Lec1: General properties of viruses
Objectives :1-Describe the structure of viruses
2-Specify the functions of viral proteins & envelope
3-List the reaction of viruses to physical & chemical agents
4-Discuss the principles of classification of viruses .
Comparison between viruses and bacteria
• No.• Property
• Viruses
• Bacteria
• 1
• Size
• 20-300 nm
• 1000 nm
• 2
• Genome
• (type of nucleic acid)
• DNA or RNA but not both
• DNA and RNA
• 3
• Cell wall
• Envelope present in some viruses
• Cell wall
• 4
• Ribosomes
• No ribosomes
• Ribosomes
• 5
• Multiplication by binary fission
• _
•
• +
• 6
• Sensitivity to antibiotics
• _
•
• +
• 7
• Growth in culture media
• Grow only in living host cell
• Grow in culture media
What are viruses?
They are small size (20-300 nm in diameter) retaining infectivity after passage through filters able to hold back bacteria.
They are totally dependent upon a living cell, either eukaryotic or prokaryotic, for replication and existence. Viruses are obligate intracellular parasites.
They possess only one species of nucleic acid, either DNA or RNA.
They have a component - a receptor binding protein for attaching to cells.
The structure of viruses:
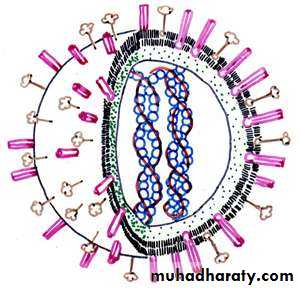
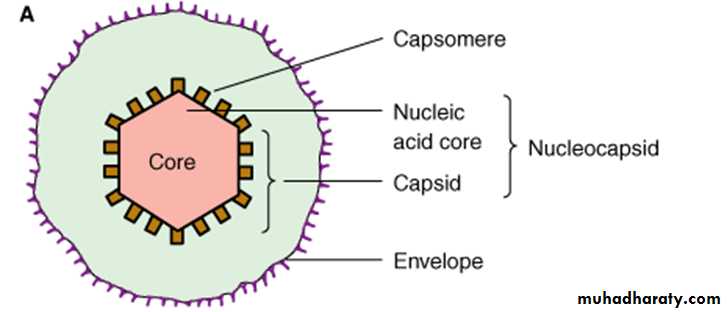
1- Viral nucleic acid:The viral nucleic acid is located internally and can be either single- or double- stranded RNA or DNA. The nucleic acid can be either linear or circular. The DNA is always a single molecule, the RNA can exist either as a single molecule or in several pieces (segmented).
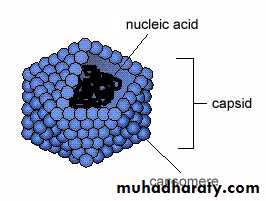
2- Capsid:
The protein shell, or coat, that encloses the nucleic acid genome and mediates the attachment of the virus to specific receptors on the host cell surface.
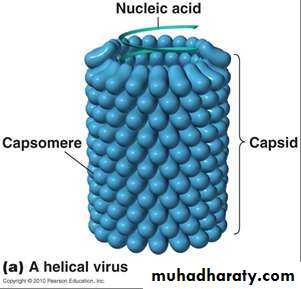
3-Capsomeres:
Morphologic units seen in electron microscopy. Each capsomere, consisting of one or several proteins.• Naked viruses are composed of nucleic acid + capsid (nucleocapsid)
4- Viral envelope :
The envelope is a lipoprotein membrane composed of lipid derived from the host cell membrane and protein that is virus- specific.• Enveloped viruses NA + capsid + envelope
• The complete virus particle is called virion
Matrix protein : mediate the interaction between the capsid proteins & the envelope proteins .
Viruses also have internal proteins,some of which are DNA or RNA polymerases.
Types of symmetry of virus particles:
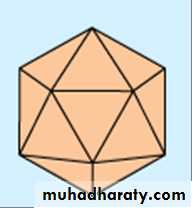
1- Icosahedral symmetryComposed of 12 vertices, has 20 faces (each an equilateral triangle) with the approximate outline of a sphere. e.g. Herpesviruses , Adenoviruses
2-Helical symmetry
In which capsomeres are arranged in a hollow coil that appears rod-shaped. The helix can be either rigid or flexible. e.g. Influenza viruses3- Complex structures
• e.g. Poxviruses
Reaction to physical and chemical agents:• Heat and cold
Viral infectivity is generally destroyed by heating at 50-60 C0 for 30 mint., hours at 20 C0, days at 4 C0. Viruses can be preserved at -90 C0 or -196 C0 (liquid nitrogens).
• PH
Viruses can be preserved at physiological PH (7.3).
• Ether susceptibility :
Ether susceptibility can be used to distinguish viruses that possess an envelope from those that do not.
• Detergents:
Nonionic detergents solubilize lipid constituents of viral membranes. The viral proteins in the envelope are released. Anionic detergents also solubilize viral envelopes; in addition, they disrupt capsids into separated polypeptides.
Reaction to physical and chemical agents:
• SaltsMany viruses can be stabilized by salt in concentrations of 1 mol/L.
e.g. MgCl2, MgSO4, Na2SO4.
• Radiation
Ultraviolet, X-ray, and high-energy particles inactivate viruses.
• Formaldehyde
Destroys viral infectivity by reacting with nucleic acid.
• Antibiotics
Antibacterial antibiotics have no effect on viruses.
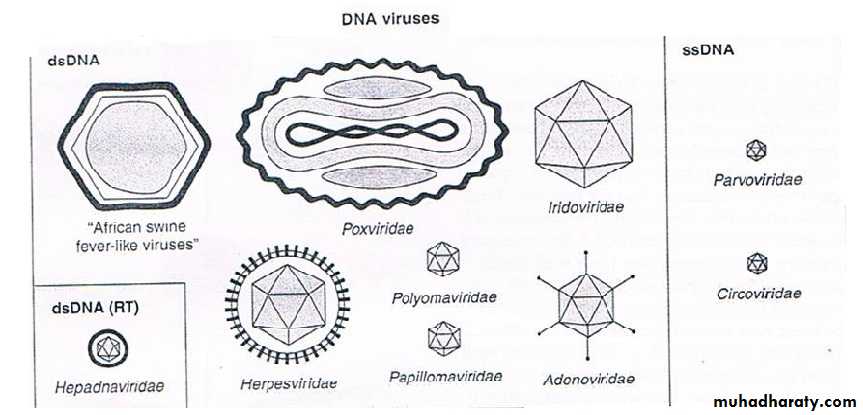
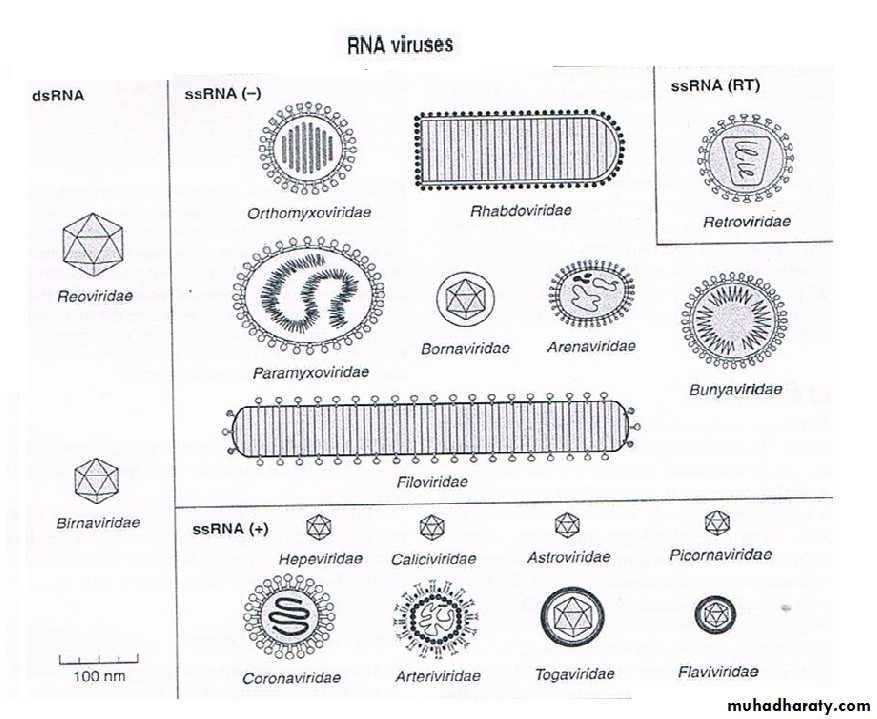
Classification of viruses
• Virion morphology
• Virus genome properties
• Physicochemical properties of the virion
• Virus protein properties
• Genome organization and replication
• Antigenic properties
• Biological properties
Universal system of virus taxonomy:
• Families – on the basis of virion morphology, genome structure and strategies of replication.Virus family names have the suffix – viridae.
• Genera – based on physicochemical or serological differences.
Genus names carry the suffix – virus.
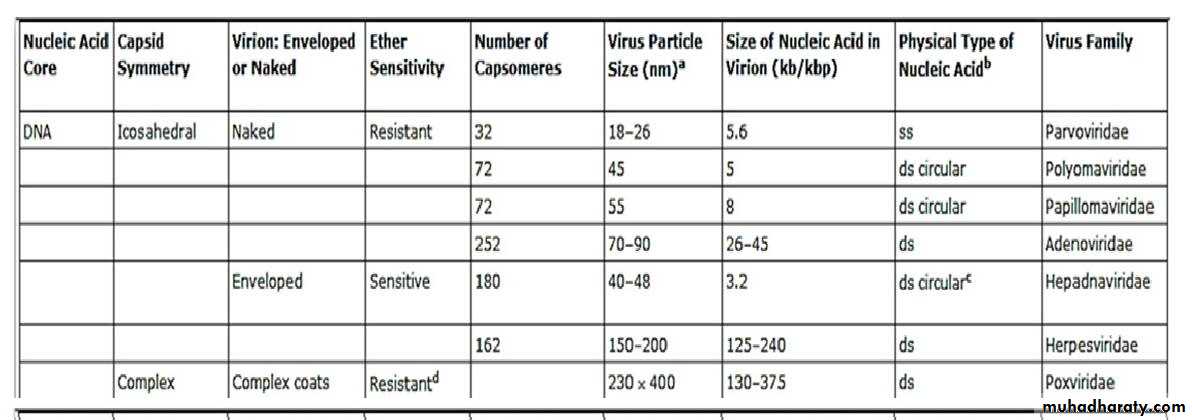
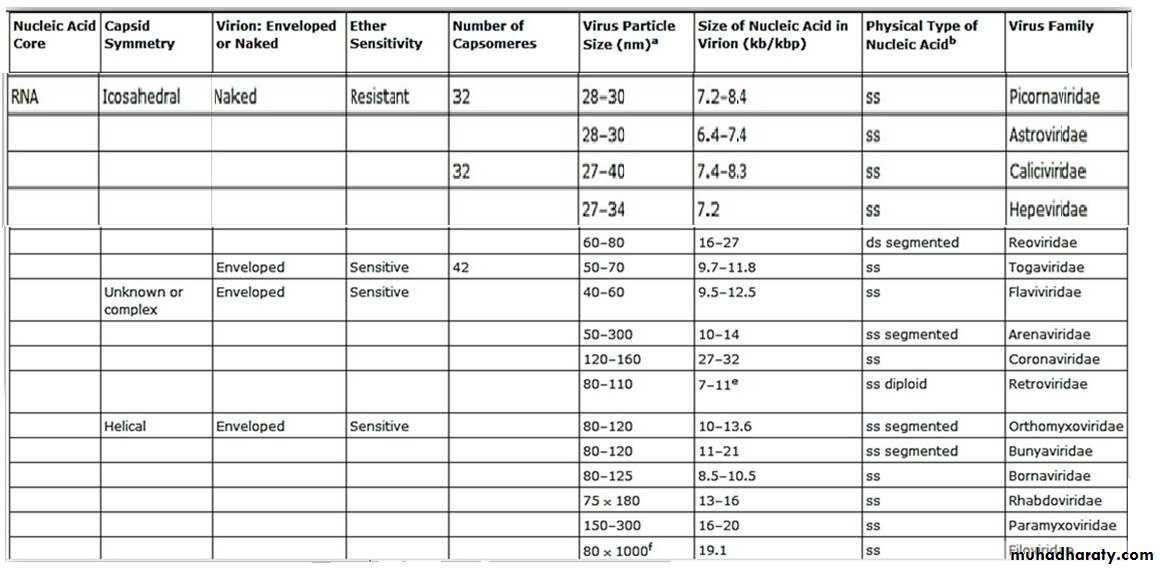
Families of Animal Viruses That Contain Members Able to Infect Human
Families of Animal Viruses That Contain Members Able to Infect Humansummary
1-Viruses range in size from(20-300nm).2-The genome of viruses either DNA or RNA single –stranded or double –stranded, linear or circular.
3-All viruses have protein coat called capsid .The capsid is composed of repeating subunits called capsomeres .Some viruses are naked while others possess envelope.
4-The capsomeres give the virus a symmetric appearance.Some have spherical (Icosahedral) symmetry whereas ,others have helical symmetry.
5- Viral surface proteins mediate attachment to host cell receptors.
6-The viral envelope is acquired as the virus exits from the cell. Enveloped viruses are more sensitive to heat , detergent ,&lipid solvents.7-The surface proteins are the targets of antibody .
8-The classification of viruses based on virion morphology, &virus genome properties.