“Malignant skin tumors”
د. عبد الرحمن عبد العزيزجراحه تجميليه - مرحلة خامسه
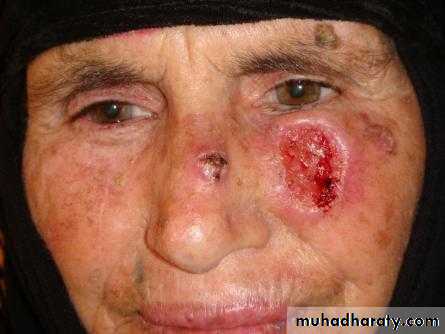
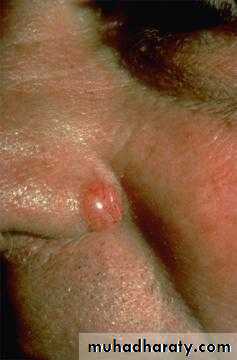
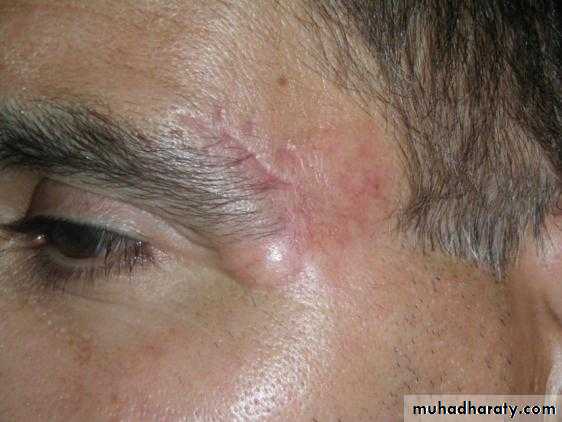
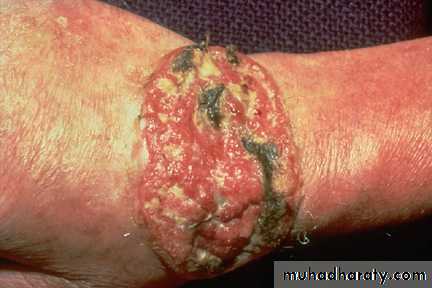
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC)
Most common, 75% of skin tumors.
Arise from basal layer of epidermis.
Affects white skin, Male: Female=3:2 .
Occurs on exposed parts: face, neck, scalp.
No metastasis.
Commonly Caucasian male older than 60 years
Clinical types:
1-nodulo-ulcerative : commonest type, usually single lesion, as pearly or translucent nodule with raised borders and telangiectasias, grow slowly, tend to ulcerate, giving rise “rodent ulcer”.2. Pigmented BCC: second most common type, combines features of nodulo-ulcerative &deep brown to lack brown to black nodule.
3-Superficial BCC: lightly pigmented erythematous patch, may be scaly, with areas of scarring, mistaken for eczema ,often multiple, on trunk.
4-Sclerosing BCC: yellowish-white, ill-defined border, resemble scar ,it showes peripheral growth with central scarring.
Diagnosis: by biopsy (FNA, incisional biopsy , excisional biopsy)
Treatment:Surgery: excision with 2-5 mm. healthy margin, & repair defect by skin graft or flap.
Radiotherapy: in large lesion, oldman, refusing operation.
Cryotherapy: for primary lesion < 2 cm., but hypopigmentation, scarring are disadvantages.
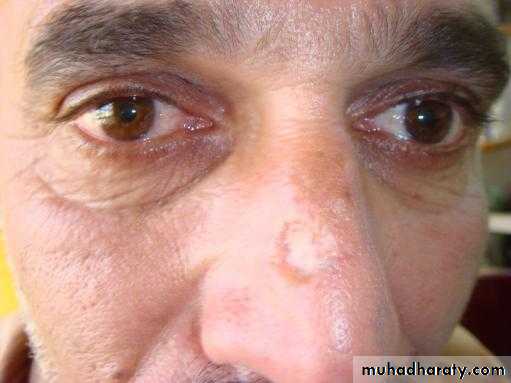
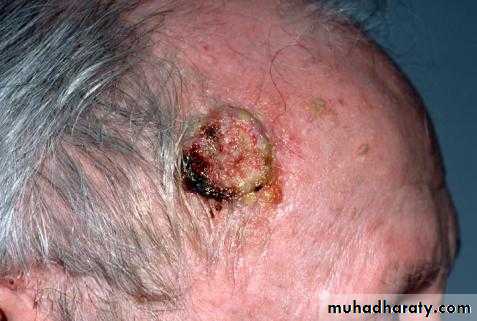
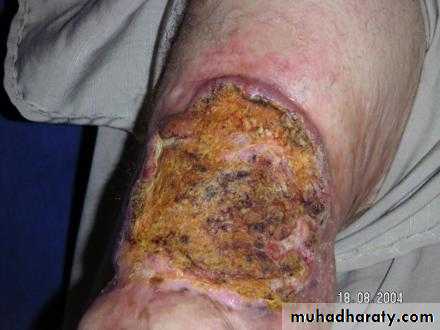
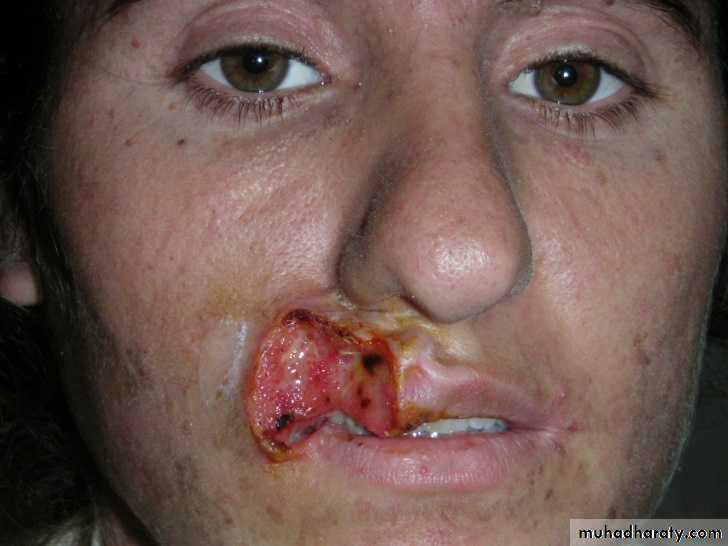
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
(SCC) is second most common skin cancer.
arises from the malignant transformation of keratinocytes in the epidermis.
arise either in normal skin or in preexisting lesion as (actinic keratosis, leukoplakia, radiation keratosis, scars( where called Marjolin ulcer).
Clinically: present as irregular ulcer, everted edge, indurated base,attached deeply, blood-stained discharge,frequent lymph n. positive.
Types:
1-slow growing : is verrucous,may be deeply locally invasive,likely to metastasise, more differentiated.
2-Rapid growing: more nodular & indurated,early ulceration with local invasion,greater metastasis, less differentiated.
Treatment: biopsy done.
1- Excision
Surgical excision with 10-mm margin
If lymph n. positive: excise lesion with lymph n. dissection.
2-Radiation therapy is best used in older patients,
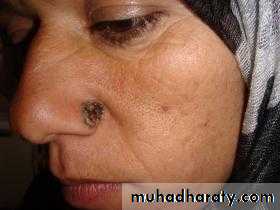
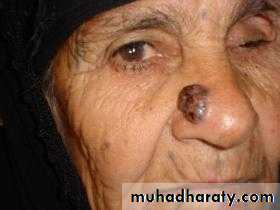
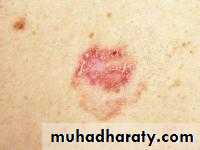
Malignant Melanoma:
result of the malignant transformation of melanocytes, the pigment forming cells.Occurs mainly in skin, also in eye, mouth,anus, vagina .
Malignant melanoma (MM) types:
1- Superficial spreading : 70% of MM, arise in a preexisting dysplastic nevus which changes slowly over several months , usually flat, later becomeirregular and elevated.
2-Nodular melanoma : 15-30%, growth deeply into dermis .
3-Lentigo maligna: 4-10%, often larger than 3 cm, flat, tan, and begin as small, frecklelike lesions. They occur in sun-exposed areas (e.g., face and neck) of older individuals.Breslow staging: based on vertical thickness of the lesion from thickest point:
Stage 1 : Thickness of 0.75 mm or lessStage 2: Thickness of 0.76-1.5 mm
Stage 3 :Thickness of 1.51-4 mm
Stage 4: Thickness greater than 4 mm
Surgical treatment:
After diagnosis by biopsy, wide excision of primary lesion & removal of lymph node involved or at high risk.
Excision with 2-3 cm healthy margin.
Elective lymph n. dissection done in lesions 1-4 mm depth, but not <1mm or >4mm.