1
BONE
AND
CARTILAGE
REVIEW FOR NBME
2004
BONE and CARTILAGE
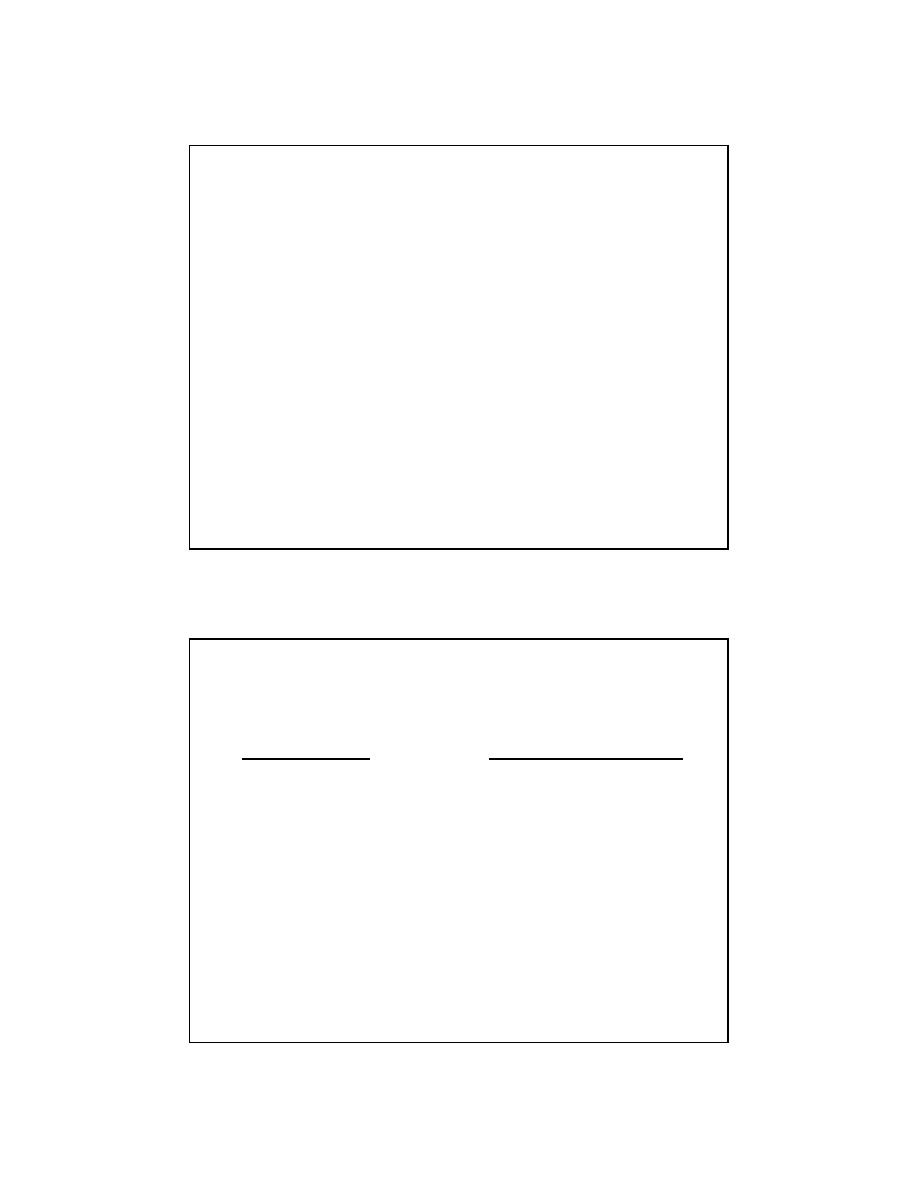
Bone (osteo)
vascular
mesodermal origin
osteoclasts
collagen type 1
appositional growth
-----
compact, cancellous,
woven
Cartilage (chondro)
avascular - diffusion
mesodermal origin
-----
collagen types 1,2
appositional growth
interstitial growth
hyaline, elastic, fibro
2
Bloom and Fawcett, 1975
HistoTime
3
HistoTime
Dr. Gwen Childs
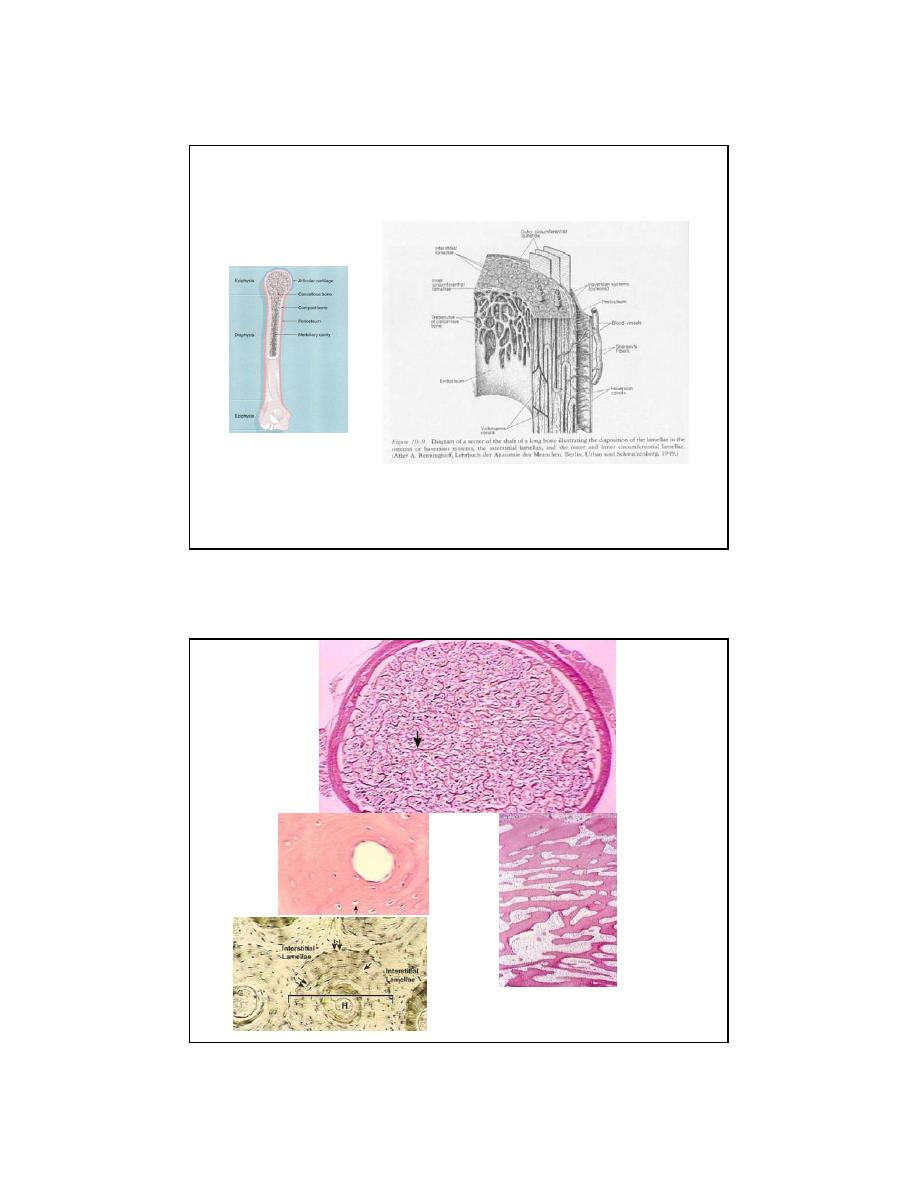
THREE CELL TYPES IN BONE
OSTEOBLAST
OSTEOCYTE
OSTEOCLAST
(
mesenchyme)
(mesenchyme)
(GM-CFU)
Young and Heath, 2000
Young and Heath, 2000
HistoTime
HistoTime
HistoTime
PD

4
OSTEOBLASTS
ORIGIN:
Mesenchymal precursor cells
Osteoprogenitor cells
- periosteum
- endosteum
APPEARANCE:
Stellate shape (versus round chondroblasts)
Basophilic = prominent RER
FUNCTION:
Make and mineralize bone
-matrix proteins:
Type 1 collagen
osteocalcin
osteopontin
osteonectin
proteoglycans
alkaline phosphatase
Use vitamin
C
when making
C
ollagen (s
C
urvy)
Become osteocytes (appositional growth)
Make factors that stimulate osteoclasts
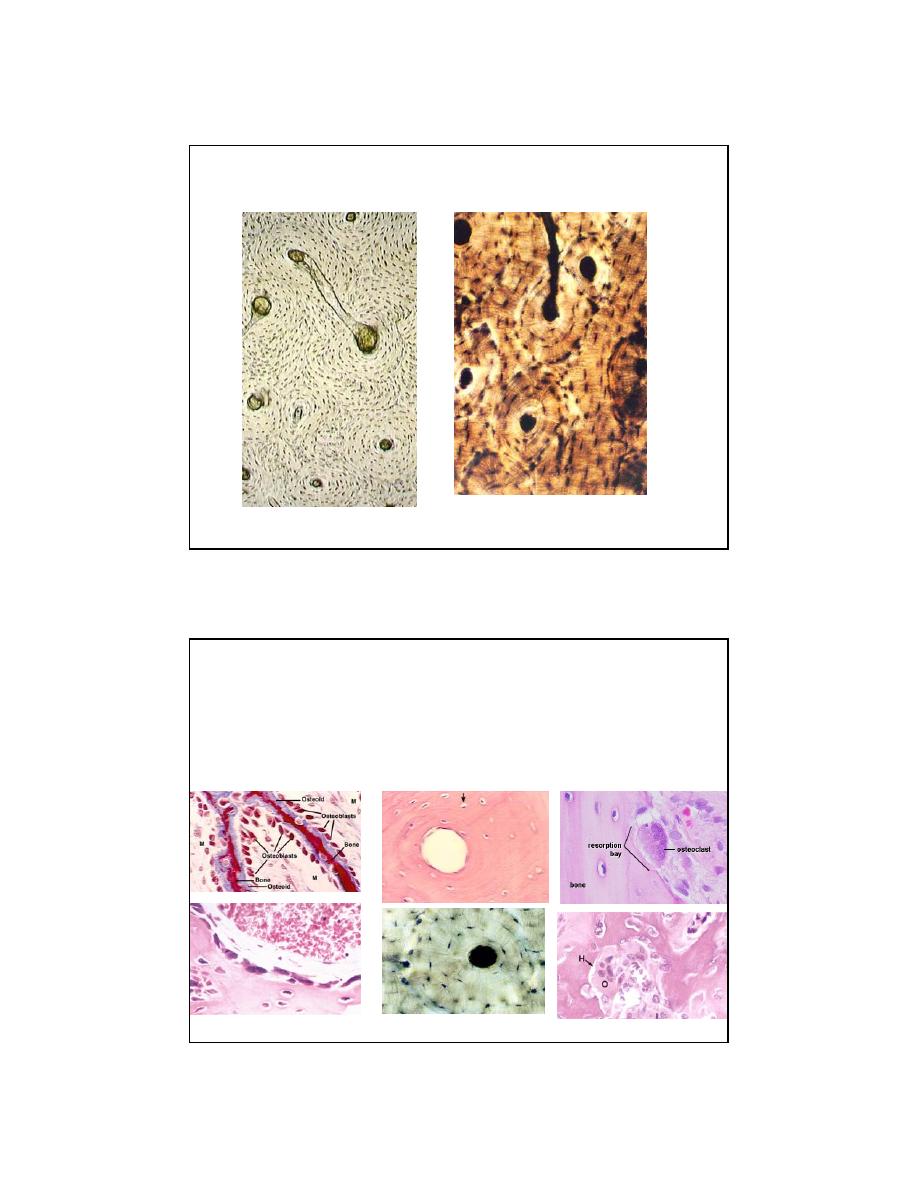
OSTEOCYTES
ORIGIN
osteoblasts (mesenchymal origin)
APPEARANCE
stellate (canaliculi, gap junctions)
trapped in bone lacunae
periosteocytic space = osteocytic osteolysis
small golgi and RER (unlike osteoblast)
nondividing (unlike chondrocytes)
FUNCTIONS
osteocytic osteolysis (plasma [Ca
++
])
mechanotransduction (factors that recruit preosteoblasts)

5
OSTEOCLASTS
ORIGIN
GM-CFU in bone marrow (think Monocyte / Macrophage)
APPEARANCE
BIG, motile
multinucleated
acidophilic
in Howship’s lacuna (Not trapped)
ruffled border
'clear zone’ (actin ring), seal
integrins
lysosomes
FUNCTION
resorb bone
mineral = hydroxyapatite (H
+
)
organic = collagen (lysosomal enz. TRAP, a marker)
OSTEOCLAST ACTIVITY
STIMULATORS
(-> increased serum calcium)
Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
through osteoBLAST
derived factors:
OPGL and OSF
IL-1, IL-6,TNF, CSF-1
-induces osteoclast
production
INHIBITORS
(-> decreased serum calcium)
Calcitonin (calcium stays)
from thyroid gland Clear
cells
Osteoprotegrin, TGF, Interferon
Bisphosphonates (Fosamax)
Tx for osteoporosis
6
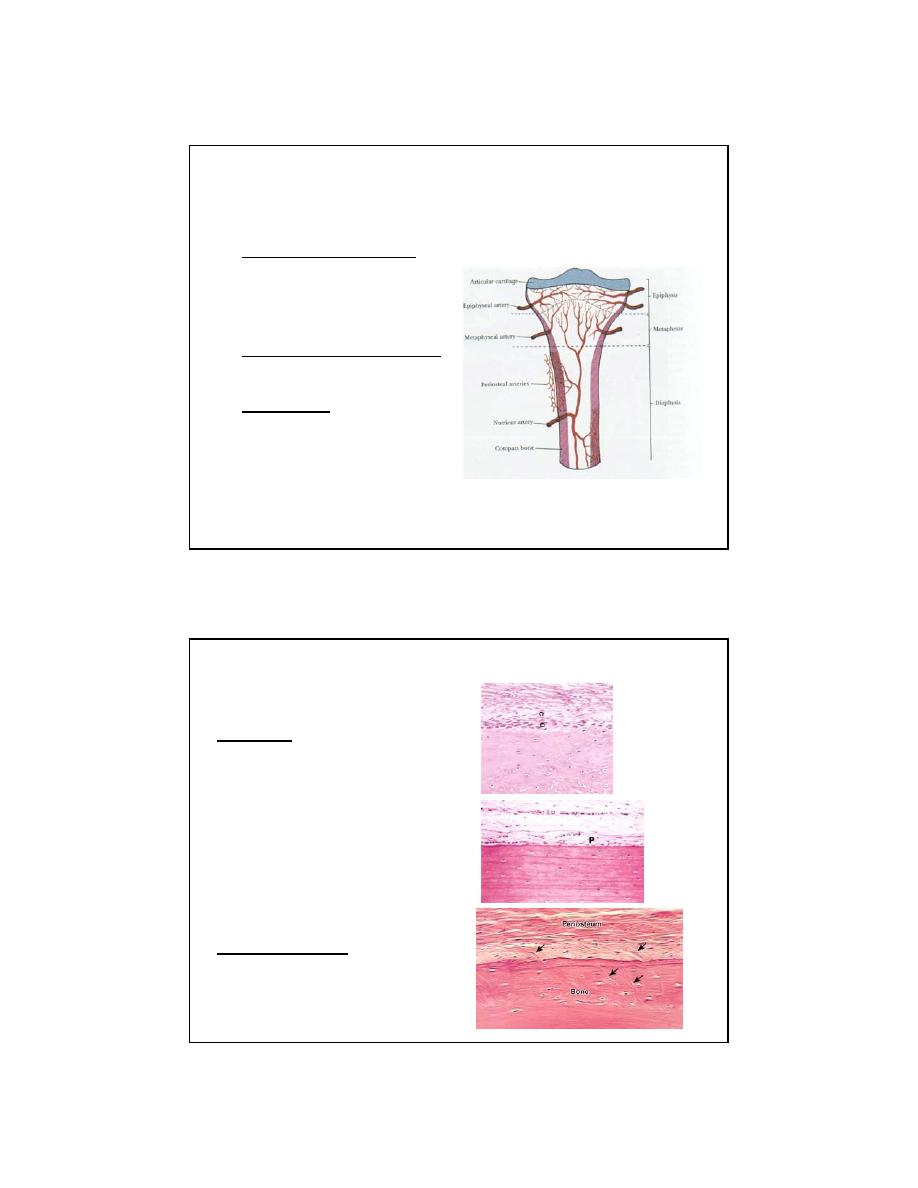
VASCULAR SYSTEM OF BONE
•
Blood supply 4 sources:
• Nutrient arteries
• Periosteal system
• Metaphyseal system
• Epiphyseal system
•
Arterial supply of the cortex
• inside to out
(centrifugal)
•
Venous flow
• Sinusoids -> cortical
capillaries -> emissary
venous system
(centripetal)
PERIOSTEUM
Layers:
Inner (cells)
• Osteoprogenitor cells
(bone repair)
Outer (fibers)
• Dense fibrous ct
• Meets joint capsule
Modification:
• Sharpey’s Fibers
(Arrows)
Active (child)
Inactive (adult)
7
Distribution of The Various Types Of
Cartilage
• Hyaline Cartilage
Most bones of the
embryonic skeleton
Articular cartilage (synovial jt)
Epiphyseal Plate
Costal Cartilage
Xiphoid process
Nasal Cartilages
Most Laryngeal Cartilages
Tracheal Ring Cartilages
Cartilage plates in large
and medium bronchi
•
Elastic Cartilage
Pinna
External Auditory tube
Eustachian Tube
Epiglottis
Laryngeal Cartilages (2)
Cartilage plates in small
bronchi
•
Fibrocartilage
Symphyses
- Intervertebral disks
- Pubic symphysis
Menisci
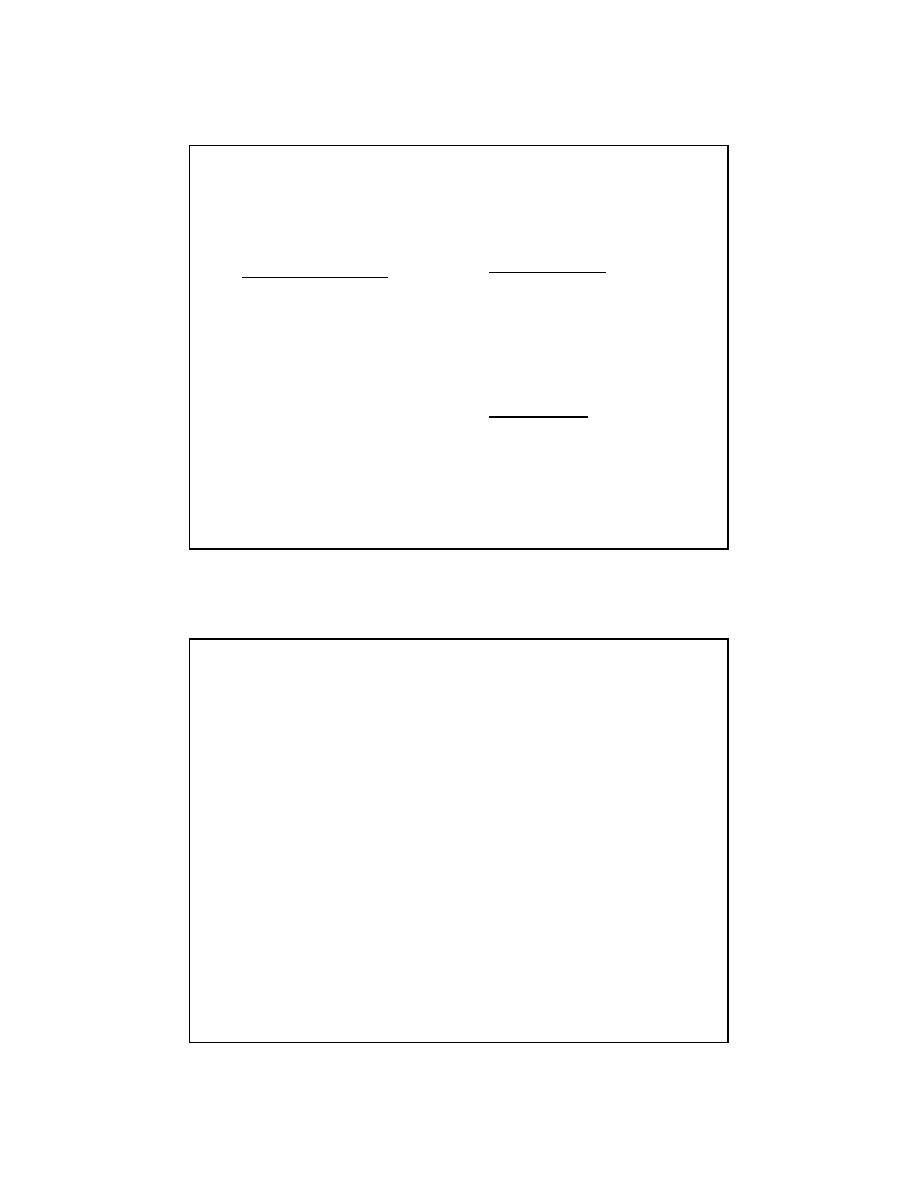
CARTILAGE
ORIGIN
mesenchyme, chondrogenic cells (bone repair)
CELLS
chondroblasts (RER,= basophilic, ROUND)
chondrocytes (divide, unlike osteocytes!!!)
GROWTH
Appositional and
INTERSTITIAL
growth
(CHONDROCYTES DIVIDE so there is interstitial growth, unlike in bone!!!)
FEATURES
9 Peri
chondrium
NOT OVER ARTICULAR CARTILAGE and not over fibrocartilage
Cell layer (chondrogenic)
Fibrous layer
9 Isogenous groups of chondrocytes (why?!)
9 Matrix
Territorial (capsular, rich in GAG’s = basophilic)
Interterritorial (less basophlic)
9 Avascular (diffusion), can form “Joint mice”

8
WHAT IS APPOSITIONAL GROWTH?
WHAT IS INTERSTITIAL GROWTH?
Hyaline
“
Glassy” matrix (Greek, hyalos, means glassy)
•
Collagen type II
•
GAG’s= chondroitin sulfate and heparan sulfate
•
articular hyaline cartilage (no perichondrium)
•
Isogenous groups (nests)
•
Endochondral bone formation
Elastic
•
Elastic fibers >
Collagen type II
•
GAG’s= chondroitin sulfate and heparan sulfate
•
Isogenous groups not as nest-like
•
Chondrocytes more abundant than in hyaline
•
special stain
Fibrocartilage (odd one)
•
Collagen type I
(acidophilic) NUMEROUS fibers!!
•
GAG’s = chondroitin sulfate and
dermatan
sulfate)
•
No perichondrium
•
Few Chondrocytes compared to hyaline and elastic
•
Isogenous groups in parallel ROWS (not nests)
9
?
SYNOVIAL MEMBRANE
• Not a true epithelium
• PRODUCES SYNOVIAL FLUID
• Not located over articular surface (ouch!)
10
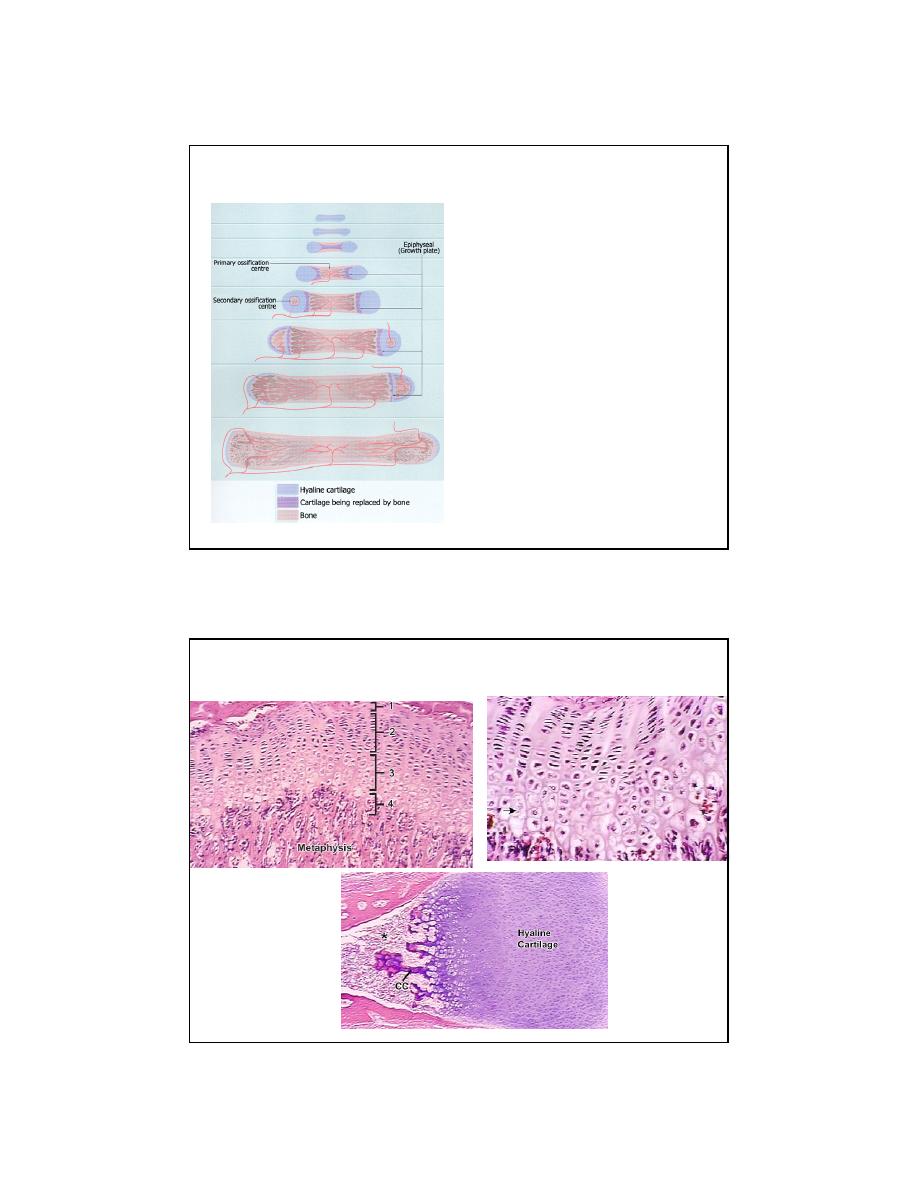
HistoTime
MODEL
PERICHONDRIUM (vasc.)
COLLAR (intramembranous ossif.)
DEATH
CALCIFICATION
1
o
CENTER OF OSSIF. (vess. progen.)
OSTEOID
MINERALIZATION
2
O
CENTER OF OSSIF. (epi., postpart)
FUSION (epi + dia)
ENDOCHONDRAL OSSIFICATION
ZONES
NAME THE ZONES
11
MINERALIZATION OF OSTEOID
(NOT JUST CALCIFICATION)
MINERALIZATION:
OSTEOBLAST – MATRIX VESSICLES (HYDROXYAPATITE)
CALCIFICATION:
CHONDROCYTES DIE
(Both require Vitamin D or Rickets in child, osteomalacia in adult)
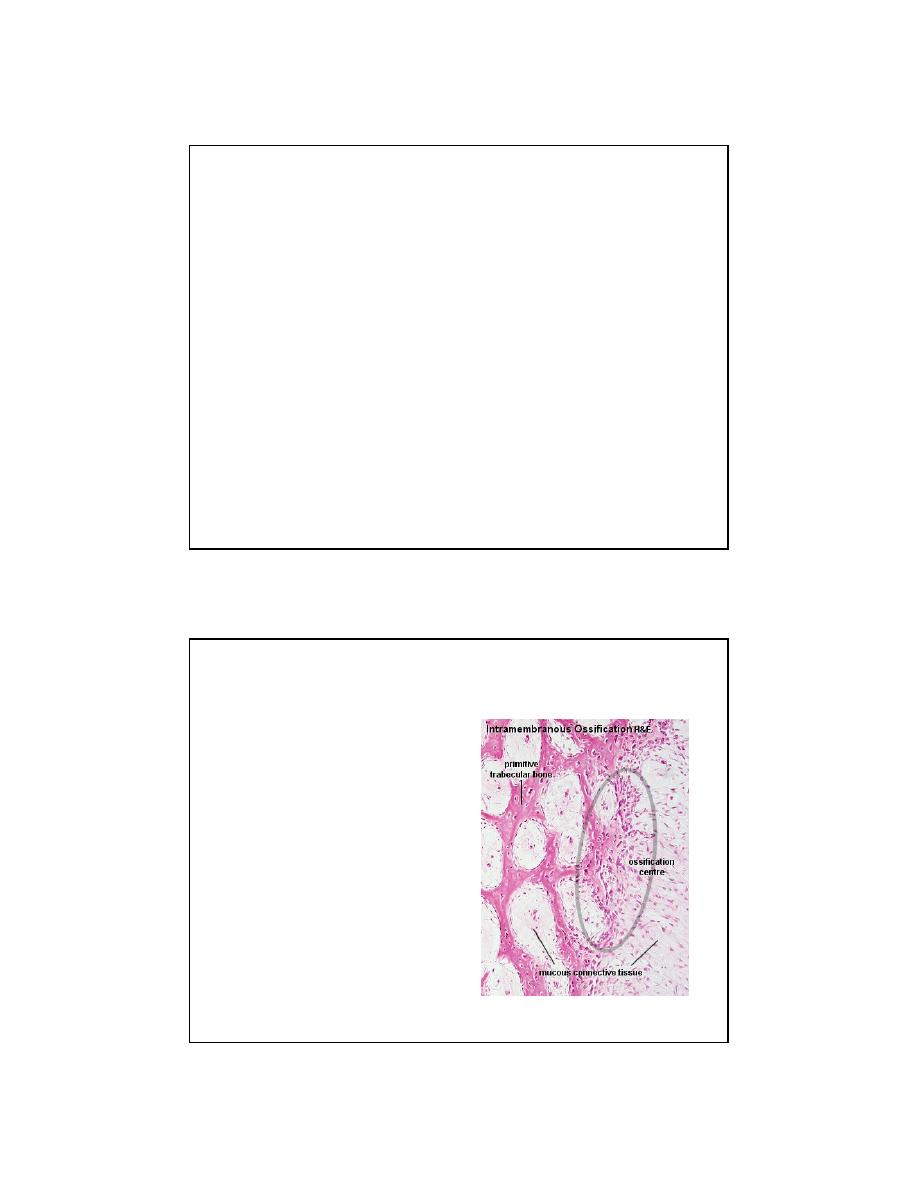
Intramembranous Ossification
• Mesenchyme
• Osteoprogenitor cells
• Osteoblasts
• Osteiod
• Woven Bone
• Remodeling
– Compact
– Cancellous
What is wrong with this picture?
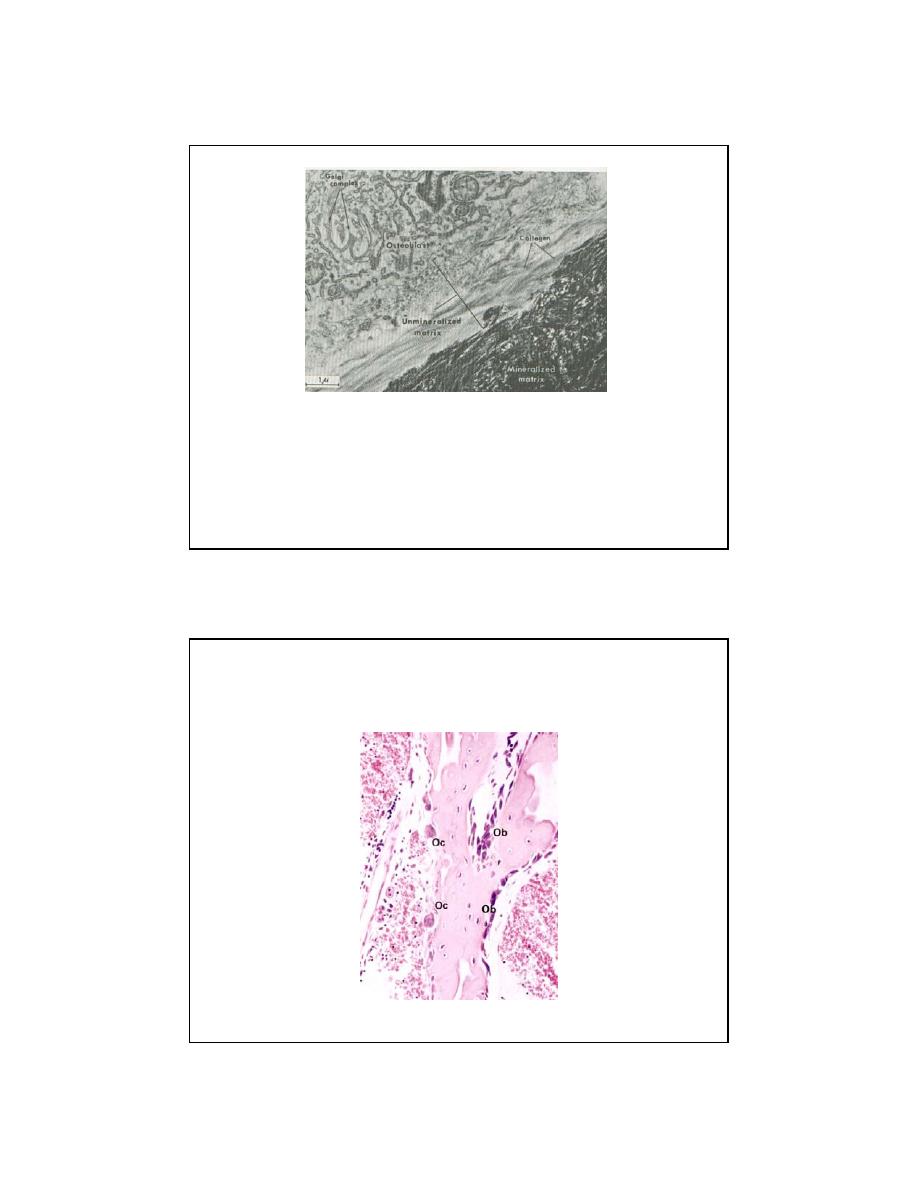
12
MINERALIZATION FRONT
What is happening here?
13
What’s going on?
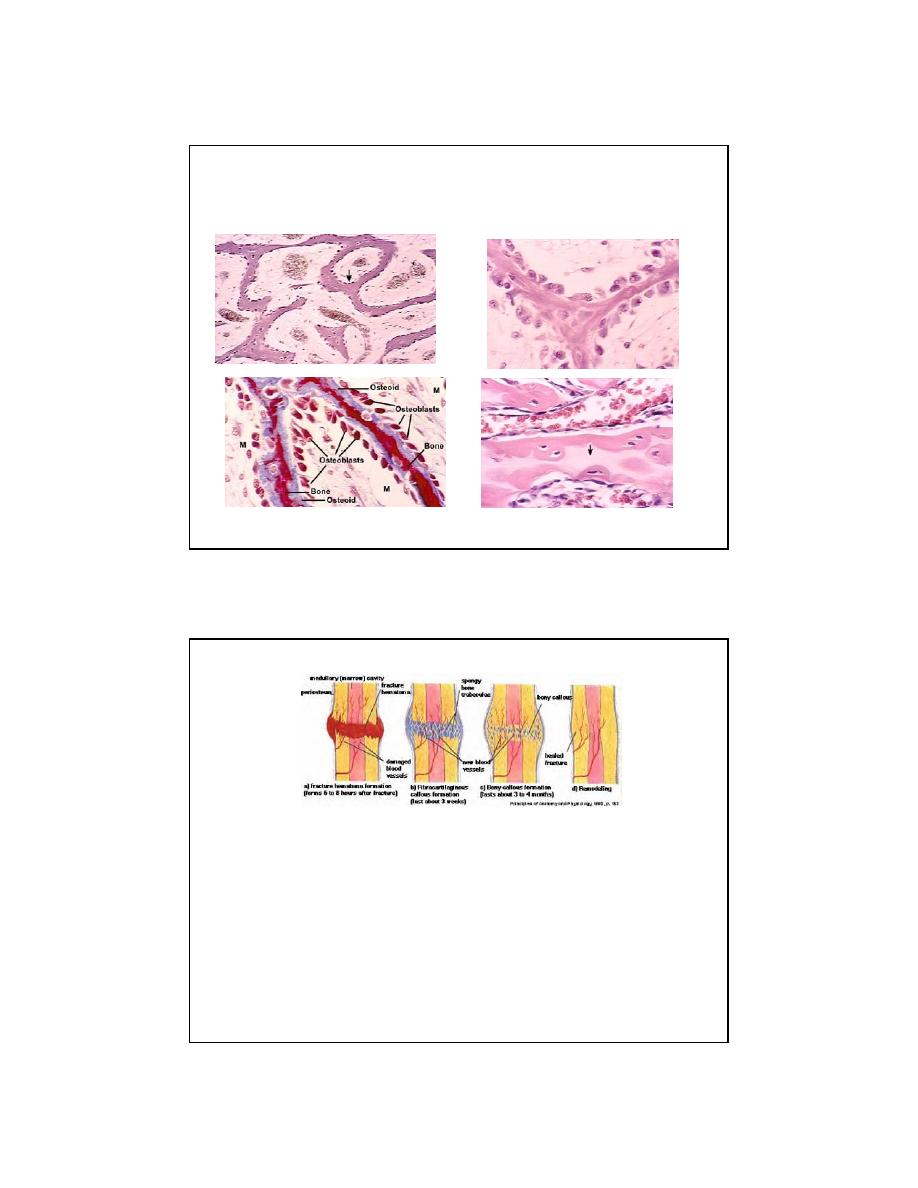
Bone Repair
•
A person breaks a bone
•
What is broken besides bone?
•
The clot organizes = granulation tissue
•
low O
2
•
Going backwards in time…
Endochondral
ossification
where vessels broken
(Fibrocartilage callus)
Intramembranous
ossification
where vessels intact
•
Fibrous (Woven) bone produced first
(after 4 - 6 weeks, remove cast)
•
Remodeled according to Wolff’s law
(for up to 2 years)

14
