
Clinical immunology
References
1.
Davidson’s principle and practice of
medicine 21
st
edn
2.
Kaplan medical immunology USMLE 1
lecture notes 2013
3.
First aid for basic sciences general
principles: Tao le and Kendall Krause
2011
1

IMMUNE SYSTEM (IS)
2

Learning objectives
Definition
Types
Functions
Examples
Summary
Quiz
3
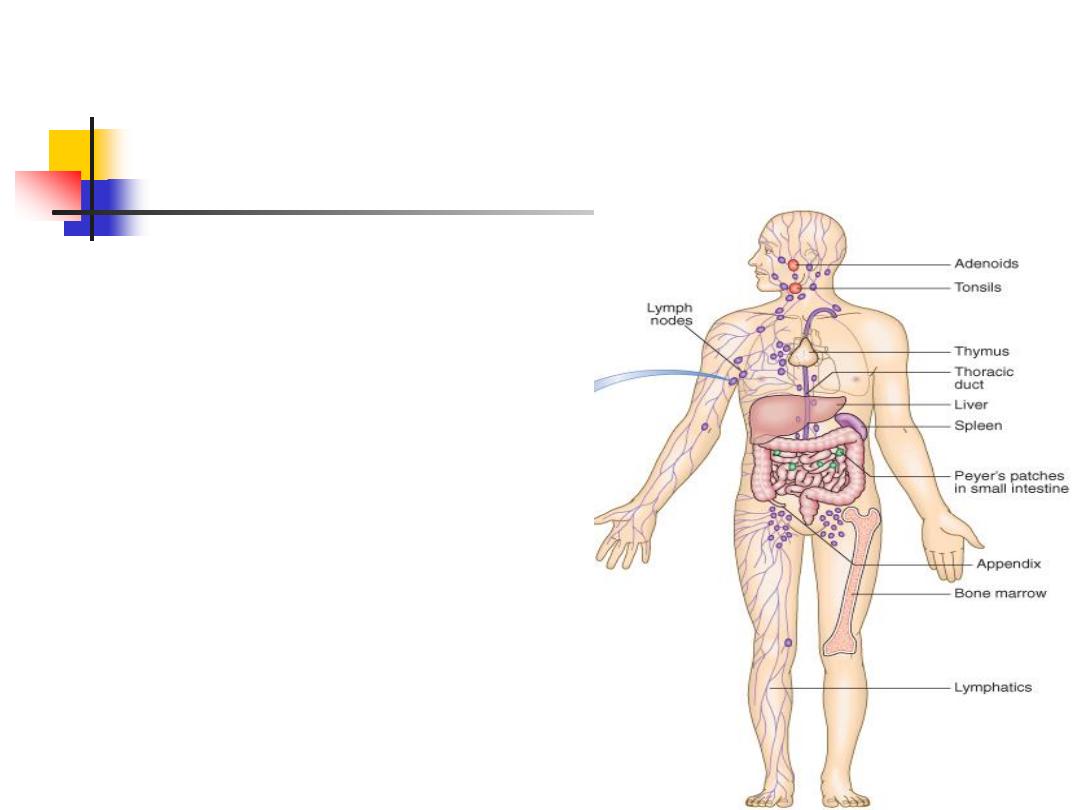
Definition:
Immune system
Is the system that protects the
host from pathogens
Minimizes self tissue damage
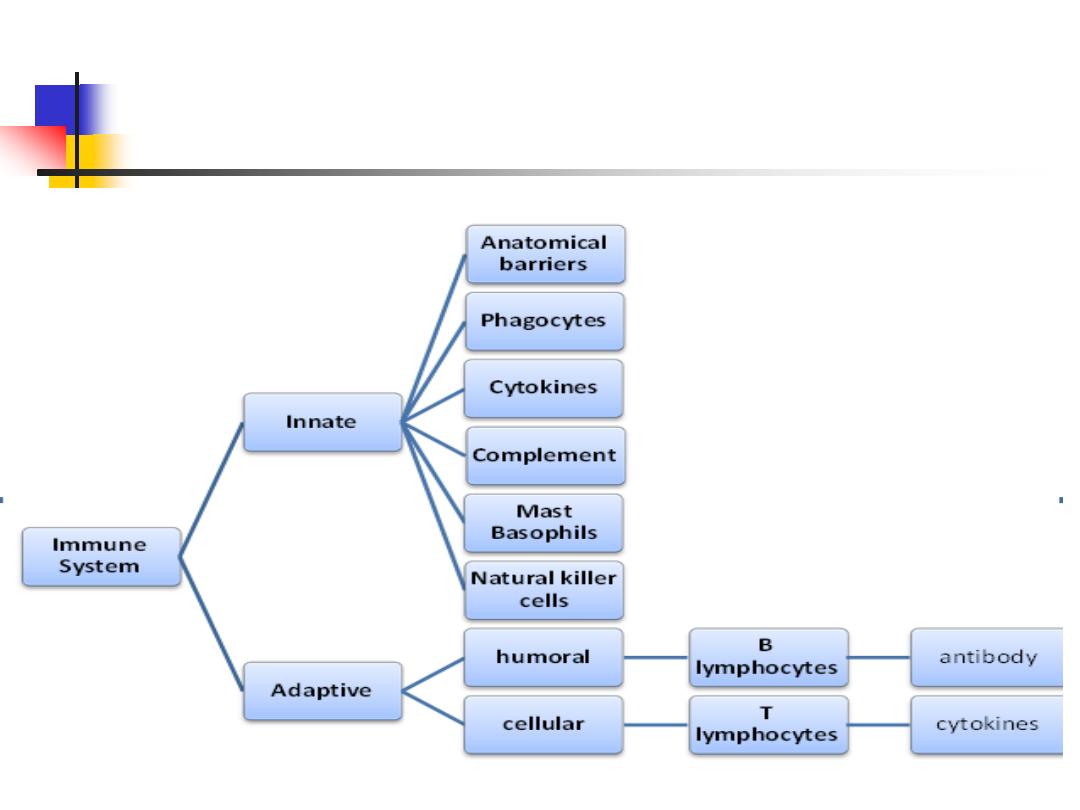
Types:
5

I-Innate immune system
Non-specific
defenses against infection
Provides
immediate protection
against an invading
pathogen
Includes:
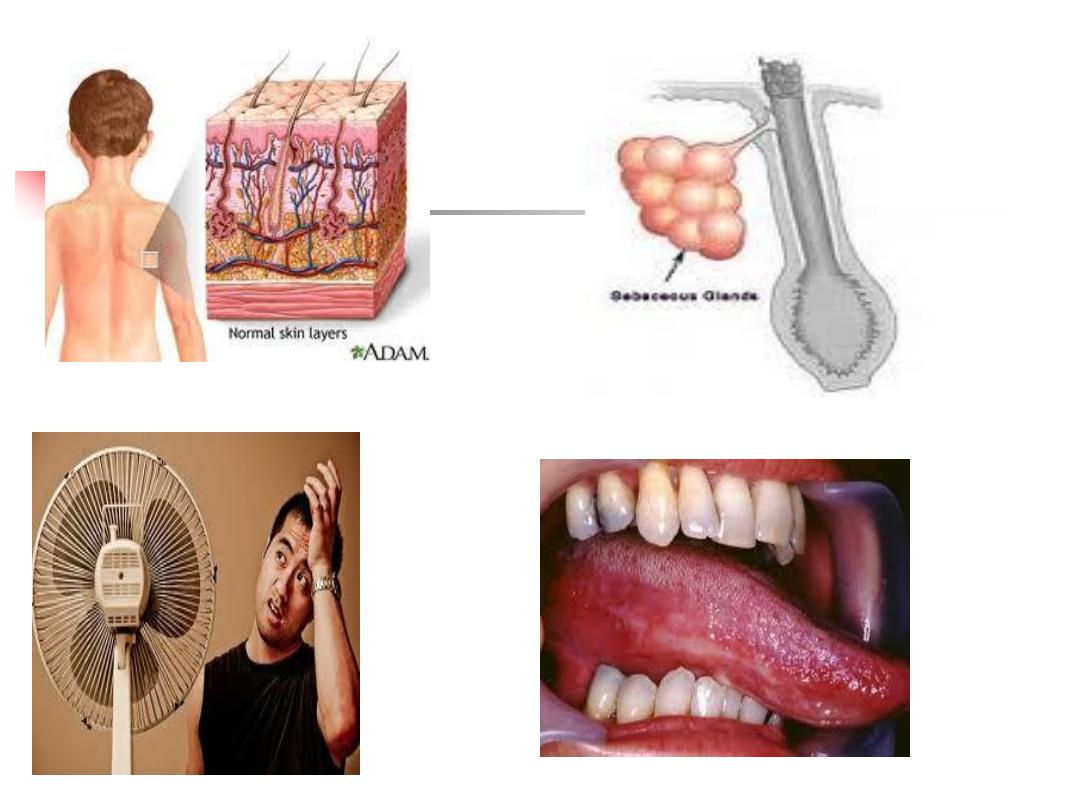
1. Anatomical barriers:
Skin
Physiological factors: as sebaceous glands
Sweat
Mucous membranes
6
7
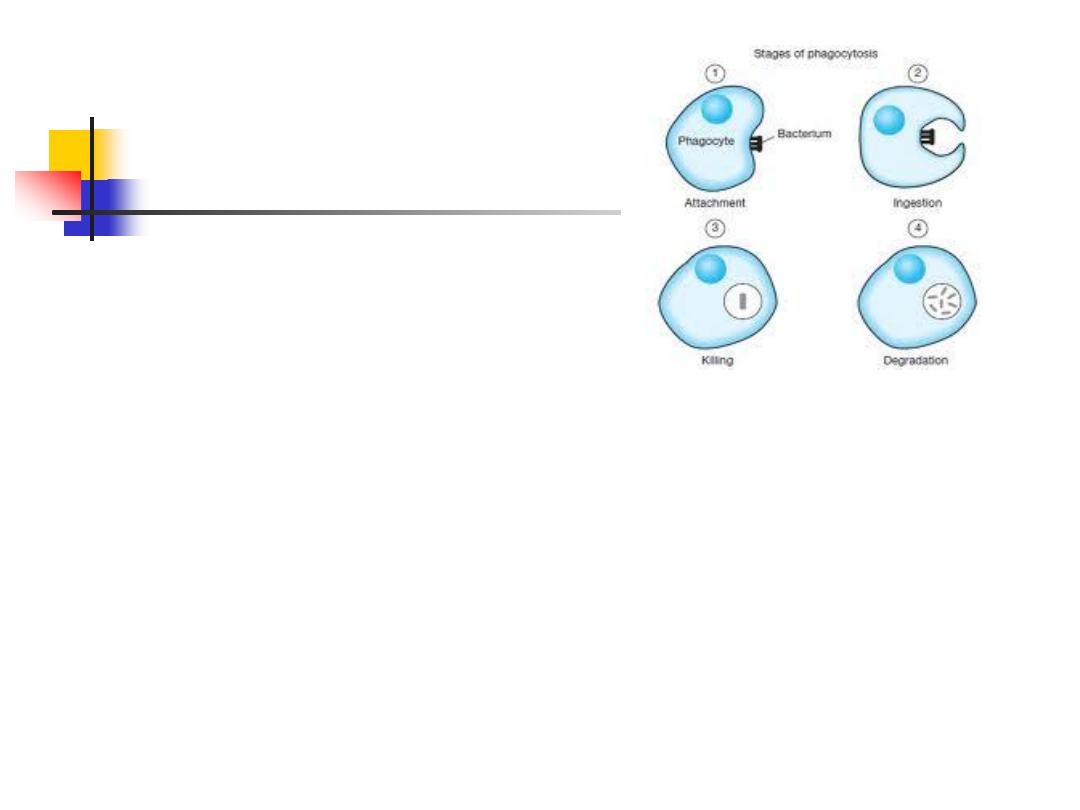
2. Phagocytes:
Specialized cells
Ingest and kill microorganisms,
Produce inflammatory molecules
Crucial for defense against bacterial and fungal
infections
8
Include:
a)
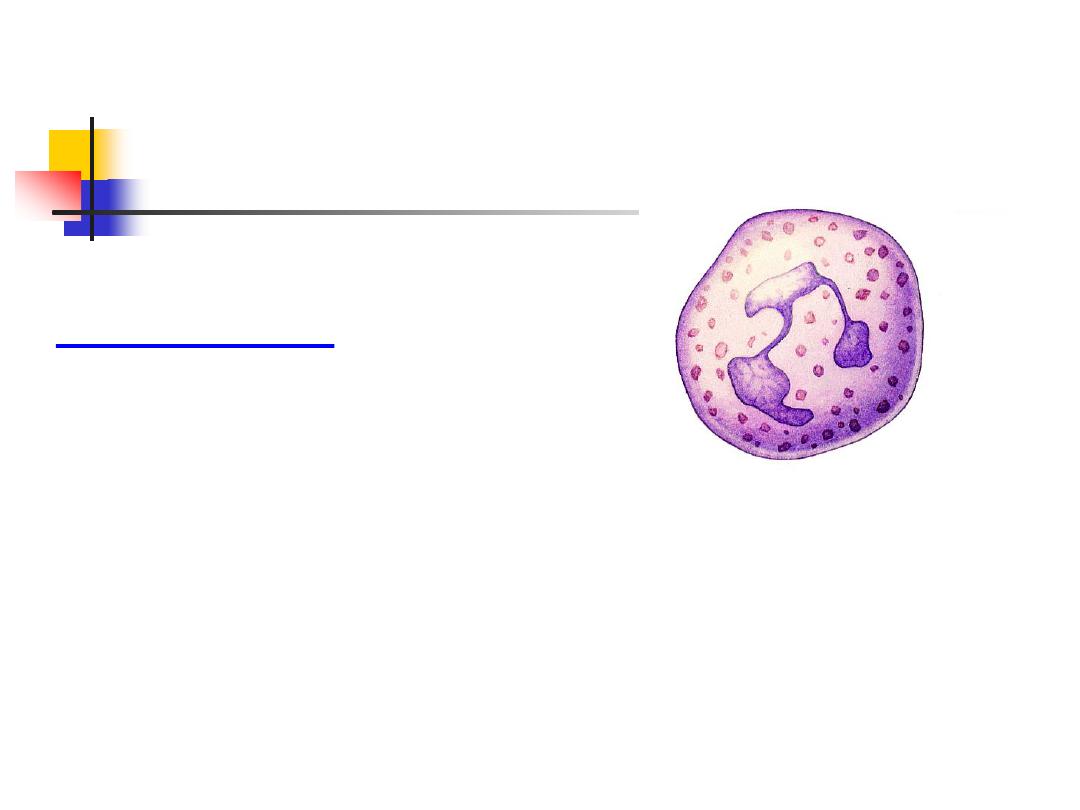
Neutrophils:
Functions:
kill microorganisms directly
facilitate the rapid transit of cells through tissues
non-specifically amplify the immune response
9
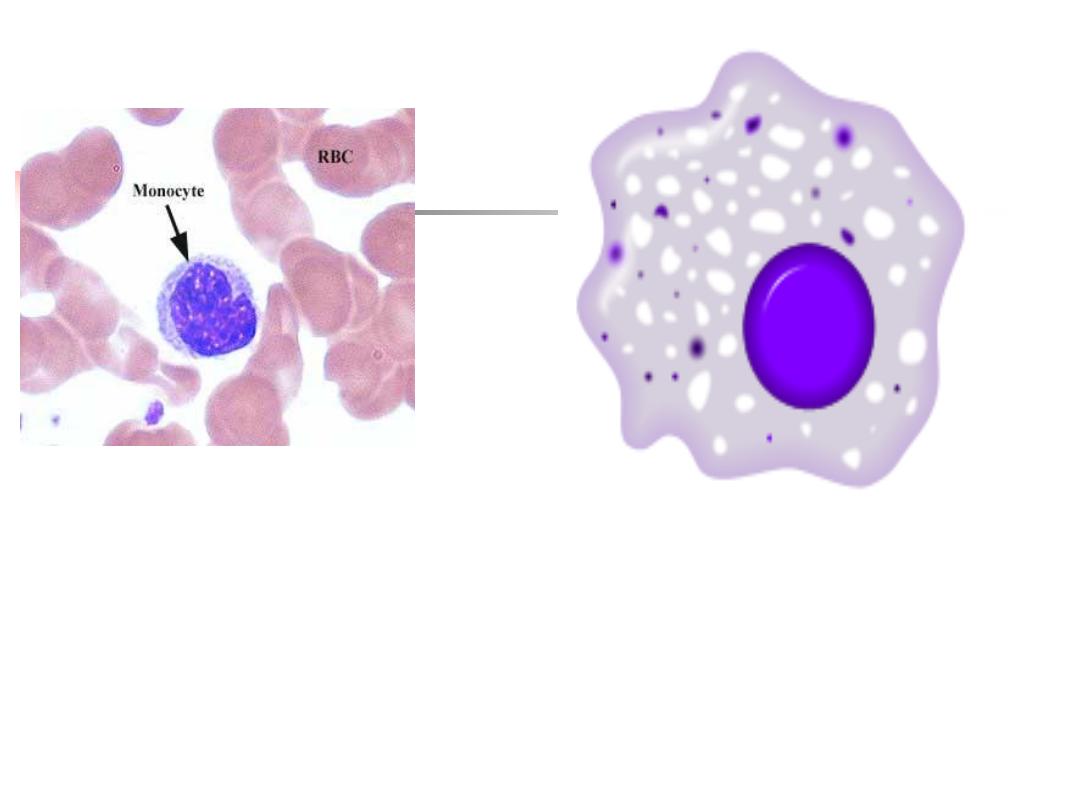
b) Monocytes and macrophages
Monocytes are the precursors of tissue
macrophages
bone marrow circulation
peripheral tissues DDx tissue macrophages
10
11

Functions:
Initiation and amplification of the
inflammatory response
Killing microorganisms
Repairing inflammation
Linking between innate and adaptive
immune system
12
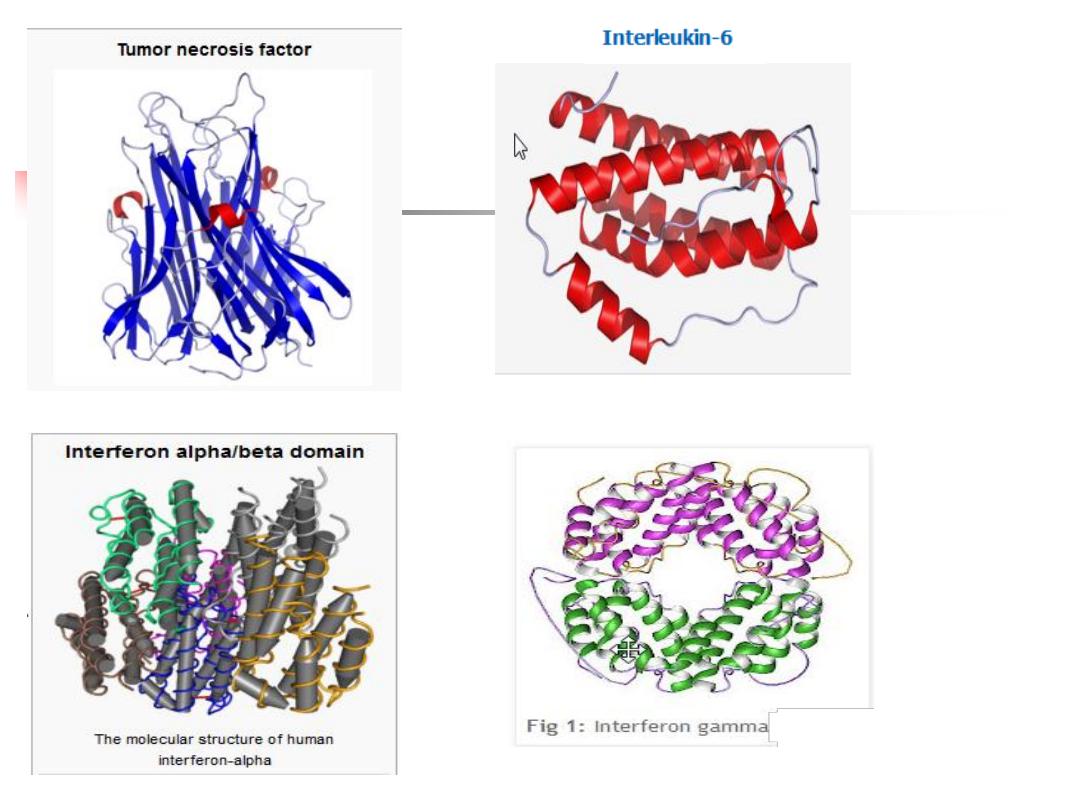
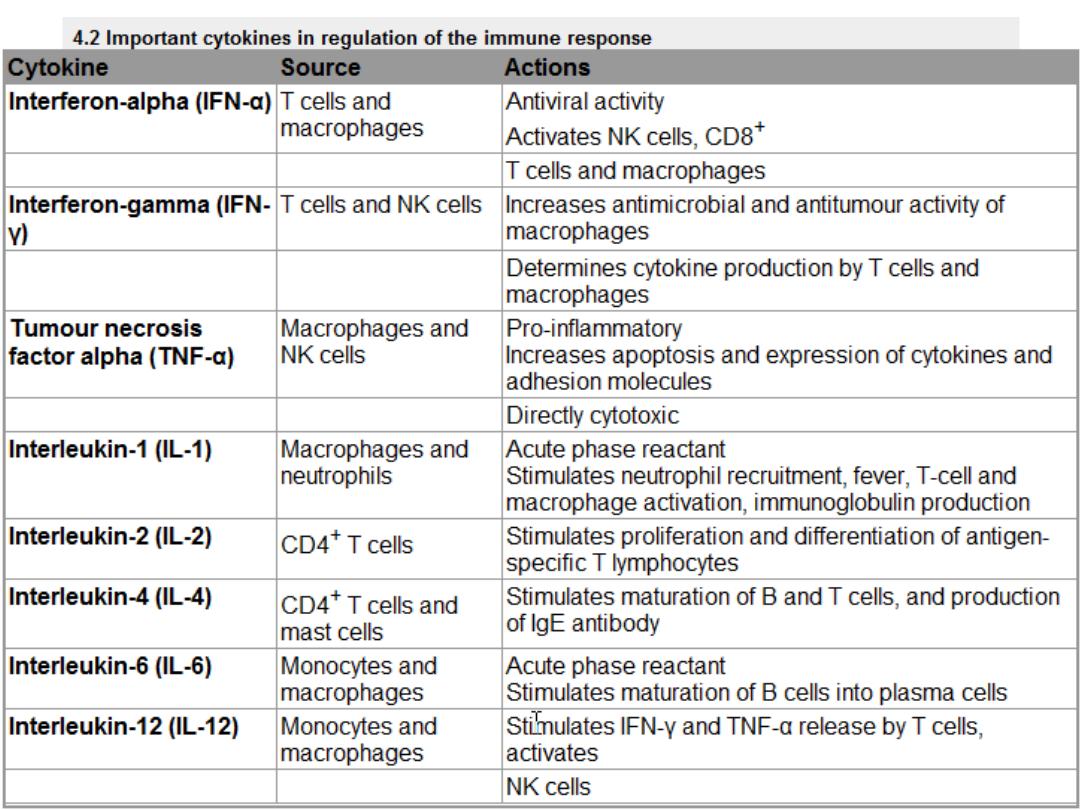
3. Cytokines:
Small soluble proteins
Act as multipurpose chemical messengers
Produced by cells involved in innate and adaptive
immune responses and by stromal tissue
13
14
15
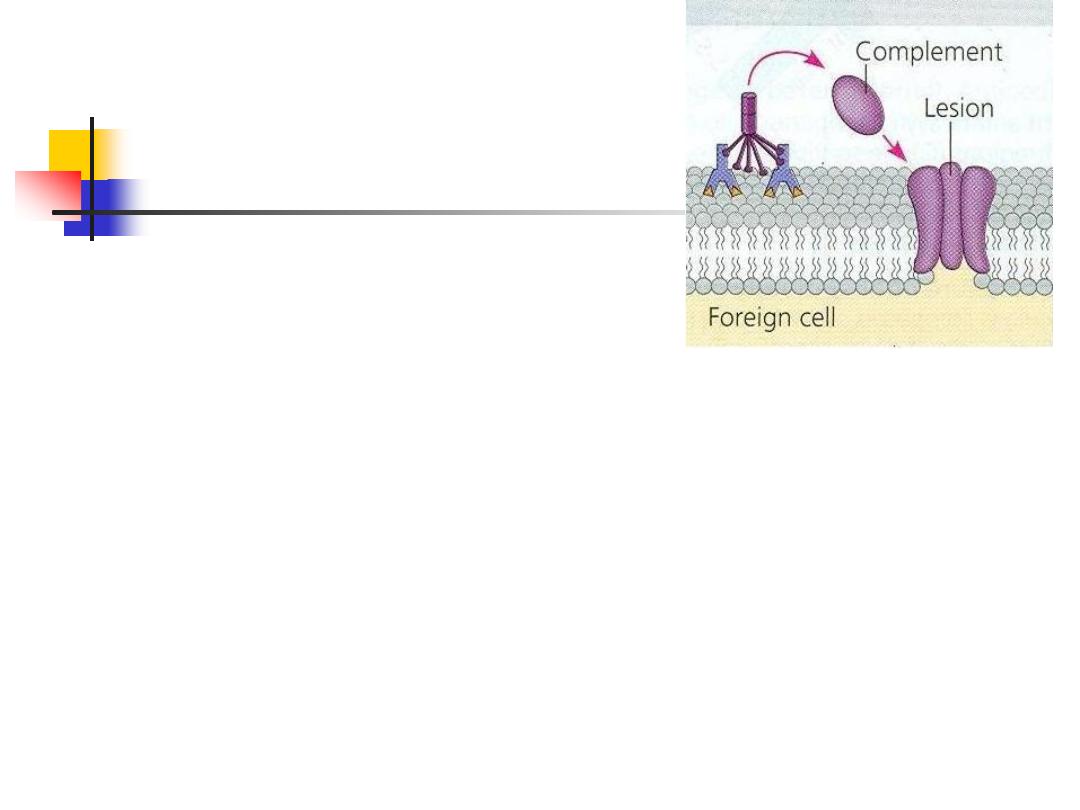
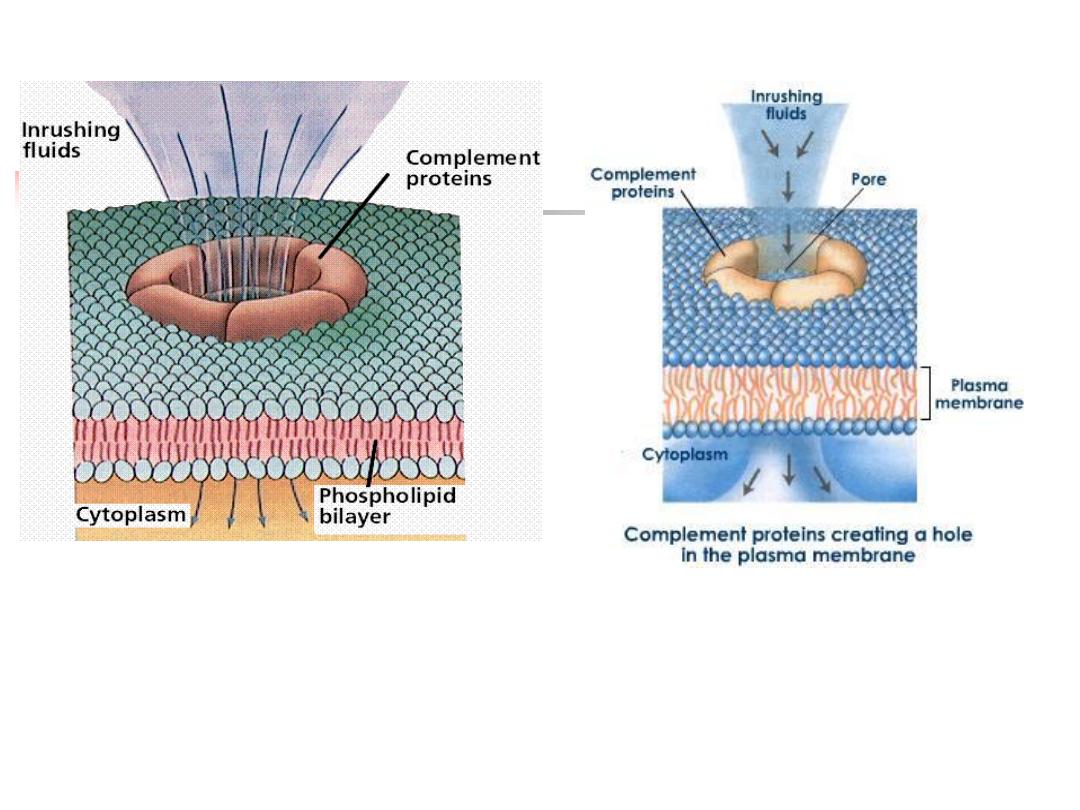
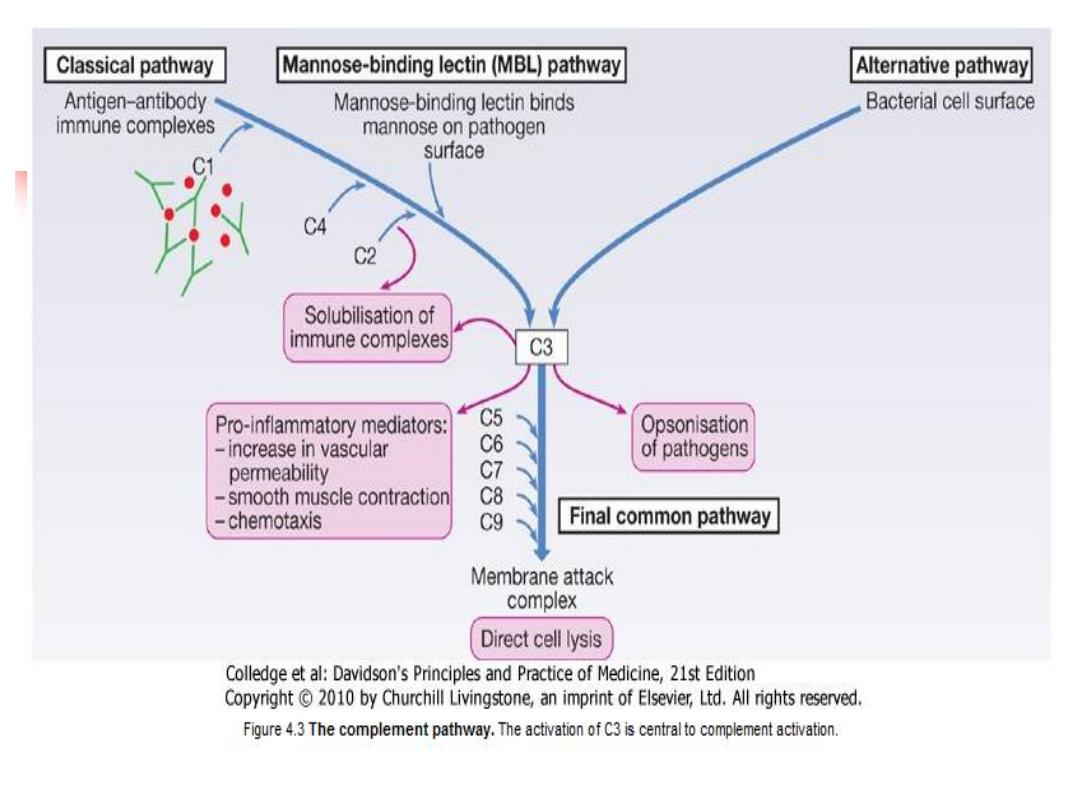
4.Complement
A group of more than 20 tightly
regulated, functionally linked proteins
Produced by the liver
16
17
18

Functions
:
1.
Defense against encapsulated bacteria such as
Neisseria
spp. and
Haemophilus influenza
2.
Act as opsonins, rendering microorganisms more
susceptible to phagocytosis by macrophages and
neutrophils
3.
Chemotactic agents: promoting leucocyte trafficking to sites
of inflammation
4.
Some fragments act as anaphylotoxins
5.
link between the innate and the acquired immune systems
6.
Dissolve the immune complexes
19

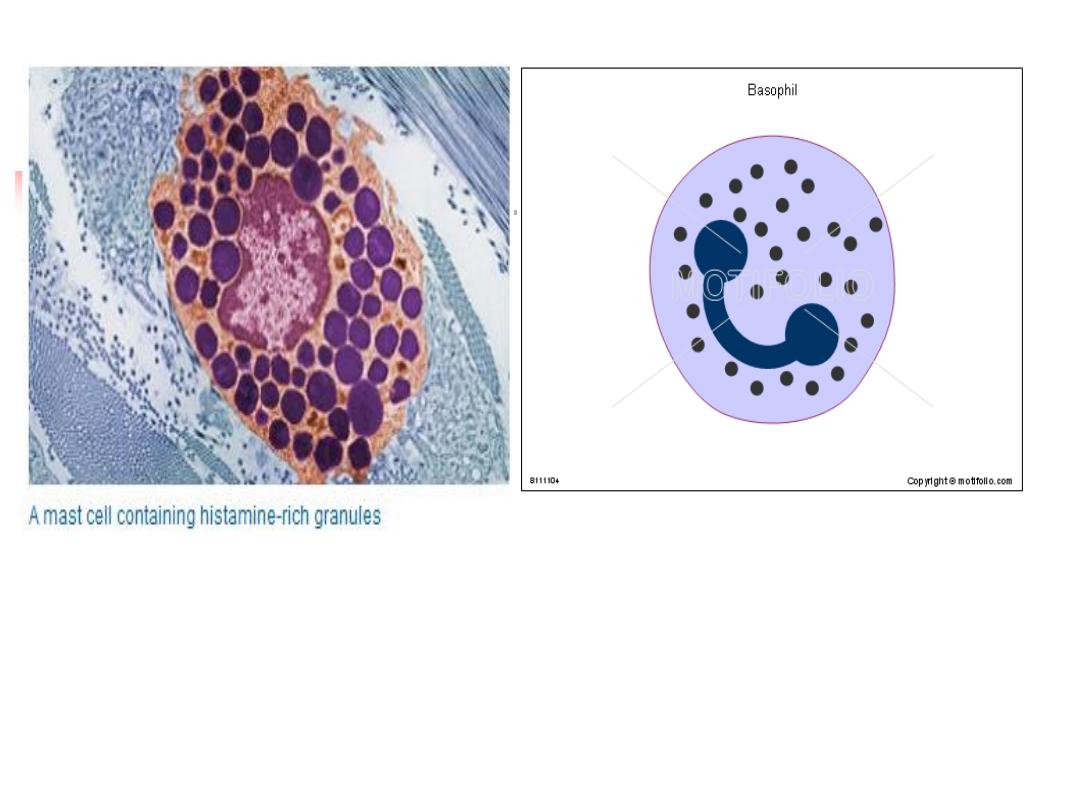
5. Mast cells and Basophils:
Are bone marrow-derived cells
Play a central role in
allergic
disorders
Mast cells
reside predominantly
in tissues
exposed to
the external environment, such as the skin and gut
Basophiles
are located in the
circulation
and are
recruited into tissues in response to inflammation
20
21
Both contain large cytoplasmic granules : histamine,
leukotrienes, prostaglandins and cytokines

22
Allergy : Activation of mast cells and basophils
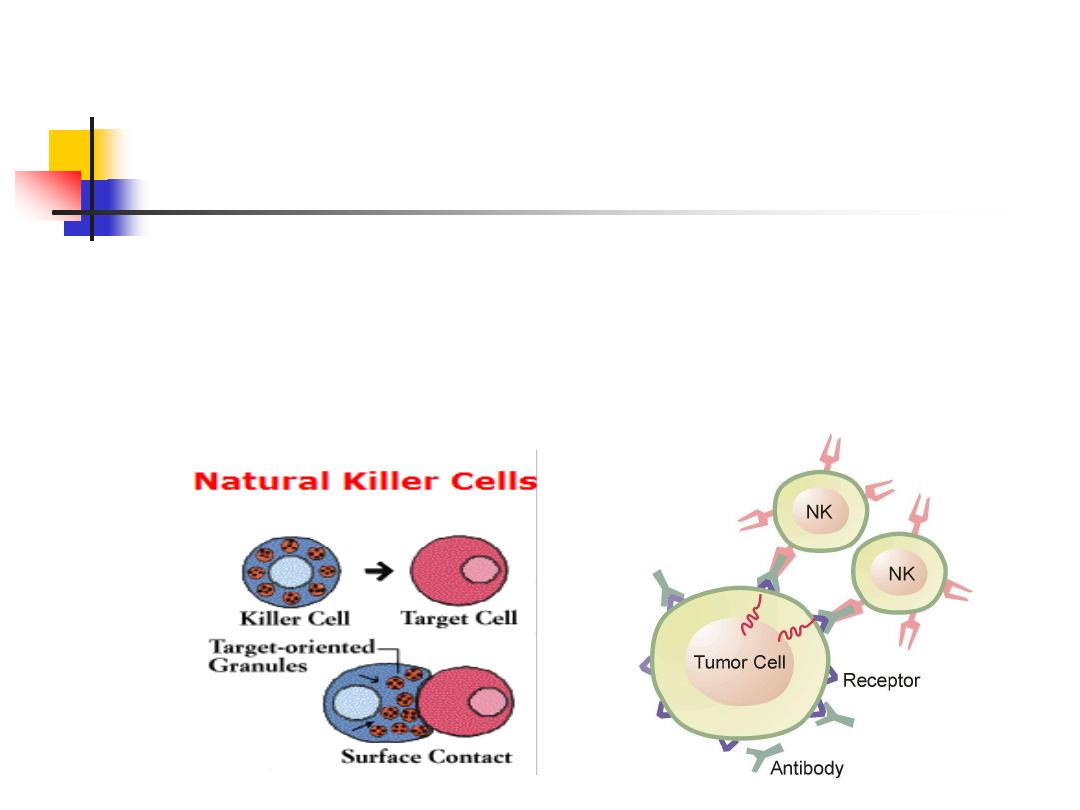
6. Natural killer cells:
Large granular lymphocytes
Play a major role in defense
against tumors and virally
infected cells
23

Express features of both the adaptive and innate
immune systems
Express a variety of cell surface receptors
stress signals
absence of HLA molecules on the surface
binding of antigen-bound IgG antibody to
surface receptors
24

II. Adaptive immune system:
Has exquisite specificity
Takes more time to develop
Gives long-lasting protection.
Possesses immunological memory
Types:
1.
Humoral immunity
: produced by B lymphocytes.
2.
Cellular immunity:
mediated by T lymphocytes.
25
1. Humeral immunity
B-lymphocyte:
Specialized cells
Arise from haemopoietic bone marrow stem cells
Major function is to produce
antibody
26
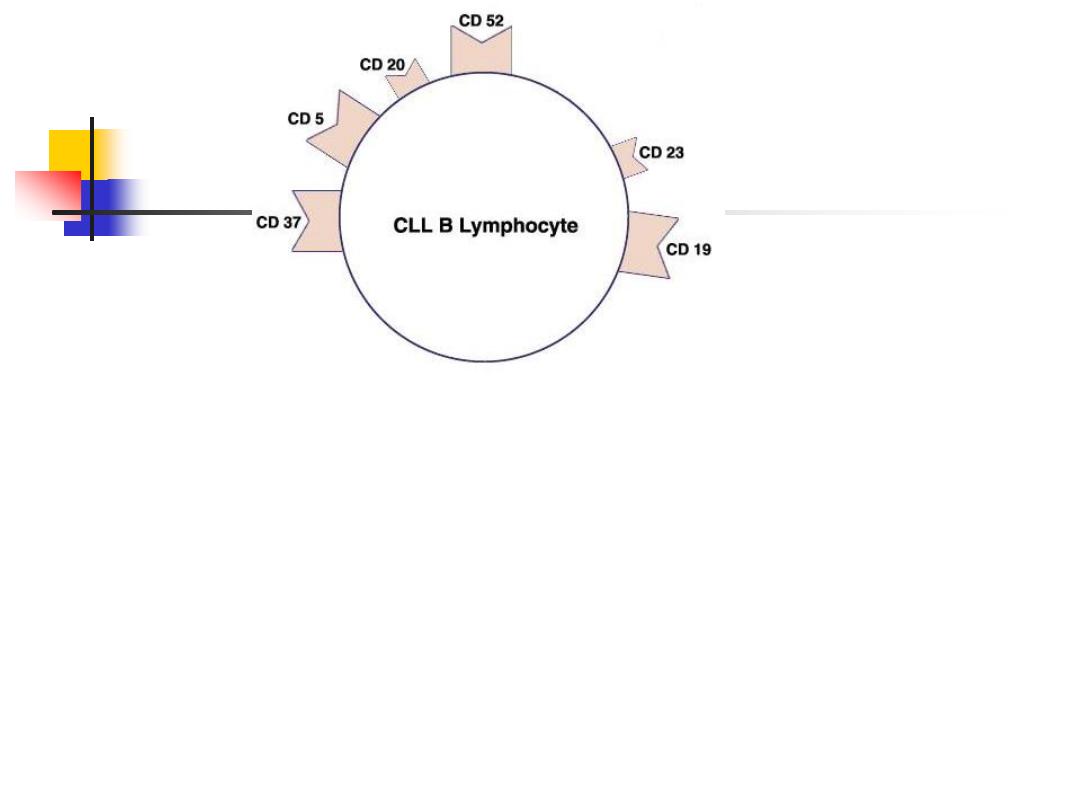
Express a unique
immunoglobulin receptor
on their
cell surface (
the B-cell receptor
).
Mature B lymphocytes can be found in the bone
marrow, lymphoid tissue, spleen, and to a lesser
extent the blood stream.
27
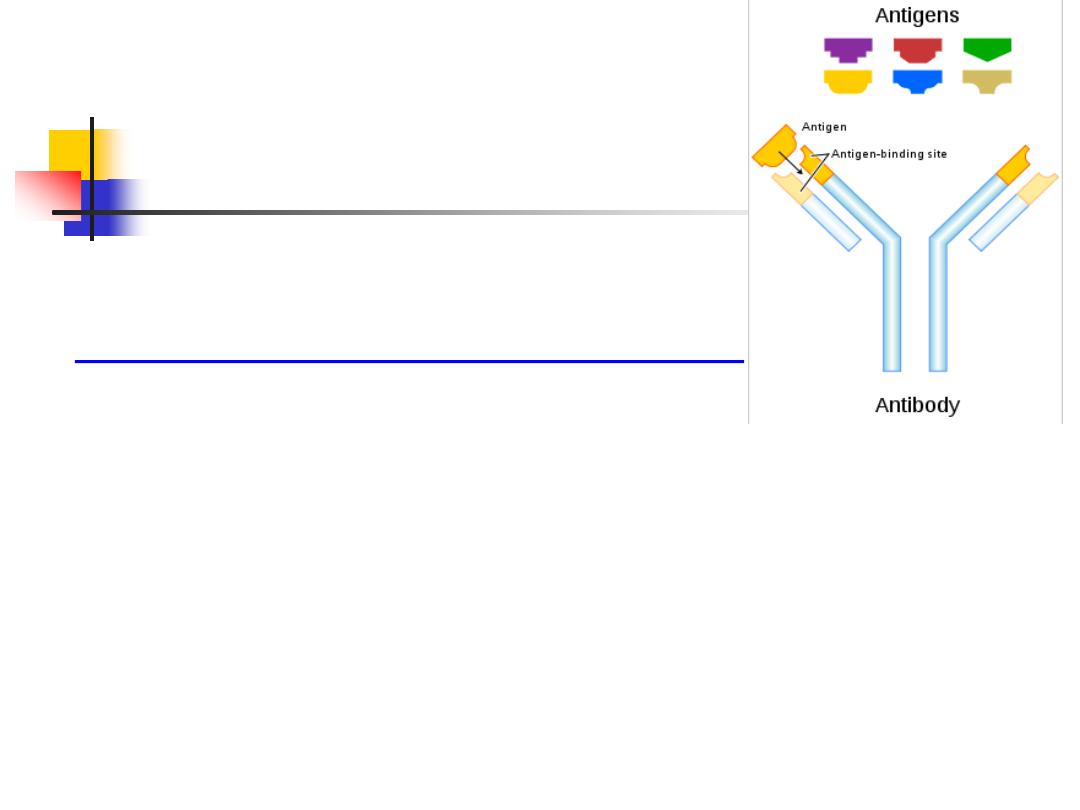
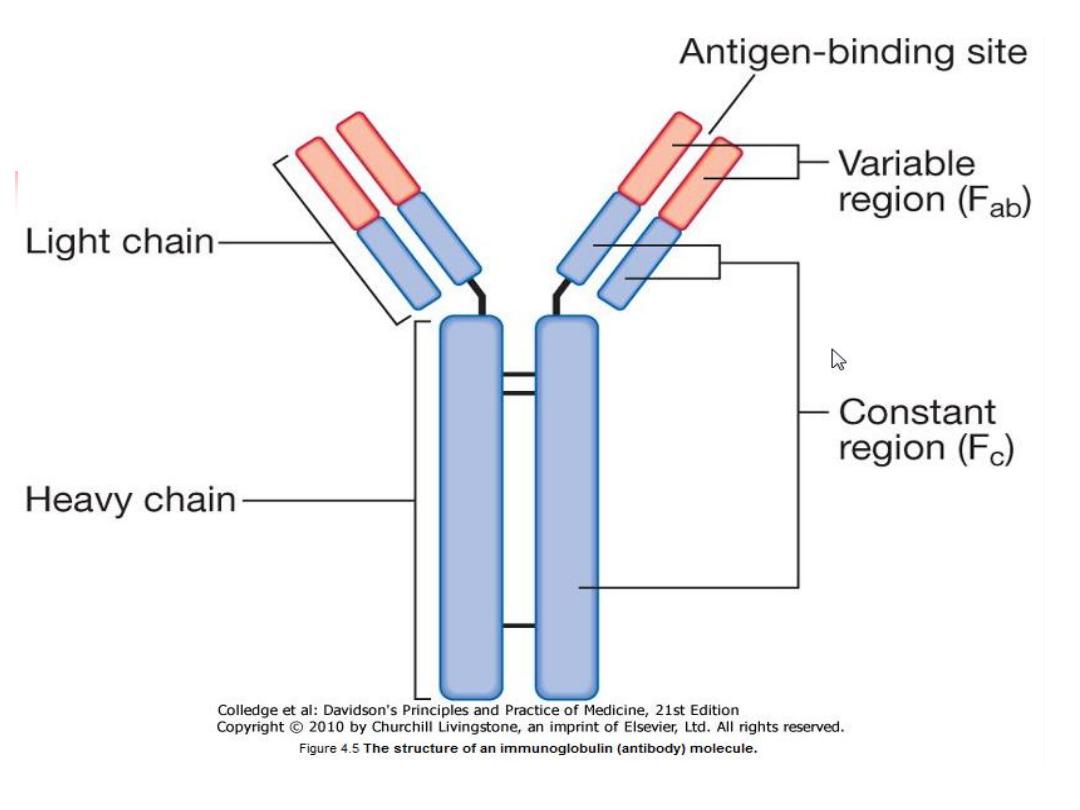
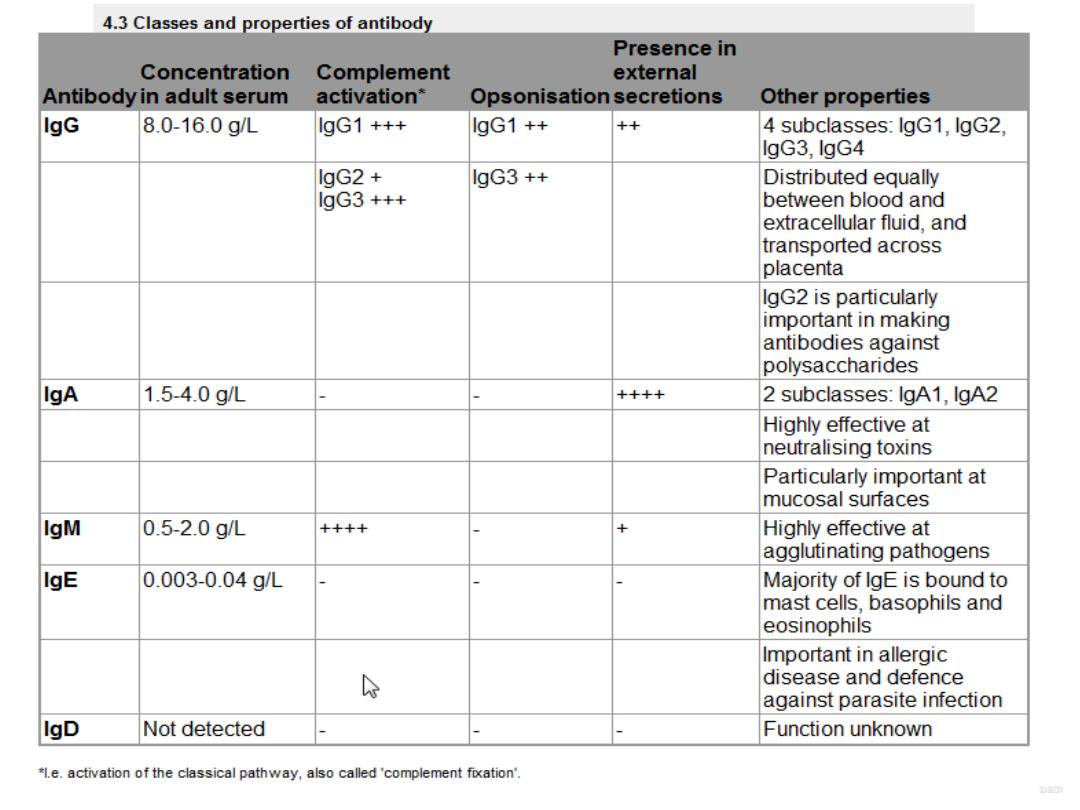
Immunoglobulins ( Antibodies):
Soluble proteins made of two heavy and two light
chains
The heavy chain determines the antibody class or
isotype, i.e. IgG, IgA, IgM, IgE, IgD
Subclasses of IgG ( IgG1,2,3,4) and IgA(IgA1,2).
28
29

Antibody Function:
1.
Facilitate
phagocytosis
[by acting as opsonins]
2.
Facilitates
cell killing
[by cytotoxic cells,
particularly natural killer cells]
3.
Trigger activation
of the
classical complement
pathway
4.
May act directly to
neutralize
the biological
activity of their
antigen
target
.
30
31
2. Cellular immunity:
T lymphocytes mediate cellular immunity
Function:
1.
Defense
against viruses, fungi and intracellular
bacteria.
2.
Immunoregulatory
role
32

T lymphocytes can be classified into 2 subgroups on the
basis of
function
, recognition of
HLA molecules
, and
expression of
cell surface proteins
.
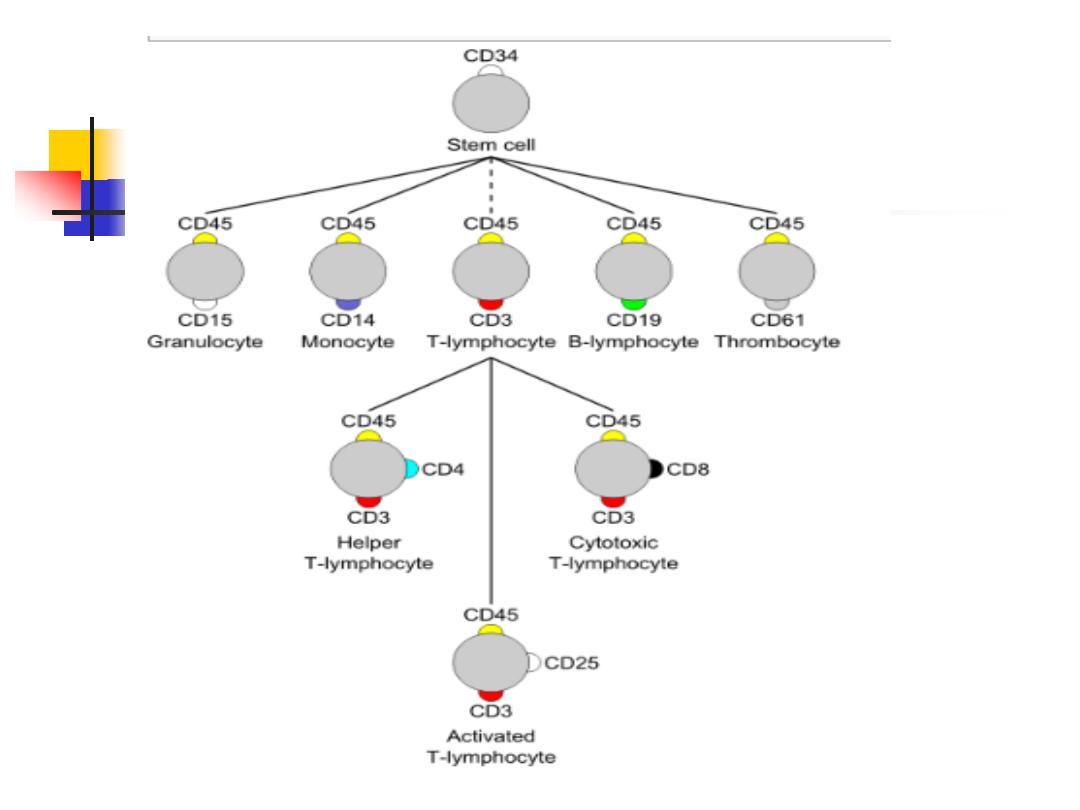
Leucocyte cell surface molecules
are named systematically
by assigning them
antigen number
[
a 'cluster of
differentiation' (CD)
] .
The CD system is commonly used as cell markers in
immunophenotyping.
33
34
T lymphocyte types:
1) CD8
+
('cytotoxic') T lymphocytes
Recognize antigenic peptides
in association with
HLA class
I
(HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-C)
Kill
infected cells
directly by producing
pore-forming
molecules such as perforin, or by triggering
apoptosis
of
the target cell
Secrete cytokines
such as IFN-γ which have antiviral
activity
35

2)CD4
+
('helper') T lymphocytes:
Recognize peptides
presented on
HLA class II
molecules (HLA-DR, HLA-DP and HLA-DQ)
Have
Immunoregulatory
functions
Produce cytokines
and provide
co-stimulatory
signals
that support the activation of CD8
+
T
lymphocytes and assist the production of mature
antibody by B cells
Interact closely with phagocytes
which
determine cytokine production by both cell types
36
37
CD4
+
lymphocytes
Th1 cells
p→IL-2, IFN-γ and
TNF-α
DHSR
Th2 cells
S→IL-4, IL-5 and IL-10
↑allergic responses
Regulatory cells
R→other CD4
+
cell
Prevent→autoimmune
diseases

Summary:
IS: a protective system
Types: Innate & acquired
Each type has components & specific
functions
38
