Salivary Glands
[د.زيد تكملة م/4]THE PAROTID GLAND
Developmental disorders
Rare
agenesis, duct atresia and congenital fistula
Inflammatory disorders
Viral infectionsMumps (most common)
acute painful parotid swelling
Mostly affects children.
spread by airborne droplets .
1–2 days fever, nausea and headache
pain and swelling in parotid glands.
pain very severe and exacerbated by eating and drinking.
Symptoms resolve within 5–10 days.
Treatment : regular paracetamol + adequate oral fluid intake.
Complications
orchitis, oophoritis, pancreatitis, sensorineural deafness and meningoencephalitis are rare.
Other viral agents that produce parotitis include: Coxsackie A and B, parainfluenza 1 and 3, Echo and lymphocytic choriomeningitis.
Bacterial infections
Acute ascending bacterial sialadenitisdehydrated elderly patients following major surgery
Reduced salivary flow ascending infection.
Staphylococcus aureus /Streptococcus viridans
Can occur with no obvious precipitating factors.
presentation tender, painful parotid swelling that arises over several hours .
generalised malaise, pyrexia and occasional cervical lymphadenopathy.
The pain is exacerbated by eating or drinking.
The parotid swelling may be diffuse/localises (lower pole of the gland)
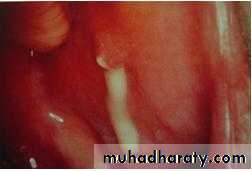
Pus may exuding from the parotid gland papilla
Treatment: - intravenous antibiotics. abscess drainage (large bore needle aspiration / drainage under general anaesthesia. Chronic bacterial sialadenitis is rare in the parotid gland.
- Recurrent parotitis of childhood- Obstructive parotitis
Papillary obstruction
less common than obstructive submandibular sialadenitis
caused by trauma to the parotid papilla
overextended upper denture flange or a fractured upper molar tooth.
inflammation and oedema obstructs salivary flow(mealtimes)
rapid onset pain and swelling at mealtimes.
untreated progressive scarring and fibrosis in and around the parotid duct papilla will produce a permanent stenosis.
Treatment: papillotomy(under either local or general anaesthesia).
Stone formation(Sialolithiasis)
- less common in the parotid gland (20 %)(submandibular gland (80 %).- Parotid duct stones radiolucent.
- Stone either proximal in the collecting duct or distal near the papilla.
- Diagnosis: Parotid gland sialography.
- Treatment: stone located in the collecting duct or within the gland endoscopic retrieval, lithotripsy or rarely parotidectomy.
Tumours of the parotid gland
- The parotid gland is the most common site for salivary tumors.Most tumors arise in the superficial lobe
80–90 % of tumours of the parotid gland are benign
the most common is pleomorphic
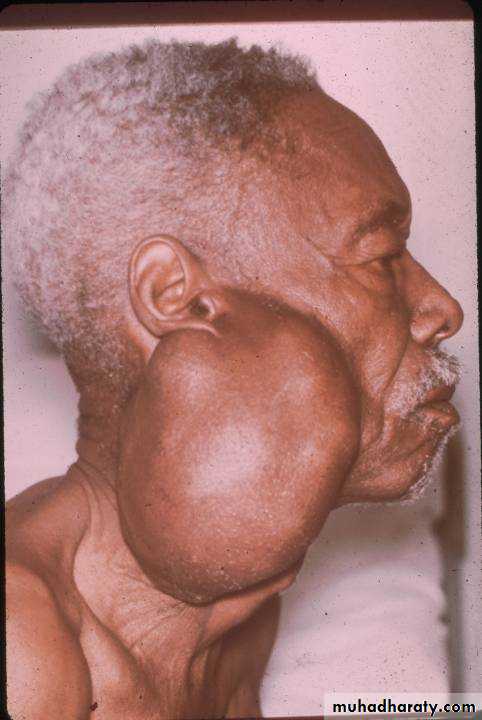
Slow growing, painless swellings below the ear, in front of the ear or in the upper aspect of the neck.
- Less commonly, tumors in accessory lobe persistent swellings in the cheek.
- Rarely, tumours in deep lobe as parapharyngeal massesdifficulty in swallowing and snoring.
Malignant salivary gland tumours are divided into two distinct subgroups:
1- Low-grade malignant tumours, e.g. acinic cell carcinoma,
are indistinguishable on clinical examination from benign
neoplasms.
2- High-grade malignant tumours :
Rapidly growing
painless swellings
discrete mass with infiltration into the overlying skin
or diffuse + hard swelling + no discrete mass(advanced disease)
- Cervical lymph node metastases.
Investigations
CT and MRI scanningFine-needle aspiration biopsy
(open surgical biopsy is contraindicated )
(no enucleation even if a benign lesion is suspected)
Treatment of parotid tumor
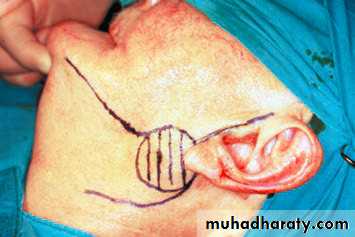
Superficial parotidectomy for Superficial lobe tumorThe aim of superficial parotidectomy is to remove the tumor with a cuff of normal surrounding tissue.
Low-grade malignant tumours superficial parotidectomy.
Radical parotidectomy
Indicated in high-grade malignant tumour(squamous cell carcinoma)
Radical parotidectomy = removal of all parotid gland tissue +sectioning of the facial nerve+ ipsilateral masseter muscle +/- neck dissection(if positive LN mets.)
Complications of parotid gland surgery:
• haematoma formation;• infection
• temporary facial nerve weakness
• transection of the facial nerve and permanent facial weakness
• sialocoele
• facial numbness
• permanent numbness of the ear lobe associated with great auricular nerve transection;
• Frey’s syndrome.
Frey’s syndrome:Frey’s syndrome (gustatory sweating)
damage to the autonomic innervation of the salivary gland with inappropriate regeneration of parasympathetic nerve fibres that stimulate the sweat glands of the overlying skin.sweating and erythema over the region of surgical excision of the parotid gland as a consequence of autonomic stimulation of salivation by the smell or taste of food.
Dgxstarch iodine test.
Rx antiperspirants( aluminium chloride)
denervation by tympanic neurectomy; botulinum toxin injection into the affected skin.
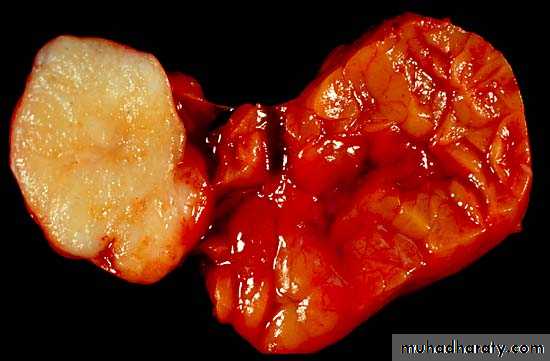
Pleomorphic adenoma
Benign Tumor
- On gross inspection : tumors is smooth and lobular and demonstrates a well defined capsule
On microscopic examination : both epithelial and mesenchymal elements are present
MOST COMMON NEOPLASM IN THE PAROTID GLAND ACCOUNTS FOR 65% OF ALL OF THE PAROTID TUMORS.
The most common salivary T.
In middle aged & more in woman than in men,
Slowly growing
Treatment :
Superficial parotidectomyWIDE RESECTION OF THE TUMOR
AVOID SHELLING OUT THE LESION
RECURRENCE: PRIMARY DUE TO INADEQUATE RESECTION
LESIONS ARE MORE AGGRESSIVE WHEN THEY RECUR
WARTHIN’S TUMOR (ADENOLYMPHOMA)
SECOND MOST COMMON PAROTID TUMOR
MALE : FEMALE 5 : 1
BILATERAL 10%
May (MULTICENTRICITY).
TREATMENT: superficial parotidectomy
90%CURED WITH RESECTION
10%RECUR DUE TO MULTICENTRICITY OR INADEQUATE RESECTION
Malignant neoplasm
Mucoepidermoid carcinomaAdenoid cystic carcinoma
Acinic cell carcinoma
adeno carcinoma
Carcinoma Ex. Pleomorphic adenoma or malignant mixed tumor
Squamous cell carcinoma
Undifferentiated carcinoma
Miscellaneous
Other diseases of salivary glands
A-Granulomatous sialadenitis:Mycobacterial infection
Sarcoidosis
B-Tumour-like lesions
Sialadenosis
C-Degenerative conditions
- Sjögren’s syndrome
autoimmune condition causing progressive
destruction of salivary and lacrimal glands.
- Benign lymphoepithelial lesion
Xerostomia(decrease salivary flow)
Sialorrhoea(increase salivary flow)