Pharmacology 2016Hypertension and CVS Diseases
Hypertension is the most common cardiovascular disease and pathophysiologically hypertension can be classified into two main groups.a. Essential or primary hypertension, where the cause for rise in blood pressure is not known. Responsible for majority of cases.
b. Secondary hypertension, where rise is due to renal disease e.g. chronic diffuse glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis; due to some vascular disease e.g. renal artery disease or due to some endocrinal disorders e.g. pheochromocytoma, Cushing’s syndrome and primary aldosteronism.
Hypertension (HT)
HypertensionBlood pressure (BP) > 140/90 mmHg
The aims in the treatment:
Decrease BPThus decreasing or avoiding the complications
Stroke
MI
Organ damages (kidneys, eyes)
Hear failure
Risk group
Age (40+)
Gender
Obesity
Stable-no movement..
Dislipidemia
Diabetis mellitus (DM)
Alcohol/cigaratte
Family history
Basic principles of treatment
Life style change (weight loss, regular excersizes,)Pharmacotherapy:
Decrease cardiac debility (B-blockers, Ca channel blockers)
Decrease in plasma volume (diuretics)
Decrease the peripheral resistance (vasodilators)
Drugs used to treat HT
DiureticsBeta Adrenoreceptor Blockers (Propranolol, atenolol,metoprolol)
ACE inhibitors
Angiotensin Receptor Antagonists
Ca++ channel Blockers (verapamil, diltiazem)
Alpha-adrenoreceptor blockers (prazosin)
Less preffered drugs:
Centrally acted drugs (alpha-methyl dopa)
Minoxidil
Hydralazine (vasoldilator)
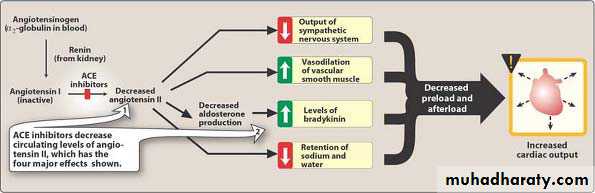
Effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors
Diuretics
Thiazide diuretics are the first choice (Hydrochlorthiazide -HCT):Delays the complications
Low side effects, not expensive
Loop Diuretics (Furosemide): Stronger..
Potassium sparing Diuretics (Sipronolactone)
The main action of thiazides is exerted on the early segment of distal tubule or cortical diluting segment. They inhibit reabsorption of sodium and chloride.
Loop Diuretics:
diuretics act primarily by inhibiting electrolyte reabsorption in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle. As much as 20% of the filtered Na+ may be reabsorbed in the loop of Henle.
These agents bind to Cl– binding site of Na+-K+-2Cl– cotransporter glycoprotein and inhibit its transport function in ascending limb of loop of Henle.
Sempathetic system antagonists
Beta adrenoreceptor blockers (their action is proved)
Alpha adrenoreceptor blockers (their action is controversial)
Ganglion Blockers (older drugs)
Renin-angiotensin system blockers:
ACE inhibitors (action is proved)AT-1 receptor blockers (new)
Renin-Angiotensin System:
Vasoconstriction ………..
Aldosterone release ……PB increase
Increase in smooth muscle cells
ACE inhibitors
Captopril, enalapril, lisinopril…These drugs act primarily by suppressing renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.
The main action of all ACE inhibitors is to inhibit conversion of angiotensin I (inactive) to angiotensin II (active). They inhibit the angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE). So, Angiotensin II production is inhibited.
Decrease in angiotensin II results in dilatation of peripheral vessels leading to a reduction in systemic vascular resistance and a decreased aldosterone secretion
ACE inhibitors
The important common side effect: Dry CoughContrandicated during pregnancy
Used for HT and congestive heart failure
Can be administered safely in patients of hypertension with diabetes mellitus or bronchial asthma
Calcium Channel blockers
Verapamil, diltiazem
Interfere with the calcium entry into the myocardial and vascular smooth muscles and thereby decreasing the availability of the intracellular calcium.
Calcium channel blockers depress the contractility of the myocardium and decrease the cardiac work and the requirement of oxygen. This effect proves to be beneficial in the treatment of angina pectoris
AT-Receptor Antagonists
Losartan, valsartan, candesartan (sartan~ssss)They are competetive antagonists of AT-1 receptors.
it has no in peptide structure
Antagonise the AT-II`s poliferative and vasoconstrictor effects.
The important difference from ACE, they do not cause dry cough/or it less.
Vasoldilators
They relax smooth blood vesselsNitric oxide donors (nitropruside)
Ca-Channel Blockers: (nifedipine, verapamil)
Potassium channel openners (diazoxide)
HT emergency:
BP = 220/130Stroke risk
Emergency treatment: (IV)
Sodium nitropuriside+Glyceryl trinitrate+ACE inh.(sublingual)
Congestive heart failure
Congestive heart failure(CHF) is a clinical syndrome with multiple causes and involve the right or left ventricle or both and in CHF, cardiac output is usually below the normal range.
Treatment principles
Decrease heart effortDecrease heart load : weight loss, dec.BP, dec blood volume (Anti-HT drugs, diuretics, vasodilators)
Strengthening heart contraction:
Cardiac glycosides, beta agonists)Decrease salt intake
Cardiac Glycosides
Digitalis:Digoxin
Digitoxin
Oubain
Digitalis lanata and D. Purpurea
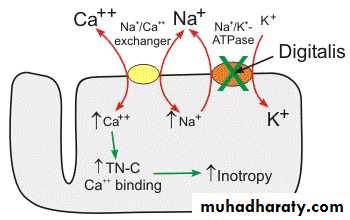
MOA of DigitalisInhibition of Na+ /K+ pump….. Intracellular Na+ concentartion increases
Accumulation of Na+/Ca++ exchange decrease…. Increases Ca ++ inside cell. Leading to
Contractility increases (+) inotropic effect
Increase in cardiac output
Drugs used in Angina pectoris
Angina pectoris is a symptom of ischaemic heart disease. It develops as a result of an imbalance between the oxygen supply and oxygen demand of the myocardium.1. Nitric oxide (NO)
Endojen NO:
Strong vasodilator
Synthesized in the endothelium tissue and thrombocytes..
2. Nitrates (Nitroglycerine /Glyceryl trinitrate (GTN)& nitrpurisiate) :
Used in HT emergency (IV infusion)Heart ache (angina pectoris treatment), <sublingual>
Pulmonary HT treatment
3. Beta blockers ( Propranolol, metoprolol,bisoprolol):
Decreases O2 requirement and work of heart muscle and therefore is effective in reducing the chest pain on exertion which occurs in angina.Antiarrhythmic Agents
Cardiac arrhythmias is a group of disorder characterized by an abnormal cardiac rhythm and arise as a result of disorders of impulse formation or conduction or both.Tachyarrhythmias (sinus rate more than 100 per minute) are produced by a disturbances of impulse generation or of impulse conduction in the heart.
Bradycardia can be due to depressed sinus automaticity and AV block. Bradyarrhythmias manifest as slow heart rate (less than 50 to 60 beats per minute in sleep)
Antiarrhythmic Agents
Class-I: Sodium channel blockers (quinidine, lignocaine)
Class-II: Beta adrenergic blockers (Propranolol)
Class-III: Potassium channel blockers: Drugs that prolong effective refractory period by prolonging action potential (amiodarone)
Class –IV: CCB (calcium channel blockers)
Others: atropine, digitalis, adenosine
Antihyperlipidemic Agents
They lower the levels of lipoproteins and lipids in blood. The plasma lipids are present in lipoproteins after combining with apoproteins. They are high density lipoproteins (HDL), low density lipoproteins (LDL), very low density lipoproteins (VLDL) and intermediate density lipoproteins (IDL).Atherosclerosis is main cause of cardiovascular deaths.
Antihyperlipidemic Agents
Hyperlipidemia :Cholesterole, TG, HDL
Genetic disordersLife style
High calorie intake in food
Cholesterole
Staturated & trans- fat
Raised levels of VLDL, LDL and IDL are atherogenic,
while HDL is protective because it facilitates removal of cholesterol from tissues.,
LDL oxidation inhibition,
Avoids thrombocyte agregation
Risk factors of Coronery Heart Disease
LDL increaseHDL decrease
Smoking
HT (BP≥ 140/90)
Type II DM
Age (male>45, female > 55)
Family history
Obesity
Plasma Lipid Levels
Cholesterole level:<200 mg/dl (normal)
200-239 mg/dl ( near to borderline)
≥ 240 mg/dl (high)
HDL-C
<40mg/dl (Low) in female <50
>60 mg/dl (high)
LDL-C
<70 mg/dl (level should be in high risk patients)<100mg/dl (optimum)
100-129 mg/dl (near to optimum)
130-159 mg/dl (borderline-high)
>190 mg/dl (very high)
TG:
<150mg/dl (normal)
150-199 mg/dl (bordeline-high)
200-499 mg/dl (high)
≥500 (very high)
Which patients should be treated?
Male and also females (postmenaposale)Age: male >45, femal >55
Cerebrovascular diseases : Statins can reduce risk of stroke
Peripheral vascula diseases
HT patients and smokers
Type 2 DM
Drugs
1. HMG CoA reductase inhibitors (statins):
atorvastatin, lovastatin,simvastatin and rosuvastatin
2. Fibric acid derivatives :Clofibrate, Gemfibrozil
3. Agents inhibiting production of VLDL and lipolysis in adipose tissue: Nicotinic acid
4. Interferes with intestinal absorption of cholesterol: Cholestyramine
5. Inhibit synthesis of LDL: Probucol
6. Miscellaneous: Gugulipid
Statins
MOA:Block the synthesis of cholesterol in liver by competitively inhibiting HMG CoA reductase (Hydroxymethyl-Glutaryl Coenzyme A Reductase) activity,
Cause depletion of critical intracellular pools of sterols and increased transcription of LDL receptors leading to enhanced removal from plasma of LDL cholesterol and LDL precursors. They also reduce hepatic synthesis of VLDL, increase plasma HDL.
Statins
Lovastatin: causes marked reduction in LDL cholesterol and also raise HDL level and may lower the triglyceride level.Simvastatin: Simvastatin, is twice as potent as lovastatin. Reduce both normal and elevated low-density lipoprotein (LDL)
Atorvastatin: reduces total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol and apolipoprotein B hypercholesterolemia and mixed dyslipidemias.
Also reduces VLDL-cholesterol and TG and produces variable increases in HDL-cholesterol and apolipoprotein A1. Atorvastatin reduces LDL-cholesterol in patients with familial hyper-cholesterolemia (FH).
Adverse effects of statins
Hepatotoxicity (ALT, AST levels should be tested before starting the treatment)
Myopathy
Drug interactions of statins with:
GemfibrosilCyclosporine
Digoxin
Niacin
Niacin (Nicotinic acid)
Vitamin B-complexHas hypolipidemic effect
Increases HDL-C level and decreases TG, and LDL-C
Also inreases LPL (lipoprotein lipase) activity which is a key enzyme in degradation of VLDL resulting in lower circulating triglycerides.