
Anaphylaxis
Angioedema
Transplantation & graft rejection
1

Learning objectives
1.Anaphylaxis
:
definition, causes, C/P, Ix, Rx
2.Angioedema
: definition, causes, C/P, IX,RX
3.Transplantation
&
graft
rejection:
definition
,
determinants, complications, classification.
4.
Complications
of
immune
suppression&
Immunosuppressive drugs
used in transplantation
5. HLA linked disorders
6.
Immunizations
:
benefit, and types
7. Summary
8.Quiz
2
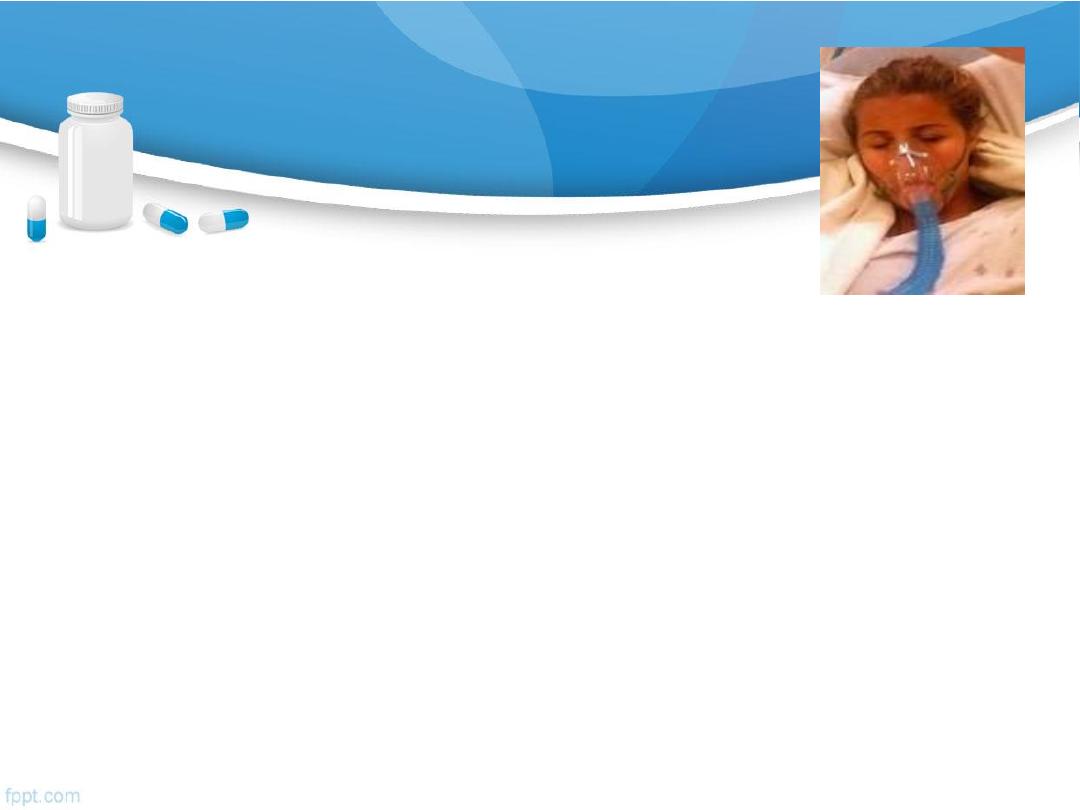

ANAPHYLAXIS
Definition
Acute medical emergency.
Systemic allergic reaction.
Due to release of histamine and other vasoactive
mediators.
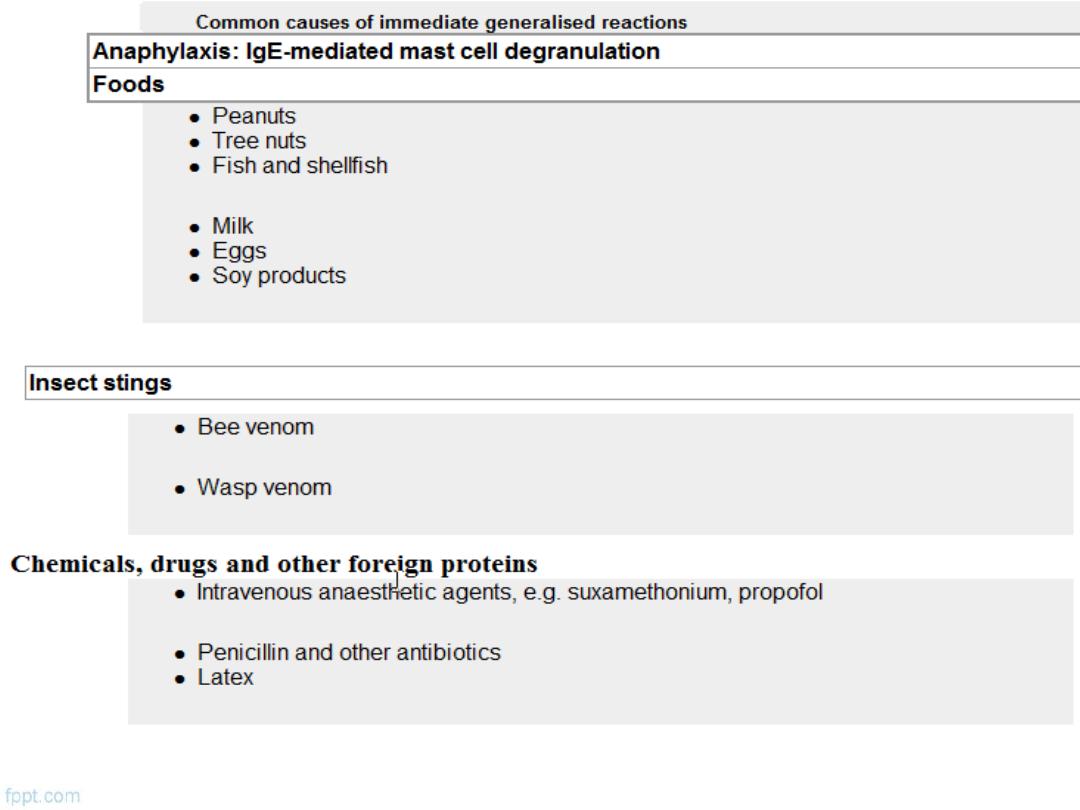
Causes
1.Anaphylaxis
: IgE mediated mast cell degranulation
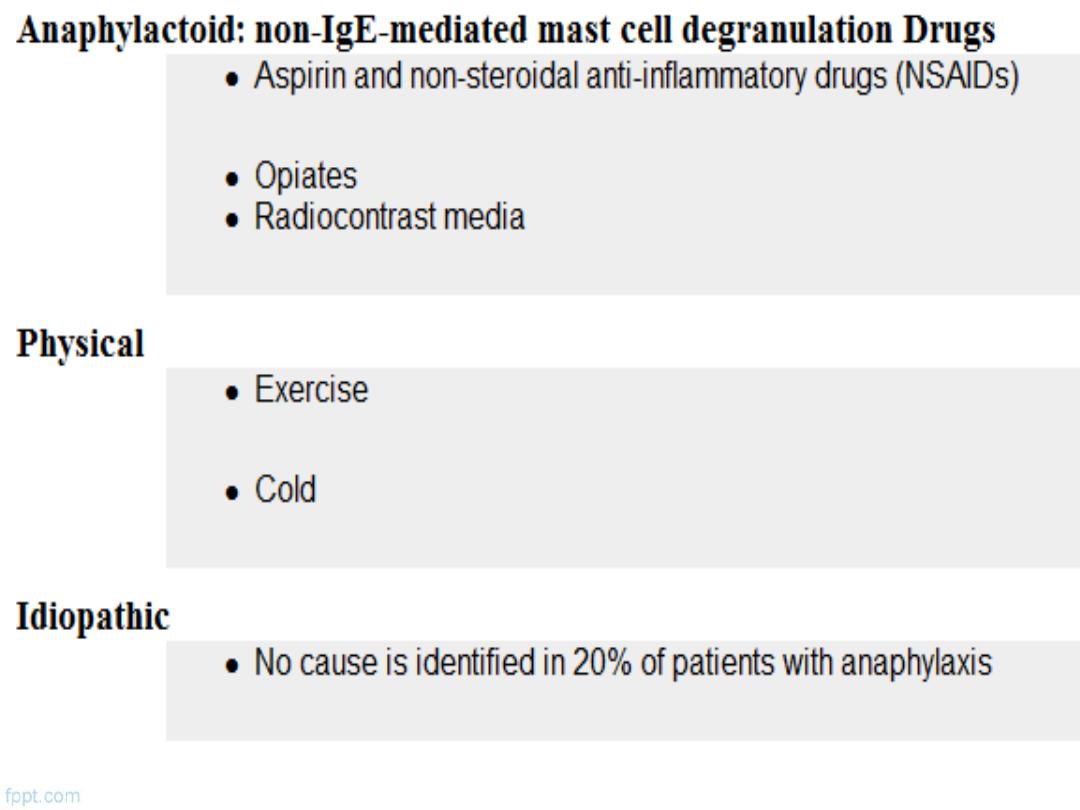
2.Anaphylactoid:
Non-IgE
3
4
5
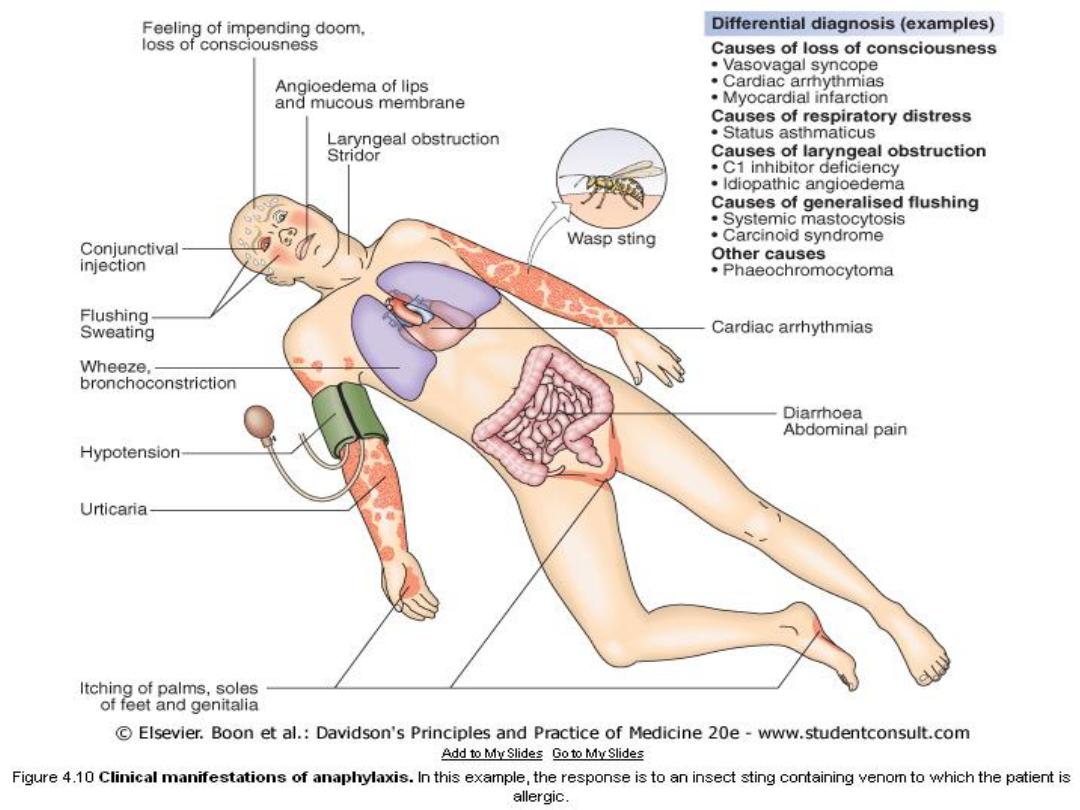
C/P of anaphylaxis
Acute severe systemic allergic reaction
PF: foods, latex, insect venom and drugs
A history of previous local allergic responses to the
offending agent
6
7

Investigations
1)Serum mast cell tryptase
2)Specific IgE tests
Management
5-immediate
management includes:
ABCDT
1)
A
:
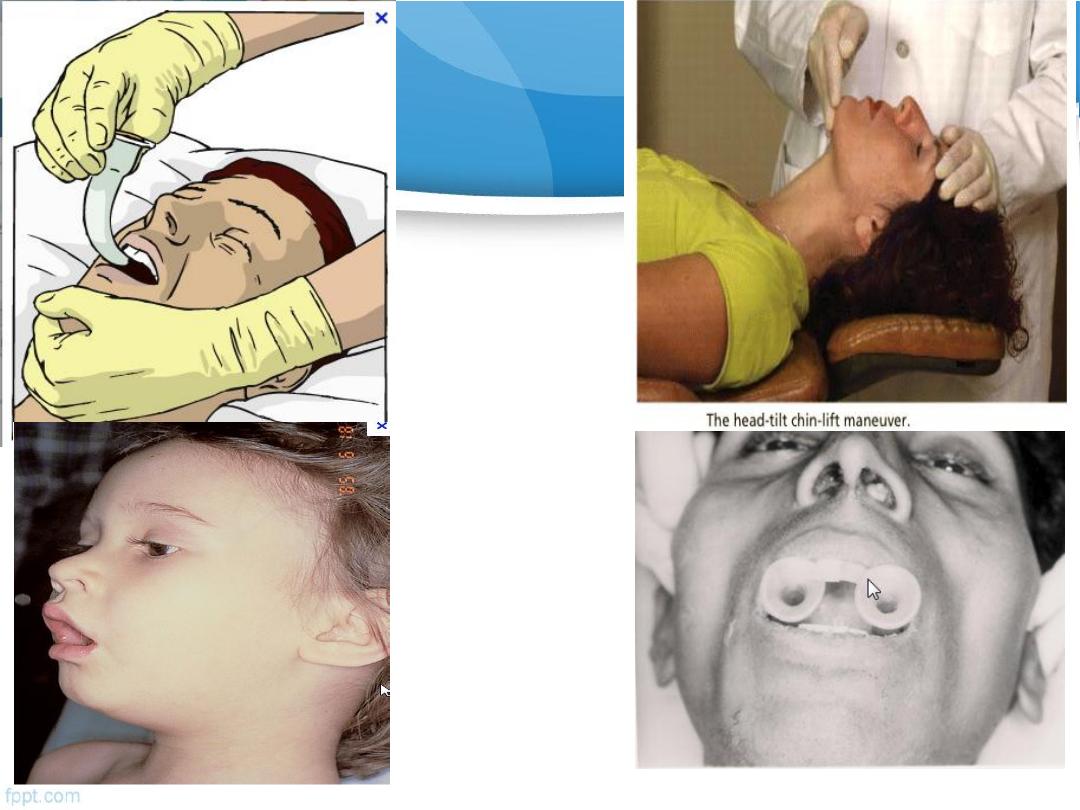
Airways
: ensuring airway patency
2)
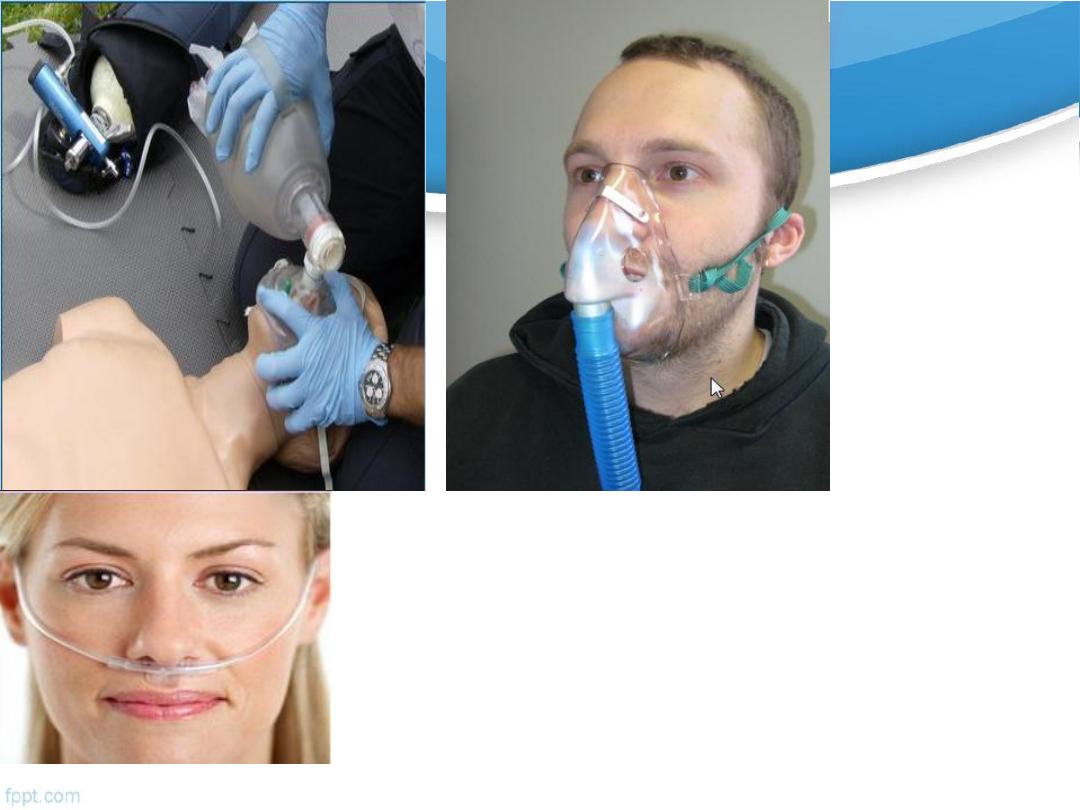
B:Breathing
: administration of oxygen
8
9
Patent airways
10
Oxygen adminstration

3) C:Circulation
: restoration of blood pressure
(laying the patient flat, i.v fluids)
4) D: Diagnosis
: anaphylaxis & risk factors
11

12
i.v fluids

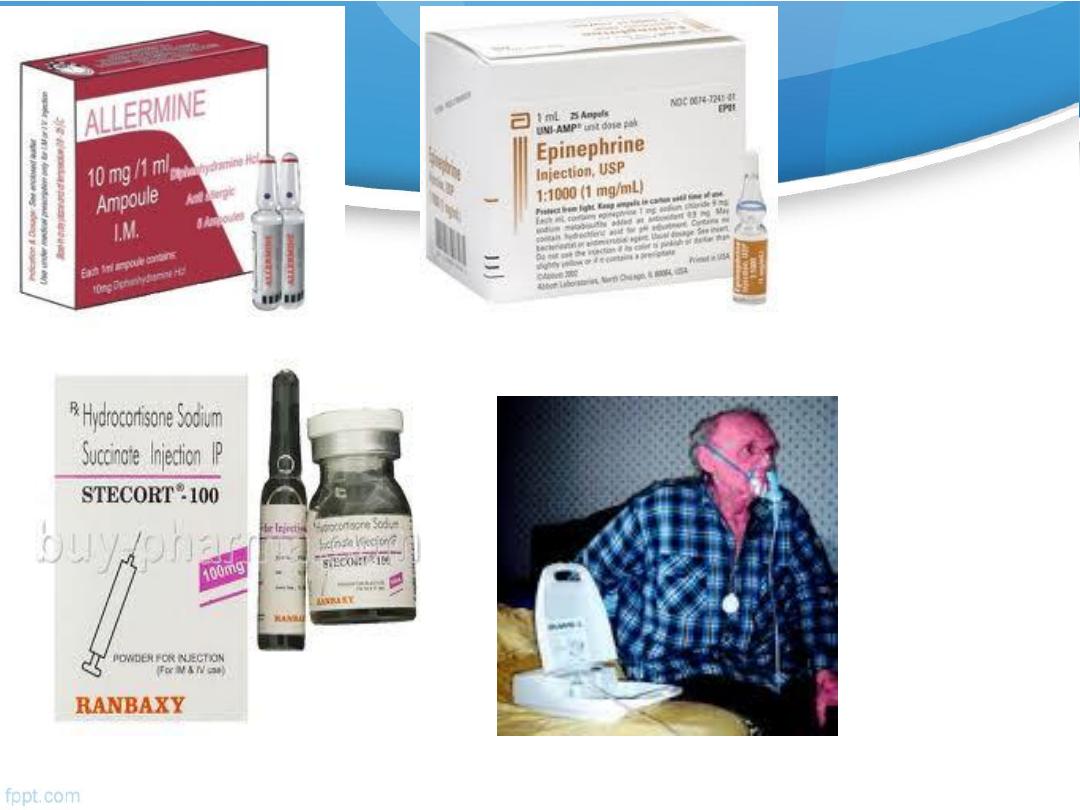
5)T: Treatment
::
Adrenaline
(epinephrine) i.m (adult dose, 0.3-1.0 ml
1:1000 solution) and repeated at 5-10 minute intervals
if the initial response is inadequate.
intravenous antihistamines
:
chlorpheneramine
10-20
mg i.m. or slow i.v. injection
Corticosteroids:
hydrocortisone 100-300 mg i.v
Supportive treatments
including
nebulised
β
2
- agonists
Identify the
trigger factor
: removal + avoidance
13
14

•
Education:
Patients who
previously experienced
an
anaphylactic
event should be prescribed
self-injectable adrenaline
and they and their families or carers should be
instructed on its use.
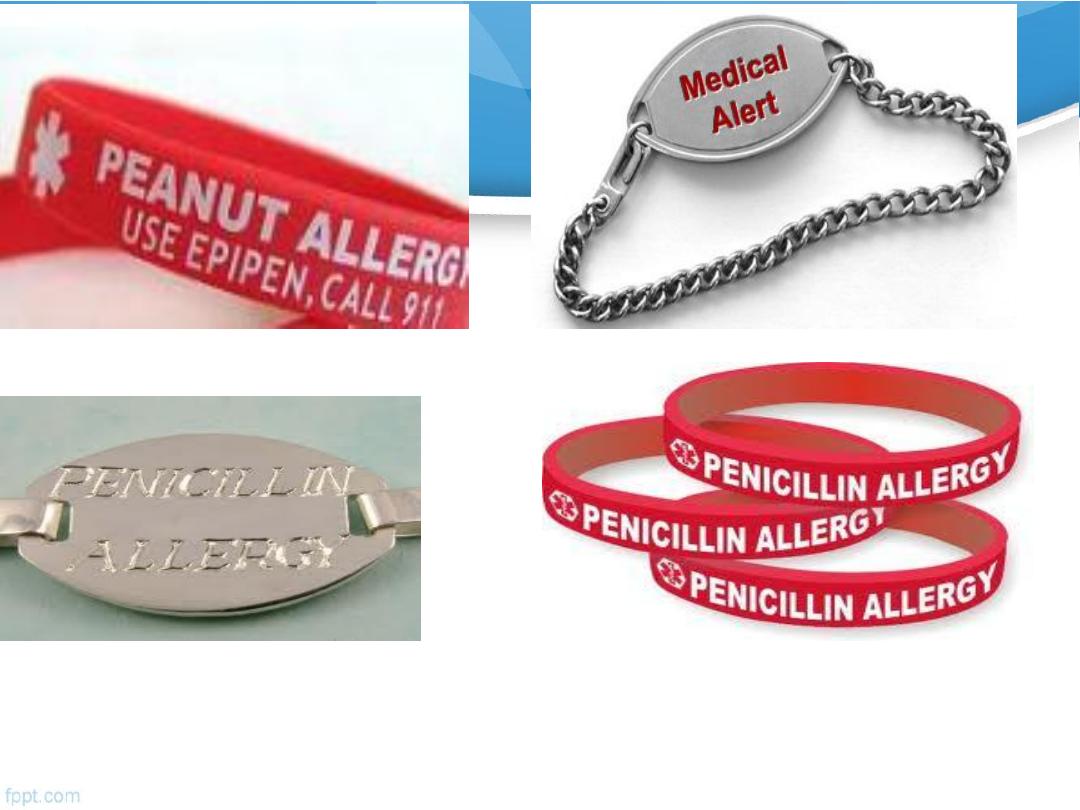
Use of a
Medic Alert bracelet
(or similar) will increase
the likelihood that adrenaline will be administered in an
emergency.
Referral to specialist assessment
15
16

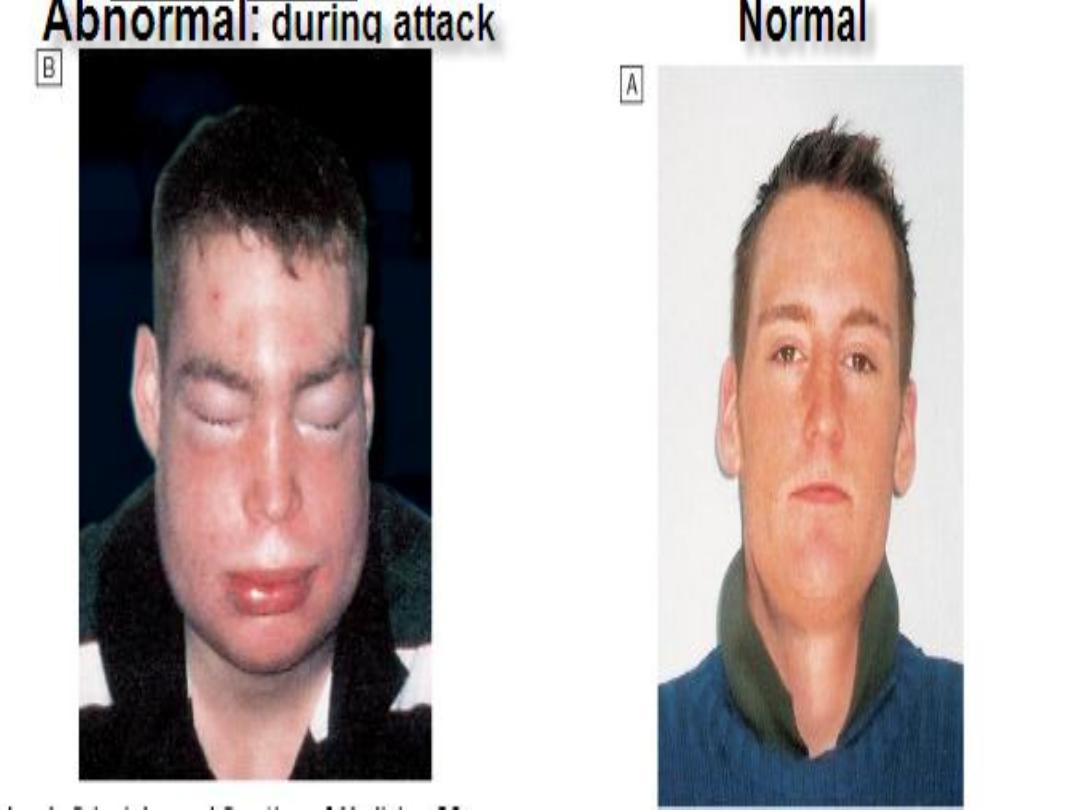
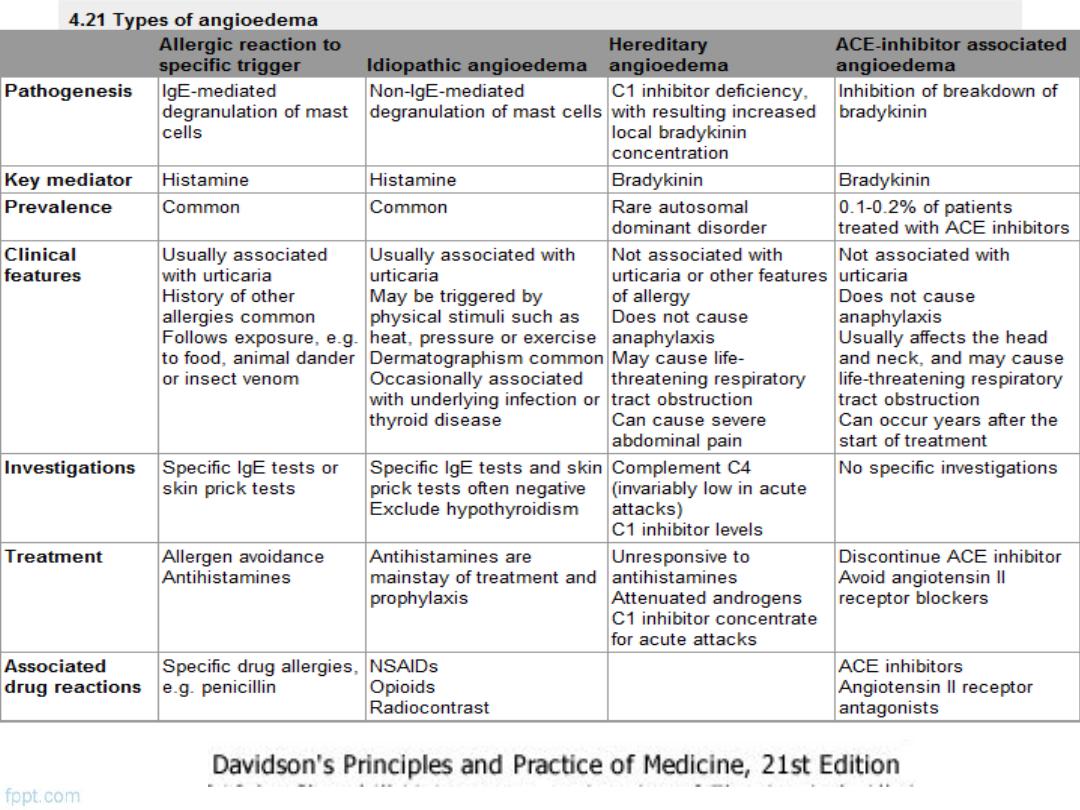
ANGIOEDEMA
Definition
Is the episodic, localized, non-pitting swelling of
submucous or subcutaneous tissues
alone
±urticaria
mechanism is degranulation of mast cells or
increased local bradykinin concentration
17
18
19

Transplantation: is the definite Rx of end organ disease.
Graft rejection: is an aggressive immune response by the
recipient.
Determined by :
the genetic disparity between the donor and recipient,
the immune status of the host and the nature of the
tissue transplanted
The most important genetic determinant is the difference
between donor and recipient HLA proteins
20
Transplantation & Graft Rejection

Value of compatible HLA loci
↓acute rejection.
↑ graft survival.
↓ intense immunosuppressive protocols.
21
Number of solid organ transplants
22
Organ
transplantation
complications
Rejection
Genetic disparity.
CD8 & macrophage mediate most of
the rejection
-swelling & pain over the allograft
GVHR
-
Allografted immune competent tissue( e. g
b.m) recognises recipient as foreign
tissue. CMI damage to the recipient
- Skin rash, diarrhea,& jaundice
23
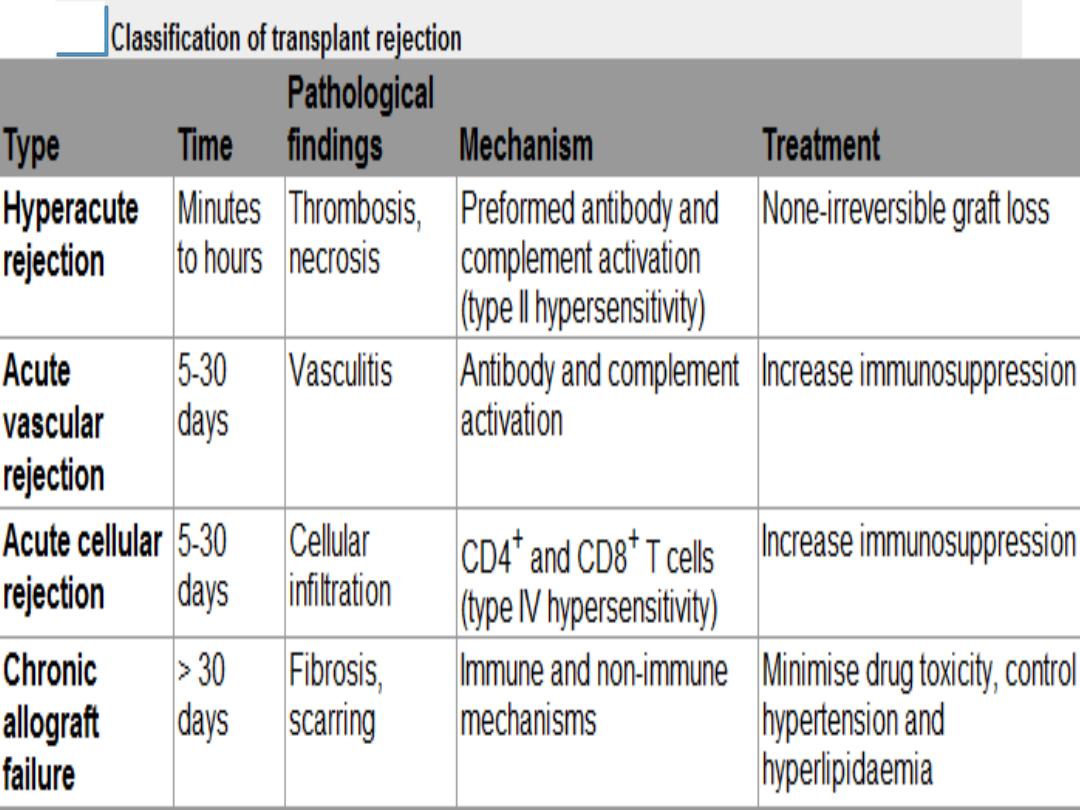
24

Acute
cellular rejection is
the most common form
of
graft
rejection.
Chronic allograft failure
(chronic rejection) is a major cause
of
graft loss.
Investigations to avoid rejection
HLA typing
Anti-HLA antibody screening
Donor-recipient cross-matching
C4d staining: useful in the early diagnosis of vascular
rejection
25

Complications Of Transplant Immunosuppression
1)
Infection
:
opportunistic infections:- CMV
-
Pneumocystis
2)
Malignancy
:
because T-cell suppression -----------------
failure to control viral infections
-Epstein-Barr virus-- lymphoma
-human herpesvirus 8----Kaposi's sarcoma
-human papillomavirus-----skin tumours
26
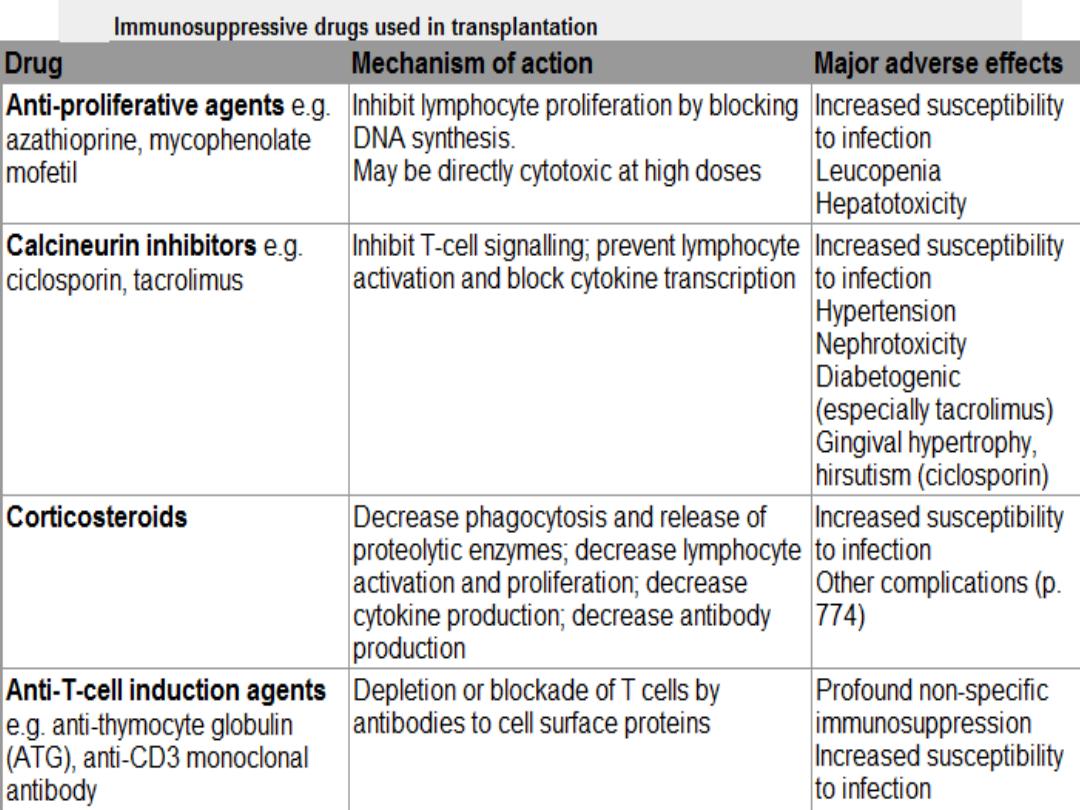
.
27
28

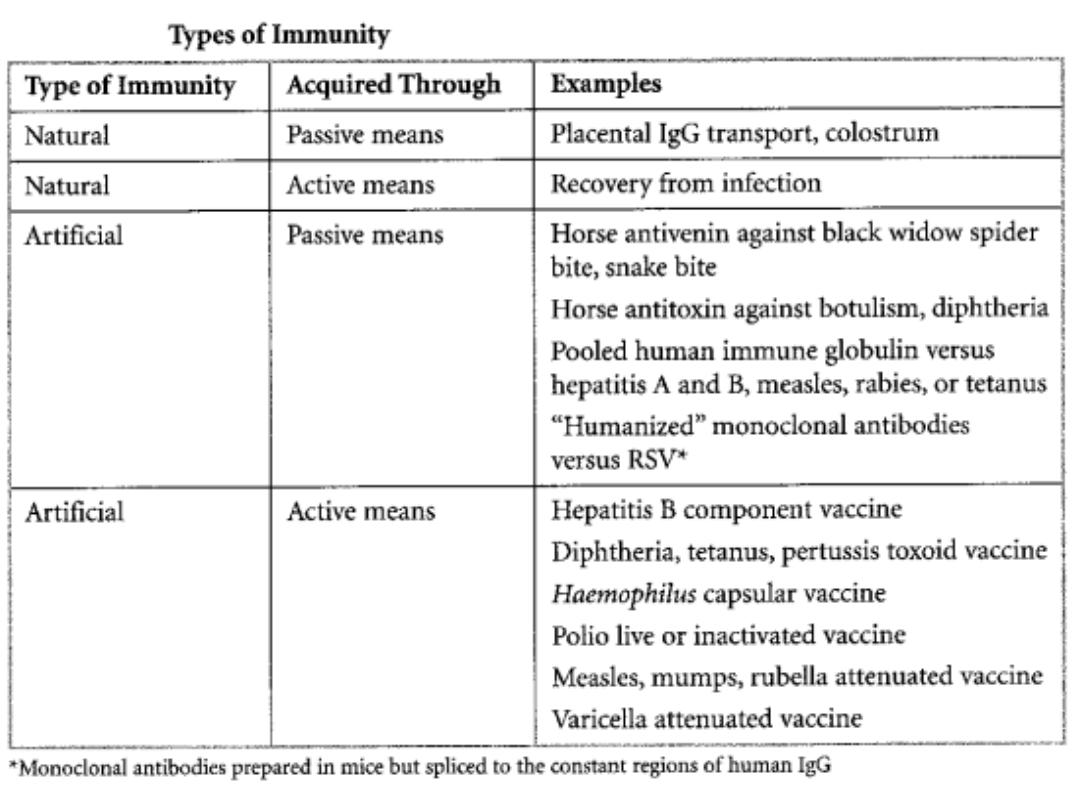
Immunization
29
30

Summary
Anaphylaxis: AME should be Dx & Rx early.
Angioedema is episodic, localized, non-pitting swelling of
submucous or subcutaneous tissues. 4 imp types.
Transplantation: is the definite Rx of end organ disease.
Graft rejection: is an aggressive immune response by the
recipient.
Organ transplantation complications: rejection & GVHR
31

Summary
Types of reject: hyperacute, acute, & chronic
Imuunosupp dr: x -proliferat, calcineurin x,corticosteroids,
x T-cell induction
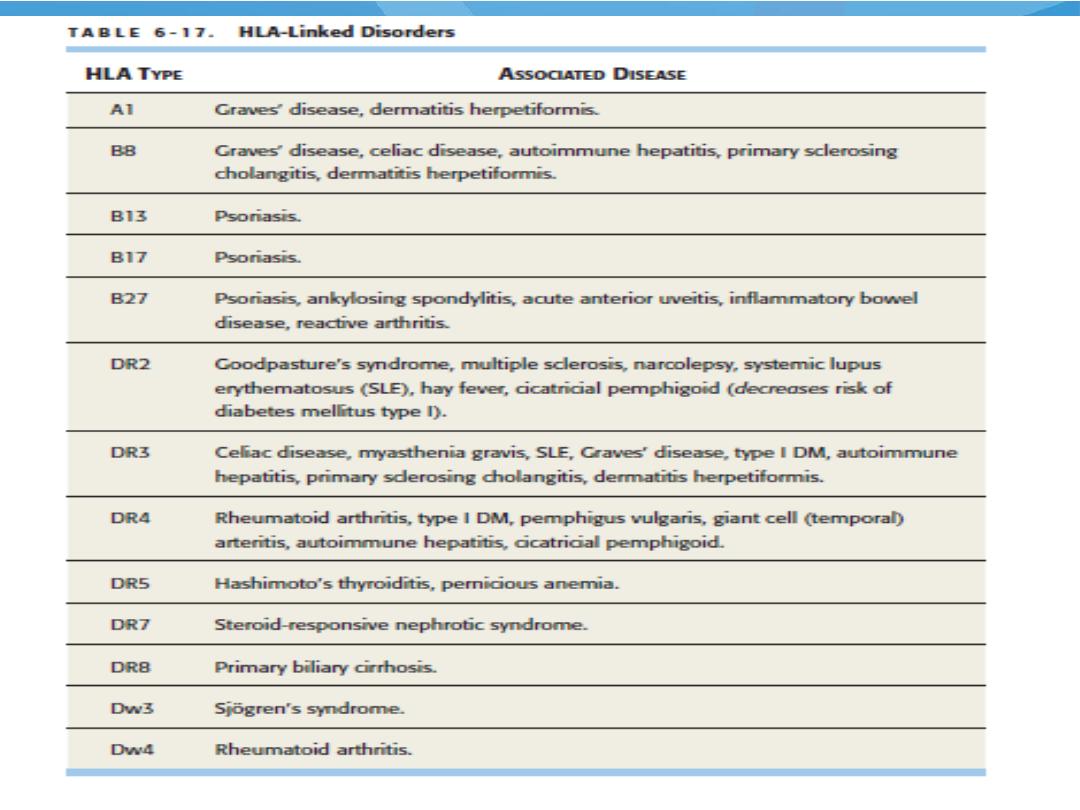
Certain disorders associated w specific HLA type.
Immunization: natural & artificial : active & passive means.
32
