
Liver Functions
The major Functions The liver
1) carbohydrate metabolism .
A) Glugconeogenesis
B) Glycogen synthesis & metabolism.
2) Fat metabolism.
A)Fatty acid synthesis
B)cholesterol synthesis &excretion
C)Lipoprotein synthesis..
D) Ketogensis .(converting)
The fatty acid ketone bodies.
3) Protein metabolism.
A) synthesis of plasma proteins.
B) Urea synthesis.
4) Hormone metabolism.
Metabolism , conjugation &excretion of
steroidal &poly peptide hormones .
5) Drugs &foreign compounds;
metabolism& excretion of drugs.

6) Liver is a good part in storage of:
a)glycogen
b)VIT . A
B)VIT . B12
C)Iron.
7) Also liver plays a good part in
metabolism & secretion of Bilirubin.
There fore ,any damage to the liver organ
may affect any of the above functions.
The most important tests used in the
diagnosis of liver diseases are S. Got, S.
Gpt , T.S. Bilirubin ,T.S. Protein &
alkaline phosphates.
The most common diseases affecting
the liver are :-
1)Hepatitis : damage to the liver
cells .

2)Cirrhosis: In this case an increase in
the fibrous tissue formation result
in shrinkage of the liver & a decrease in
the hpatocellur function .
.
3) Tumours :most frequently are
secondary. Metastases from cancers of
the large bowel ,stomach &the bronchus
.
4)Obstruction of the bile flow :
This due to pathological diseases or
presence of stones.

__Jaundice :
It’s the yellowish discoloration of the
tissue due to the deposition of Bilirubin
. the state indicated when the value if s .
Bilirubin is about 2.0 mg./l00 ml. or
more .
Hyper Bilirubinaemia can be caused
by:
1)Increase production of Bilirubin.
2)Impaired metabolism
3)Decreased excretion. or
4)Combination of the above causes.
Major cause of Jaundice.
1)prehepatic:
A) Haemolysis.
b) Ineffective erythropoieses .

2) hepatic : pre. Microsomal : drugs
e.g.Rifampicin which interfers with the
Bilirubin up take .
Microsomal : pematurity ; vital
hepatitis , Gilbert،s syndrome , najjar
syndrome .
Post . Microsomal : impaired
excretion; hepatitis, drags , Intra hepatic
obstruction , hepatitis , cirrhosis ,
lymphoma , tumors…etc.
3)post hepatic : Gall stones ; biliary
stricture ; carcinoma of the pancreas or
biliary tract or cholingitis. .
Biochemial Assessmet of liver function
.
S – Bilirubin
1) Haemotylic jaundice :-
T.S. Bilirubin is high especially the
uncojugated form.
Enzymes :-
S. GOT
S. GPT SLIGHTLY
Urine urobilinogen is in the urine i
.e. Bile pigment positive while Bile
salt negative.___
In Crigle – Najjar syndrome ; the
unconjugated form of Bilirubin is
highly increased (the free form ).

Conjugated hyper – bilirubinaemia
This condition is result due to a
leakage of Bilirubin from either
hepatocytes or the biliary system in
to the blood stream. The water
soluble
(the conjugated form ), enters the
systemic circulation then excreted
into the urine to a deep orange –
brown color ( tea – color ) .
Here ; Bile salt positive
While , Bile pigment Negative
Plasma Enzymes
The enzy mes are used in the
assessment o f liver function are : s .
Got &s. Gpt .to gather with s .
Alkaline phosphatase & 8-glutamy
transferase ( GGT).

Here ;S . Gpt & S . Alk. phosphatase
are more specific for liver diseases .
Increase in S. Got & S. Gpt reflect
cell dama ge; in this case , S.levels
of the enzymes increase 20 times
than the normal range in hepatitis.
While in obstractive jaundice: S .Alk.
phosphatase increase 10 times
than the normal range . 8 – glut
amyl tran ferase ( GGT) , is also
increase in liver disease .
Thane fore , s. levels of the enzymes
are very useful in following up the
progress of liver diseases .
prothrombin time is also affected in
liver disease ; as the activity of vit .
K-dependent clotting factors are
synthesized by the liver . (
factor vII ) .

An increase in the prothrombin
Time is often an early feature of
acute liver diseases .
Plasma proteins :
Protein is synthesized in the liver ,
so its conc. in the plasma reflect
the functional capacity of the
liver. Its value decrease in
chronic liver disease , but it is usually
normal in the early stages of a cute
hepatitis .
In plasma immunoglobulin conc.
may be noticed in alcoholic liver
disease . IGA , IgG in acute
hepatitis & Igm in primary biliary
cirrhosis .
There fore , plasma proteins are of
diagnostic value in the liver
diseases .

In sever cases , hepatic failure may
develop , but most patients
eventually recover completely .
S.GOT& S G PT increase then
return to normal after recovery
with in 20 – 30 days . While in cases
with hepatits
B &C Virsuses, the enzymes remain
elevated .Infection with hepatitis A
never leads to chronic disease.
chronic hepatitis :
It is a hepatic inflammation remain
for more than six months . There are
man y causes , e.g. Autoimmune
heparitis, chronic infection with
hepatitis B or C & alcohol.

Auto immune typically occurs in
young women although it can
occur in either cases .
Plasma Got & Gpt are usually
elevated .
A cute liver failure :
It is a state of sever liver
dysfunction . It can be hyper acute
developing within seven days of the
onset of jaundice . It is a rare
condition. Toxin & hepatitis are the
most frequent causes . Acute liver
failure is often accompanied by
renal failure .It is represented with
hyponatraemia , hypocacimia and
hypoglycemia. lactic acid acidosis
many develop as a result of failure
of hepatic gluconeo genesis from
lacta
te.

Alumina in chronic liver disease
8 – globulin in cirrhosis ,
especially autoimmune diseases .
∞- antitrypsin in cirrhosis due
∞- anti try sin deficiency . ∞-
fetoprotein is highly in primary
hepatocellur carcinoma .
Liver diseases
1- A cute hepatitis : it is usually
caused by viral infection ,A ,
B , C , D , & E or by toxin e.g.
alcohol , parcetamol , car
bon tetra chloride ( ccl4 ) or
fungal toxins. Patients may
represent with jaundice .
Bilirubin and urobilinogen
are usually detectable in

urine . At the same time s.
level of Bilirrubin is also
increase.
Cirrhosis :
Causes of cirrhosis include
chromic excessive alcohol in
take ; auto immune diseases e .
g . auto immune hepatitis
,primary biliary cirrhosis
persistence B or C virus and
various inherited metabolic
diseases , such as Wilsons
disease ….etc . metabolic and
clinical abnormalities may occur
later on . causes of death
include uncontrolled bleeding
.. spaticaemia . Long
prothrombin time . and

elevated level of s . bilirubin are
detected .
Tumours and infilitrations :
The liver is a common site for
tumour metastasis . pr imary
tumours are associated
with cirrhosis , hepatitis B & C
and various carcinogens .
Plasma α- fetoprotein is
elevated.
Infilttrative conditions which
Can affect the liver include
lymphomas and amyloidosis.
Patients with such conditions
and with
Intrahepatic tumours are
often not jaundiced. The

only biochemical abnormality
may be an increase
In plasma Alkaline phosphatase
activity.
Inherited abnormalities of
Bilirubin metabolism
There are four conditions in
which jaundice is caused by
inherited abnormality of
Bilirubin metabolism . Gilberts
,crigler – najjar , Dubin – Johnson
& rotor syndromes.
Gilberts syndrome affects 2-3%
of the population but the
others are rare . The jaundice
of Gilberts syndrome is
typically mild & present only

intermittently . It is often
noticed after an infection
or a period of deceased of food
in take . The liver is
histologically normal .
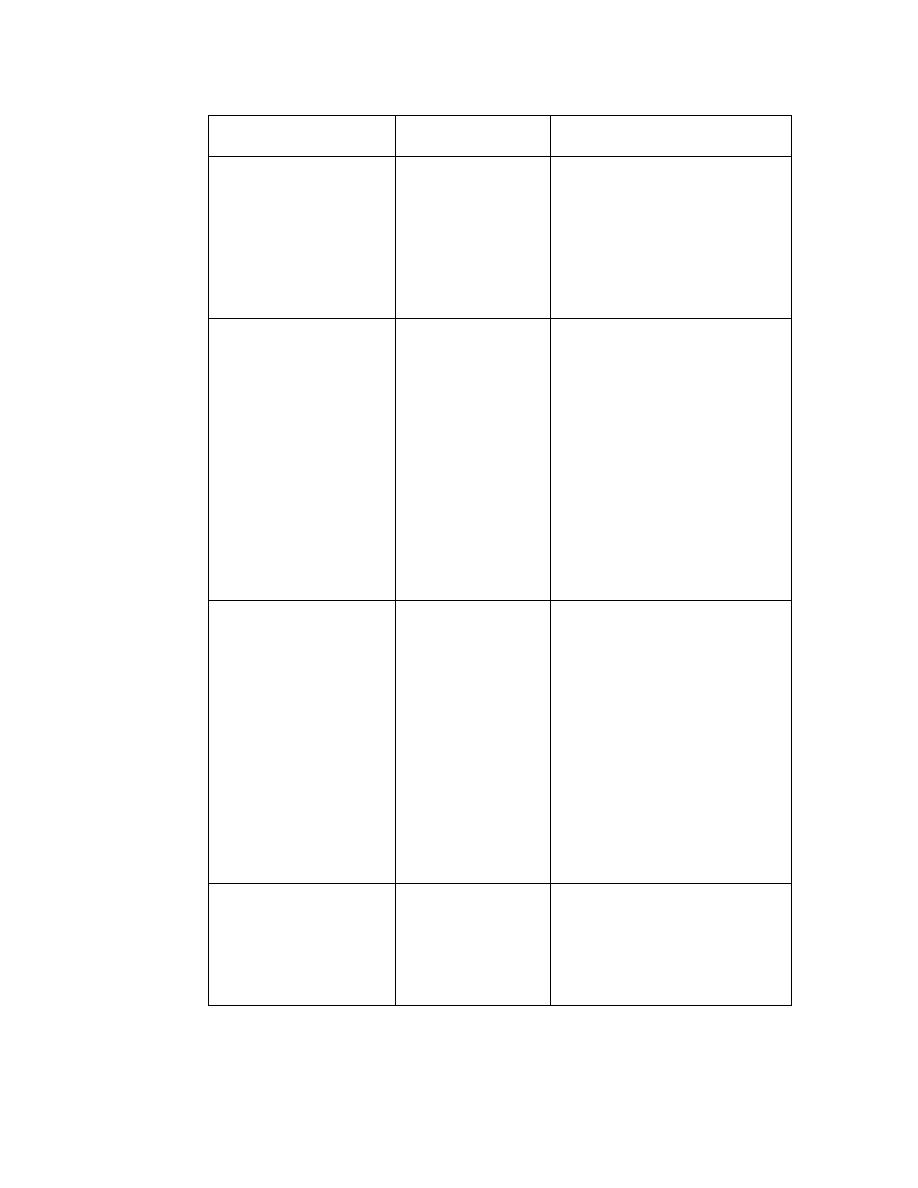
defect clinical features
Gilberts
decreased
conjugati
on.
mild or increase
the
uncongated bili .
Crigler
_Najjar
a)Absenc
e of
conjugati
ng
enzyme
b) partial
defect.
Increase the
free form.
Dubin_John
son
Decrease
d hepatic
excrtion
of Bili.
Mild
hyperbilirubinae
mia ,hepatic
pigment
disposition
(melanim),
bilirubinuria.
Rotor
Unknown Similar to Dubin
but not
pigmentation.

uncommon liver diseases:
Wilsons disease is an Inherited
abnormality of copper metabolism .
characterized by decreased biliary
excretion of copper. Copper is
deposited in the liver . patients with
Wilsons diseases may present either
in child hood with hepatitis
accompanied in many cases by
haemolysis & renal tubular defect or
in young with cirrhosis .
The biochemical features of Wilsons
disease are a decreased in plasma
cerulo plasmin conc. A low plasma
copper & renal excretion of copper .
Gallstones
Consist mainly of chol. , calcium ; salts
and bilirubin . Gall stones may be

silent but it causes can biliary colic
and obstruction . biochemical tests
may be of value in the management
of such cases . S.Alk. phosphatase
increase
S GOT
SGPT Moderate increase.
T . S . Bilirubin - especially the
conjugated form .
