MULTIPLE MYELOMA
(MM)
objective:
definition of MMand
biochemical investigation in diagnosis of this
disease
Basil O M Saleh
MULTIPLE MYELOMA (MM)
•
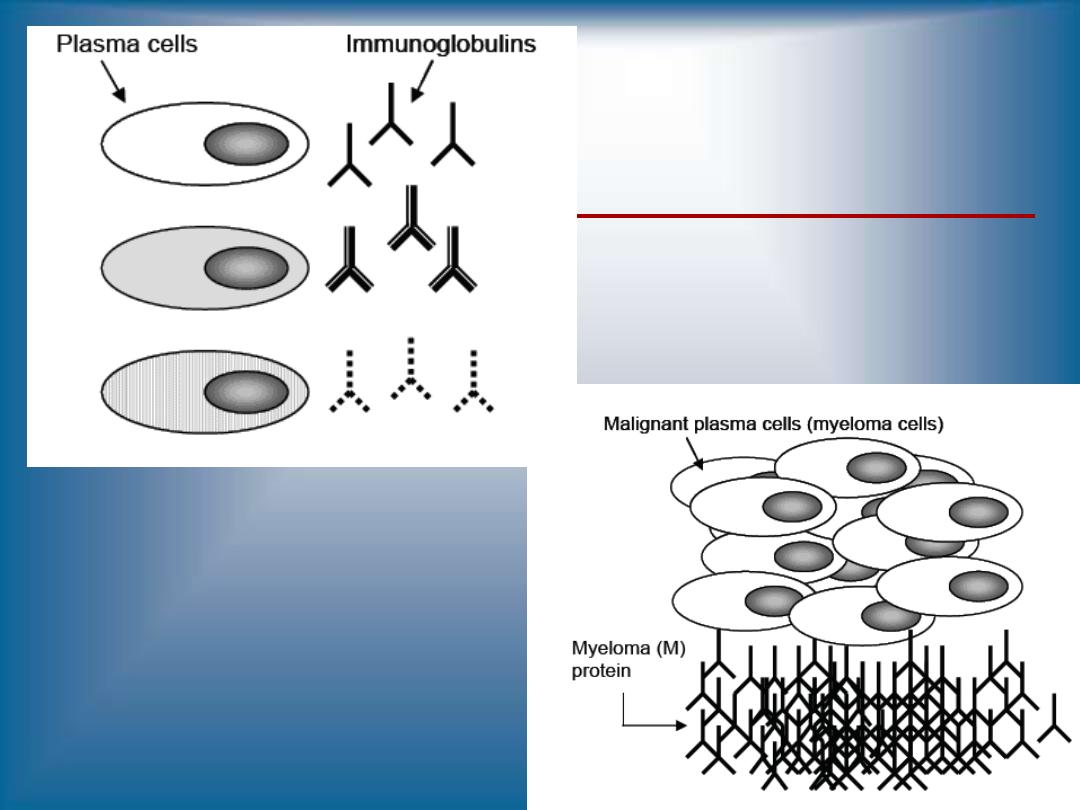
A neoplastic (malignant) proliferation of a
single clone of plasma cells in bone marrow
•
Major laboratory diagnostic criteria
•
>10% plasma cells in bone marrow
•
Complete or incomplete monoclonal
immunoglobulin(s) in serum and/or urine at
elevated concentrations
•
Monoclonal Immunoglobulins (Antibodies)
•
Monoclonal proteins, M proteins or paraproteins
•
Non-functional
PARAPROTEINS
("M-proteins")
Greatly
increased
amounts
of
some
normally-
undetected serum protein is called paraproteinemia,
and the abnormally-increased protein is called a
paraprotein
or
M-protein.
("M" means both monoclonal and myeloma, the
usual
cause
of
an
M-protein.)
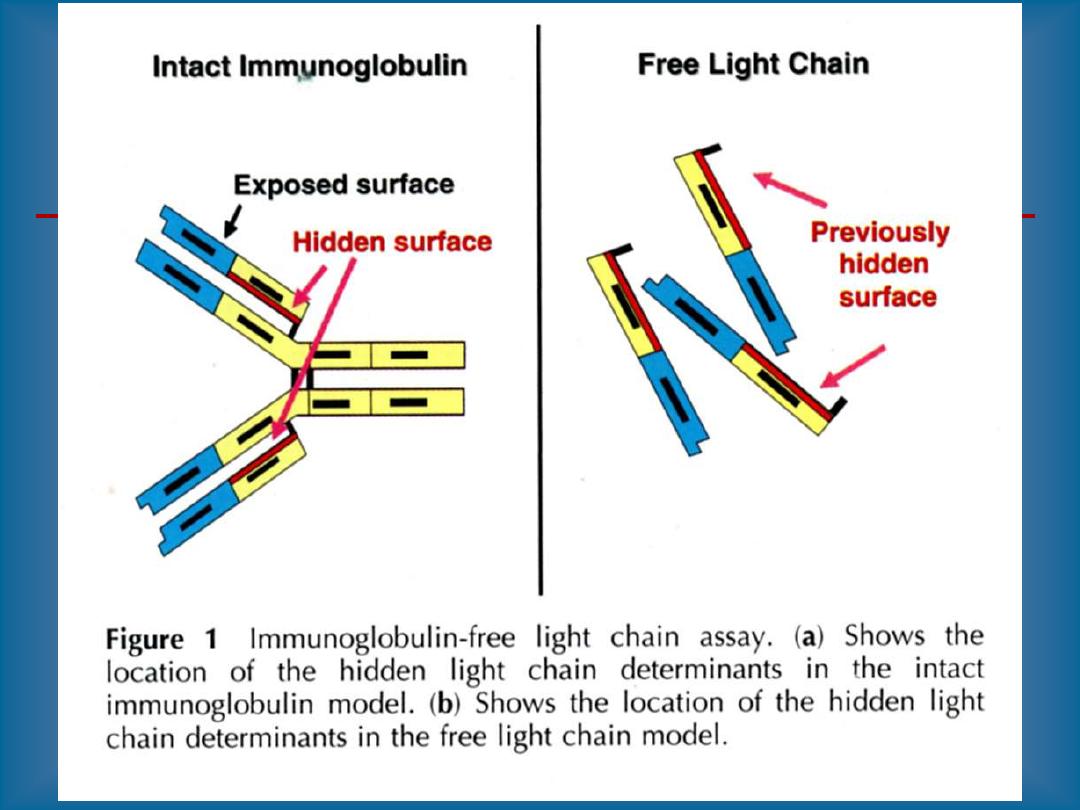
Most often, the paraprotein is all or part of an
immunoglobulin
molecule.
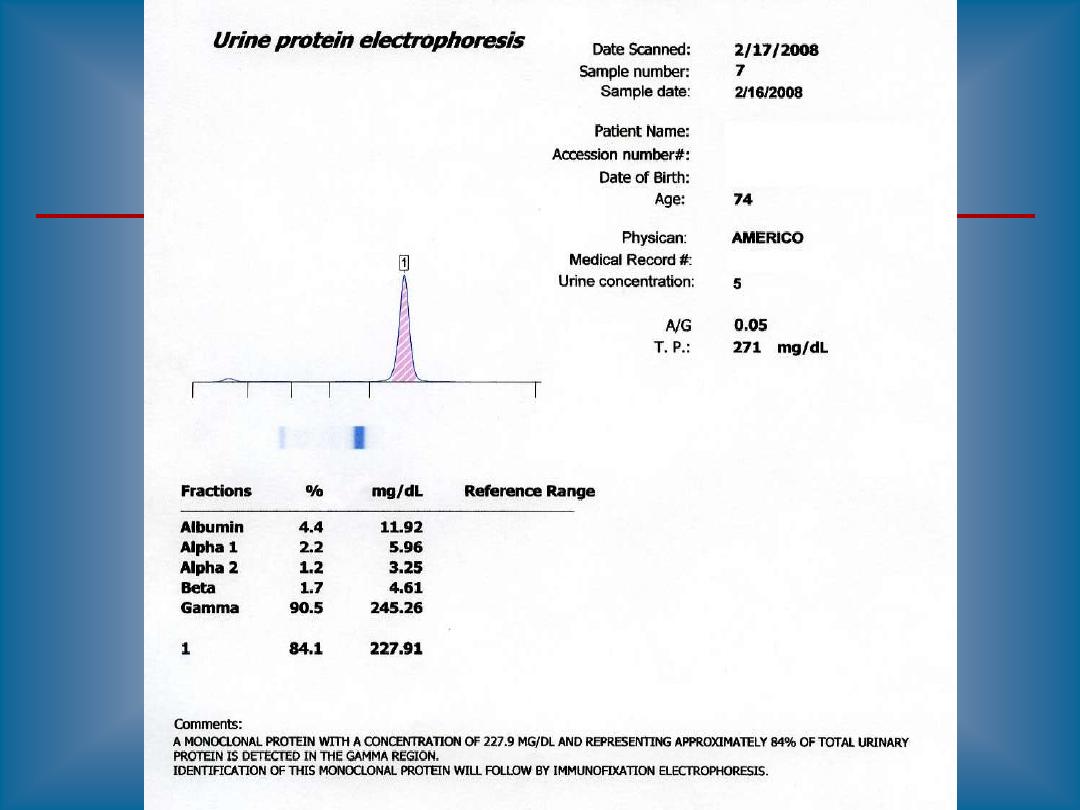
Especially if the paraprotein is light chains, it may
spill into the urine ("Bence-Jones proteinuria").
You can test urine for Bence-Jones protein by
yourself, using a test tube and a Bunsen burner.
Bence-Jones protein precipitates on heating (around
40-60), then redissolves just before the urine boils.
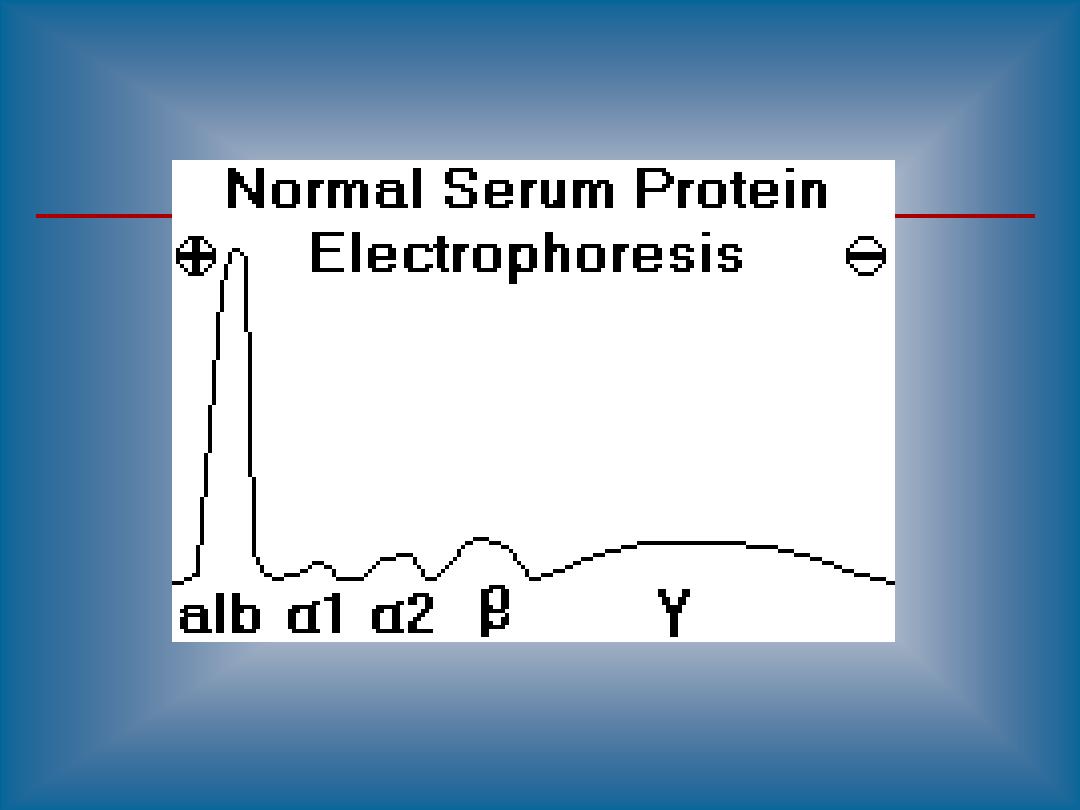
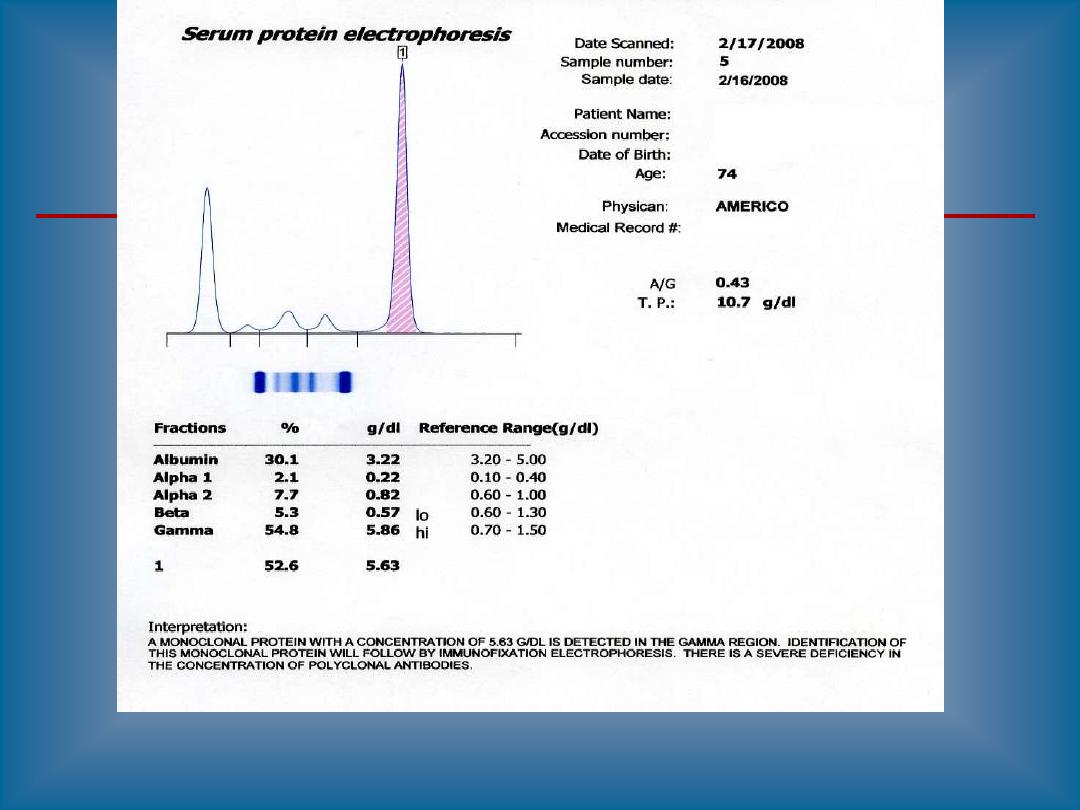
Paraprotein appears as a sharp peak (a "spike"),
most often in the gamma region, though it may be
anywhere.
Such a peak indicates the presence of a monoclonal
gammopathy
A majority of detected monoclonal gammopathies are
the result of plasma cell myeloma. These patients
typically have depression of other gamma globulins
and
albumin.
Some other causes of monoclonal gammopathies
include:
Waldenstrom's
macroglobulinemia
heavy
chain
disease
CLL,
lymphoma,
amyloidosis
(occasional
cases)
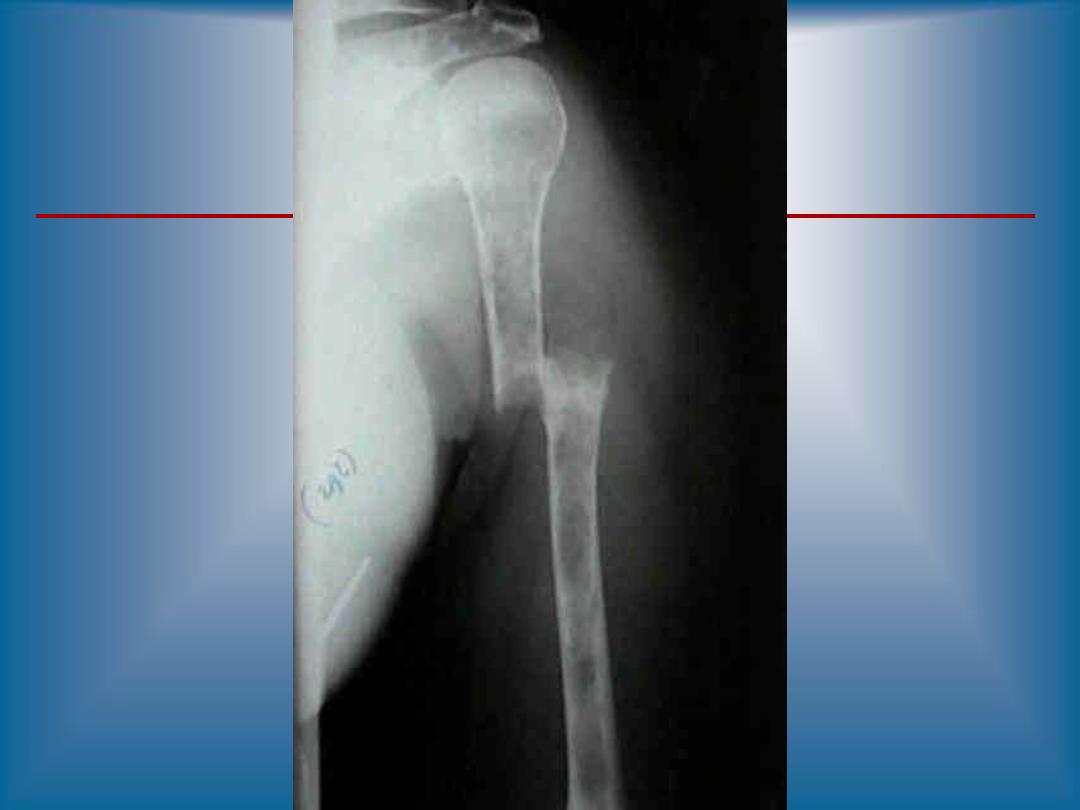
RADIOLOGY DIAGNOSIS OF
MULTIPLE MYELOMA
•
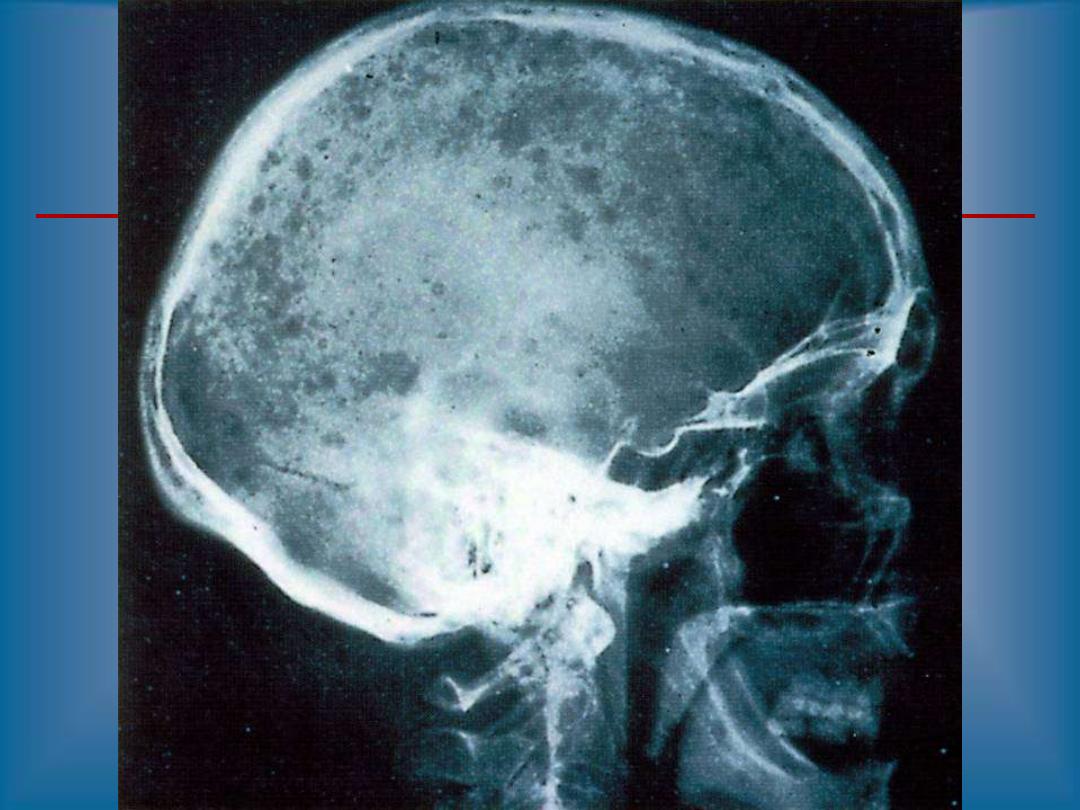
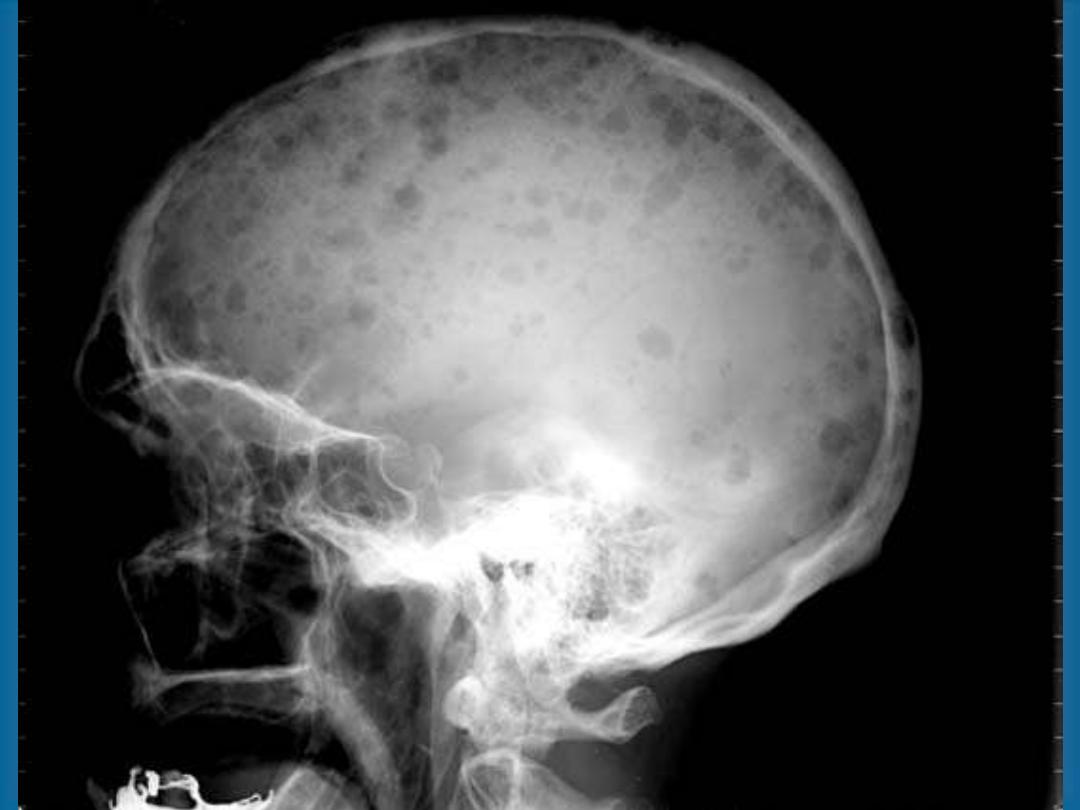
Skeletal bone X-ray series
•
Skull, spine, ribs, arms, legs and pelvis
•
Alternative procedures
•
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
•
Computed tomography (CT)
•
Computerized axial tomography (CAT)
•
Lytic bone lesions and/or pathologic fractures
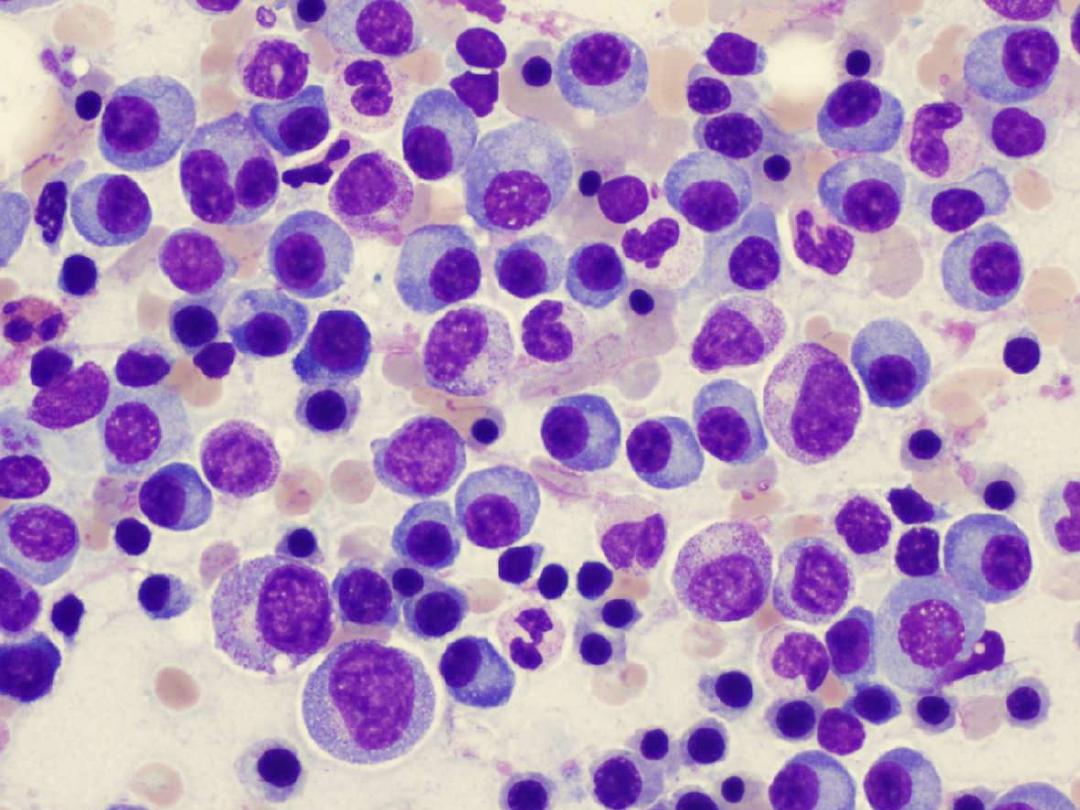
Laboratory analysis
1. significant increased ESR(erythrocte
sedimentation rate) > 90 mm3/hr.
2.Serum protein electrophoresis SPE(M band)
3.Bence Jones protein BJP in urine(positive
band)
4. hypercalcemia & hyperphosphatemia
5. hyperuremia & hypercreatininemia
6. hyperuricemia
7. decreased Hb
8. Hypoalbuminemia
8. Noarmal ALP
These investigation results depend on
stage of MM, for example; incresaed
urea, creatinine, uric acid and
decreased s. albumin occurr when
kidney integrity and function dcline
because of precipitation of BJP in it.
