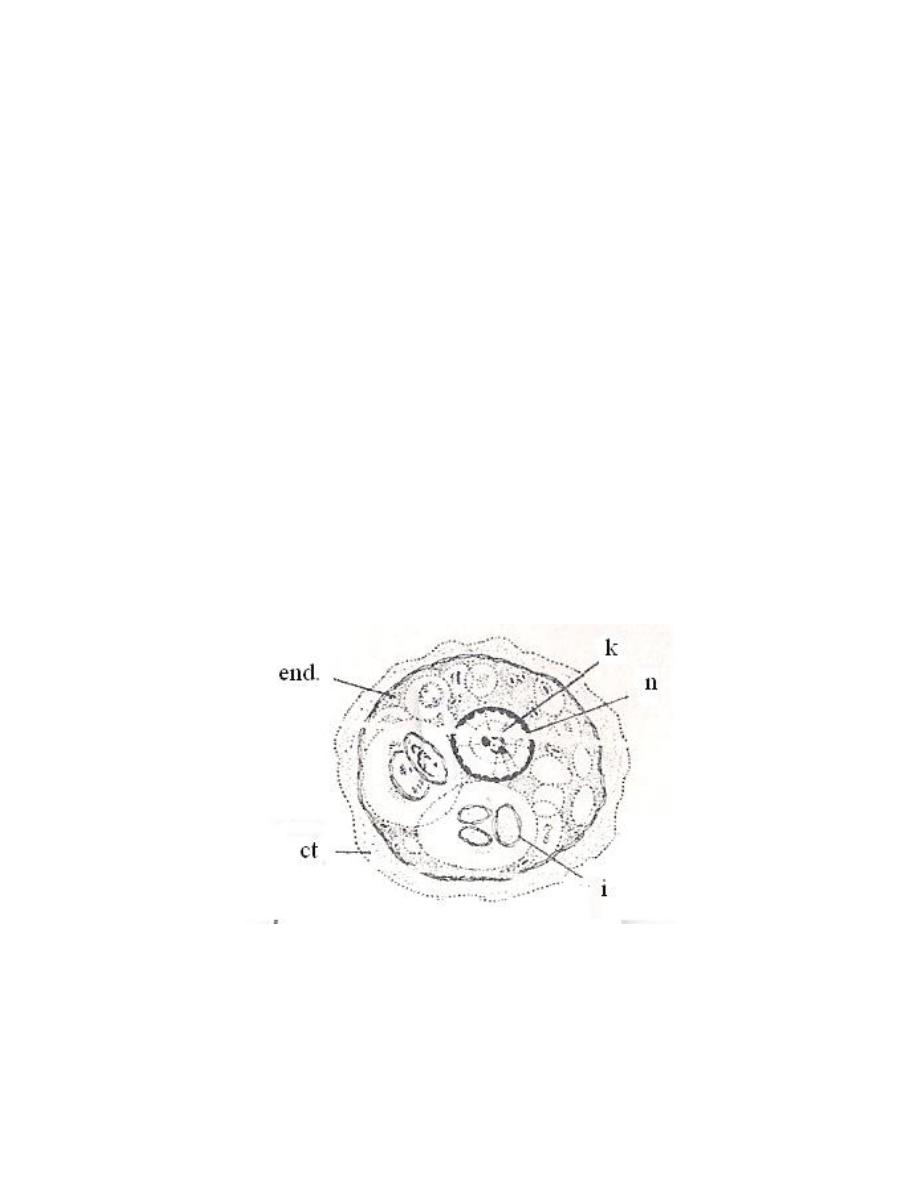
Entamoeba gingivalis
It is mouth parasite firstly discovered in 1849 in the tarter of the teeth.It is
cosmopolitan amoebae ,the general incidence is estimated in at least 50%of
persons with diseased gums and tonsils .It is non pathogenic and isolated from
healthy mouth but mainly it is isolated from diseased mouth with oral abscesses
,dental carries and other inflammatory conditions in the mouth.This amoeba exist
in trophozoite stage only ,so it is transmitted through the droplets of saliva or
through intimate contact of one person to another while kissing .
This amoebae is actively motile by multiple pseudopodia .
Ectoplasm is clear, well differentiated from granular endoplasm. Endoplasm
contain many food vacuoles, some of them with diagnostic rounded dark – staining
bodies represent the nuclei of ingested white blood cells and epithelia cells. The
nucleus is histolytica type.
Diagnosis: by demonstration of trophozoites in materials removed from gingival
margin or from between the teeth or cavities of decayed teeth. The presence of this
amoeba in the mouth suggests the need for better oral hygiene.
أ . صباح النجار
Lec. 4
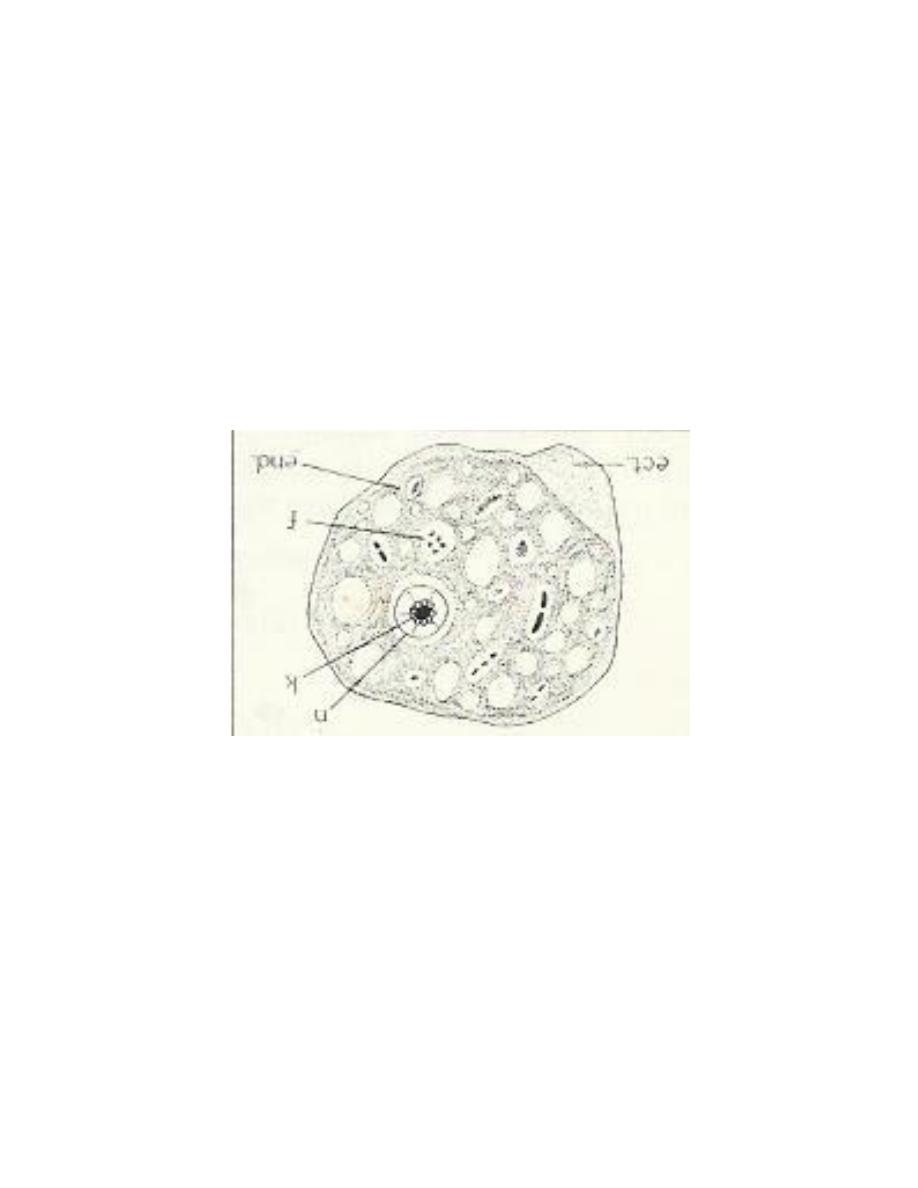
Iodamoeba butschlii
It is cosmopolitan amoeba, but it is less common than E. coli, it is non
pathogenic commensal living in the lumen of large intestine. This amoeba has
trophozoite and cyst stages.
Iodamoeba butschlii
Trophozoite
Trophozoite: small, sluggish, ectoplasm no well differentiated from endoplasm.
The nucleus spherical, characterized by having central large karyosome surrounded
by achromatic granules. There are 1 or 2 glycogen mass in cytoplasm.
The cyst is irregular in shape with single nucleus only, cyst contain well
distinct glycogen mass which stain golden brown with iodine solution so this
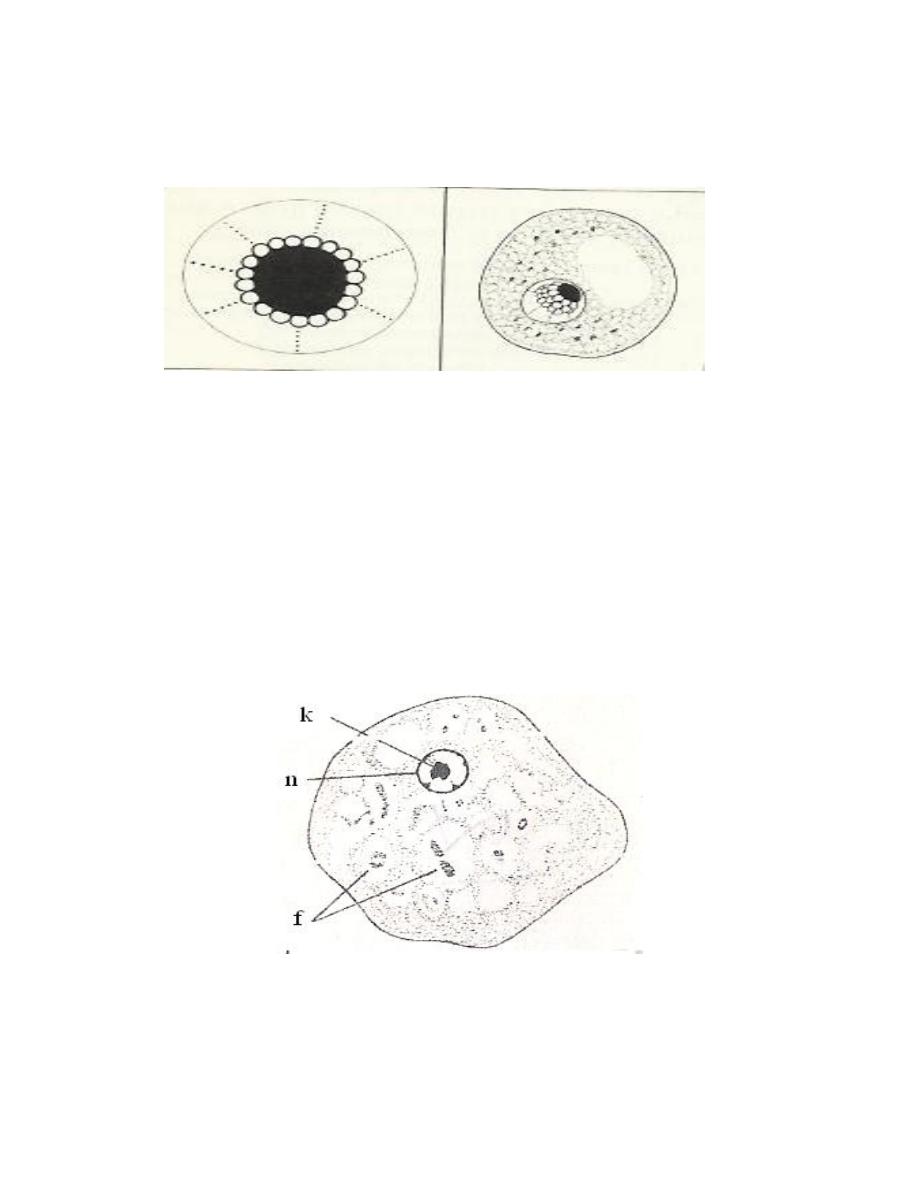
amoeba called Iodamoeba. The nucleus has large compact eccentric karyosome
and around this karyosome there are achromatic granules.
Nucleus Cyst
Iodamoeba butschlii
Endolimax nana
Cosmopolitan amoebae, found in trophozoite and cyst stage. It is
commensal, living in cecum and lower levels of large intestine.
Trophozoite: small, sluggishly motile, ectoplasm differentiated from endoplasm. It
has single nucleus with large pleomorphic or lobulated karyosome.
Endolimax nana
trophpzoite
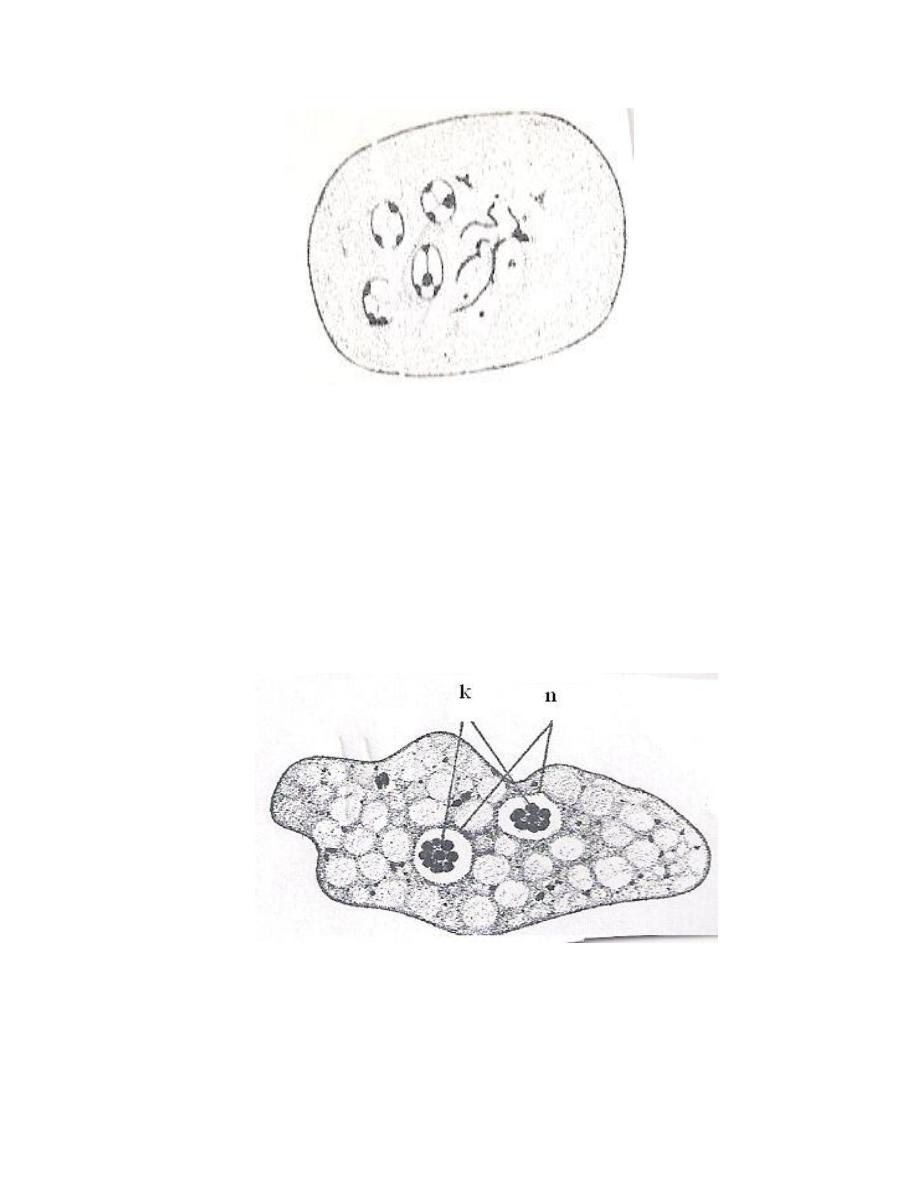
Cyst: Spherical or oval in shape, mature cyst contain 4 nuclei.
Diagnosis: by demonstrate troph. or cyst stage in stool specimen.
Dientamoeba fragilis
It was generally regarded as an amoeba, but it is placed with flagellates
because it has some characters of Trichomonads. It is cosmopolitan parasite, but
because of its small size, it might sometimes overlook in fresh Preparation.
Dientamoeba fragilis trophozoite

It is only known in trophozoite stage, it lives in mucosal crypts of cecum and
rectum.
Trophozoite is small, sluggishly motile, it has 2 nuclei, the nucleus
characterized by having central karyosome consisting of 4 – 8 granules. The mode
of transmission is unknown, possiblly may be achieved by direct or indirect contact
with the trophozoite. Also it has been suggested that this amoeba may be
transmitteda through the ova of certain helminthes.
Pathogenicity: In most persons it causes no harmful effects. Pathogenicity has been
suspected when it has been the only organism identified in case of anorexia,
abdominal pain and diarrhea.
Diagnosis: by demonstrate trophozoites in formed or diarrhic stool.

Free – living Pathogenic amoebae
Some free-living amoebae (facultative) can cause serious even fatal
disease if reach human body. These amoebae has found to have the ability to
live in the tissues of mammals.
It can invade human nervous system, usually result in the death of the
patient.
Naegleria fowleri (brain – eating amoeba)
It causes primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM) in humans. It is
cosmopolitan, mainly in North America, Western Europe, Africa, Japan and
Australia.
The amoebae found in warm fresh water of ponds, lakes, pools and moist
soil.
Morphology: It is the only amoebae which is found in 3 forms; flagellate
trophozoite, amoeboid trophozoite and cyst stages.
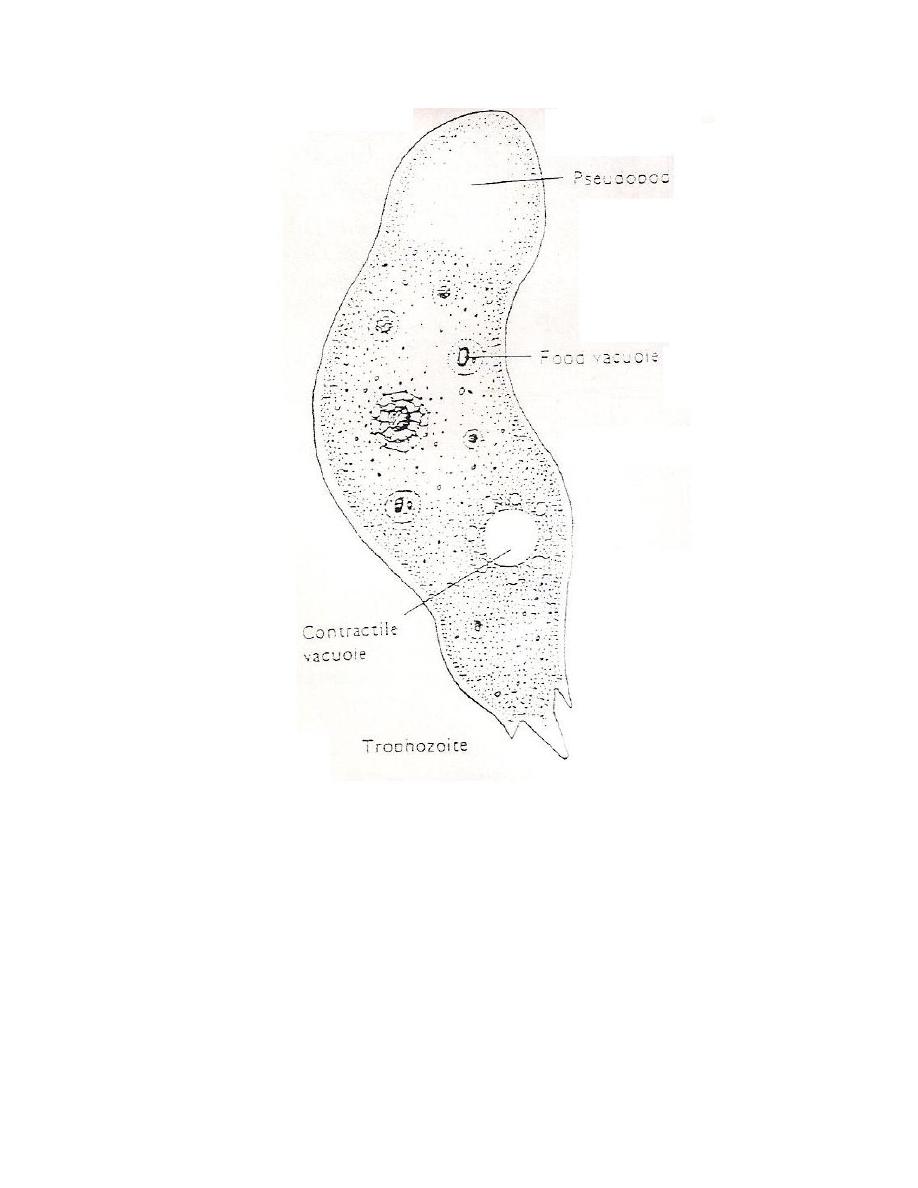
Amoeboid Trophozoite: It is the only form known to exist in humans. It is
characterized by having single nucleus surrounded by halo and it move by
pseudopodia. The pseudopodia form at different points along the cell, thus
allowing the change direction,it contain contractile vacuole and food vacuoles .
In their free – living state, the trophozoite feed on bacteria, in tissues,
trophozoite phagocytize RBCs, white blood cells and destroyed tissues.
Free – Living Pathogenic amoebae

Some free-living amoebae (facultative) can cause serious even fatal disease
if reach human body. These amoebae has found to have the ability to live in the
tissues of mammals.
It can invade human nervous system, usually result in the death of the
patient.
Naegleria Fowleri (brain – eating amoeba)
It causes primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM) in humans. It is
cosmopolitan, mainly in North America, Western Europe, Africa, Japan and
Australia.
The amoebae found in warm fresh water of ponds, lakes, pools and moist
soil.
Morphology: It is the only amoebae which is found in 3 forms; flagellate
trophozoite, amoeboid trophozoite and cyst stages.
Amoeboid Trophozoite: It is the only form known to exist in humans. It is
characterized by having single nucleus surrounded by halo and it move by
pseudopodia. The pseudopodia form at different points along the cell, thus
allowing the change direction. In their free – living state, the trophozoite feed on
bacteria, in tissues, trophozoite phagocytize RBCs, white blood cells and destroy.
Flagellate Trophozoite: Pear shape biflagellated form, occurring when the
amoeboid trophozoite exposed to a change in ionic concentration such as in
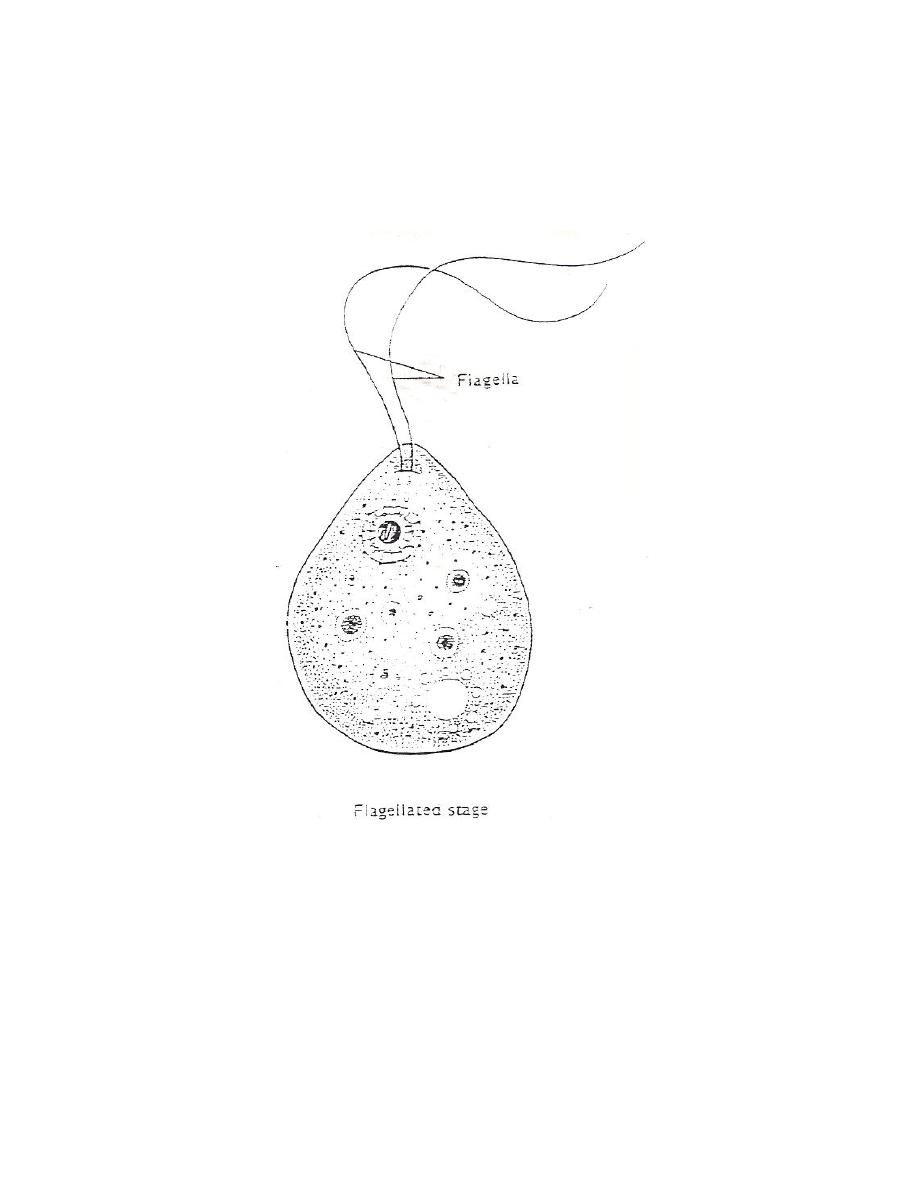
distilled water. The transformation of amoeboid form to flagellated form occurs
within few minutes
.
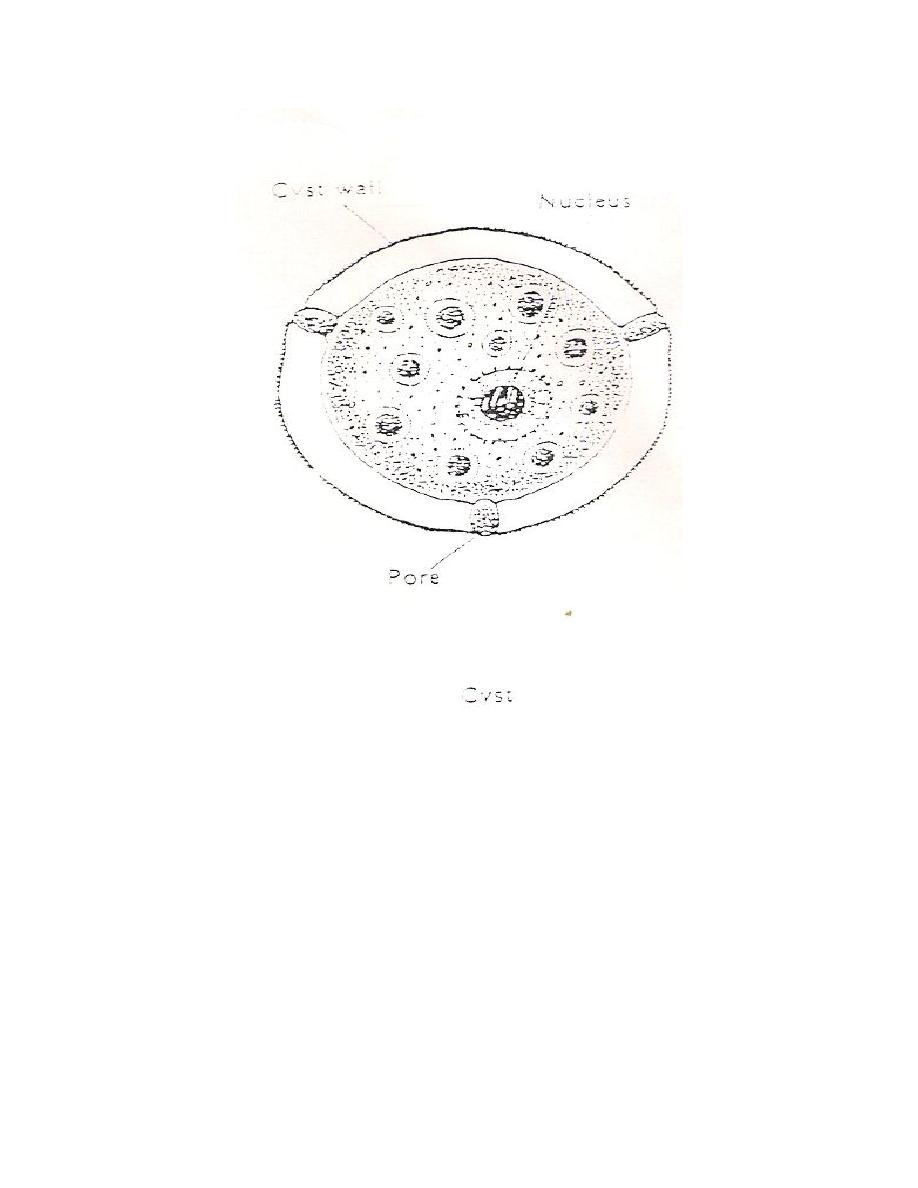
Cyst Stage: Amoeboid trophozoite encyst due to unfavorable conditions e.g.,
crowding, desiccation and cold tempreture below 10
o
c. the cyst has thick cystic
wall and there are pores in cystic wall, the nucleus is similar to amoeboid form.
Life Cycle: Amoeboid trophozoite transform into flagellated form in vitro after
being transferred to water from a tissue or culture. The flagellated form do not
divide but rather lose their flagella and convert back into the amoeboid form. Cyst
formation is known to exist only in external environment. Humans infected by
swimming in contaminated stagnant water. Amoeboid trophozoite enter human
body through nasal mucosa and often migrate to the brain, causing rapid tissue
destruction.
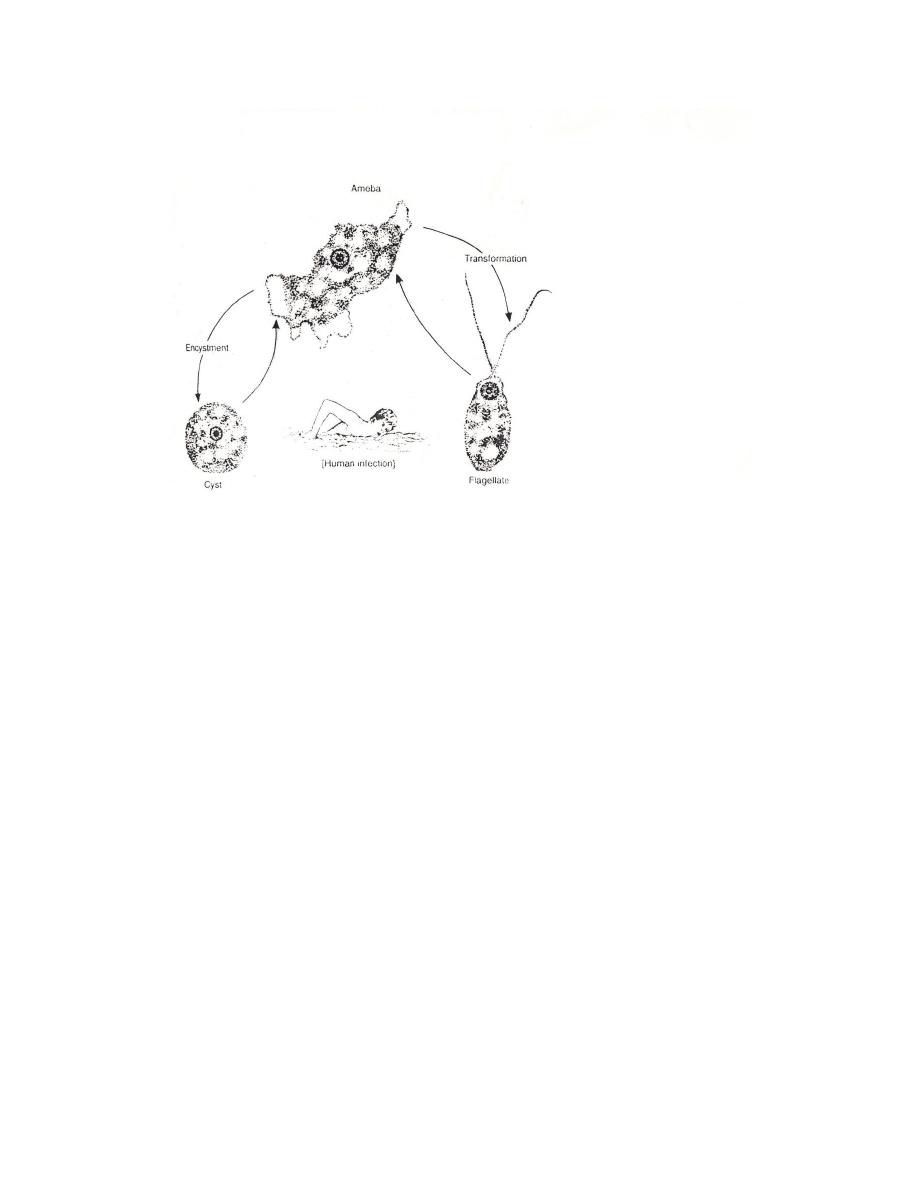
: Life cycle of Naegleria fowleri
Pathogenicity and Symptomatology:
The amoebae enter nasal passages when the persons swimming or has
contact with warm water, moving along olfactory nerve, through cribriform plate
into the cranial cavity. In the brain the amoebae remain associated with
membranous covering of the brain, the meninges, where they evoke an
inflammatory response.
Early in the infection the patient complains of upper respiratory tract
symptoms e.g. raning nose, sore throat, fever and headache. Within 2 – 3 days the
headache becomes more sever and there may be vomiting, stiff neck, mental
confusion, coma as a result of intracranial pressure. Death usually with 10 days of
the onset of symptoms.

Diagnosis:
1- Direct demonstration of motile amoebae in unstained CSF or nasal
discharge.
2- Stained smear of CSF.
3- Stained section of brain tissue at autopsy.
4- Culture on non-nutrient agar medium coated with E. coli bacteria.
5- Serological tests.
Acanthamoeba Spp.:
It causes granulomatous amoebic encephalitis and amoebic keratitis. It is
cosmopolitan but are not necessarily associated with warm water, it is found in
moist soil and in the air and water. It is found in only two form; the trophozoite
and cyst, and either of these can be a source of infection.
Amoeboid trophozoite has spikey pseudopodia and a nucleus with large,
central karyosome similar to the nucleus of Naegleria.
Host – Parasite Interactions
The amoebae probably enter respiratory system, or perhaps the skin, then
migrate to CNS via the blood.
Once in the brain, it cause granulomatous encephalitis, which means that a
more or less discrete mass of inflammatory cells and amoebae are found in the
meninges and superficial layers of the brain. The lesion do inexorable leading to
death of the patient. Most patients with GAE do not have normal immune system.
GAE has been seen in AIDS patients.

Amoebic Keratitis:
Acanthamoeba spp. Caused ulcers of the cornea of eye in humans. Cornea is
invaded when there is trauma in the eye or the presence of amoebae in water. In
most instances, there is an association with wearing contact lenses and a failure to
clean them properly. Corneal lesions are painful and differentiation must be made
from herpes simplex virus.
Diagnosis:
1- By finding amoebae in wet mounte (10% KOH) of corneal ulcer scraping or
in stained smear.
2- By isolation of amoebae form contact lenses or washing solutions.
