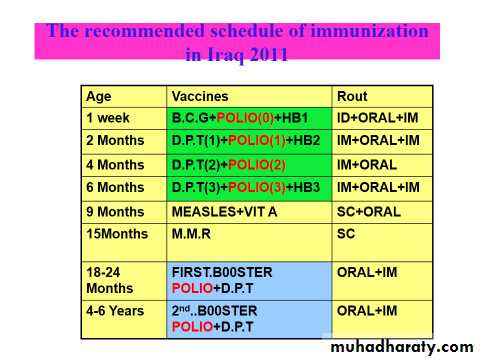
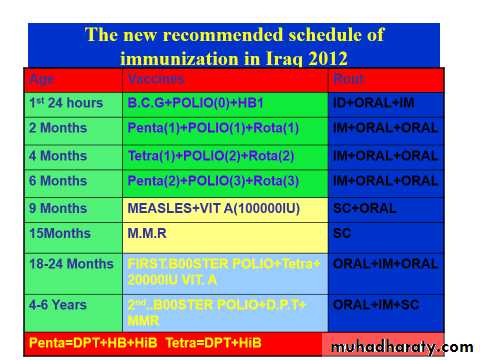
Updates in Iraq national program of immunization 2012
مكتب الجامعة للطباعة والاستنساخطب مجتمع \د.زيد شندالة \محاضرة 7
عدد الاوراق :6
السعر :250
مكتب الجامعة للطباعة والاستنساخ
طب مجتمع \د.زيد شندالة \محاضرة 7
عدد الاوراق :6
السعر :250
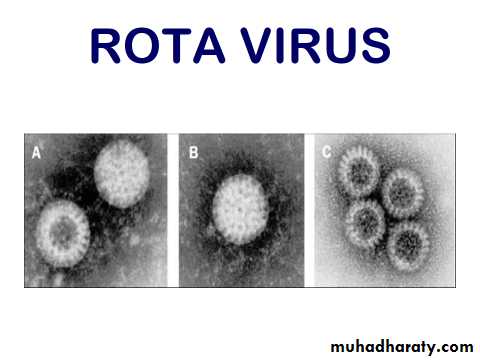
ROTA VIRUS
First identified in 1973 by Bishop (wheel-shaped).There are six species of this virus, referred to as A - F.
Responsible for 5% to 10% of all gastroenteritis episodes among children < 5 years of age.
Most common cause of severe diarrhea in under 5 years.
Responsible for up to 500.000 diarrheal death each year worldwide.
Rota virus Epidemiology
All children has at least 1 infection by age 5 years.
Highest infection rates between 3months-3years.
Reservoir: Human
Transmission: Fecal-oralTemporal pattern: Fall and winter (temperate areas)
Communicability: 2days before to 10days after onset
Rotavirus Immunity
First infection usually dose not lead to permanent immunity.Reinfection can occur at any age.
Subsequent infections generally less severe.
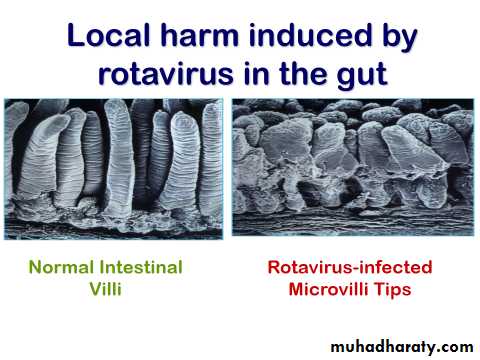
Rotavirus Clinical Features
Incubation period 1-3 days.Variable clinical presentation asymptomatic to severe diarrhea.
Confirmation requires laboratory testing (enzyme immunoassay or RT-PCR).
Rotavirus vaccines
There are two rotavirus vaccines.
RV5 (RotaTeq), is a live oral vaccine manufactured by Merck and licensed by the FDA in 2006
RV1 (Rotarix), a live oral vaccine manufactured by GlaxoSmithKline, was licensed by the FDA in 2008
Rotavirus vaccine ,storage and handling
Provided as a single 2ml oral dose In a buffered stabilizer solution.Store at (2°- 8° C).
Shelf life of properly stored vaccine is 24 months.
Do not freeze.
Administer as soon as possible after being removed from refrigeration.
Rotavirus vaccine recommendations
Routine immunization of all infants without contraindications .Administered at 2, 4 , 6 months of age.
First dose should be administered between 6 and 12 weeks of age (until age 13 weeks).
Do not initiate series after 12 weeks of age.
3 doses better to be completed within 26 weeks of age
Minimum interval between doses is 4 weeks.
Do not administer ANY dose on or after age 32 weeks , even if fewer than three doses have been administered.
Do not repeat dose if infant spits out or regurgitates vaccine.
Administer simultaneously with all other indicated vaccines.
Rotavirus vaccine Contraindications
Severe combined immune deficit disease (SCID)Severe allergic reaction to a vaccine component or following a prior dose of vaccine
Patient with problem of glucose- galactose or sucrose malabsorption
Rotavirus vaccine precautions
Recent receipt of blood product.Altered immunity (child & household contact).
Acute, moderate to severe gastroenteritis or other acute illness.
pre- existing chronic GI disease.
Preterm infants
Infants with history of intussusceptions.
Infants of HIV mother
Intussusception & Rota teq vaccine
The phase 3 clinical trials to study the occurrence of intussusceptions in Rota teqMore than 69,000 infants, of whom half received vaccine and half received a placebo.
In the 42 days after vaccination 6 cases of intussusceptions were diagnosed among the vaccinated infants and 5 cases were diagnosed among the placebo recipients.
HAEMOPHILUS INFLUENZA
Haemophilus Influenza, history
In 1892 it was first described by PFIEFFER
In 1920 WINSLOW give name Haemophilus
Gram negative coccobacillus
Enter through nasopharynx and colonize and may remain only transiently or for several months in the absence of symptoms (Asymptomatic carrier)
Haemophilus Infleunza (Hib)
Reservoir:Only human (asymptomatic carrier)
Transmission:
Respiratory droplet, Hib doesn’t survive in the environment.
Clinical features:
Invasive diseaseA-Common
Meningitis 50-65%
Pneumonia
Epiglottitis
Arthritis
Cellulitis
B- less common
Osteomyelitis
Pericarditis
Acute bronchitis
Otitis media (5-10% due to Hib)
Global Burden of Hib diseases:
1. Mortality:400,000 deaths/year out of 2 million deaths /year due to ARI
The case-fatality rate in Hib meningitis is 2%–5%, despite appropriate antimicrobial therapy.
Haemophillus influenza type-b-vaccines
Hib polysaccharide vaccine.Available in 1985.
Not effective in children younger than 18 months of age.
Hib polysaccharide conjugated vaccine.
Available in 1987.conjugation:
chemical bonding process of the polysaccharide to carrier protein, immune response will be:-
Effective below 18 months of age.
Repeated doses elicit booster response.
Vaccination schedule
All infants, including those born prematurely , should receive a primary series of conjugate Hib vaccine.
Primary series is 3 doses 2,4,6 months of age.
The recommended interval between primary series doses is 8 weeks with a minimum interval is 4 weeks.
Booster dose is recommended at 12-15 months.
Conj-Hib Vaccine given before 6 weeks of age may induce immunological tolerance to subsequent doses of Hib vaccine.
((Hib vaccine should never be given to a child younger than 6 weeks of age))
Use in older children and adults:
Generally not recommended for persons older than 59 months of age.Consider for high risk persons:
Asplenia.
Immune-deficiency.
HIV.
Hib vaccine precaution and contraindication
Anaphylactic reaction to previous dose.Moderate or severe acute illness.
Age younger than 6 weeks.
Vaccine Storage and Handling
All Hib conjugate vaccines should be stored at 2-8 c must not freeze.
Should be used within 24 hours of reconstitution.