
CHOLESTEROL

OBJECTIVES:
1.
For cholesterol:
a) list its physiological functions
b) describe its synthesis
c) list groups of hormones produced
from it
2.
For bile acids (salts):
a) list their physiological functions
b) describe their synthesis
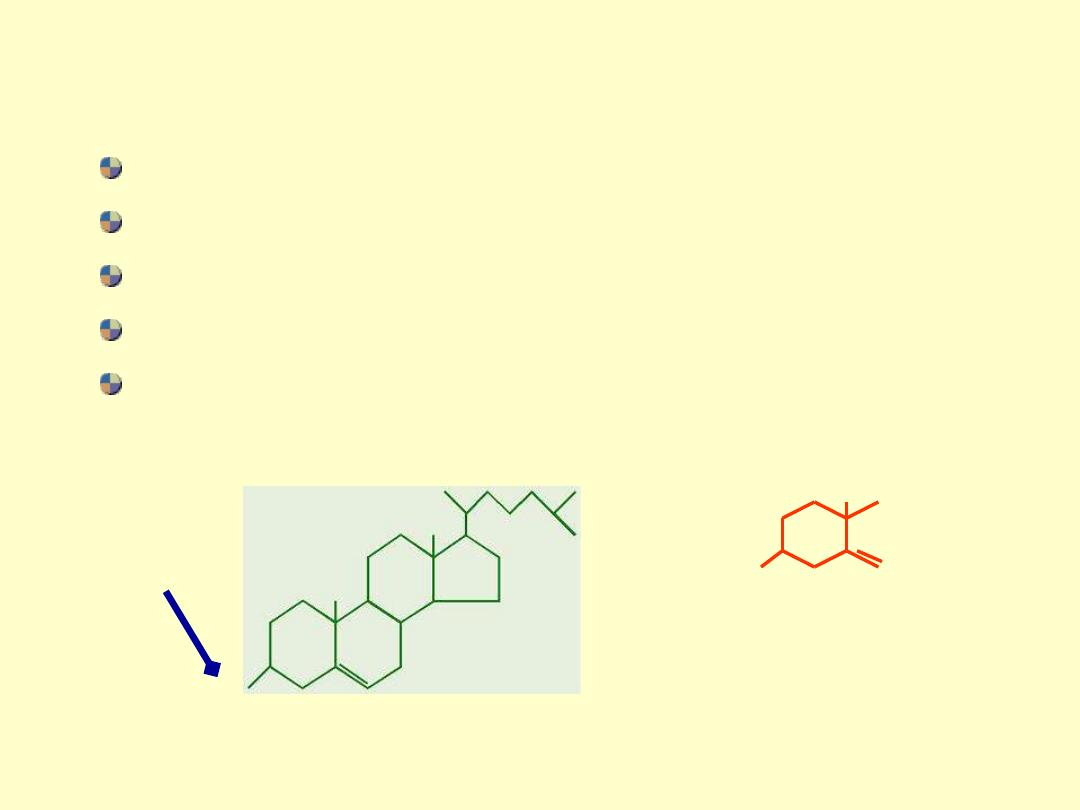
CHOLESTEROL FACTS
synthesized from acetyl CoA and eliminated as bile acids
precursor of all other steroids in the body
- in foods of animal origin
amphipathic lipid (hydrophobic and hydrophilic portions)
storage form is cholesterol ester found in most tissues.
HO
hydrophilic
O
||
R-C-O
Cholesterol ester (1
st
ring only)
R = fatty acid hydrocarbon chain
essential structural component of membranes
transported in the circulation in lipoproteins
CHOLESTEROL FACTS

The physiological roles of cholesterol include:
a) an important lipid component of biological membranes,
b) precursor of steroid hormones and
c) source of bile acids.
ROLES OF CHOLESTEROL
AND BILE ACIDS (SALTS)
Bile acids are polar derivatives of cholesterol and aid in:
a) lipid digestion
b) lipid absorption
c) cholesterol excretion

Cholesterol synthesis pathway
Mevalonate
Active Isoprenoids
(C
5
)
Squalene
(C
30
)
3ATP
CO
2
Several
Condensation Steps
3ADP
NADPH
NADP
+
Stage 2
Squalene
(C
30
)
Cyclization
Squalene
epoxidase/
cyclase
Lanosterol
(C
30
)
(4-ring structure)
O
2
NADPH
NADP
+
Stage 3
Stage 4
Lanosterol
(C
30
)
(19 steps)
O
2
NADPH
NADP
+
3 CH
3
Cholesterol
(C
27
)
Acetyl CoA
(C
2
)
HMG-CoA
HMG-CoA
Reductase
Mevalonate
(C
6
)
NADPH
NADP
+
Stage 1
Figure 2. The four stages of cholesterol biosynthesis
rate-determining step
cholesterol is feedback inhibitor
mevalonate is feedback inhibitor
target site for statin drugs

HMG-CoA reductase is the
regulatory enzyme of cholesterol
pathway synthesis. It is inhibited
by antihyperlipidaemic drug;
statin and dietary cholesterol, but
stimulated by Insulin through
decreasing c AMP.

Bile acids synthesis
The initial reaction, 7
-hydroxylase, in the
conversion of cholesterol to bile acids.
Cholesterol + NADPH + O
2
7-hydroxycholesterol + NADP
+
7
-hydroxylase
Rate-determining step
Repressed (decreased synthesis) by bile salts
Induced (increased synthesis) by cholesterol

Primary bile acids are : cholic
acid and chenodeoxycholic
acid(synthesized from cholesterol
in the liver)
Secondary bile acids are: deoxy
cholic acid and lithocholic
acid(from primary in S.I by
intestinal flora).
activated to turn
on pathways
Cholesterol
Pregnenolone
Progesterone
11-Deoxy-
cortisone
21-hydroxylase
Progesterone
Aldosterone
General pathways for the synthesis of aldosterone
and cortisol in the adrenal cortex
11-Deoxy-
cortisol
Progesterone
Cortisol
21-hydroxylase
HO
Vitamin D
3
Diet
HO
OH
25(OH) D
3
Liver
25-
OHase
OH
HO
OH
1,25(OH)
2
D
3
(active hormone form)
Kidney
1-OHase
HO
7
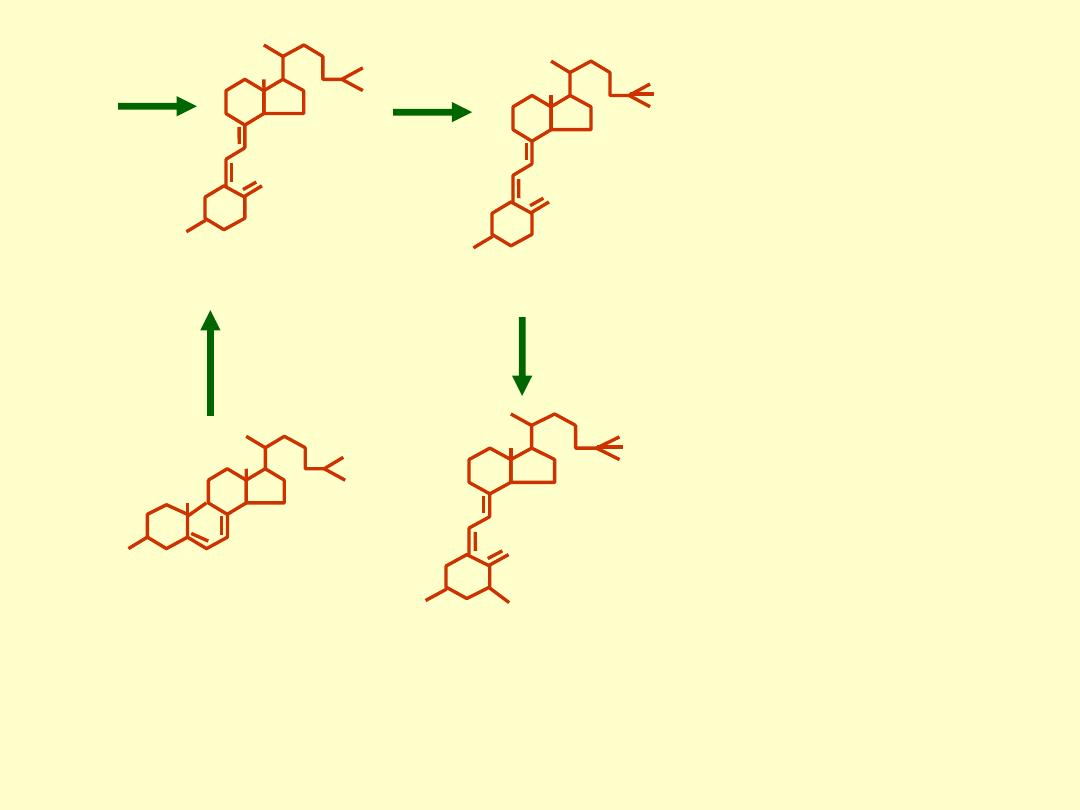
Provitamin D
3
(7-dehydrocholesterol:
Intermediate in
cholesterol synthesis)
UV from
sunlight
Skin
Figure 7. Photobiosynthesis of vitamin D
3
and its metabolism
Specific receptors in
intestine, bone,
kidney
Ca:
Intestinal absorption
Renal reabsorption
PO
4
:
Intestinal absorption
Renal reabsorption
OHase =
hydroxylase
