
1
Histamine & Histamine Antagonist
Lec: 1
Dr. Mohammed Rashad
Histamine
Endogenous substance.
Autacoids.
Neurotransmitter.
Distribution: in exposed organs.
In all body tissues & fluids.
Synthesis:
Histidine
→ Histamine
Storage sites: secretory granules in mast cells with –ve Protoglycans as
heparin.
Release of histamine
1. Heat & Ca
++
dependent degranulation :
Ag , E ⟶ sensitization
Ag , G , M ⟶ degranulation
1. Heat & Ca
++
independent degranulation :
Morphine , d-Tubocum , Amine AB , Venom , trauma .
2
Inactivation of released histamine
Transport processes ⟶ dilution .
Enzymatic metabolism .
CH
3
transferase (tissues).
Histaminase ( O2 ) ⟶ T & Blood for hitamine and food .
Hitamine receptor subtype
Sites of hitamine receptor
H1 : Brain , heart , B.V , GIT , Bronchi .
H2 : Brain , heart , B.V , parietal cells .
H3 : CNS , PNS (presynaptic)
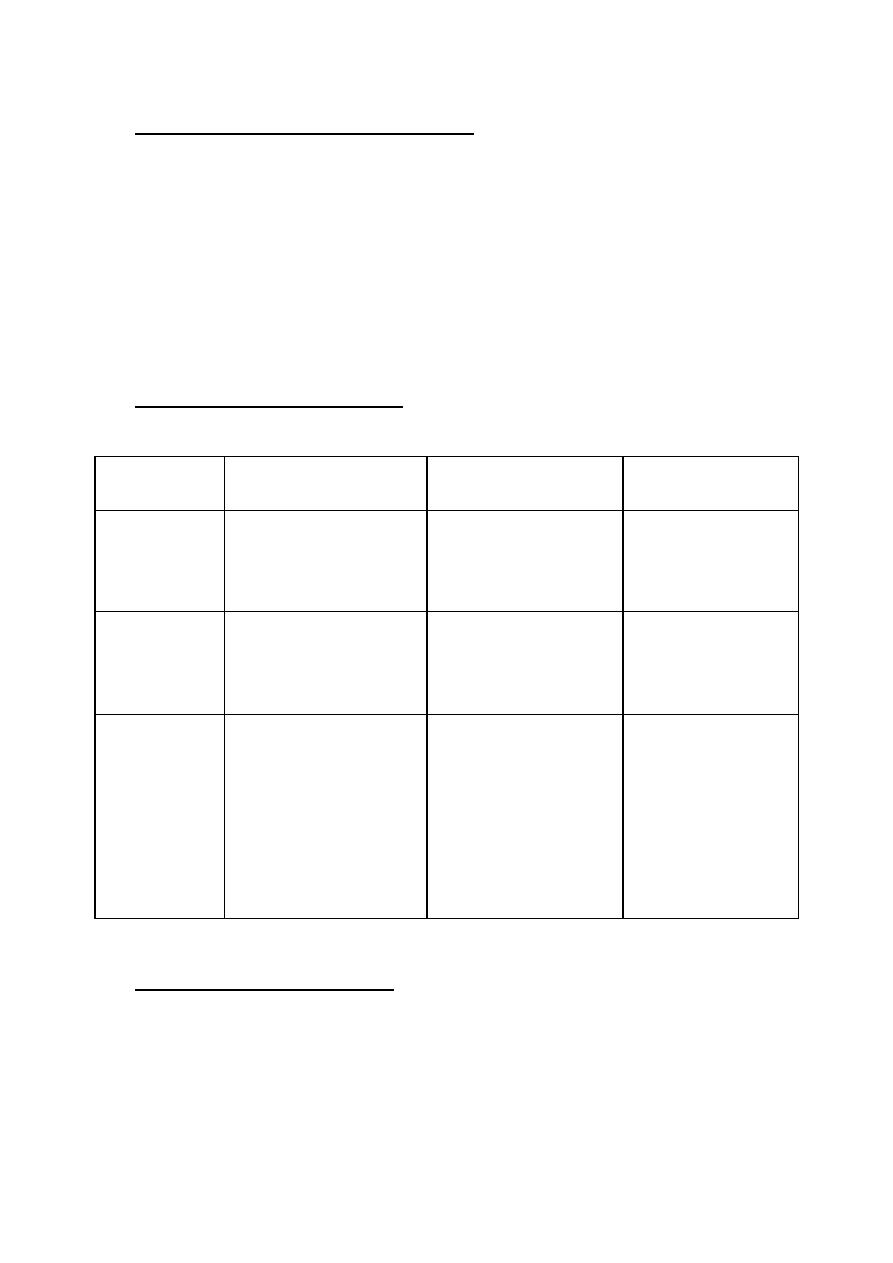
Receptor
Mechanism
Agonist
Antagonist
H1
⇧
IP3 , DAG
Histamine
Triprolidine
H2
⇧
cAMP
Impromidine
Ramitidine
H3
G-protein coupled
CH
2
histamine
Thioperamine
3
Autoinhibitory ++ ⟶ ⇩ Histamine
On vagal nerve ++ ⟶ ⇩ Acetylcholine
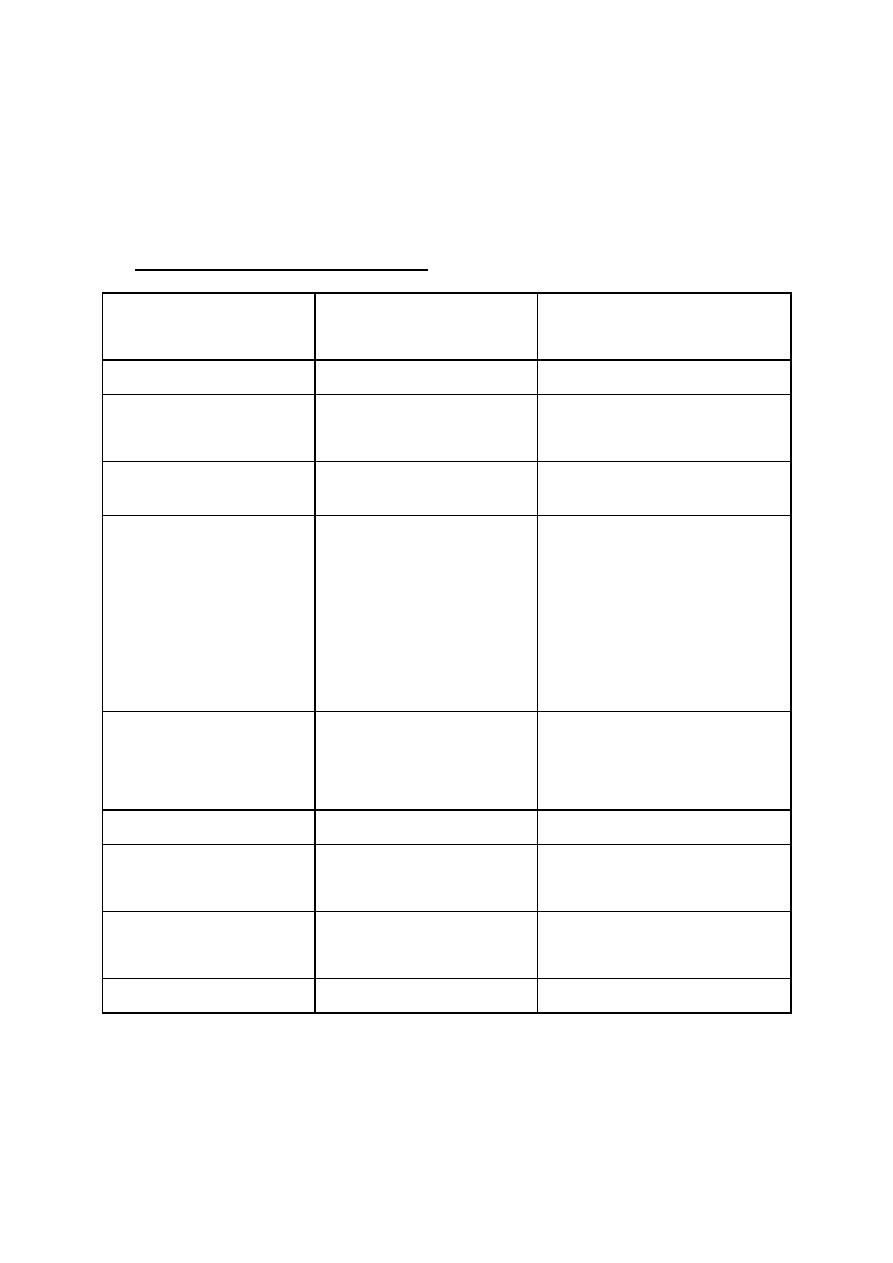
Receptors (types & response)
Organ
Types of receptor
Histamine mediated
response
Mast cell
H2
Feed back control
CNS
H1
H1 , H2
Sedation
Antiemetic
Sympathetic N.S
H2
--of sympathetic
transmission
Heart
H2
H2
H1
H1
H1 , H2
+ve chronotropic
+ve inotropic (ventricle)
+ve inotropic (atrium)
Prolong A-V conduction
⇧
Coronary blood flow
Arteries
Great
Small
H1
H1 , H2
Contraction
Relaxation
Stomach
H2
++ HCl
Ilium
H1 +++
H2 +
Contraction
Relaxation
Bronchi
H1 +++
H2 +
Bronchoconstriction
Uterus
H2
Relaxation

4
Pharmacological effects
++ H1 ⟶ cGMP ⇧
++ H2 ⟶ cAMP ⇧
1) Cardiovascular system :
⇩ BP .
+ve inotropic & chronotropic .
Flushing face .
Throbbing headache .
VD of arterioles , capillaries , venules .
Edematous swelling (⇧permeability)
2) Respiratory system :
Bronchoconstriction .
⇧Broncho_secretion .
Asthmatics are more sensitive to histamine
3) Glandular tissue :
⇧Release of catecholamines from adrenal gland .
⇧Secretion of gastric HCl & pepsin .
⇧Secretion of salivary gland .
4) Intradermal (test) effects
Lewis triple response line :
Flush (VD of capillary) localized red – blue .
Flare (VD of arterioles) diffuse redness .
Axon reflex (cut nerve) ⟶ abolish flare .

5
Wheal (VD of capillaries) swelling
⇧Permeability ⟶ edema .
The bone response is accompanied by transient pain and itching , this
skin test quantify allergic response .
5) Anaphylaxis :
Antigen in food or injectant ⟶ mast cell damage ⟶ release its content
and this lead to:
a) ⇩ BP b) Bronchoconstriction
c) Urticasia
d) Abdominal cramps .
Life threatening :
Adrenaline .
Antihistamine .
Corticosteroids .
Clinical uses
1. Testing gastric HCl secretion :Pentagastrin is currently used lead to
much lower adverse effect.
2. Diagnosis of pheochromocytoma : this test is now obstete .
3. Pulmonary function testing : histamine aerosol (protective test)
for bronchial hyperactivity .
Contraindications
1. Asthmatics .
2. Active ulcer disease .
6
3. GIT bleeding .
Adverse effects
Dose related (like histamine release) : Hypotension , tachycardia ,
headache , flushing , bronchoconstriction , GIT upset .
Also after ingestion of spoiled fish (scombroid fish poisoning) : due
to histamine produced by bacterial action on flesh of fish.
Histamine agonists
Histamine
Betazole (H2:H1 – 10:1)
Impromidine (H2:H1 – 10000:1)
α-CH3 histamine (H3 agonist)
Histamine Antagonists & Histamine Antagonism
1. Inhibition of histamine synthesis.
2. Prevention of histamine release from store site.
Mast cell stabilizer : Salbutamol , Epinephrine , Theophyllim ,
Coritcosteroids , Cromolyn Na
+
3. Blocking of histamine receptor :
H1 blockers ⟶1
st
generate
⟶ 2
nd
generate
H2 blockers …………

7
4. Reverse the effects of histamine (physiological antagonists)
epinephrine & histamine on bronchi .
Histamine release inhibitors
Cromolin , Nedocromil Na
+
Poorly absorbed.
Administered by inhalation.
- - histamine release & other autacoids from mast cell.
Used prophylactically in asthma : Nedocromil Na
+
more effective in
bronchospasm of exercise & colol
Adverse effects : at application site.
Dry mouth.
Sore throat .
Done By: Basheer Aladdin
