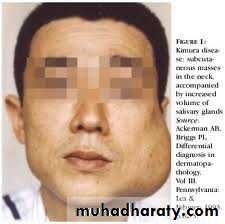
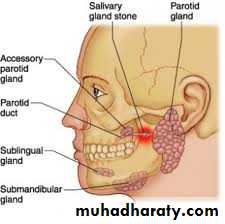
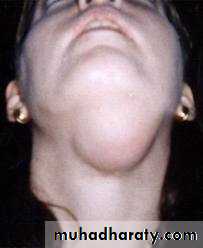
Salivary glands
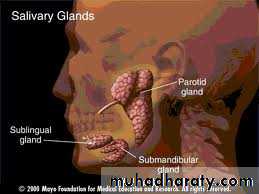
TypesMajor salivary glands:
- parotid g.
- Submandibular g.
- Sublingual g.
Minor saliovary gland :
consists of 750 g scattered through out the submucosa of the oral cavity,oropharynx, hypopharynx,larynx and parapharyngeal spaceSurgical anatomy
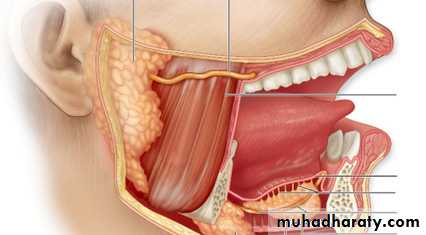
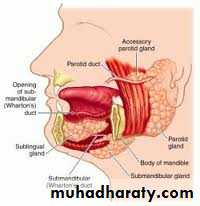
Parotid gland:
-largest g.
-related to facial n which pass through the g and divides it to superficial and deep lobe .
- the duct (stensen’s duct)cross the masseter m.then the buccinator m . And inter the oral cavity through a small papillae opposite the 2nd upper moler .
Submandibular gland :
It lies in the digastric tiangle the anterior portion extend in contact with the floor of the mouth, the duct (wharton’s)open near the frenulum of the tongue.The sublingual gland
Lies in contact with the submandibular duct . It is short ,multiple ducts enter directly to the floor of the mouth .Surgical physiology
Amount of saliva from1 -1.5 liter/24h.Content :water+Ca and Phosphate salts.
It assist in food lubrication and swallowing ,cleaning of mouth, mediate taste sensation and initiate digestion of starch by amylase.
Parotid g. secreats mainly serous saliva.
Submandibular g. mixed (mucous ,serous)rich in Calcium.
Diseases of salivery glands
1- Developmental disorders:-Aplasia
-Duct atrasia
-Salivery fistulae (congenital)
-Accessory lobe 20%
2- Infections:
A- acute bacterial sialoadenitis:- Affect mostly the parotid glands
- Usually staph. aureus or strept. veridance
- In elderly dehydrated ,teminal pt ,after major surgery with poor oral hyogen or when patient nil by mouth(post operative ).
- Stone obstruction
- Sjogren syndrom.
Clinical presentation
Sever pain in the parotid region.Pain is exacerbated by eating or drinking and resolution of pain within 1 hour.
Swelling localized in the lower pole of the gland(gravity).
No fluctuation because tight fascia , only redness and edema.
We can see pus coming out from the opining of the duct in oral cavity.
Diagnosis
Never to do sialography in the acute phase.
U/S of the gland either dilatation of the acinae or abscess .
CT of the glands
Treatment
Mouth toiletRehydration
Local heat
Antibiotics (against G+)
Surgical drainage :if no response after 48 h must be UGA and pus for C/S and drain left.
aspiration s.t. also may be effective.
B- Chronic bacterial sialoadinitis
Usually due to chronic obstruction by stoneMore common in the submandibular g.
Either unilateral or bilateral.
Clinically :- attacks of pain and swelling after meal .
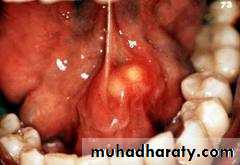
- redness of the orifice of the duct at the side of the frenulum .
- swelling filling the floor of the mouth.
Treatment
The gland has poor capacity for recovery after infection .So after dealing with the infection we have to excise the gland or diletation of the stricture .
C- recurrent sialadinitis of chilhood
Of unknown aetiology and prognosisThe age between 3-6y
Clinically: - rapid swelling with pain after chewing lasts for 3-7 days.
- usually unilateral but 2nd episode may be the other side.
- systemic manifistation.
Diagnosis
Sialogrphy with punctate sialactasis.or snow storm appearance .Treatment : message &antibiotic
- if recurrent give antibiotic as prophylaxis for months or years .spontaneous resolution at puberty .
- surgical excision only in resistant cases.
D -Viral parotitis (mumps)
Is the commonest cause of infection in children.Clinically : 1-pain and swelling of one or both sides with fever .
2- resolve spontaneously after 5-10 days. with lifelong immunity.
E- Granulomatus infection
It is a specific infection .either mycobacterial infection or sarcoidosis .(rare) affect the L.N.of the gland.
3- Obstruction
Papillary obstruction:rough upper molar tooth irritate the papilla and cause inflammation edema.
Stone formation (sialolithiasis)
Predisposing factors :-Stases
- Infection
INCIDENCE
Submandibular g. stone to parotid 50:1Why ?
The cource of the duct transverse and against gravity .(stasis)
The secretions contain ca.
the opining of the duct in the floor of the mouth liable to block by food particles
Clinical presentation
The stone lie in the hilum of the gland or in the duct .The patient complaining from frequent attacks of pain and swelling or just discomfort.
Bimanual palpation feel stone in the floor of the mouth .
May present as acute attack of sialadinitis
Asymptomatic .
Investigations
plain X-ray : 80% opaque due to ca carbonate or phosphate .Sialography :used for parotid stone mainly if radiolucent as filling defect .
Treatment
1- ductal stones:
- Gentle probing and dilatation of the papilla
Theraputic sialendoscopy
Slit the duct longitudinally intra orally
Shock wave (lithtrepsy) rare
2- Stone within gland substance :
Needs excision of the gland.
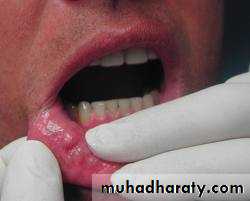
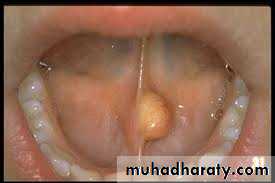
Mucoceles
Mucous retention cyst in the minor salivary gland due to mechanical damage to the gland or its duct in the lower lip. The cyst not more than 1 cm and tense sessile bluish swellingTreatment :the underlying gland should be excised completely ULA .
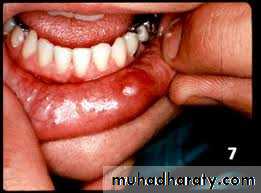
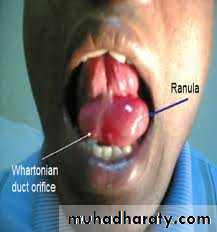
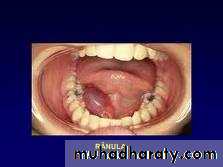
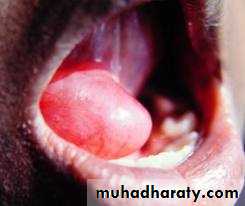
Ranula (frog belly)
It is a large mucocele which arise from the sublingual gland .As bluish swelling in the floor of the mouth anteriorly displacing the tongue .
It may go through the mylohyoid to reach the submental space (plunging ranula).
Treatment :deroofing or marcepialization
4- Drug induced swelling
Chloramphinicol ,tetracyclin .Endocrine and metabolic enlargment .
5-Salivery fistulae
Causes :1- accidental trauma.
2- surgical complication .
3- stone ulcerating to mouth (internal fistulae).
Investigation :sialography.
Treatment :1- canulation of distal part of duct from inside of mouth and trial of repair.
2- if this fails then excision .
3- if internal fistulae no need for treatment.
Thanks