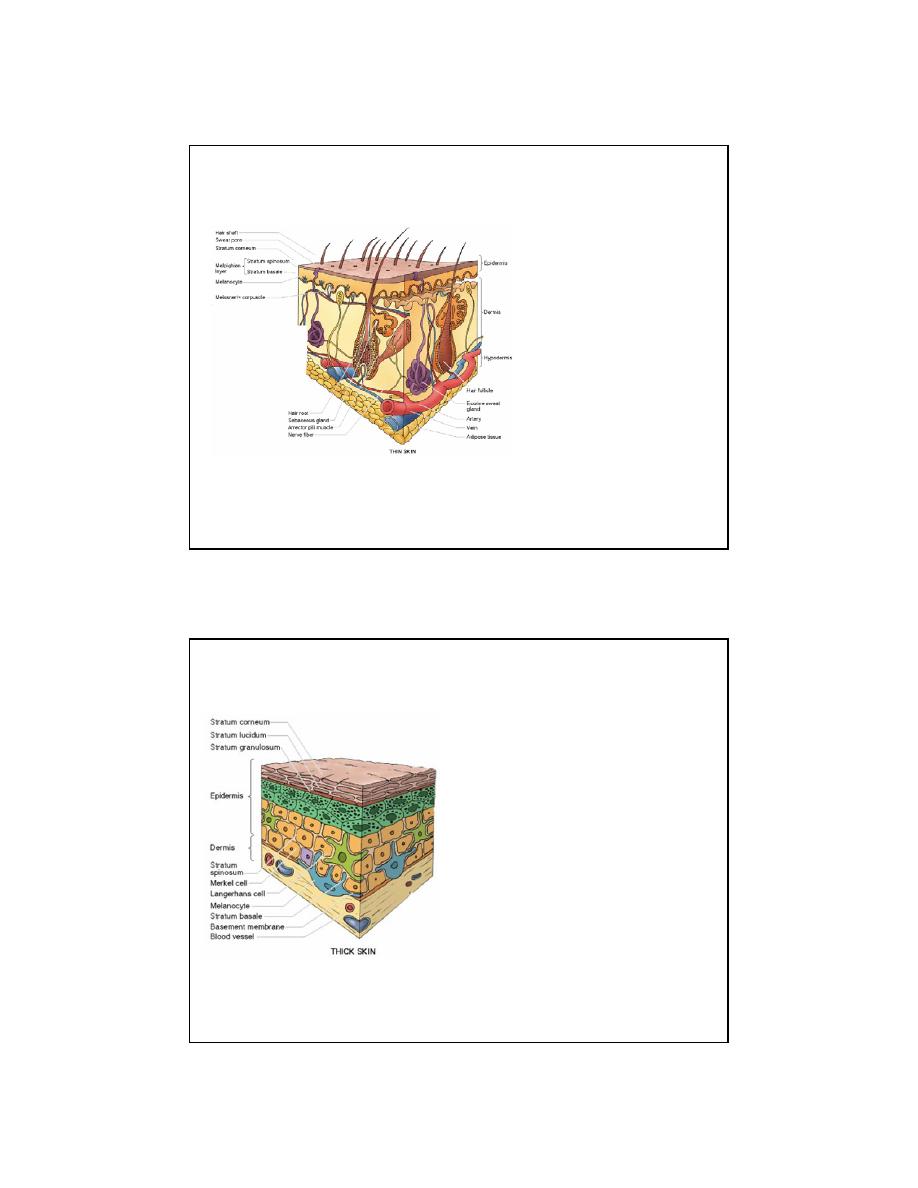
1
•
Epidermis
• Stratified, squamous
keratinized epithelium
• Appendages
• hair follicles
• nails
• sweat glands
• sebaceous glands
• mammary glands
• Dermis
• Dense, irregular
connective tissue
•
Hypodermis
• Superficial fascia
Cell Types in Epidermis
• Keratinocytes:
• intermediate filament is keratin
• Langerhans Cells
• dendritic cells
• present antigen
• vermiform/Birbeck granules
• Merkel Cells: mechanoreceptors
• Melanocytes: produce melanosomes
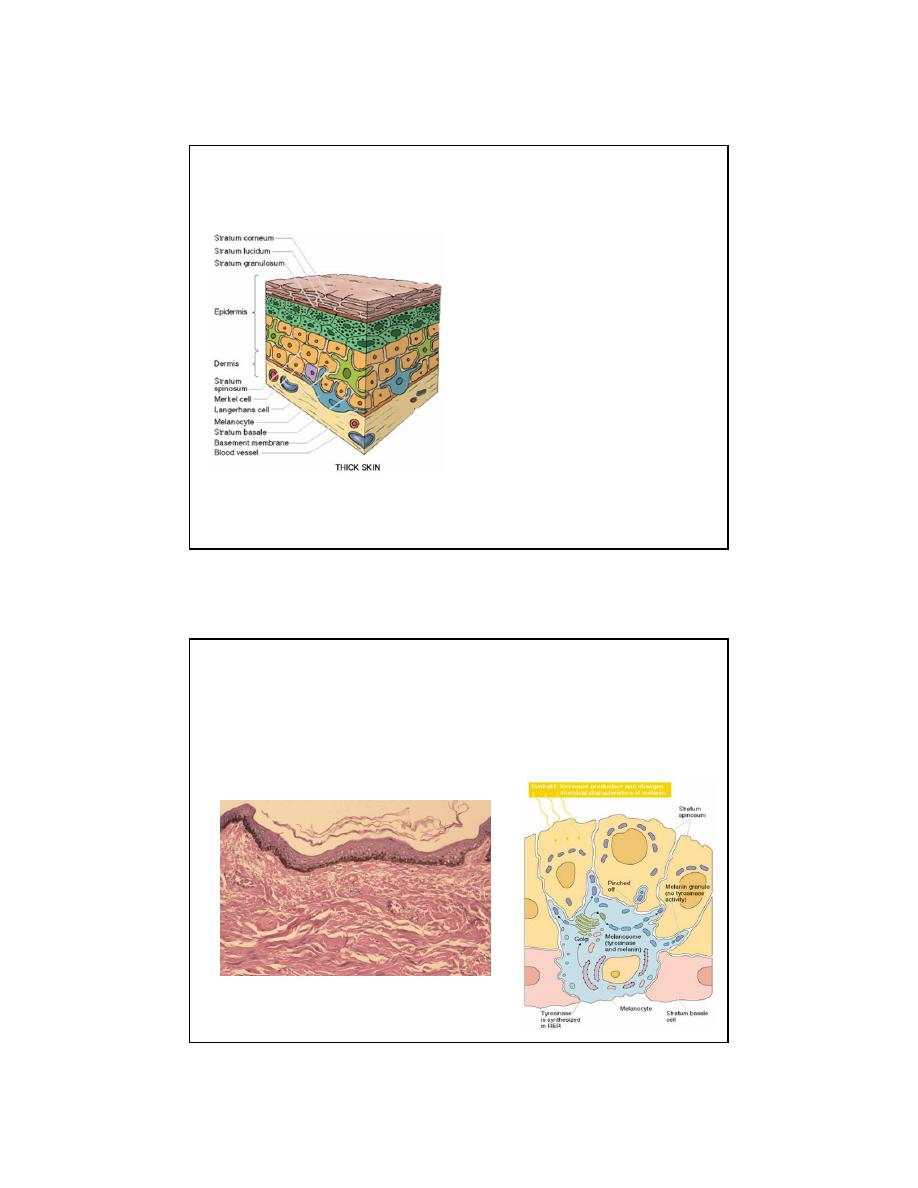
2
Keratinocyte Cytomorphosis
• Stratum basale
• proliferative
• Stratum spinosum
• desmosomes
• lamellar/membrane-coating
granules
• involucrin
• Stratum granulosum
• keratohyalin granules
• filaggrin
• Stratum lucidum
• thick skin
• Stratum corneum
Melanocytes
• Melanin synthesized in melanosomes within melanocytes
• Melanin in synthesized from tyrosine by tyrosinase enzyme
• Tyrosinase activity is UV-inducible
• Cytocrine secretion of melanin granules into keratinocytes
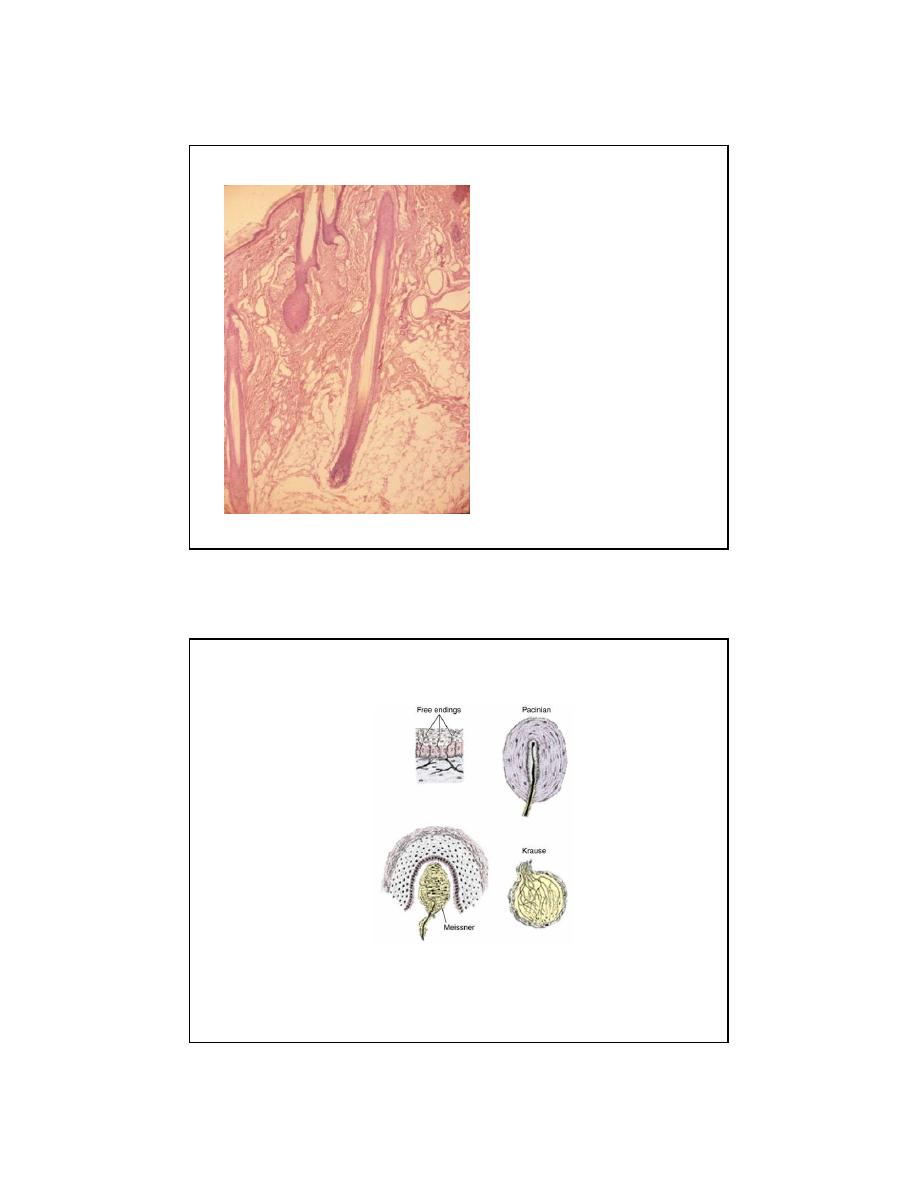
3
•Papillary dermis: numerous cells
• Fibroblasts
• loose collagen
type III: reticular fibers
type VII: anchoring fibrils
• fine elastic fibers
• Capillaries and
arteriovenous anastamoses
• Immune system cells
• Mechanoreceptors
• Free nerve endings
• Meissner’s corpuscles
• Krause’s corpuscles
•Reticular dermis: fewer cells
• Fibroblasts
• type I collagen
• thick elastic fibers
• Sweat glands
• Hair follicles
• Arrector pili muscles
• Sebaceous gland
• Mechanoreceptors
• Pacinian corpuscles
• Ruffini corpuscles
Sensory Mechanoreceptors
in the Integument
Meissner
Dermal papillae
Light touch
Free nerve endings
Epidermis and dermis
Krause
Cold?
Mechanical stimuli
Pacinian
Reticular dermis
Pressure
Vibration
Course touch
Tension
Ruffini
(not shown)
Tensile force
4
Eccrine Sweat Gland
• Simple coiled tubular gland
• Sympathetic, cholinergic innervation
• Duct
• Stratified cuboidal
• Opens on surface of epidermis
• Resorbs potassium, sodium and
chloride ions
• Excretes urea and lactic acid
• Secretory unit
• Mixed cuboidal, columnar, and
pseudostratified
• Merocrine mechanism
• Dark cells
• Clear cells
• Contractile myoepithelial cells
Apocrine Sweat Gland
• Simple or branched coiled tubular
gland
• Sympathetic, adrenergic innervation
• Duct
• Stratified cuboidal
• Opens into hair follicle
• Secretory unit
• Large lumen stores secretion
• Cuboidal or columnar
• Merocrine mechanism
• Odorless viscous secretion
• Hormonally responsive, begin to
function at puberty
• Contractile myoepithelial cells
• Restricted distribution: axilla, anus,
areola, auditory canal, eyelids
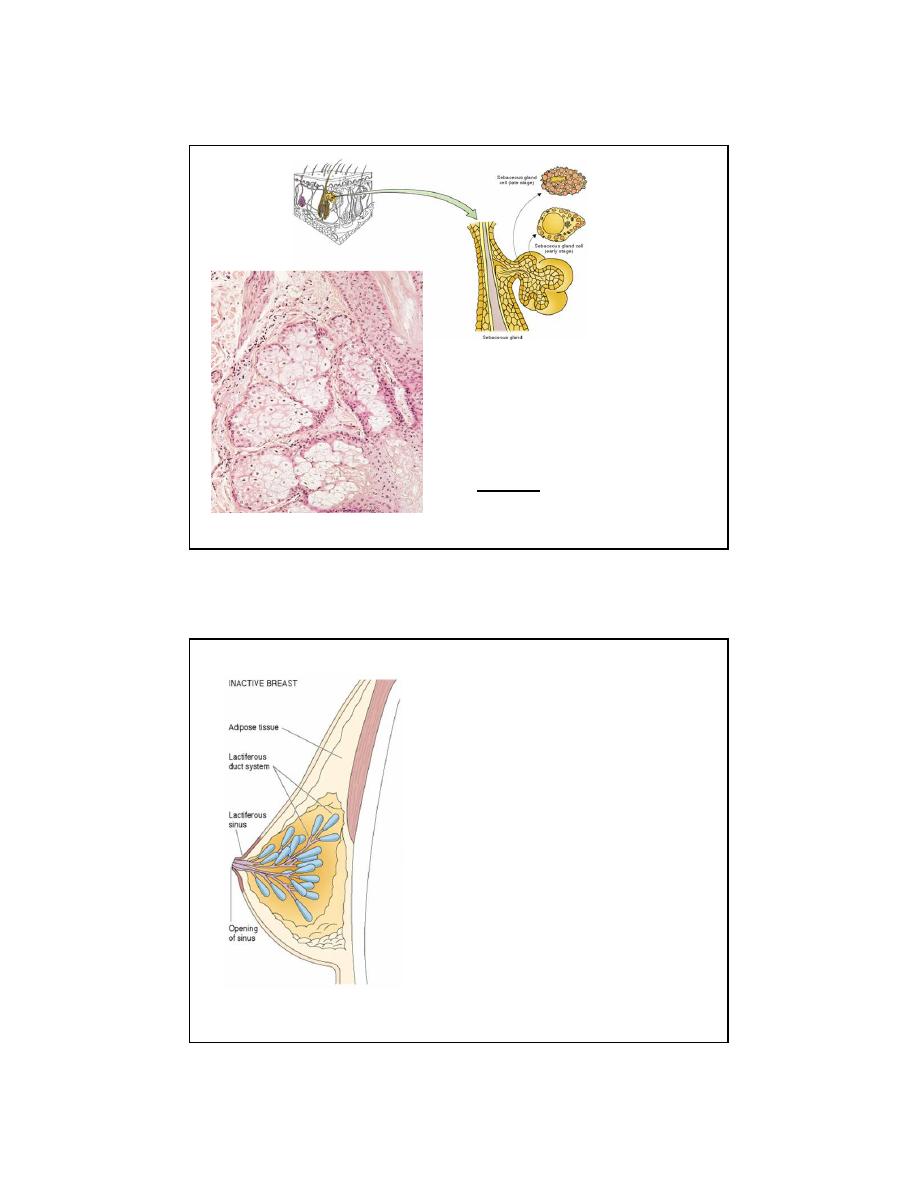
5
Sebaceous
Gland
• Branched tubuloalveolar gland
• Duct
• Stratified squamous
• Usually open into hair follicles
• Secretory unit
• Acini contain small basal cells and
large round cells that fill the lumen
• Holocrine mechanism
• Oily sebum secretion
• Hormonally responsive
Mammary Gland
• Compound tubuloalveolar gland
• 15-20 lobes separated by connective
tissue (collagen and adipose)
• each lobe is drained by a lactiferous
duct leading to the nipple
• lactiferous sinus near distal end of duct
• near nipple, duct is stratified squamous
• throughout duct and sinus: stratified
cuboidal
• small ductules leading to lactiferous
duct: simple columnar
• Identical in male/female until puberty
• estrogen and progesterone (ovary)
• prolactin (anterior pituitary)
• Inactive gland
• similar to lactating, but alveoli are not
developed

6
• During pregnancy
• Elevated progesterone and estrogen
(ovary and placenta)
• Ducts grow and branch
• Alveoli develop and mature
• cuboidal cells
• myoepithelial cells
• Colostrum accumulates
• will be ejected day 1-3
• contains lymphocytes, monocytes,
antibodies, lactalbumin, minerals,
electrolytes
Lactating Mammary Gland
• Prolactin surge
(anterior pituitary)
• Stimulates milk production
• day 4-continuous
• Contains proteins, lipids,
antibodies, lactose, vitamins,
minerals, electrolytes
•
Oxytocin
(posterior pituitary)
• Stimulates milk ejection
or “let down”
