9.6x10
760 -6
The pressure of 1 cm of air = 1,3 x 10 atm
