COMA
ObjectivesTo roughly understand the anatomical basis of Consciousness
To know the common causes of coma
To know the basic management of patients with coma.Definition
Consciousness?A state of awareness of self and environment and responsiveness to external stimulation and inner need.
- Adams -
Aetiology
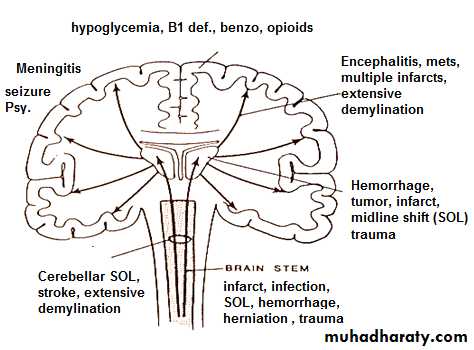
Metabolic-extrinsic: Alcohol
substance abuse
Drugs
heavy metals and poisons
Aetiology
Metabolic-intrinsic: fluid (Shock) and electrolytes
Nutritional
Endocrine
Organ failure
Aetiology
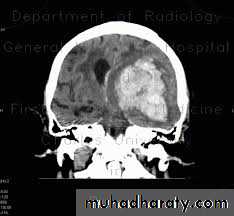
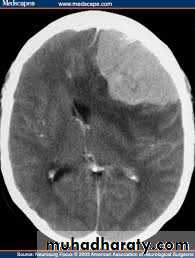
Structural- Supratentorial
Traumatic
Vascular
Inflammatory
Neoplastic
Degenerative
Aetiology
Structural
- Infratentorial
Traumatic
Vascular
Inflammatory
Neoplastic
Degenerative
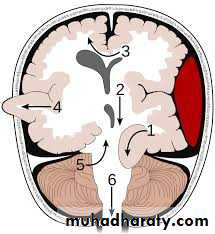
Brain Herniation
Supratentorial herniation
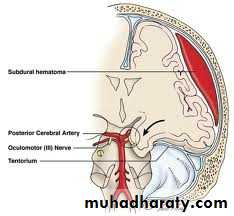
• Uncal (transtentorial)• Central
• Cingulate (subfalcine)
• Transcalvarial
Infratentorial herniation
• Upward (upward cerebellar or upward transtentorial)
• Tonsillar (downward cerebellar)
Workup
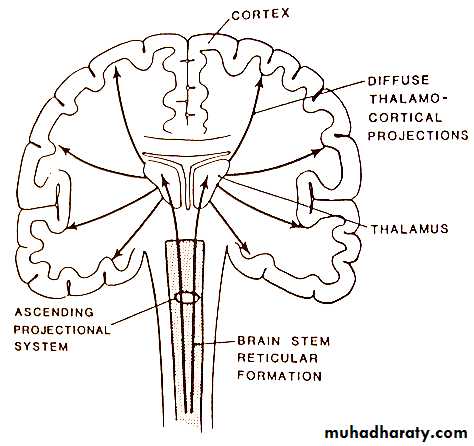
How bad it is?Is it Coma?
Is it metabolic x Structural?
Supra x Infra _tentorial?
Workup
ABC
History
[Hypoglycemia, B1 def., Narcotic, Benzodiazipine] immediate correction
Physical examination
WorkupPhysical examination
Medical exam.
Neurological exam.Neuro-exam
Goals-functional assessment!
-Is there structural brain damage?-Supra x Infra tentorial?
-Differential diagnosis of Coma
Neuro-exam
Consciousness:Responses to painful stimuli?
R/O locked in state,
Vegetative state,
Minimally conscious state
Glasgow-Coma scale
Neuro-exam
Ocular:Hutchison's pupil -uncal herniation
Miotic sluggishly reacting to light – pontineMidsized or Mydriatic fixed to light – Midbrain
Neuro-exam
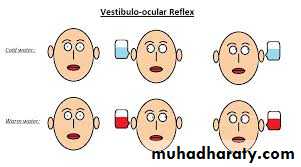
Oculo-cephalicVestibulo-ocular
Neuro-exam
Rest of Cranials:-Fundoscopy
-V: blink
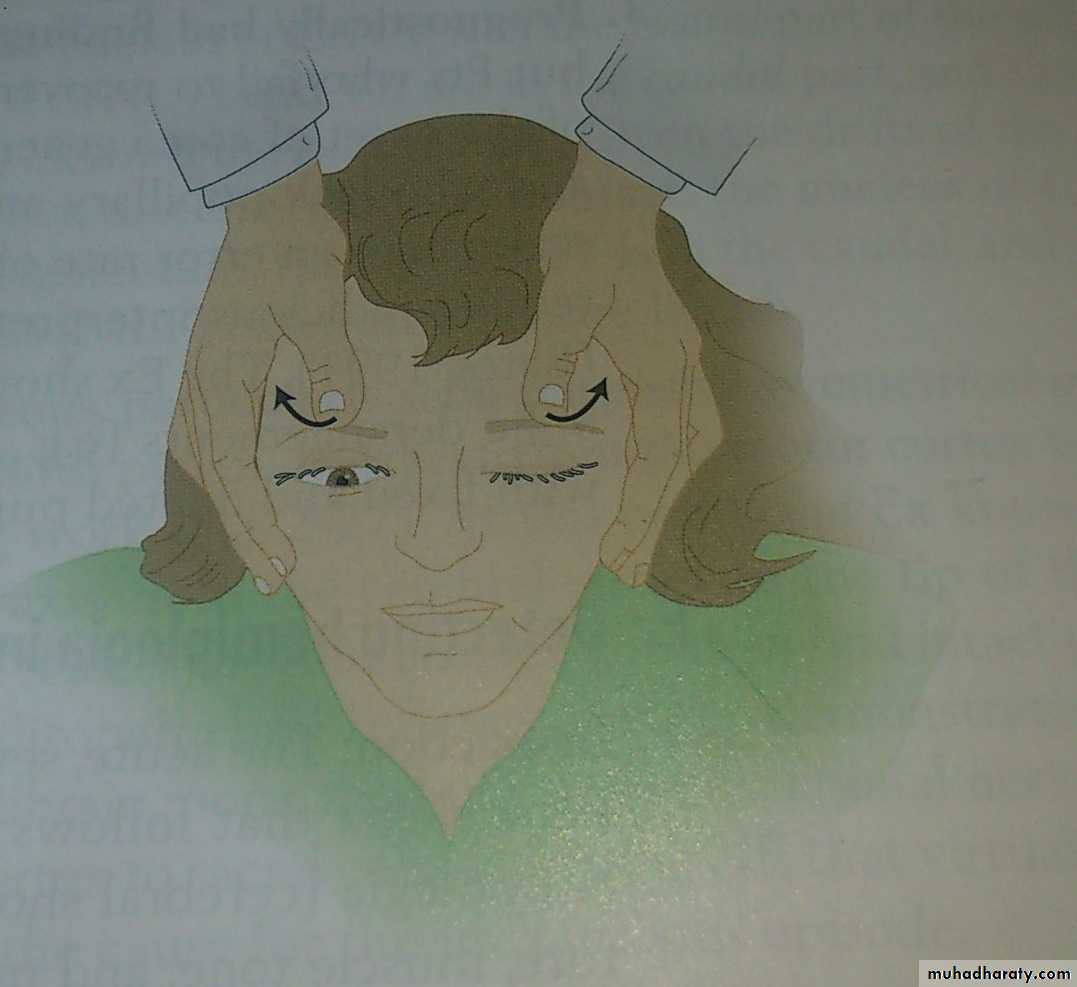
-VII: cheeks and Eyes: Eyelid release test
-Gag
Neuro-exam
Respiratory patterns: Poorly localizingCheyne-Stokes : Supra-tentorial /metabolic
Central neurogenic hyperventilation: Midbrain/pons
Apneustic (short-cycle Cheyne-Stokes): pons/medulla
Ataxic (Biot): medulla
Intermittent: medulla
Neuro-exam
Motor system
Signs of hemiplegia
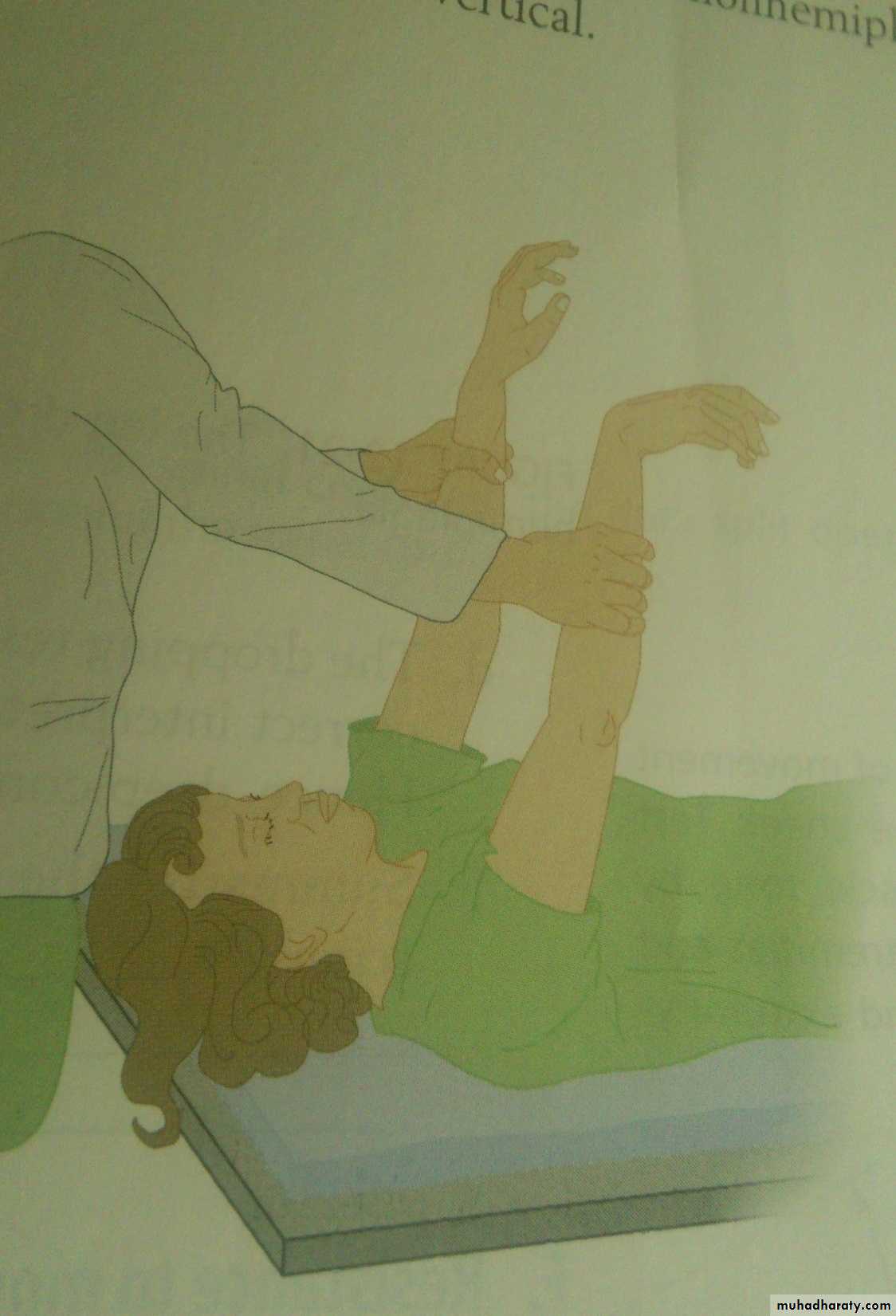
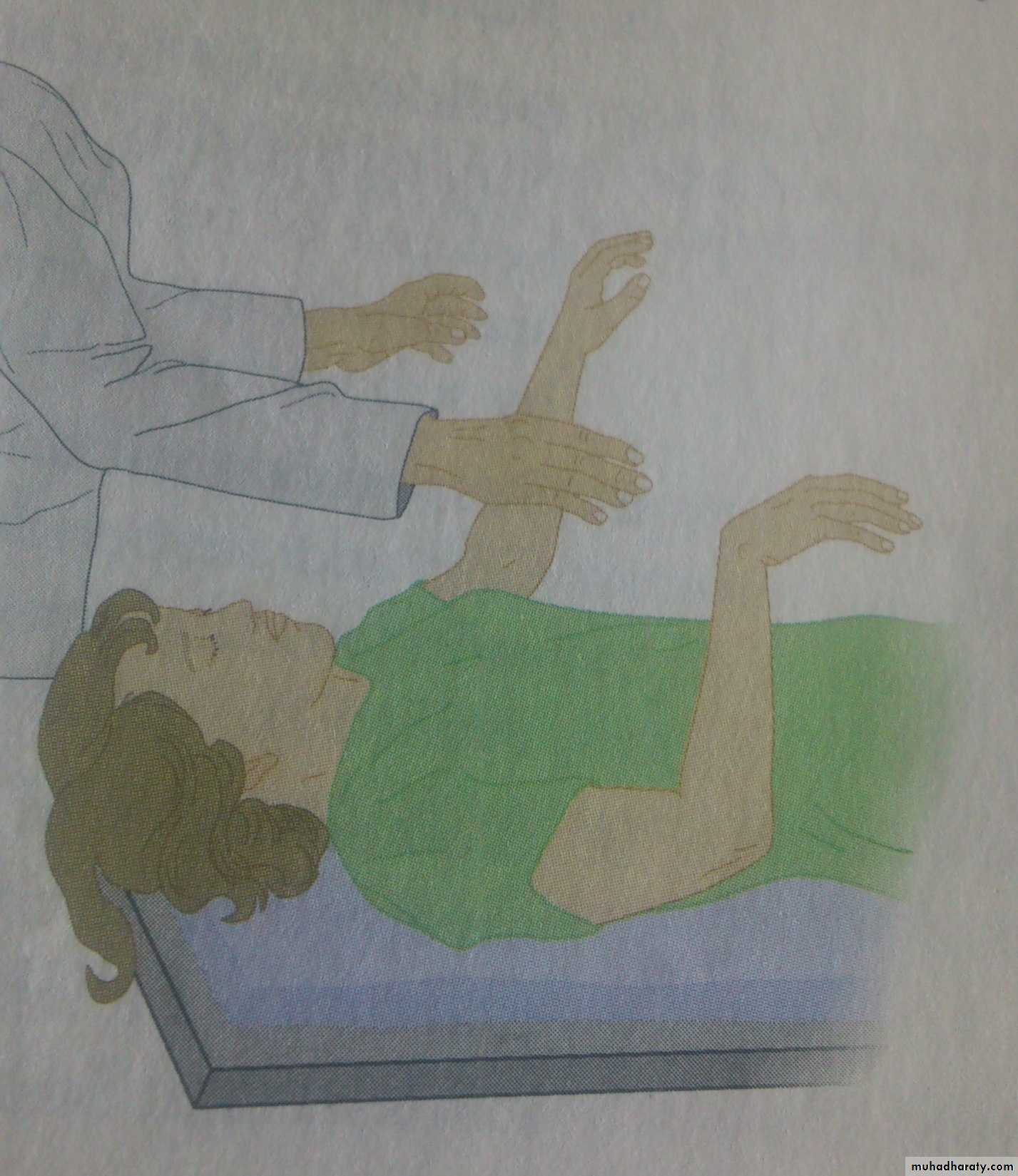
-wrist-dropping test
Arm-dropping test
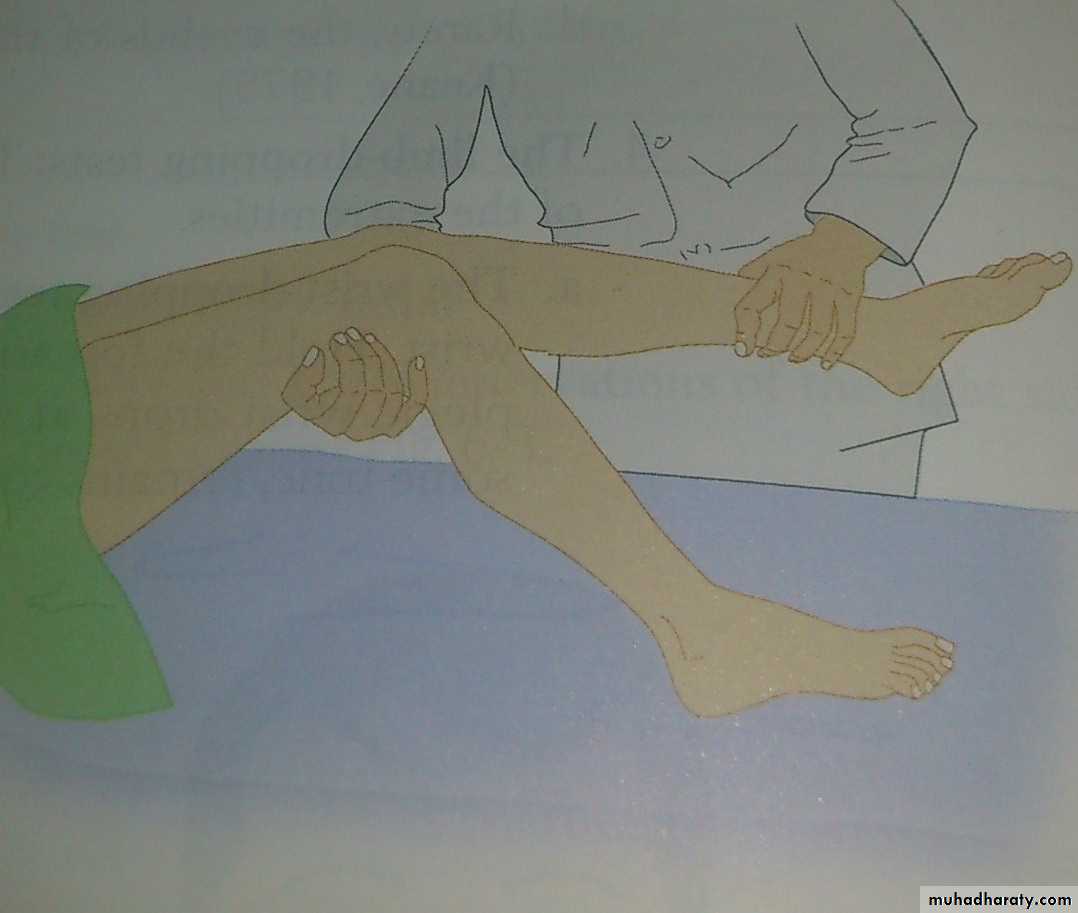
Legs-dropping test
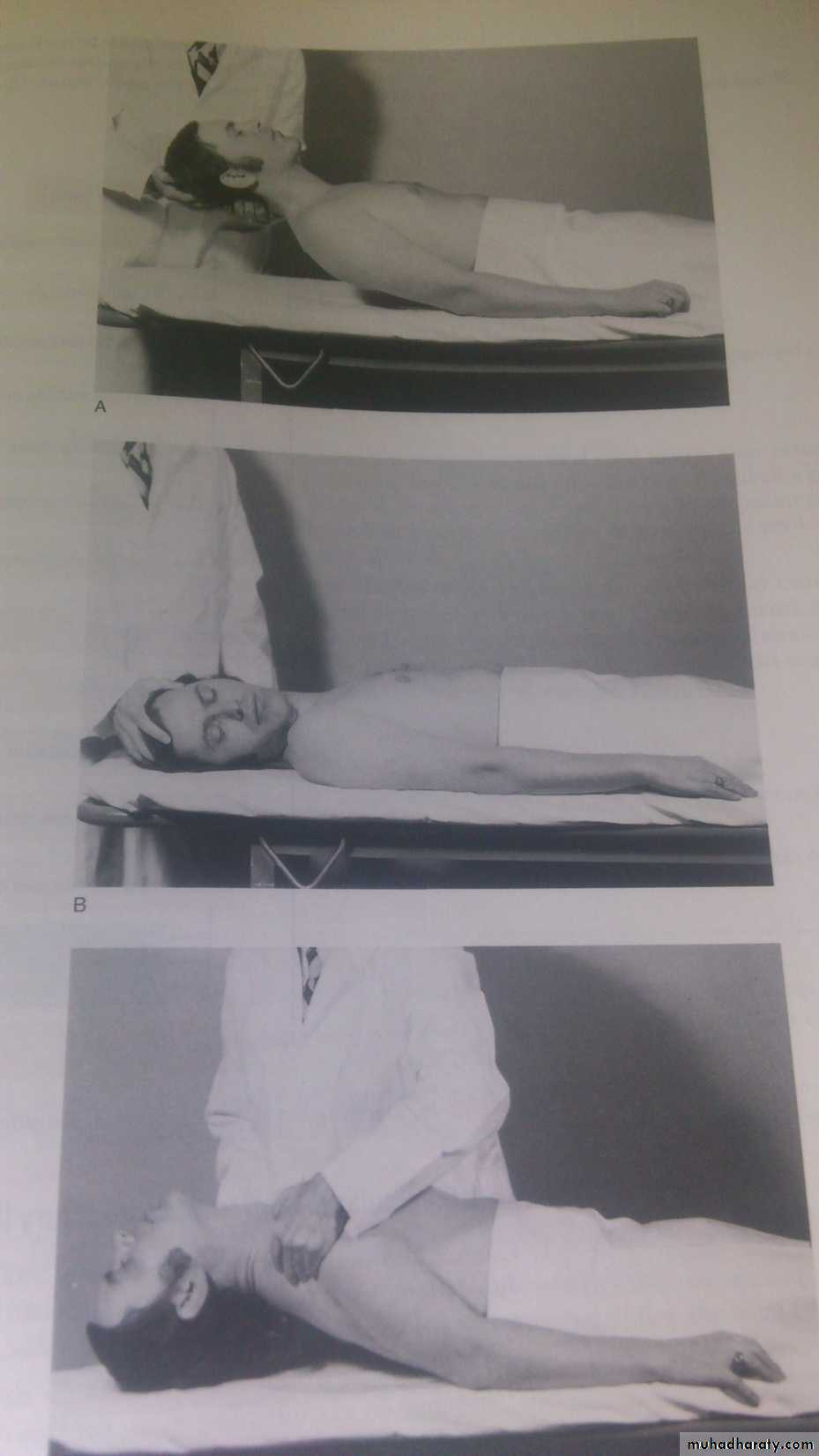
Driven postures: Decorticate, Decerebrate.
Neuro-exam
Meningeal Irritation Signs- Neck stiffness
-Kernig’s sign
-Brudzniski’
Further assessment
. Investigations-Blood
-Bed side
-Imaging
-Toxicology