Fourth stage
Surgery(Urology)Lec-
Dr.Alshahwani
10/3/2015
Neurogenic bladder-The urinary bladder is probably the only visceral smooth muscle that is under complete voluntary control from cerebral cortex
-It has both somatic & autonomic innervations
-The functional features include:
A normal capacity of 400 – 500 ml
Sensation of fullness
Volume change without change in intraluminal pressure
Initiation & maintenance of contraction until bladder is empty
Voluntary initiation or inhibition of voiding
The sphincteric unit:
In both male & females, two sphincters:Internal : involuntary smooth muscle sphincter, at bladder neck
External : voluntary striated muscle sphincter, from the prostate to membranous urethra in males & at mid urethra in females
Innervation :
Parasympathetic : S 2 – 4
Symp. : T10 – L 2
Somatic motor innervation :S 2 – 3 though the pudendal N.
Classification of neurogenic bladder
Upper motor neuron , spastic , uninhibited ((injury above spinal cord micturition center))
Lower motor neuron, flaccid , atonic, areflexic ((injury in the pelvic nerves or spinal micturition center))
N.B. :Spinal shock
- Immediately after injury, regardless of the level, there is a stage of flaccid paralysis with numbness below the level of the injury that lead to bladder overfilling to the point of overflow incontinence & rectal impaction.-It last few weak up to 6 months during this the bladder should be drained by a catheter
Clinical picture
-UMNL : reduced capacity , involuntary detrusor contraction , high intravesical detrusor pressure , spasticity of pelvic striated M. , autonomic dysreflexia in cervical cord lesions-LMNL : large bladder capacity, lack of voluntary detrusor contraction, low intravesical pressure, deceased tone in external sph.
N.B.: full neurologic examamination Is required for those patients
Investigations
UrinalysisRenal function test
Imaging study
Instrumental exam. Cystoscopy
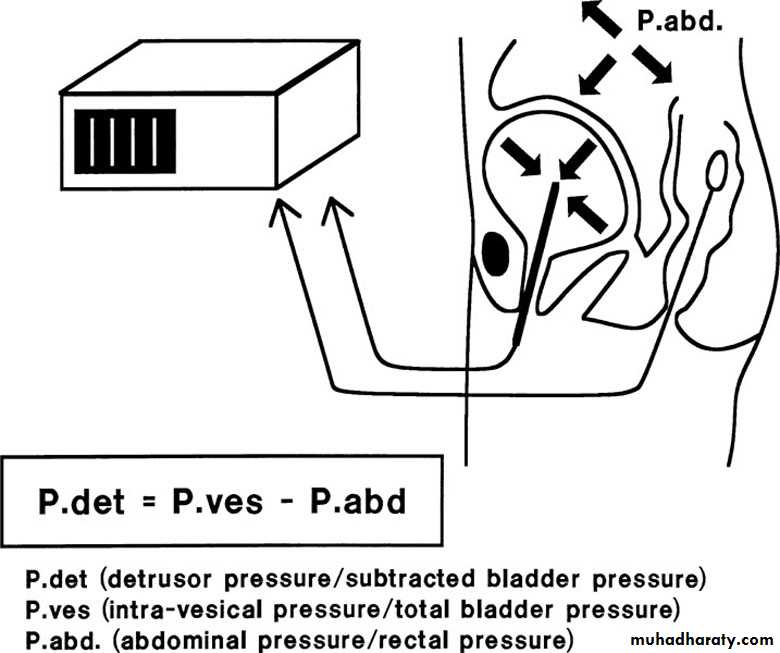
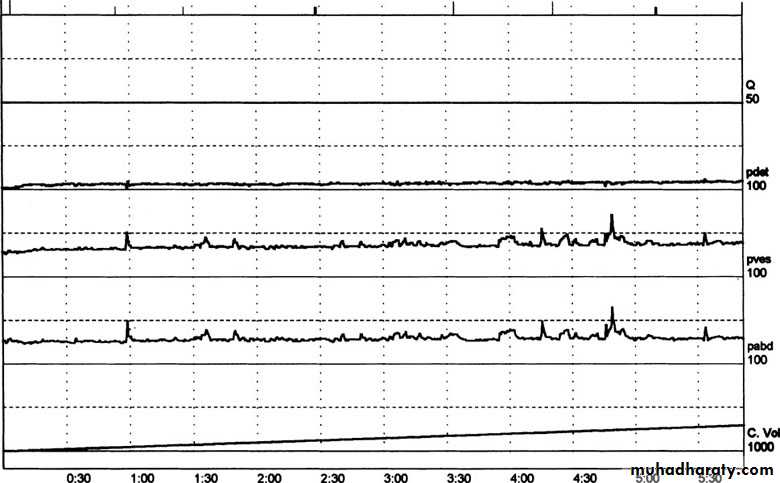
Urodynamic studies
"UDS"
Differential diagnosis
Cystitis
Chronic urethritis
Vesical irritation 2ry to psychic disturbance
Interstitial cystitis
Cystocele
Infravesical obstruction
Treatment
-The treatment is guided by the need to restore low pressure activity to the bladder in order to preserve renal function, continence, & control infection-Spinal shock ---> bladder drainage is required by intermittent catheterization , indwelling catheter or suprapubic cystostomy
- Increase fluid intake to 2 – 3 l/day
- Spastic neuropathic bladder ---> many options:
Voiding by trigger tech.
Anticholinergic medications (parasympatholytic drugs) like oxybutynin(ditropan) 5mg 2-3 times /day
Indwelling catheter or CIC
Condom catheter & leg bag
Sphincterotomy
Sacral rhizotomy at S 3-4
Neurostimulation
Urinary diversion
-Flaccid neuropathic bladder ---->
Crede maneuver ( manual suprapubic pressure) accompanied by straining
Bladder training & care , voiding every 2hr
CSIC every 3-6 hr
TUR in hypertrophied bladder neck or BPH
parasympathmimetic drugs like bethanecol chloride( Urecholine) 5 – 50 mg every 6-8hr
complications
Infection : cystitis, periurethritis, prostatitis, epididymoorchitis, pyelonephritis
Hydronephrosis
Calculus
Renal imperment
Autonomic dysreflexia:
- dramatic elevation in systolic &/or diastolic pressure, increase pulse pressure, bradycardia, headache, piloerection. brought by over distention of the bladder in patients with cord lesion above T1
-Treatment of autonomic dysreflexia :
immediate catheterization
oral nifedipine (20mg) 30 min before cystoscopy as prophylaxis
alpha adrenergic blockers
prognosis
The greater threat to those patients is progressive renal damage caused by:
pyelonephritis
calculosis,
hydronephrosis