Wheezing in infants
A wheeze is a musical and continuous sound that originates from oscillations in narrowed airways.Wheezing is heard mostly on expiration as a result of critical airway obstruction.
Acute bronchiolitisPredominantly a viral disease. Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is responsible for >50% of cases .Other agents include parainfluenza ,adenovirus, Mycoplasma, and, occasionally, other viruses.
Acute bronchiolitis is characterized by bronchiolar obstruction with edema, mucus, and cellular debris.
CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
The infant 1st develops a mild upper respiratory tract infection with sneezing and clear rhinorrhea.fever of 38.5–39°C
Gradually, respiratory distress ensues, with paroxysmal wheezy cough, dyspnea, and irritability.physical examination
wheezing.The degree of tachypnea does not always correlate with the degree of hypoxemia or hypercarbia
nasal flaring and retractions.
fine crackles or overt wheezes, with prolongation of the expiratory phase.
Hyperinflation of the lungs may permit palpation of the liver and spleen.
DIAGNOSIS
The diagnosis is clinical, particularly in a previously healthy infant presenting with a first-time wheezing episode during a community outbreak.
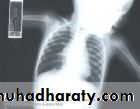
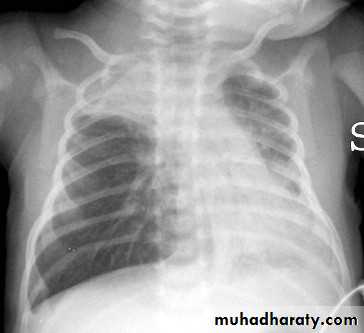
chest radiography reveals hyperinflated lungs with patchy atelectasis.
The white blood cell and differential counts are usually normal.
Viral testing
TREATMENT
Infants with acute bronchiolitis who are experiencing respiratory distress should be hospitalized.mainstay of treatment is supportive.
If hypoxemic, the child should receive cool humidified oxygen.
The infant may be fed through a nasogastric tube.
Frequent suctioning of nasal and oral secretions often provides relief of distress or cyanosis.
TREATMENT
A trial dose of inhaled bronchodilator may be reasonable, with further therapy predicated on response in the individual patient.
Corticosteroids are not recommended in previously healthy infants with RSV
TREATMENT
Ribavirin, an antiviral agent administered by aerosol, has been used for infants with congenital heart disease or chronic lung disease.Antibiotics have no value unless there is secondary bacterial pneumonia.
No support for RSV immunoglobulin administration during acute episodes of RSV bronchiolitis.
PROGNOSIS
The case fatality rate is <1%, with death attributable to apnea, uncompensated respiratory acidosis, or severe dehydration.Infants with conditions such as congenital heart disease, bronchopulmonary dysplasia, and immunodeficiency often have more severe disease, with higher morbidity and mortality.
PROGNOSIS
There is a higher incidence of wheezing and asthma in children with a history of bronchiolitis unexplained by family history or other atopic syndromes.PREVENTION
pooled hyperimmune RSV intravenous immunoglobulin (RSV-IVIG) and palivizumab, an intramuscular monoclonal antibody to the RSV F protein, before and during RSV season.Palivizumab is recommended for infants <2 yr of age with chronic lung disease (bronchopulmonary dysplasia) or prematurity.
Meticulous handwashing is the best measure to prevent nosocomial transmission.
Wheezing associated conditions
Bronchial asthma
Cystic fibrosis
Congenital malformations (Rings and slings )
Foreign body aspiration
Gastro esophageal reflux
Trauma and tumors
Bronchial asthma
Asthma is characterized by airway inflammation, bronchial hyperreactivity, and reversibility of obstruction .Of all the infants who wheezed before 3 yr old, almost 60% stopped wheezing by 6 yr.
Risk factors for persistent wheezing included maternal asthma, maternal smoking, allergic rhinitis, and eczema at <1 yr of age.Cystic fibrosis
Persistent respiratory symptoms, digital clubbing, malabsorption, failure to thrive, electrolyte abnormalities, or a resistance to bronchodilator treatment .Congenital malformations
External vascular compression includes a vascular ring, or a vascular slingCardiovascular causes of wheezing include dilated chambers of the heart, and pulmonary edema .
Foreign body aspiration
78% of those who die from foreign body aspiration are between 2 mo and 4 yr old.Atypical histories or misleading clinical and radiologic findings may be misdiagnosed with asthma or another obstructive disorder as inflammation and granulation develop around the foreign body.
Gastroesophageal reflux
Can cause wheezing with or without direct aspiration into the tracheobronchial tree.Without aspiration, the reflux is thought to trigger a vagal or neural reflex, causing increased airway resistance and airway reactivity
Trauma and tumors
Accidental or nonaccidental aspirations, burns, or scalds of the tracheobronchial tree can cause inflammation of the airways and subsequent wheezing.Any space-occupying lesion either in the lung itself or extrinsic to the lung can cause tracheobronchial compression and obstruction.
PNEUMONIA
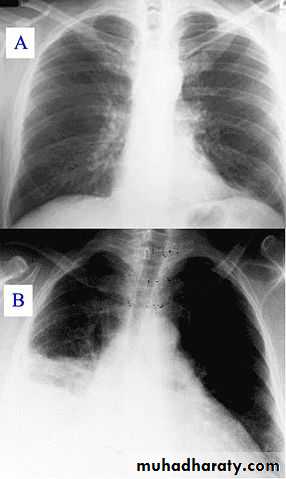
Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) :acute infection of the pulmonary parenchyma in a patient who has acquired the infection in the community, as distinguished from….hospital-acquired pneumonia (nosocomial).
Viral pneumonia
Most children younger than 5 years of age who are admitted to the hospital with pneumonia have viral pneumonia .Viral pneumonia does not require antibiotic therapy, unless a mixed infection or secondary bacterial infection is suspected.
Typical bacterial pneumonia
Typical bacterial pneumonia may occur in children of all ages.Streptococcus pneumoniae is the most common type of bacterial cause of pneumonia in children of all ages.
S. aureus
Strept pyogenes
H. influenzae type b ,nontypeable H. influenzae, and M. catarrhalis.
Antibiotic regimens include:
amoxicillin,Ceftriaxone or cefotaxime .Atypical bacterial pneumonia
(M. pneumoniae and Chlamydia pneumoniae) is most common in children older than 5 years.
Antibiotic include:
Erythromycin or AzithromycinFor children older than 8 years: Doxycycline
Nosocomial pneumonia
S. aureus, Enterobacteriaceae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and anaerobes.Acceptable broad-spectrum empiric regimens include an aminoglycoside plus:
Piperacillin-tazobactam or Meropenem.clindamycin plus an aminoglycosides
Aspiration pneumonia
Appropriate antibiotics regimens for hospitalized children include:
Clindamycin or Meropenem
Immunocompromised host : vancomycin if methicillin-resistant staphylococcus is considered.
and possibly trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for Pneumocystis jirovecii.
DURATION OF TREATMENT
Uncomplicated cases :7-10 days or at least one week beyond resolution of fever.