اساسيات الطب
المحاضره االولى
د.مها
Health
: is the absence of diseases
What are the concept of health? (Changing concept of health).
1-
biomedical concept
|absent of disease , body is a machine and the disease is an
outcome of the breakdown of that machine | .
2-
ecological concept
, dynamic equilibrium between man and his environment.
3-
psychosocial concept
, advances in social science showed that health is not only a
biomedical phenomenon but one is influenced by social, psychological,
cultural,economic and political factors of the people concerned so health is both a
biological and social phenomenon.
4-
holistic concept
, recognizes the strength of social, economic, political and
environment influences on health .
*Health is a state of complete physical, mental and social wellbeing and not merely
an absence of disease or infirmity
. (1948)
The ability to lead a socially and economically productive life.
(1984)
What are the
spectrum of health?
1- Positive life
2- better health
3- freedom from sickness
4- unrecognized sickness
5- mild sickness
6- severe sickness
7- death
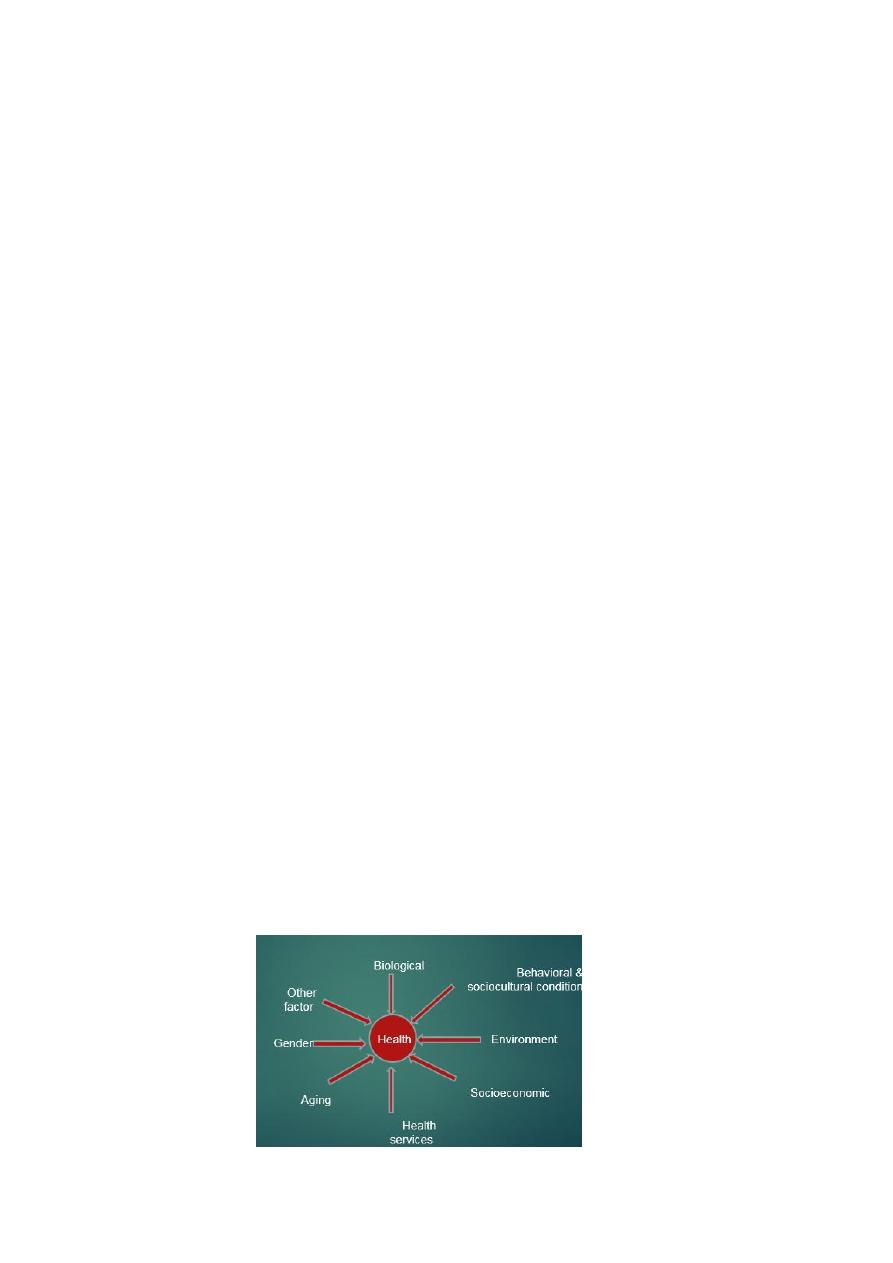
Determinants of health

Concept of disease
Disease process is
1- illness : is a subject state of a person who feels aware of not being well
with evident sign and symptoms.
2- sickness : is a state of social dysfunction.
3- disease : is maladjustment (physiological) of the human being to
environment.
Natural history of disease refers to the progress of a disease process in an
individual over time, in the absence of intervention.
The process begins with
exposure
to or accumulation of factors capable of
causing disease
Without medical intervention, the process ends with
1- recovery
2- Disability.
3- death.
Concept of prevention
: is always better cure, as per the natural of history
disease epidemiology has derived to 4 levels of prevention disease .
1- primordial prevention :
prevention of the emergence or development
of risk factors and for chronic disease
For example many health
adult health problems (e.g., obesity, hypertension)
have their early origins in childhood, because this is the time when lifestyles are
formed (smoking, eating patterns, physical exercise).

Efforts are directed towards discouraging children from adopting harmful
lifestyles .
The main intervention is through individual and mass education.
2- primary prevention
:
Measures of prevention undertaken during the phase
of pre-pathogenesis (phase of susceptibility)
Involves two sub-steps: A- Health promotion and B- specific protection
A- Health Promotion : Steps undertaken to improve the level of general
health and well being so that conditions for initiation of disease process
are prevented.
These steps are not specific for any disease or a group of diseases.
It includes
1- improvement in the overall socio-economic status of the population,
2- health education
3- feeding programmes for mothers and children,
4- promotion of breast feeding,
5- promotion of small family norms,
6- education
7- motivation for healthy lifestyle.
B-
Specific Protection :
include measures to prevent the initiation of specific diseases or a group of
diseases.
For Examples
Immunization to protect against specific diseases
Fortification of foods with specific nutrients (as salt with iodine)
Use of condoms to protect against sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)
Use of helmets to protect against head injuries
3- secondary prevention
These include all actions undertaken at the stage of early pathogenesis
(asymptomatic disease) with a view to halt the progress of disease at it’s
earliest, incipient stage, by “early diagnosis and prompt treatment”.
classical example is “screening for disease” for breast cancer (using
mammography) and cervical cancer (using pap smear).
medical examinations of school children, of industrial workers and various
disease screening camps.
4- Tertiary prevention :
These include all measures undertaken when the disease has become
clinically manifest or advanced, with a view to prevent or delay death,
reduce or limit the impairments and disabilities, minimize suffering and to
promote the subject’s adjustment to irremediable conditions.
Tertiary prevention has two types of approaches :

1- disability limitation : These include all measures to prevent the
occurrence of further complications, impairments, disabilities and
handicaps or even death
2- rehabilitation (being well ) :
stands for the combined and coordinated
usage of all the available medical, social, educational and vocational measures,
for training the person to the highest level of functional ability.
The sequence with which a disease turns into a handicap is as follows :
Disease : This is a pathological process and it’s manifestations which
indicate a departure from the state of perfect health.
Impairment : This is the actual loss or damage of a part of body anatomy
or an aberration of the physiological functions that occurs consequent to
a disease.
Disability : This is defined as the inability to carry out certain functions or
activities which are otherwise expected for that age / sex, as a result of
the impairment.
Handicap : This is the final disadvantage in life which occurs consequent
to an impairment or disability, which limits the fulfillment of the role a
person is required to play in life.
Lecture 2 , health service philosophy
The purpose of health care services is to improve the health status of the
population. So these services should be
1- Comprehensive: include all care
2- Accessible : physical, economical, social and cultural
3- Acceptable : to all
5. Community participation
6. Appropriate; relevance to essential human needs , priorities and
policies.
7.Adequate; proportionate to requirements.
8. Available; present at any time
9. Affordable : at a cost the community and country can afford.
10. Feasible
Health care system represented by the following sectors:
1- Public health sector: primary health centers, hospitals
2- Private sector: hospitals, clinics, nursing homes.
3- Voluntary health agencies.
4- National health programmes.

Level of health care
1- primary
2- secondary
3- tertiary
For more information plz go to page 2
Health team : patient care almost always requires team work
Type of health work
1- community health team
2- hospital teams
The team must have a leader who should be able to
1- evaluate the team adequately
2-knows the motivation of each member
Health care system in Iraq
Iraq had developed a centralized free health care system in the 1970s
intensive model of
-
using a hospital based, capital
Iraq developed
a Westernized system
of sophisticated hospitals with
advanced medical procedures during the last years, provided by specialist
physicians (public sector).
Health care system in Iraq are managed by Ministry of Health. In 2008, it
was reported that 1,989 PHC centers giving services to all Iraqi
population.
Lecture 4 | pollution
What are the type of pollution
1- air pollution
2- water pollution
3- noise pollution
4- land pollution
Natural air pollution can include
1- smoke from wild
2- methane released from live stock
3- Volcanic reuptions
Air pollution affect the respiratory tract resulting In
1- immediate effect , acute bronchitis, dyspnea, suffocation and death.
2- delayed effect, chronic bronchitis, lung cancer, asthma, emphysema
and respiratory allergy .

Water pollution can be categorized into 2 groups
1- point sources like
Waste products from factories
Sewage system
Power plants
Underground coalmines
Oil wells
2- non-point sources such as
Rain or snow when it move through the ground and picks up pollutants
towards a major body water .
The run of fertilizers from anamals and crop land
Air pollutants getting washed or deposited to earth
Storm water
Effect the water on health
Water born disease such as , diarrhea , cholera , typhoid fever, malaria ,
trachoma ..
Lecture 5, herbal medicine
conventional medicine
in place of
Alternative medicine: used
using special diet to treat cancer instead of chemotherapy, surgery, etc...
conventional medicine
together with
used
Complementary medicine:
using aroma therapy to relieve discomfort following surgery
Alternative medicine
Nutritional therapies
Supplementation
Relaxation therapies
Exercise
Manipulative therapies
Aromatherapy
Homeopathy
Traditional Chinese Medicine
Herbal Medicine
Origin of herbal medicine:
Primitive men and women treated illnesses using plants, animal parts, and minerals not
part of a common diet, Physical evidence goes back 60,000 years to the burial site of a
Neanderthal man who was buried with 8 species of plants
Powerful ingredients.
Only 15%
of estimated plant species on earth have been investigated for possible Medicinal
uses.
The world Health organization estimates that 80% of the earth population today depends on
plants to treat common ailments.

Herbal medicine :
Plant derived medicines at pharmacological doses where effects
can be measured Symptom based approach to diagnosis
Most common form of alternative medicine.
How do herbs and drugs differ?
Potency
Side effects
Cost
Target
How are herbs and drugs alike
Therapeutic chemicals
Discovery
Administration
Research/testing
Side effects/toxicity
Phytochemicals :
No magic, diets high in fruits, grains, legumes reduce the risk of a
number of diseases, including cancer, diabetes, high blood pressure.
Phytochemicals are the biologically active substances in plants that are
responsible for giving them color, flavor and natural disease resistance.
Classes of phytochemicals
Phenols
Quinones
Flavones, flavanoids
Tannins
Coumarins
Terpenoids
Alkaloids
Polypeptides
How to chose an herbal remedy
Drug interactions
Types of herbs
Specifics
Tonics
The “anti’s
”
Adaptogens: sedative
Bitters ,| Carminatives: release gases,| DEMULCENTS,AND | XPECTORANTS ..

METHODS OF ADMINISTRATION:
Capsules
Fresh vs. dry
Teas, infusions, decoctions
Tinctures, glycerides
Infused oils
Essential oils
Sprays
Tablets
Standardized extracts
Simple or formula
It is necessary for pharmacists to know about basic principles of traditional
medicine for
two reasons
:
1- To be in a position to advise patients who may wish to consult an
alternative practitioner.
2- Traditional use is a common starting point in the ongoing search for new
drugs.
The Diseases in Traditional Systems are Classified into
I- Minor or Self-Limiting Disorders LIKE aches and pain, flatulence, diarrhea.
II- Chronic or Serious Disorders LIKE cancer and some genetic disease .
Traditional Medicine (TM), usually means a lack of specific dose, it is more
:
THE DOSE
..
How much
to take the remedy rather than
How
concerned with
ملزمه رقم: هظحلام
3
و
6
ما
.لخصتهم

محاضره
7
د. هيثم
Medical terminology
Approximately 75% of Medical Terms are based on either Greek or Latin
Word Parts - Building Blocks of medical term
Medical terms are built from word parts with some or all of the following components:
1. Word roots
2. Suffixes
3. Prefixes
4. Combining vowels
5.comining forms
How to Define Medical Terms
Terms can easily be defined by determining the meaning of their parts.
Read left to right, but define by interpreting the suffix, then the prefix, then the combining form.
e.g. Define heminephrectomy?
prefix Root suffix
hemi- neph -ectomy
(Half) (Kidney) (Removal)
Then heminephrectomy means Remove half of kidney

Word root
The word root is the central and foundation of the medical term Usually indicates the part of
the body involved All medical terms must have one or more word roots
You have to know this part
Gastr- = stomach
Gardi - = heart
Arth - = joint
Ophthal- = eye
Nephr- = kidney
combining vowel
Usually an ‘o’ and occasionally an ‘I’
Has no meaning of its own
Makes pronunciation easier
Can be found between word roots
Can be found between word roots and a suffix
When a vowel is added to a root word, it is called a combining form
Examples of combining form according to systems
1- Combining form for Body Systems Cardiovascular
angi/o
vessel
aorto/o
aorta
arteri/o
artery
cardi/o
heart
coron/o
heart
phleb/o
vein
ven/o vein
2- Combining form for Body Systems Digestive
an/o
anus
append/o
appendix
cholecyst/o gallbladder
col/o
colon
duoden/o
duodenum
esophag/o
esophagus
gastr/o
stomach
hepat/o
liver
ile/o
ileum

jejun/o
jejunum
or/o
mouth
pancreat/o
pancreas
pharyng/o
pharynx
proct/o
aus and rectum
rect/o
rectum
sigmoid/o
sigmoid
stomat/o
mouth
3- Combining form for Body Systems Endocrine
adren/o
adrenal
hypophys/o pituitary
oophor/o
ovary
ovari/o
ovarian
orchi/o
testis
pancreat/o
pancreas
parathyroid/o parathyroid
pituitar/o
pituitary
thym/o
thymus
thyroid/o
thyroid
4- Combining form for Body Systems Reproductive
cervic/o
cervix
vagin/o
vagina
hyster/o
uterus
mamm/o
breast
uter/o uterine
oophor/o
ovary
salping/o fallopian tube
balan/o
penis
orch/o
testis
prostat/o
prostate
scrot/o scrotum
5- Combining form for Body Systems Skeletal
arthr/o
joint
chondr/o
cartilage
cost/o
rib
crani/o
skull
ligament/o
ligament

my/o
muscle
muscul/o
muscle
myel/o bone marrow
oste/o
bone
pelv/o
pelvis
vertebr/o
vertebra
6- Combining form for Body Systems Respiratory
alveol/o
alveolar
bronch/o
bronchial tube
cyan/o
blue
laryng/o
larynx
nas/o
nose
rhin/o
nose
pharyng/o
pharynx
phren/o
diaphragm
pneumon/o
lung
tonsill/o
tonsils
trache/o
trachea
7- Combining form for Body Systems Urinary
cyst/o
urinary bladder
nephr/o
kidney
ren/o
renal
pyl/o
renal pelvis
ureter/o
ureter
urethr/o
urethra
8- Combining form for Body Systems Nervous
cerebell/o
cerebellum
cerebr/o
cerebrum
encephal/o
brain
medull/o
medulla
myel/o spinal cord
neur/o
nerve
9- Combining form for Body Systems Miscellaneous
aur/o
ear
ot/o
ear
cutane/o
skin
derm/o
skin
myring/o eardrum
ocul/o
eye
onych/o
nail
ophthalm/o
eye
pil/o
hair
retin/o retina
trich/o
hair
ungu/o
nail
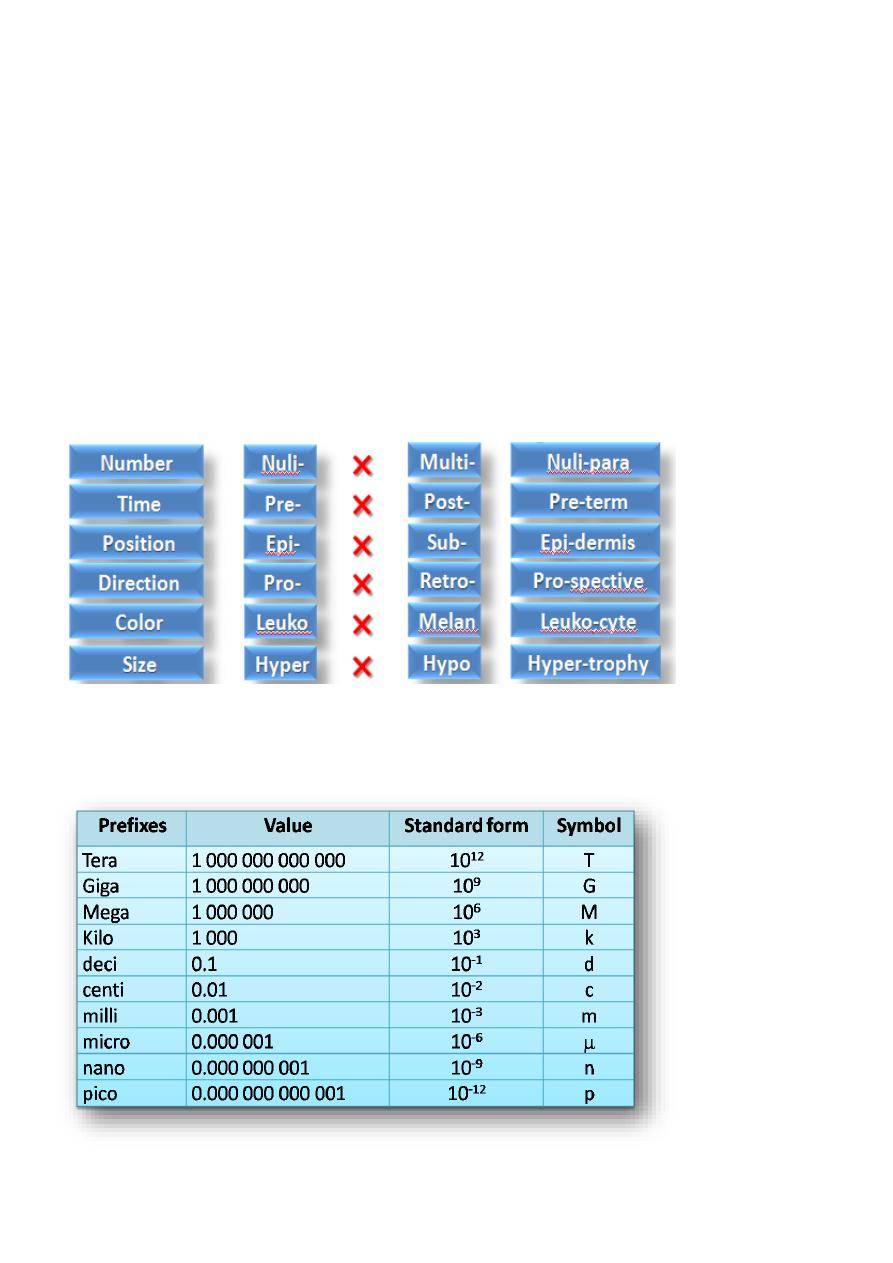
Prefixes
Syllable located at the beginning of a word Changes the meaning of the word Usually
indicates a number, time, position, direction, color, size etc. or sense of negation
Numerical prefixes

Color prefixes
Suffixes
Suffix is the word part attached to the end of the word root to modify its meaning.
The suffix usually indicates the surgical procedure, diagnosis & pathology.
All medical terms must have a suffix.
Surgical suffixes

If singular form of term end in, the plural is usually formed by changing to
Suffixes
Suffix – Noun

Suffixes – Adjective
Numerical prefixes
= quadrant
¼
Semi , hemi
=
½
0 = nulli ,
1= mono , uni , prim
2= bi , di
3= tri , ter
4= tetra , quadni
5= Penta , quinque
6= hexa , sexa
7= hepta
8= octa
9= nona
10= deca
ODAY ABDULQADER , GOOD LUCK
