Microbial Genetics
DNA replication is semi-conservative:What does it mean?
DNA ReplicationDuring cell division, each daughter cell inherits 2 DNA strands, One is old and one is new.
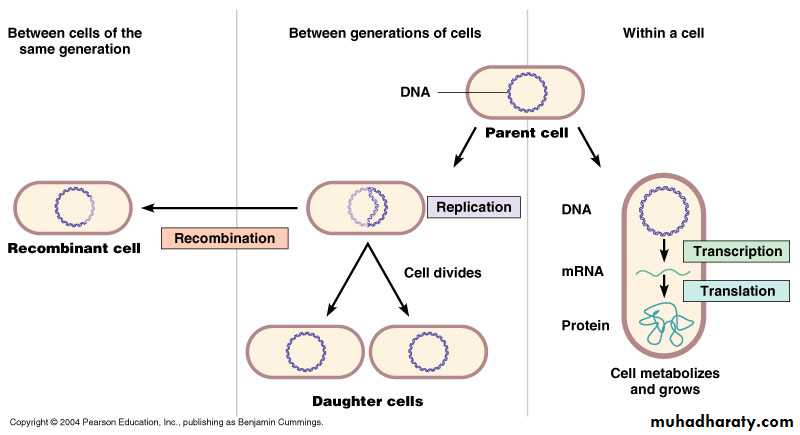
Flow of Genetic Information
Genetic information can be transferred either:Within the cell itself (in this case the genetic information is used to produce proteins needed for the cell function).This is called “Gene expression”
Or from parent cell to daughter cells (during cell division). This is called “Replication”
Or from one cell to another cell of same generation, resulting in new combinations of genes ”Recombination”
Flow of Genetic Information
Gene Expression and Protein Synthesis
Gene (DNA) contains all the information needed by cell to make a particular protein. But, how the gene changes to a protein?DNA------- mRNA------ protein
transcription translation• Transcription and processing of the newly made mRNA occurs in the nucleus of the cell.
• Once a mature mRNA transcript is made it is transported to the cytoplasm for translation into protein.
• Transcription and processing of the newly made mRNA occurs in the nucleus of the cell.
• Once a mature mRNA transcript is made it is transported to the cytoplasm for translation into protein.
• Transcription and processing of the newly made mRNA occurs in the nucleus of the cell.
• Once a mature mRNA transcript is made it is transported to the cytoplasm for translation into protein
• Transcription and processing of the newly made mRNA occurs in the nucleus of the cell. Once a mature mRNA transcript is made it is transported to the cytoplasm for translation into protein.
Central Dogma of Molecular Genetics
Gene Expression and Protein Synthesis
• Transcription and processing of the newly made mRNA occurs in the nucleus of the cell.• Once a mature mRNA transcript is made it is transported to the cytoplasm for translation into protein.
• Transcription and processing of the newly made mRNA occurs in the nucleus of the cell.
• Once a mature mRNA transcript is made it is transported to the cytoplasm for translation into protein.
• Transcription and processing of the newly made mRNA occurs in the nucleus of the cell.
• Once a mature mRNA transcript is made it is transported to the cytoplasm for translation into protein
• Transcription and processing of the newly made mRNA occurs in the nucleus of the cell. Once a mature mRNA transcript is made it is transported to the cytoplasm for translation into protein.
Transcription and processing of the newly made mRNA occurs in the nucleus of the cell (eukaryotic cell) or nuclear area (prokaryotic cell)
Once a mature mRNA transcript is made it is transported to the cytoplasm for translation into protein
Transcription
Double stranded DNA is transcribed into single stranded messenger RNA (mRNA)5’
3’5’
3’
Promoter
Terminator regionCoding region of gene
Transcription: Initiation
In case of eukaryotic cell:
Ist step in transcription process is the binding of Transcription Factors to promoter region of gene.This is followed by binding of RNA polymerase to Transcription Factors.
In case of prokaryotic cell:There is no transcription factors and RNA polymerase binds directly to promoter region of gene.
Transcription Factors
Transcription: Elongation
RNA polymerase begins to move downstream in 5’ to 3’ direction , unwinding and making RNA copy of DNATranscription: Termination
RNA polymerase reaches Terminator region
RNA polymerase detachesmRNA Transcript is released
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
Ways in which RNA & DNA differ:mRNA is single stranded
Sugar is ribose
(U) instead of (T)
A-U base pairing
Now the mRNA moves into cytoplasm to be translated into a protein.
Genetic Code
• How does the nucleotide sequence of mRNA specify the specific order of amino acids in a protein? The answer lies in what is known as the genetic code.DNA: triplet code e.g. TAC CAC CCC GCC ATC
mRNA: codon AUG GUG GGG CGG UAG
(complimentary to triplet code of DNA)Amino acid sequence Met- Val- Gly- Arg- Stop
Genetic CodeCodons: code for the production of a specific amino acid
20 amino acids
3 base code
Degenerative: more than 1 codon codes for an amino acid
Universal: in all living organisms
Genetic Code
Translation : Initiation
. 1st step in translation is the attachment of the small ribosomal subunit (30S) to mRNA at the start codon (AUG)
.This is followed by the recruitment of large subunit (50S)
. On the assembled ribosome (70s) , tRNA carries amino acid to the ribosome..Each tRNA matches and binds to a specific codon.
. If codon does not match, tRNA rejected.Translation: Initiation
On assembled ribosome, a tRNA carrying the first amino acid is paired with the start codon on the mRNA. The place on ribosome where the 1st tRNA is located is called P site. tRNA carrying the 2nd amino acid approaches.
P site
Translation : Elongation
A site next to P site, the second codon of the mRNA pairs with a tRNA carrying the second amino acid (A site).
Translation : Elongation
The 1st amino acid joins the second amino acid by a peptide bond
The 1st tRNA is released.Translation : Elongation
The ribosome moves along the mRNA until the 2nd tRNA is in the Psite, and the process continues.
Translation
As ribosome continues to move along the mRNA, new amino acids are added to the polypeptide.
Translation : Termination
When the ribosome reaches a stop codon, the polypeptide is released.
Stop codons are UGA, UAA, UAG.
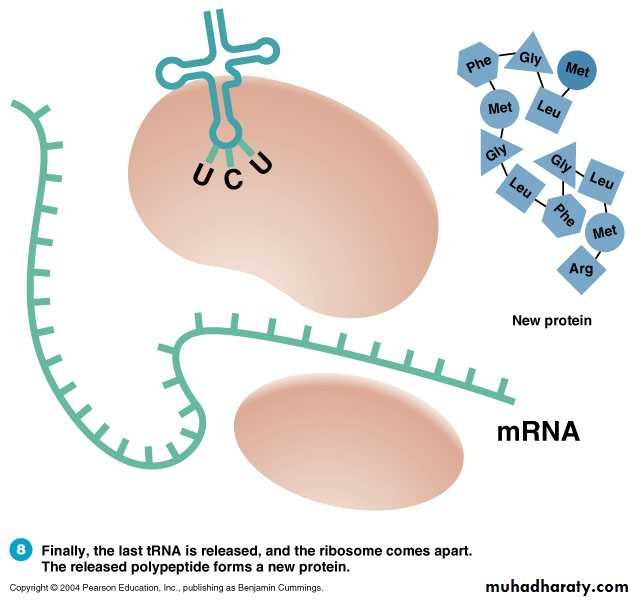
Translation: TerminationFinally, the last tRNA is released, and the ribosomes comes apart.The released polypeptide forms a new protein.
Types of RNA
Three types:mRNA: messenger RNA
Contains 3 bases ( codon)
rRNA: ribosomal RNA
Comprises the 70 S ribosome
tRNA: transfer RNA
Transfers amino acids to ribosomes for protein synthesis
Contains the anticodon (3 base sequence that is complimentary to codon on mRNA)