Vitamin A (retinol)
Metabolites: are retinaldehyde and retinoic acidFunction
retinaldehyde is important of visionretinoic acid for the cell growth and differentiation
retinoid synthetic molecule
Vitamin A (retinol)
plays a role iniron utilization
humeral immunity
T cell–mediated immunity
natural killer cell activity phagocytosis
Vitamin A (retinol)
MetabolismThe liver contains 90% of the vitamin A is bound
to retinol-binding protein transthyretin
trimolecular complex specific cell-
surface receptors bound to a series of
cellular retinol-binding proteins, function as
transporting agents as well as co- ligands for
certain nuclear receptors that act as transcription factors.( retinoid-mediated gene transcription) receptors for cell proliferation and differentiation
Vitamin A (retinol)
Dietary source
animal source: liver and fish (excellent source)plant source : dark-green vegetable and fruits
Vitamin A (retinol)
Deficiencychronic dietary deficit (developing countries)
Southern Asia, Sub-Saharan Africa, some areas of Latin America
More than 125 million preschool-age children with vitamin A deficiency, ~4 million have an ocular manifestation of deficiency .
A quarter of a million children each year developed blindness.
Vitamin A (retinol)
2. Malabsorption: celiac disease, short bowel syn.3. Zinc deficiency: interfere with vitA mobilization from the liver
4. Alcohol : interfere with conversion of retinol to retinaldehyde in the retina (dehydrogenase)5. Drugs : interfere with the absorption of vitA
neomycin, cholestyramine
Vitamin A (retinol)
Clinical features
night blindness (loss of dark adaptation)
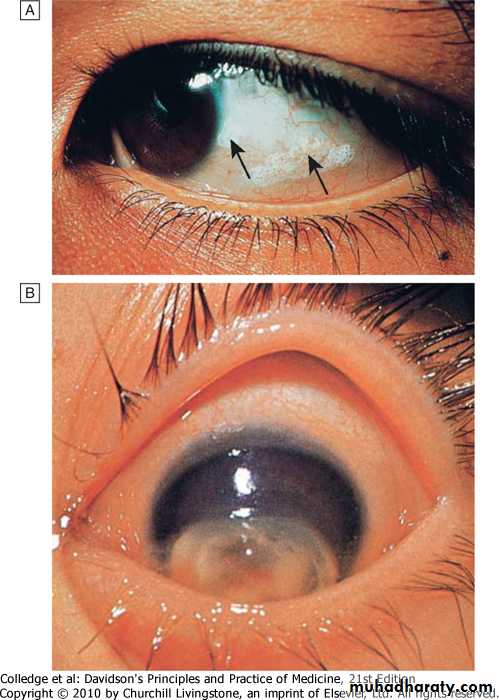
conjunctival xerosis (dryness) (xerophalmia)
Bitot's spots (white patches of keratinized epithelium on the sclera)
Keratomalacia (softening of the cornea) leads corneal ulceration and necrosis result in corneal scarring
increased risk of infection dysentery respiratory disease.
Downloaded from: StudentConsult (on 29 October 2011 12:19 AM)
© 2005 ElsevierVitamin A (retinol)
DiagnosisSerum retinol level
Test of dark adaptation
Impression cytology of the conjunctiva
Store assessment by liver BX
Vitamin A (retinol)
Treatment
30mg IM or 60mg orally
Vitamin A supplementation can markedly reduce risk of child mortality where deficiency is widely prevalent.
NB. Used in patient with M3 leukemia and cystic acne
Vitamin D
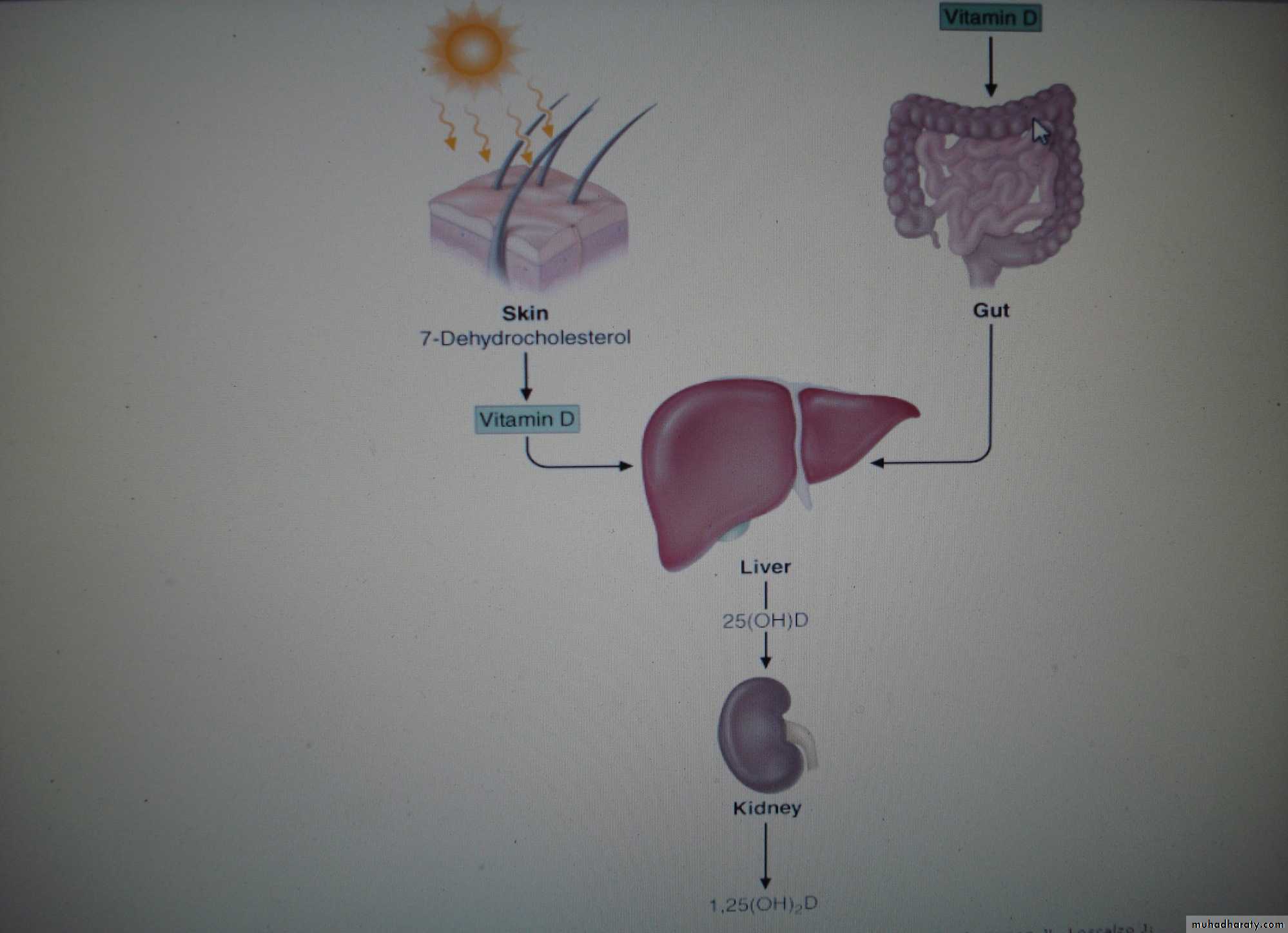
Synthesis and Metabolismsteroid hormone involved in mineral ion homeostasis
can be synthesized In response to ultraviolet radiation of the skin (a photochemical cleavage from 7-dehydrocholesterol).
source
animal sources(vitD3): dairy products, fish oils egg yolks
plant sources (vitamin D2): cereals
Vitamin D
Causes of the deficiencyVitamin D deficiency
Impaired cutaneous production
decrease dietary
Malabsorption
Accelerated loss of vitamin D
Increased metabolism (barbiturates, phenytoin, rifampin)
Impaired enterohepatic circulation
Vitamin D
Clinical features1. Asymptomatic (Mild to moderate deficiency)
2. Osteomalacia (defective bone mineralization)
Muscle and bone pain
Malaise
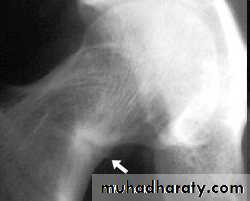
Fragility fracture( pseudofractures)
Proximal myopathy ( wadling gait)
Bone tenderness
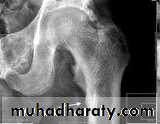
3. Rickets ( growth retardation, bone deformities)
Looser zone
Looser zone
Vitamin D
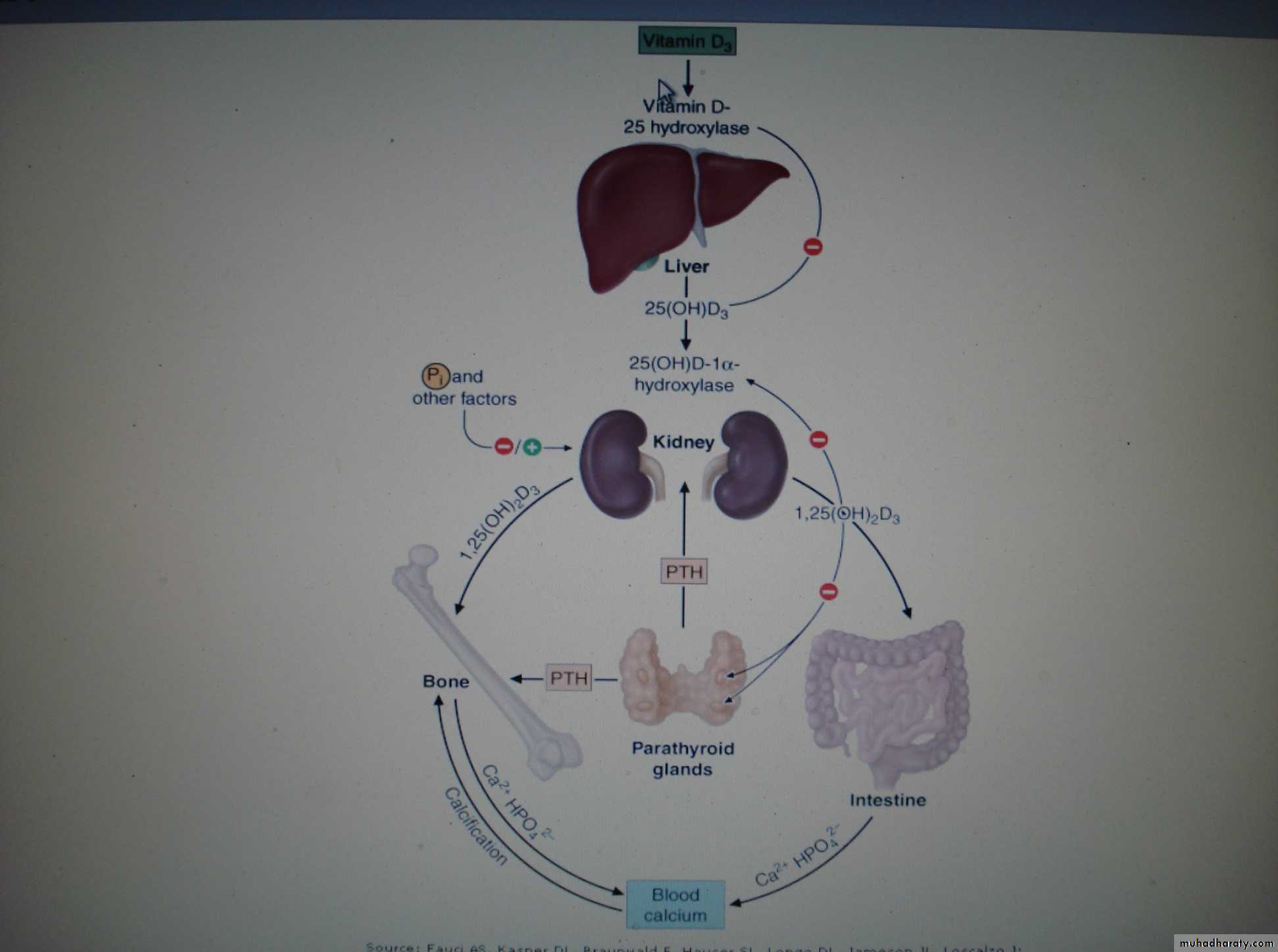
DiagnosisBiochemical tests
decrease serum 25(OH)D
low or normal s. Ca. , ph.
increasing PTH levels
increase alkaline phosphatase
2. Radiological tests of oteomalacia
decrease in cortical thickness
osteopenia of the skeleton
pseudofractures, or Looser's zones in the ribs and pelvis and long bones and vertebra
3. Bone biopsy
Vitamin D
Treatment
VitD 50,000 IU weekly for 3–12 Weeks followed by maintenance therapy (800 IU daily).
Calcium supplementation include 1.5–2.0 g /d
800 IU of vitamin D, with calcium supplementation, decreases the risk of hip fractures in elderly women.
Vitamin E ( tocopherols)
Functionacts as antioxidant and radical scavenger which protects low-density lipoprotein and polyunsaturated fats in membranes from oxidation.
Absorption and Metabolism
After absorption, vitamin E is taken up from chylomicrons by the liver, and a hepatic tocopherol transport protein mediates intracellular vitamin E transport and incorporation into very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL).
Vitamin E ( tocopherol)
Dietary sourcewidely distributed in the food supply
High: sunflower, soybean and corn oils
meats, nuts, and cereal grains
small amounts : fruits and vegetables.
Vitamin E ( tocopherol)
Causes of the deficiency:1. Dietary deficiency ( does not exist).
2. prolonged malabsorptive diseases.
3. prolonged cholestasis
4. abetalipoproteinemia cannot absorb or transport vitamin E.
5. A familial form of isolated vitamin E deficiency (defect in the tocopherol transport protein).
Vitamin E ( tocopherols)
Clinical features
axonal degeneration of the large myelinated axons and results in posterior column
Peripheral neuropathy
Sensory ataxic gaitOphthalmoplegia
skeletal myopathy
pigmented retinopathy
Vitamin E ( tocopherols)
Diagnosislow blood levels of tocopherol
Treatment
800–1200 mg of tocopherol per day.
Vitamin k
Functionvitamin K1, phylloquinone, from vegetable and animal sources
vitamin K2, menaquinone, synthesized by bacterial flora and found in hepatic tissue
Vitamin K3, menadion, synthetic
required for the carboxylation of glutamic acid, which is necessary for calcium binding to -carboxylated proteins such as prothrombin (factor II); factors VII, IX, and X; protein C; protein S).
Vitamin k
Dietary Sources
green leafy vegetables (spinach)
liver
vegetable oils : olive, soybean oils.
Vitamin k
Causes of the deficiency1. small-intestinal disease (e.g., celiac disease)
2. cholestatic liver disease.
3. Broad-spectrum antibiotic treatment.
3. drug therapy, the antiobesity drug orlistat
Vitamin k
The diagnosiselevated prothrombin time or reduced clotting factors
vitamin K may also be measured directly.
Treatment
Vitamin K deficiency is treated using a parenteral dose of 10 mg.
Thanks