
Polymerase Chain Reaction(PCR)

History
PCR was first conceived in April,
1983
by Kary Mullis.
Mullis and Faloona, 1987.
Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro
via apolymerase-catalyzed chain
reaction.
In
1989
PCR was selected as the major
scientific development and Taq DNA
polymerase as molecule of the year by
the science magazine
In
1993
Kary Mullis was awarded the
Nobel Prize in chemistry for this
achievements.
Kary B. Mullis

PCR
is in vitro method for enzymatically amplifying defined
sequences of DNA (or RNA) into large quantities in a few hours.
PCR
Specifically targets and amplifies a SINGLE sequence
from within a complex mixture of DNA.

PCR requirements
Starting nucleic acid - DNA/RNA
Tissue, cells, blood, hair root, saliva, semen
Heat-stable DNA polymerase
e.g. Taq
Polymerase
•
Thermus aquaticus
DNA polymerase
•
Thermophilic organism
•
Enzymes resistant to high temperatures 95ºC
•
72-74ºC optimum
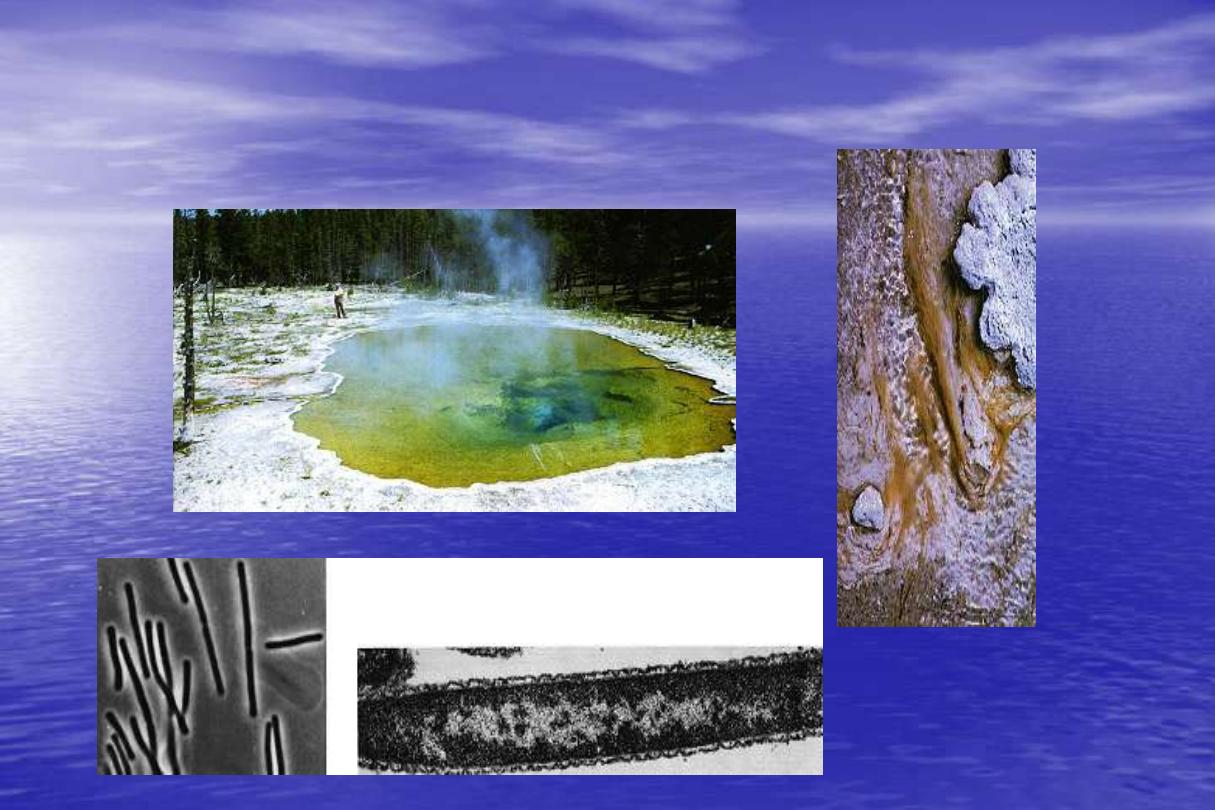

Thermus aquaticus:
PCR requirements
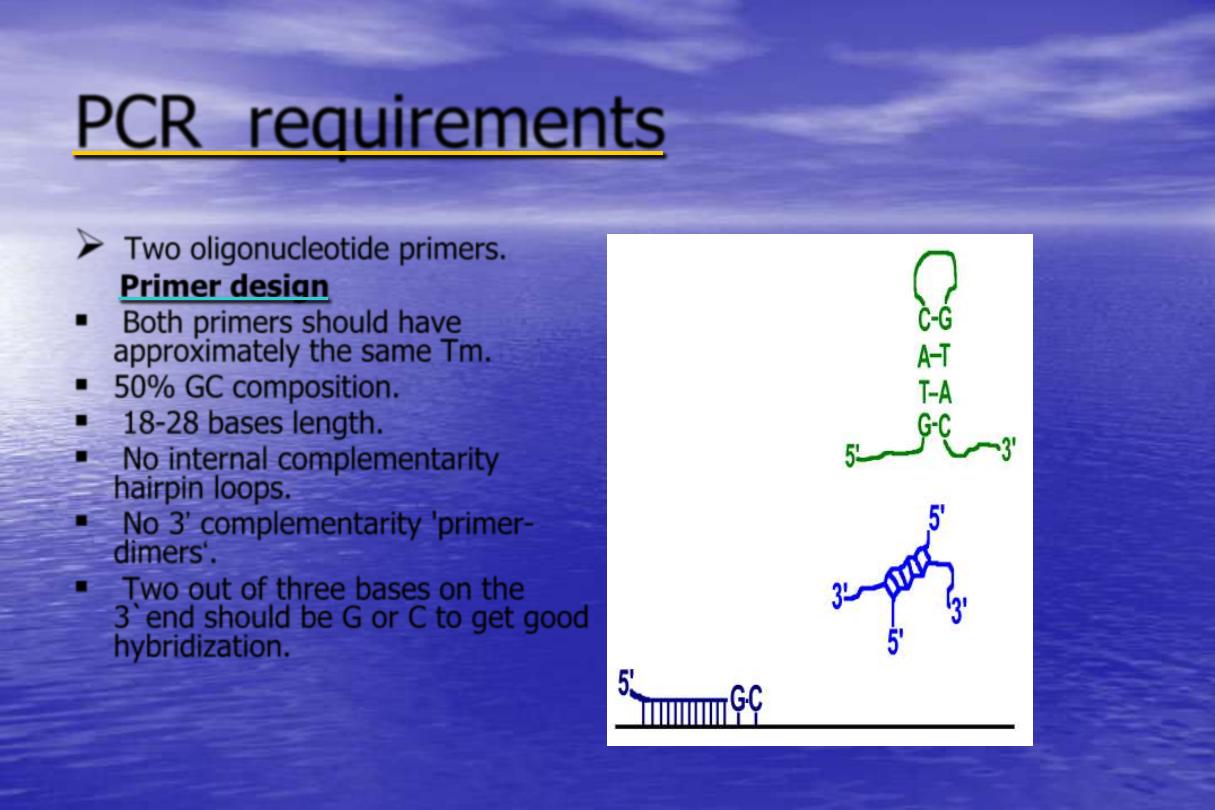
Two oligonucleotide primers.
Primer design
Both primers should have
approximately the same Tm.
50% GC composition.
18-28 bases length.
No internal complementarity
hairpin loops.
No 3‟ complementarity 'primer-
dimers„.
Two out of three bases on the
3`end should be G or C to get good
hybridization.
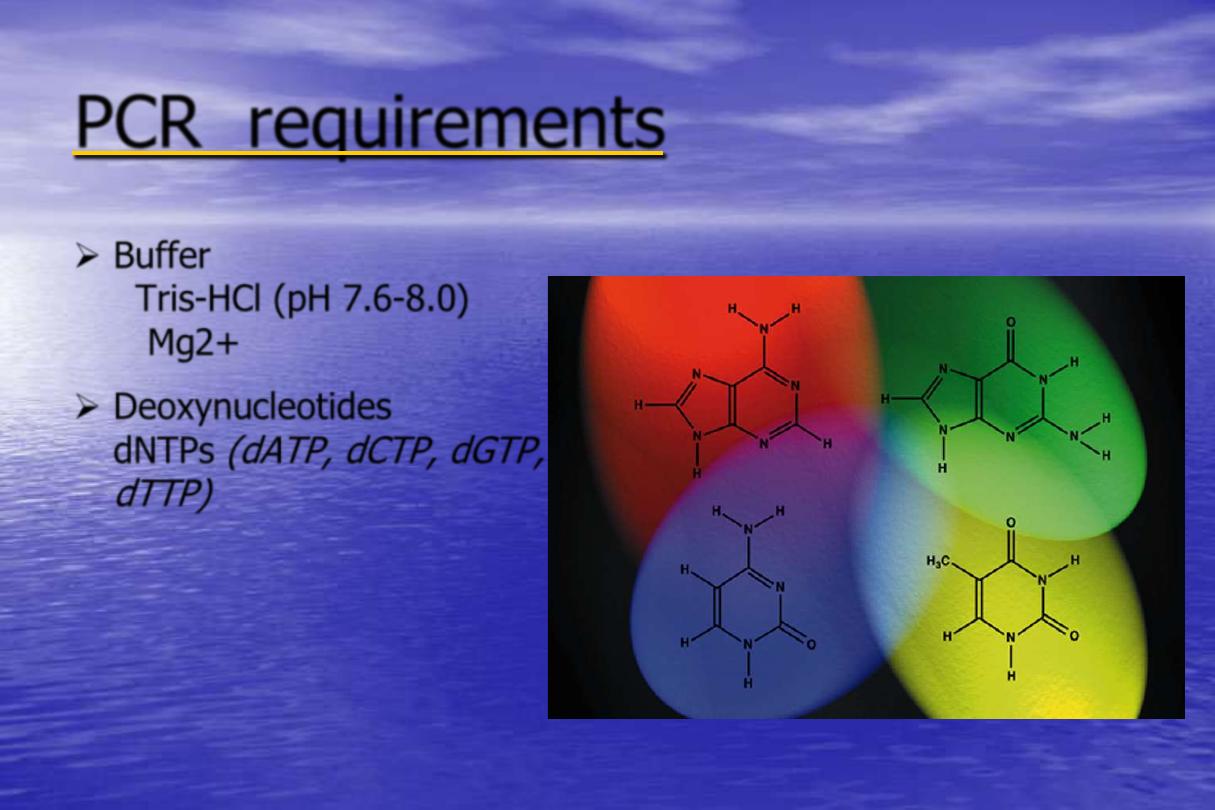
PCR requirements
Buffer
Tris-HCl (pH 7.6-8.0)
Mg2+
Deoxynucleotides
dNTPs
(dATP, dCTP, dGTP,
dTTP)
Adenine
Guanine
Cytosine
Thymine
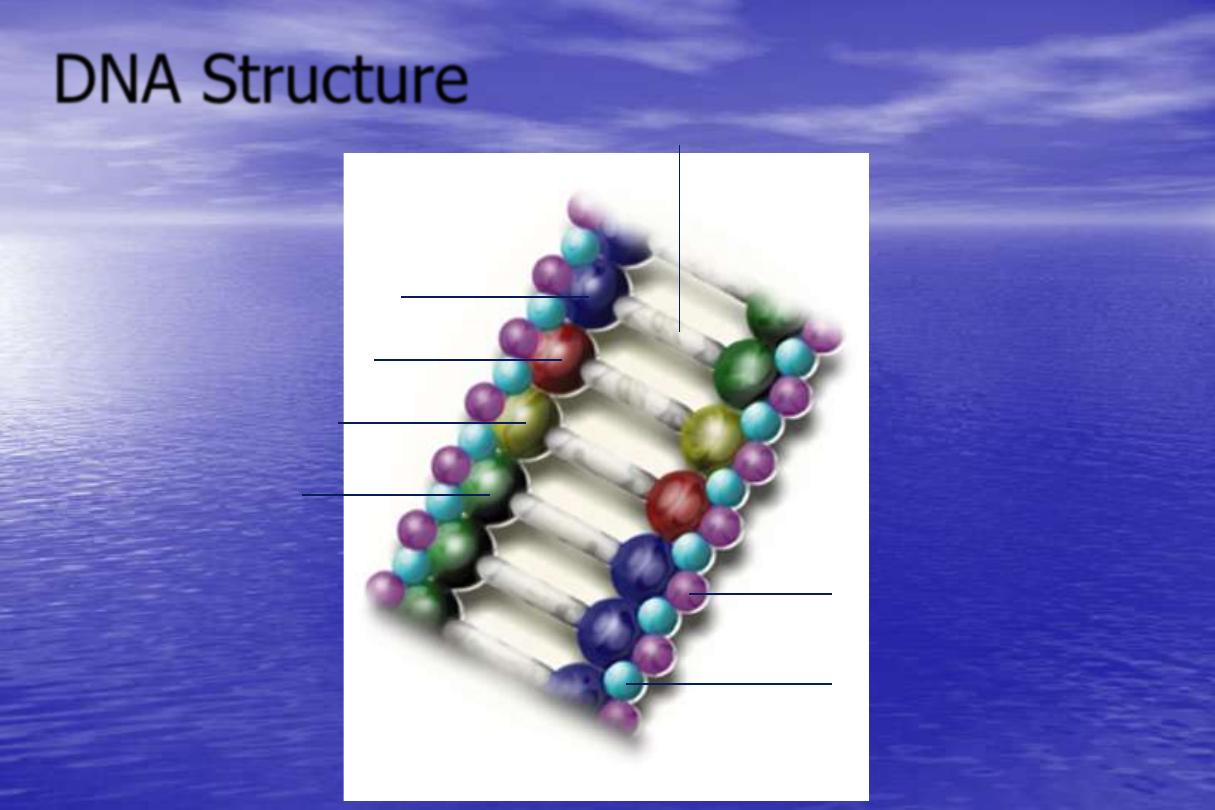
DNA Structure
Hydrogen Bonds
Cytosine
Adenine
Thymine
Guanine
Deoxyribose
(Sugar molecule)
Phosphoric Acid
(Phosphate molecule)

How PCR works:
•
Begins with DNA containing a sequence to be amplified and a pair of synthetic
oligonucleotide primers that flank the sequence.
•
Next, denature the DNA to single strands at 94˚C.
•
Rapidly cool the DNA (37-65˚C) and anneal primers to complementary s.s. sequences
flanking the target DNA.
•
Extend primers at 70-75˚C using a heat-resistant DNA polymerase such as
Taq
polymerase derived from
Thermus aquaticus
.
•
Repeat the cycle of denaturing, annealing, and extension 20-45 times to produce 1
million (220)to 35 trillion copies (245) of the target DNA.
•
Extend the primers at 70-75˚C once more to allow incomplete extension products in
the reaction mixture to extend completely.
•
Cool to 4˚C and store or use amplified PCR product for analysis.

PCR Steps
Thermal Denaturation
Initial denaturation temperature of
94ºC for 8 min.For subsequent cycles,
94ºC for 1-2 min.is usually adequate.
Primer Annealing
The temperature and length of time
required for primer annealing depends
on the base composition and the length
and concentration of the primers.
Primer Extension
Primer Extension is typically carried
out at 72ºC ,which is close to the
temperature optimum of the Taq
polymerase.
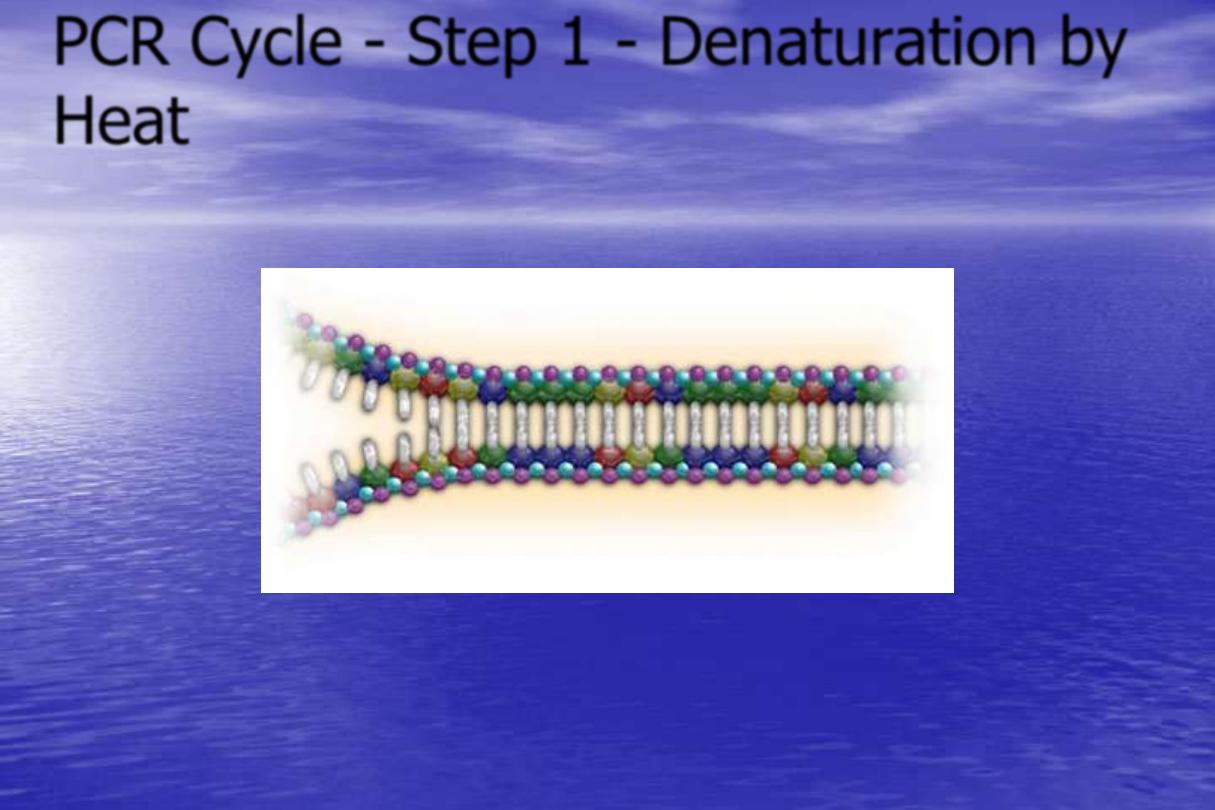
PCR Cycle - Step 1 - Denaturation by
Heat
Target Sequence
Target Sequence
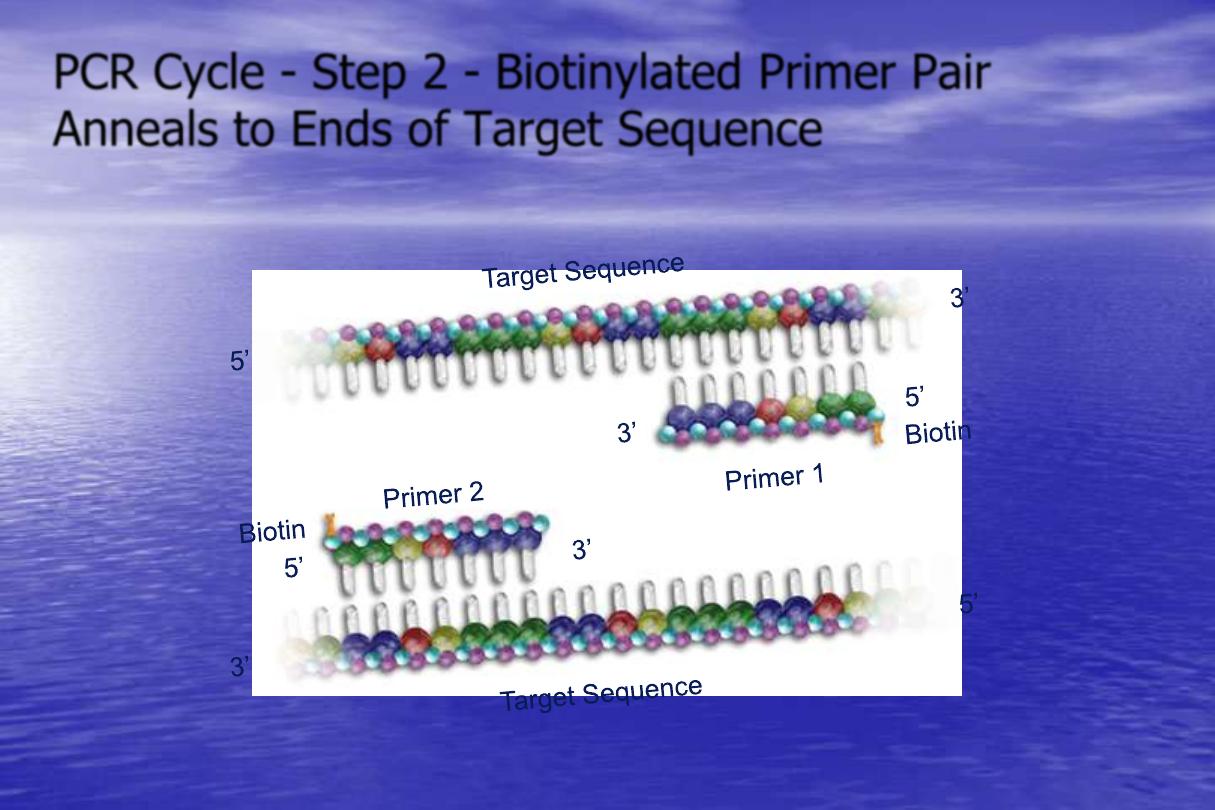
PCR Cycle - Step 2 - Biotinylated Primer Pair
Anneals to Ends of Target Sequence
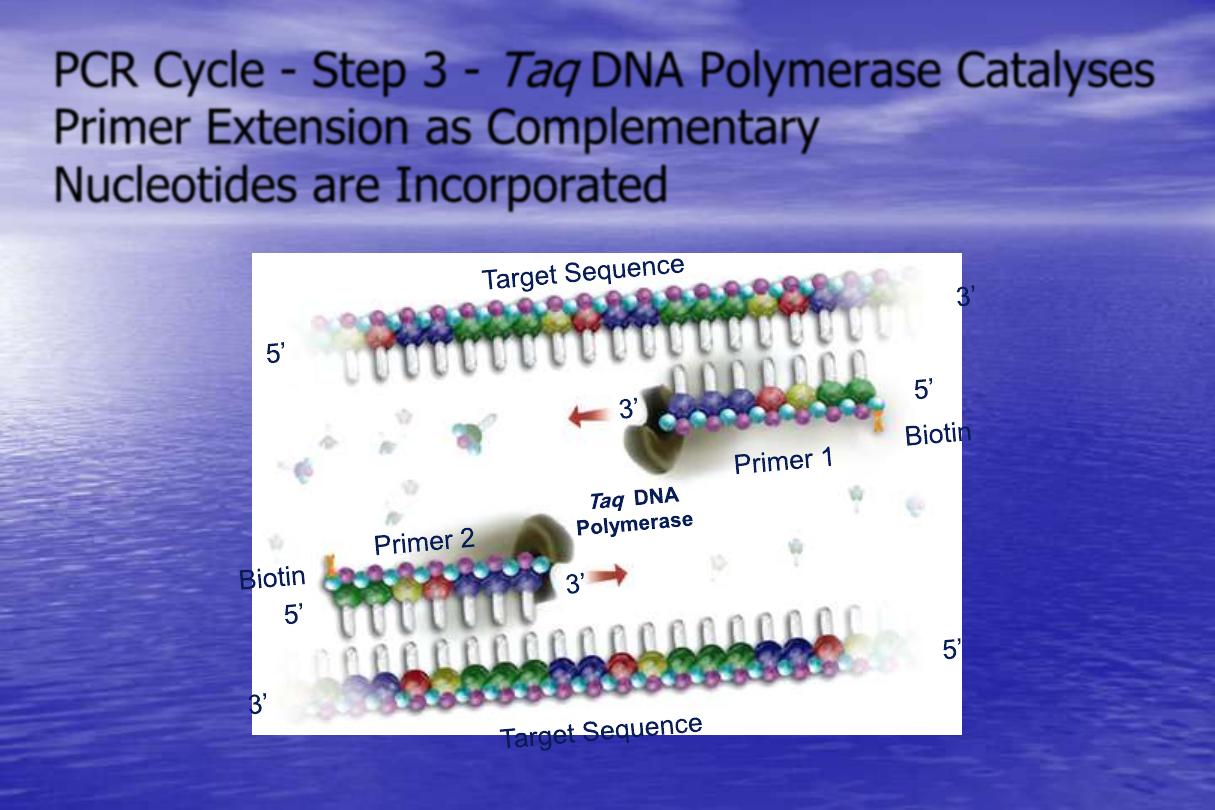
PCR Cycle - Step 3 -
Taq
DNA Polymerase Catalyses
Primer Extension as Complementary
Nucleotides are Incorporated
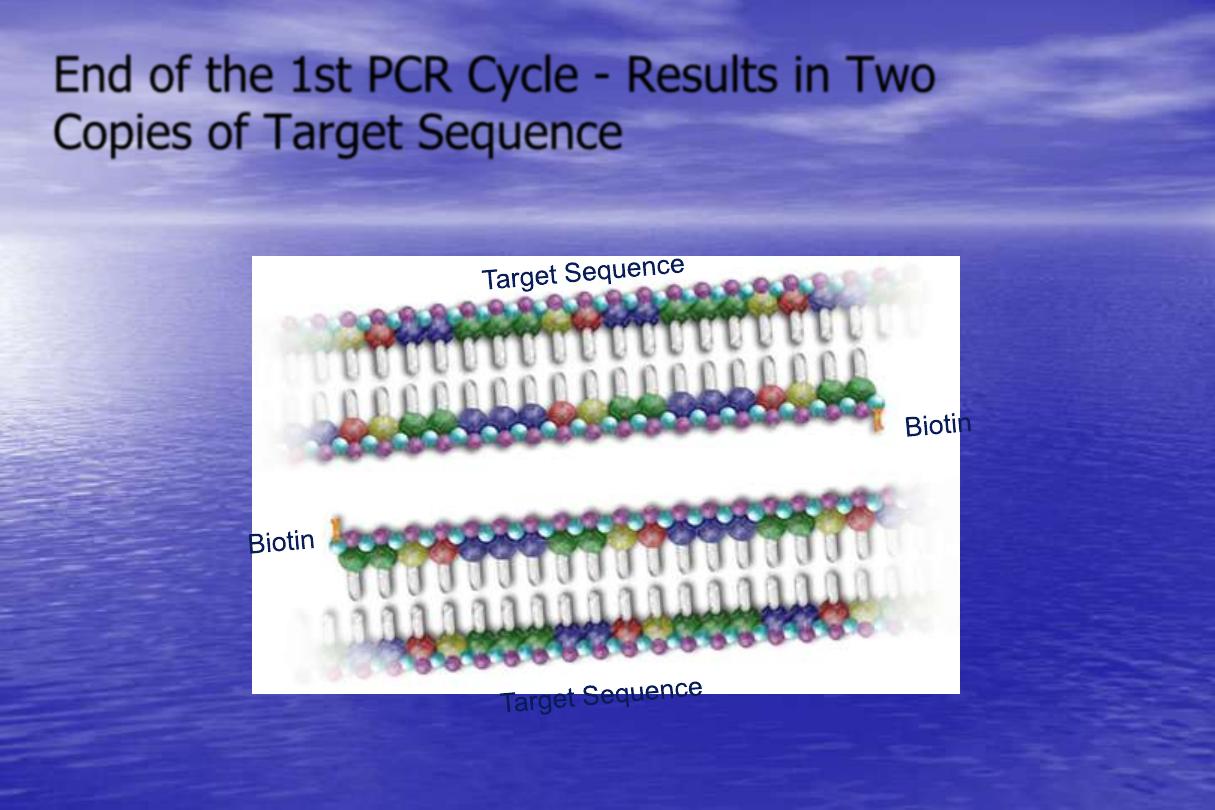
End of the 1st PCR Cycle - Results in Two
Copies of Target Sequence
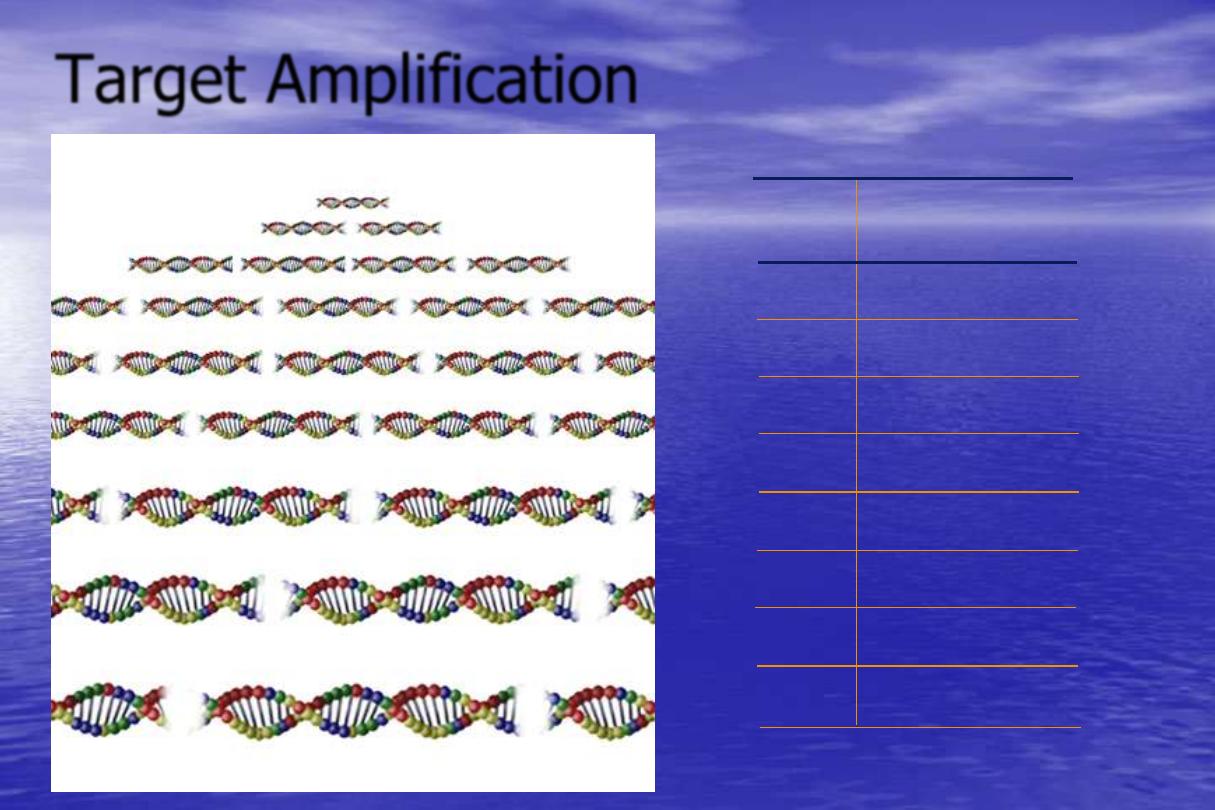
Target Amplification
No. of
No. Amplicon
Cycles
Copies of Target
1
2
2
4
3
8
4
16
5
32
6
64
20
1,048,576
30
1,073,741,824
1 cycle = 2 Amplicon
2 cycle = 4 Amplicon
3 cycle = 8 Amplicon
4 cycle = 16 Amplicon
5 cycle = 32 Amplicon
6 cycle = 64 Amplicon
7 cycle = 128 Amplicon

PCR Protocol
mix DNA, primers, dNTPs,
Taq, buffer, Mg2+
program thermocycler for
times and temps
denaturation
annealing
extension
20-40 cycles
analyze amplified DNA
(amplicons)
Thermal Cycler
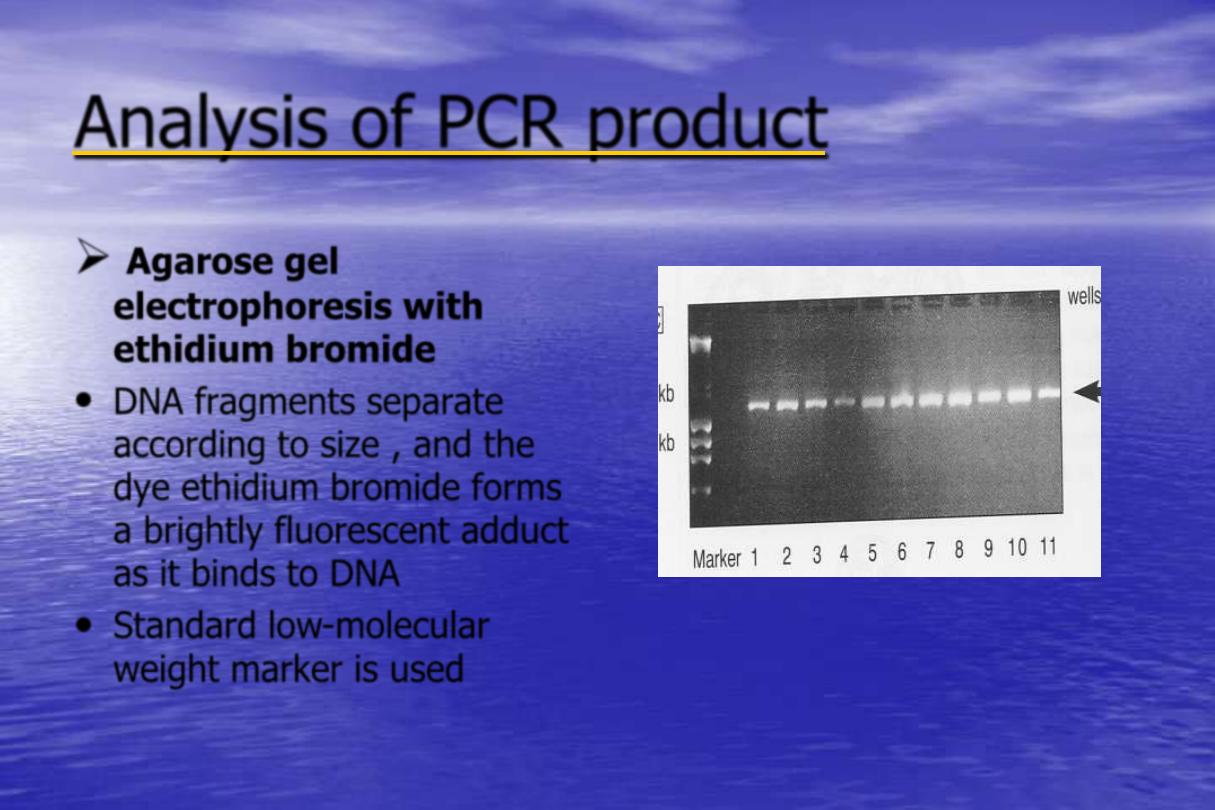
Analysis of PCR product
Agarose gel
electrophoresis with
ethidium bromide
•
DNA fragments separate
according to size , and the
dye ethidium bromide forms
a brightly fluorescent adduct
as it binds to DNA
•
Standard low-molecular
weight marker is used

Analysis of PCR product
Southern blot analysis
•
The DNA is hybridized with a radioactively-
labeled DNA (a "
probe
") , then exposed to X-
ray film , DNA fragments appeared as dark
bands on the film, known as an autoradiogram
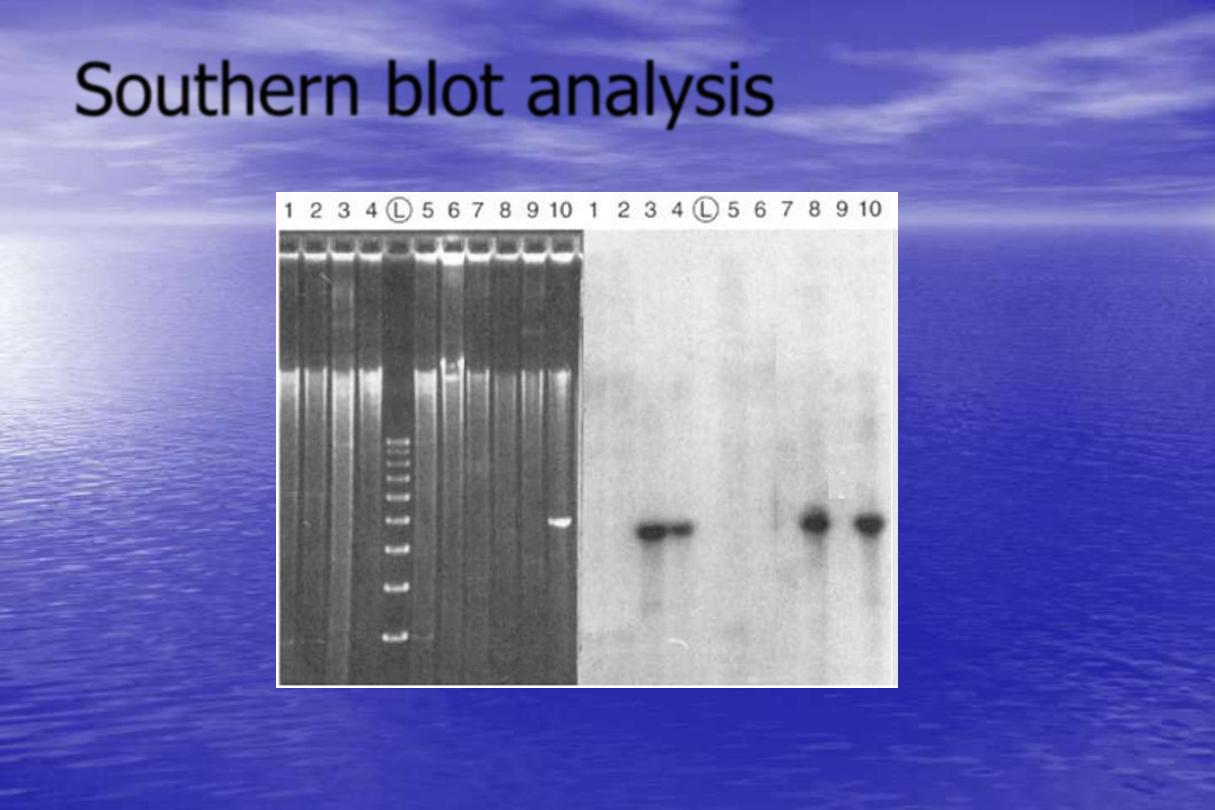
Southern blot analysis
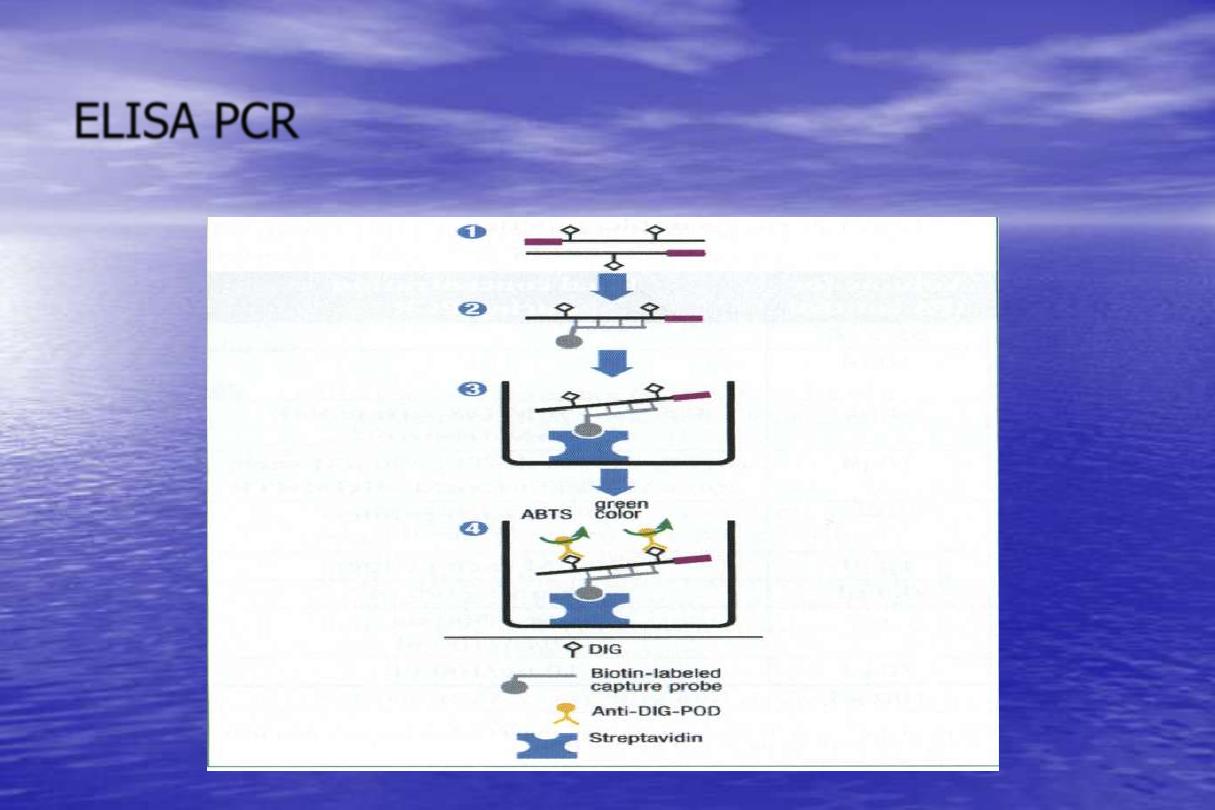
ELISA PCR

PCR)
-
Reverse Transcription ( RT
RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription-PCR) is a modification of
in which an
strand is first reverse transcribed into its
complement or
, followed by amplification of the resulting
DNA using
.
Any type of RNA (mRNA , tRNA , rRNA , total , viruses) can be
analyzed .
RNA is reversed transcribed by reverse transcriptase enzymes.
e.g. AMV : Avian Myeloblastosis Virus.
MMULV:Molony Murine Leukemia Virus
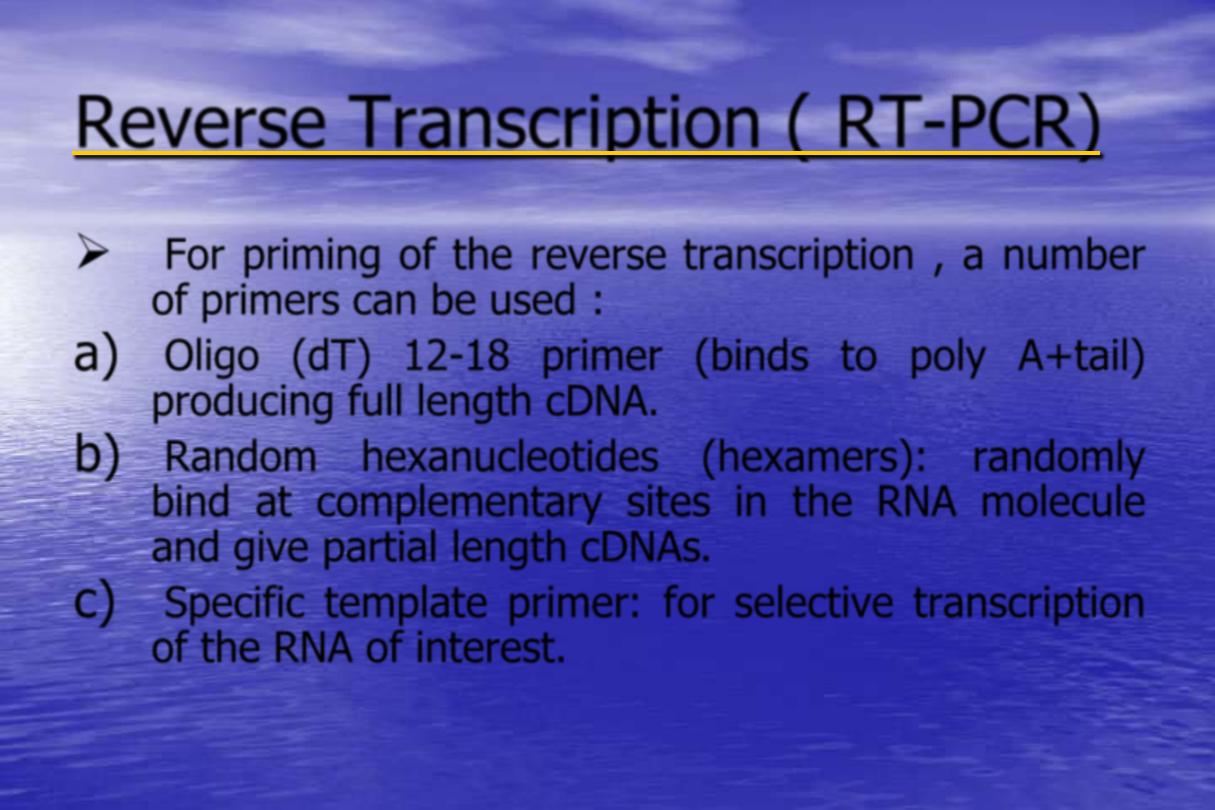
PCR)
-
Reverse Transcription ( RT
For priming of the reverse transcription , a number
of primers can be used :
a)
Oligo (dT) 12-18 primer (binds to poly A+tail)
producing full length cDNA.
b)
Random hexanucleotides (hexamers): randomly
bind at complementary sites in the RNA molecule
and give partial length cDNAs.
c)
Specific template primer: for selective transcription
of the RNA of interest.
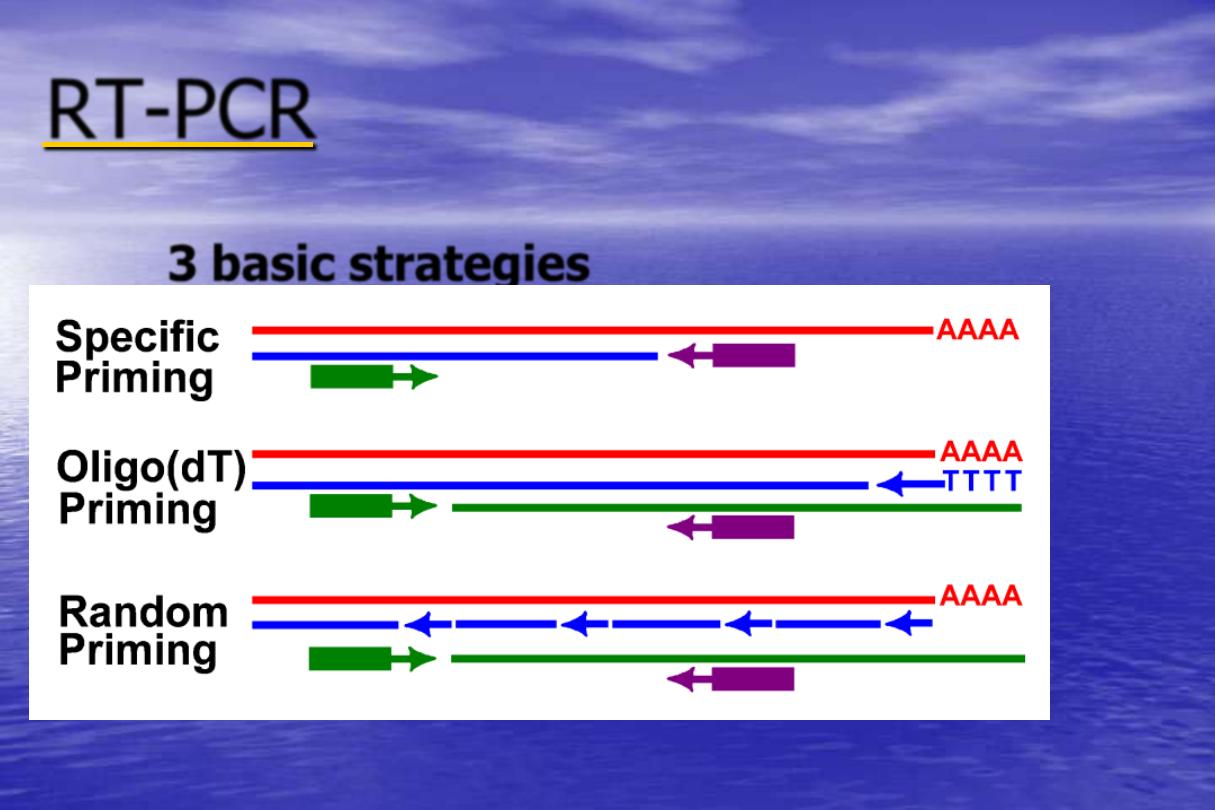
PCR
-
RT
3 basic strategies
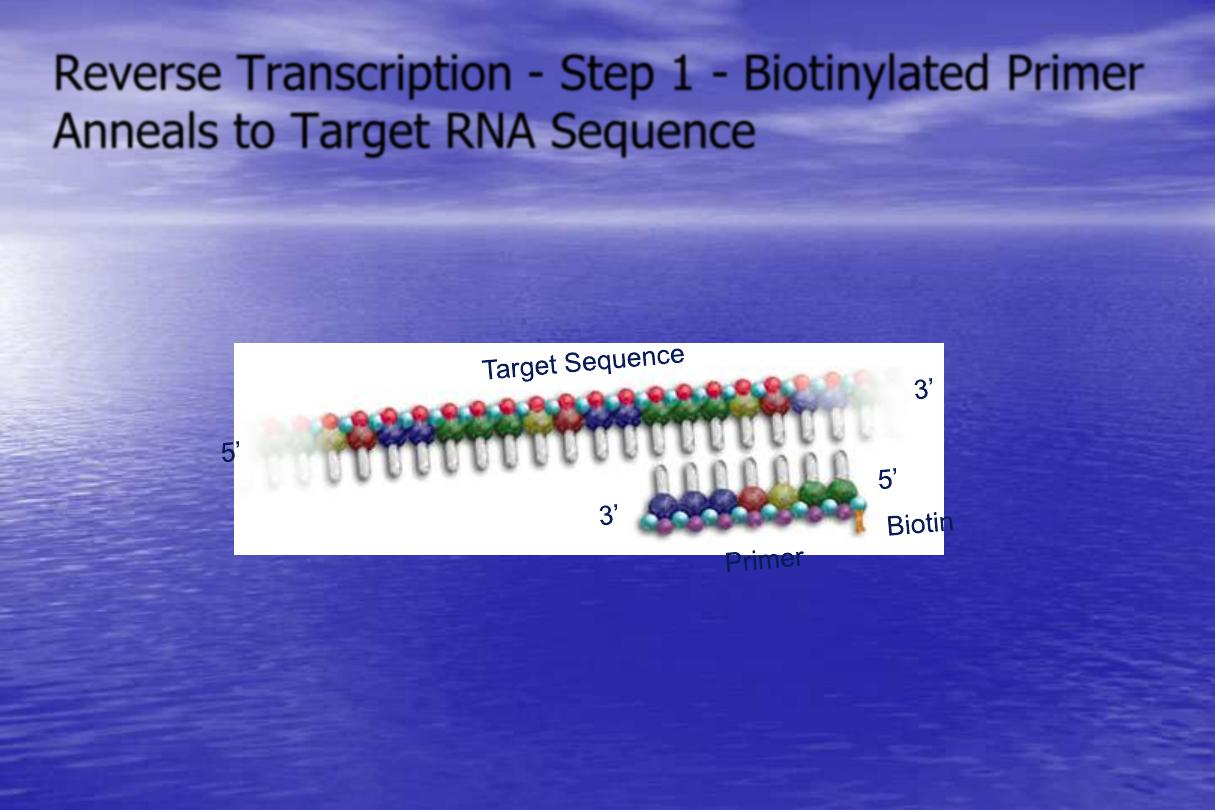
Reverse Transcription - Step 1 - Biotinylated Primer
Anneals to Target RNA Sequence
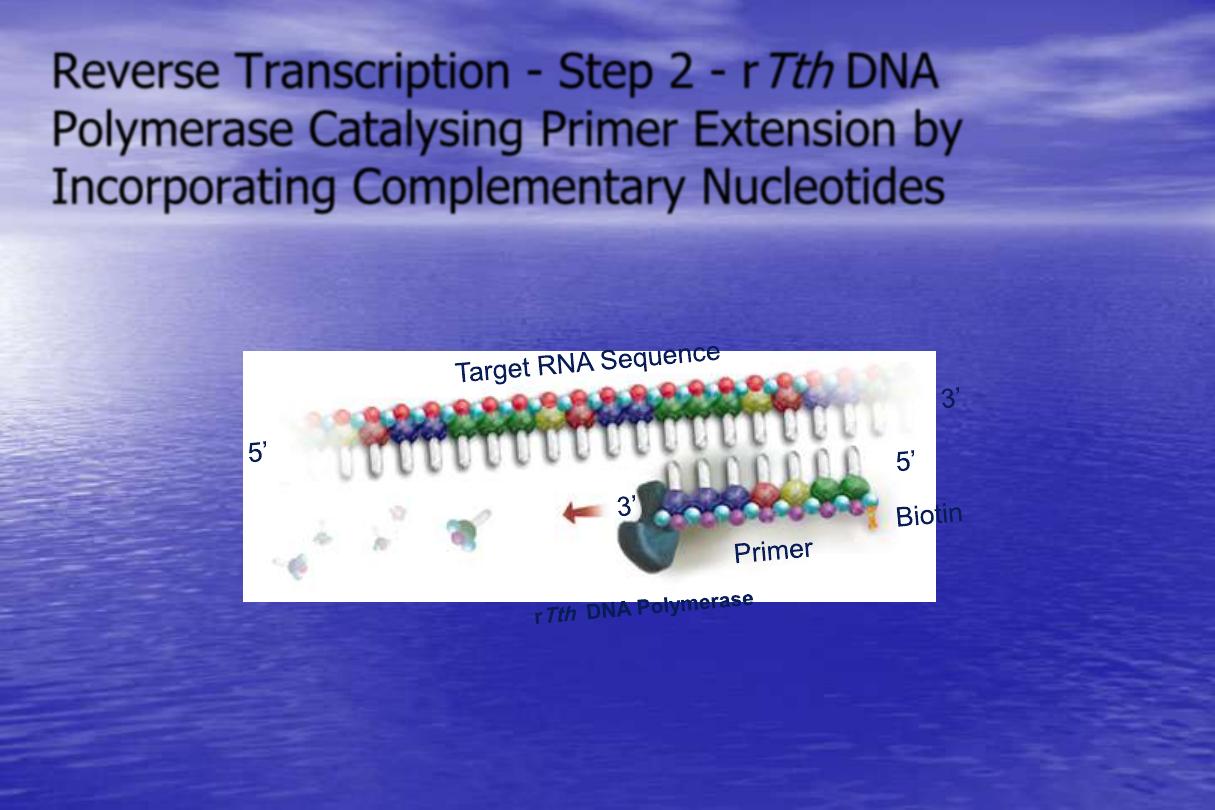
Reverse Transcription - Step 2 - r
Tth
DNA
Polymerase Catalysing Primer Extension by
Incorporating Complementary Nucleotides
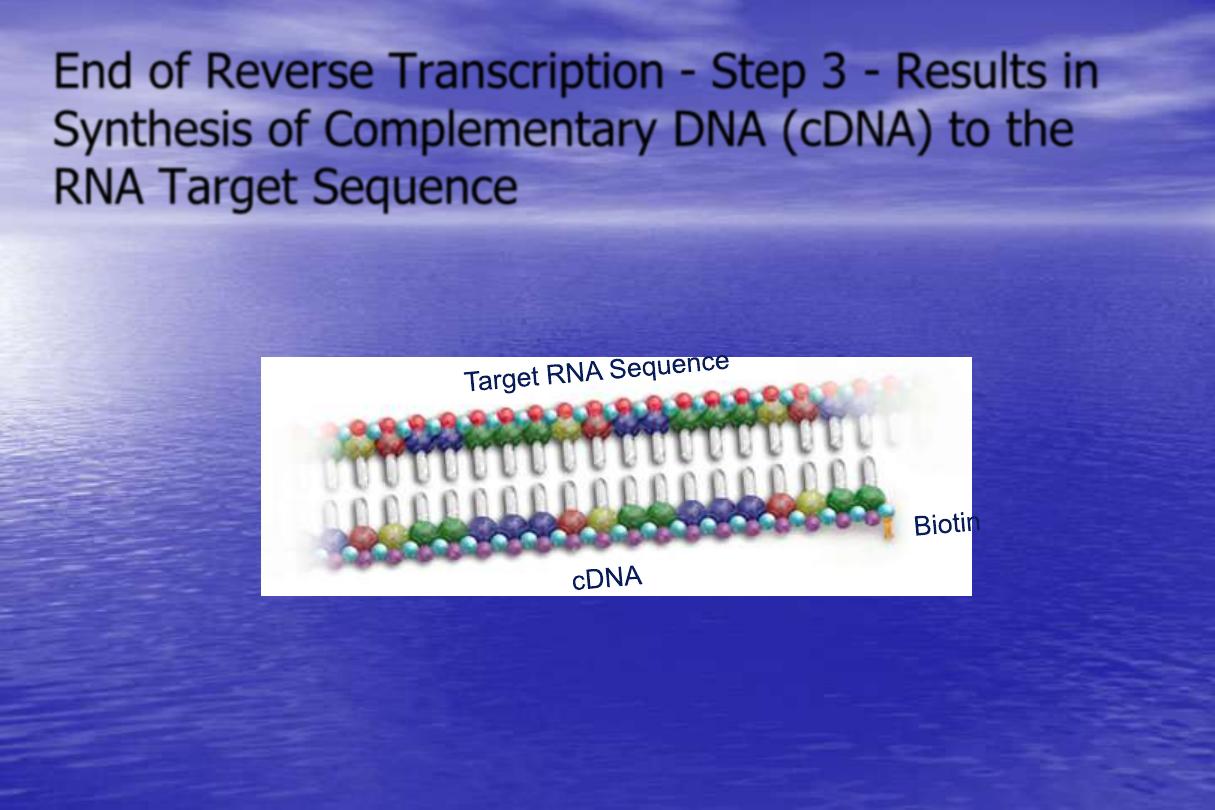
End of Reverse Transcription - Step 3 - Results in
Synthesis of Complementary DNA (cDNA) to the
RNA Target Sequence
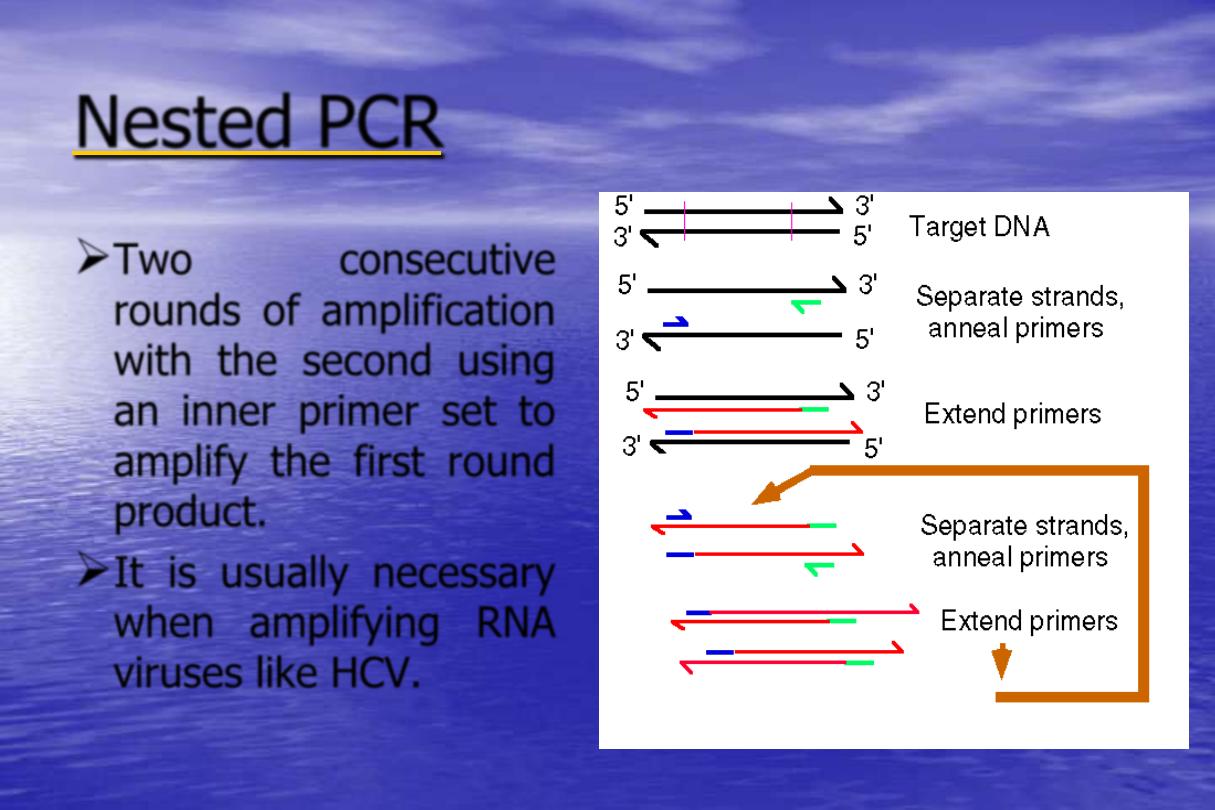
Nested PCR
Two
consecutive
rounds of amplification
with the second using
an inner primer set to
amplify the first round
product.
It is usually necessary
when amplifying RNA
viruses like HCV.

Hot Start PCR
Highly specific and robust PCR amplification.
A simple modification of the original PCR process in
which the amplification reaction is initiated at an
elevated temperature
This Hot Start process is facilitated by using Gold DNA
polymerase
Gold DNA polymerase is a modified version of Taq DNA
polymerase. This new enzyme is inactive at room
temperature which allows premixing of all reagents
without worry of primer-dimer formation or pre-PCR
mispriming.

PCR Contamination
•
There are three main sources of PCR contamination:
1- PCR product from previous amplifications (carryover
contamination).
2- Cloned DNA previously handled in the lab.
3- Sample to sample contamination.

Principles of contamination
avoidance
1- Strict physical separation of individual PCR- related
maneuvers:
Sample preparation stage.
PCR setup stage.
Post PCR stage ( No equipments should leave this
room, this location is considered the most likely
source of contaminating amplicons).

Principles of contamination avoidance
2- Laboratory practice designed to minimize the risk of contamination.
All PCR reagents should be aliquoted.
Use and change gloves frequently.
Positive displacement pipettes or aerosol resistant tips should be used.
Re-usable glassware, plasticware should be acid decontaminated .
If possible , different personnel should be allocated to the pre-PCR and
post PCR parts.
Lab coats must be worn in all area , the coat worn in post-PCR must
never be worn in pre-PCR.
Always work in one way direction from pre-PCR to post-PCR.
Recently, closed systems for PCR product analysis have been developed,
such as TaqMan system.

Principles of contamination avoidance
3- Use of specific anti-contamination measures:
UV irradiation to damage any contaminating DNA prior
to the addition of DNA template.
Restriction enzyme treatment to restrict any
contaminating sequence prior to the addition of DNA
template.
e.g.MspI , DNase I
Incorporation of dUTP instead of dTTP and treatment
with uracil N glycosylase (UNG).

Detection of contamination
To facilitate the monitoring of contamination positive and
negative controls should be included.
Positive Control:
to reduce the possibility of false
negative arising as a result of inadequate extraction of
nucleic acid.
Negative Control:
to monitor for false positive due to
contamination.

Applications of PCR
Genetic fingerprinting
Forensic analysis at scene of crime to identify a person
who suspected of committing a crime by comparing his
or her DNA with a given sample (blood, hair,
semen….etc) obtained from a crime scene.
Paternity testing
Analysis of ancient DNA.

Applications of PCR
Cloning genes.
Genetic diagnosis - Mutation detection
PCR facilitates the advancement of prenatal diagnosis of
genetic defects such as:
Cystic fibrosis
Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Haemoglobino pathies.
Mutagenesis to investigate protein function.
Quantitate differences in gene expression by Reverse
Transcription (RT)-PCR.

Applications of PCR
Detection of pathogens especially when applied
to those which are:
Difficult or costly to culture.
Slow growing.
Present in low concentration.
Hazardous to propagate in the lab.

Time PCR
-
Real
Quantitative PCR technique allows the simultaneous
amplification and detection of the target.
Is called
“real-time PCR”
because it allows the scientist
to actually view the increase in the amount of DNA as
it is amplified.

Time PCR
-
Real
TaqMan real-time PCR.
SYBR Green real-time PCR.
Molecular beacon real-time PCR.

time PCR
-
real
®
TaqMan
Principle:
This technology is based on detection of a
fluorescent signal produced proportionally during the
amplification of a PCR product. A probe is designed to
anneal to the target sequence between the forward
and reverse primers. The amount of fluorescence
released during the amplification cycle is proportional
to the amount of product generated in each cycle.

time PCR
-
real
TaqMan
TaqMan Probe
The probe consist of two types of fluorophores,the reporter at
the 5‟ end of the probe and the quencher at the 3‟ end of the
probe.
During PCR the 5‟ nuclease activity of the polymerase degrades
the probe into fragments and separates the quencher from the
reporter, and allows the reporter to emit a strongly fluorescent
signal.
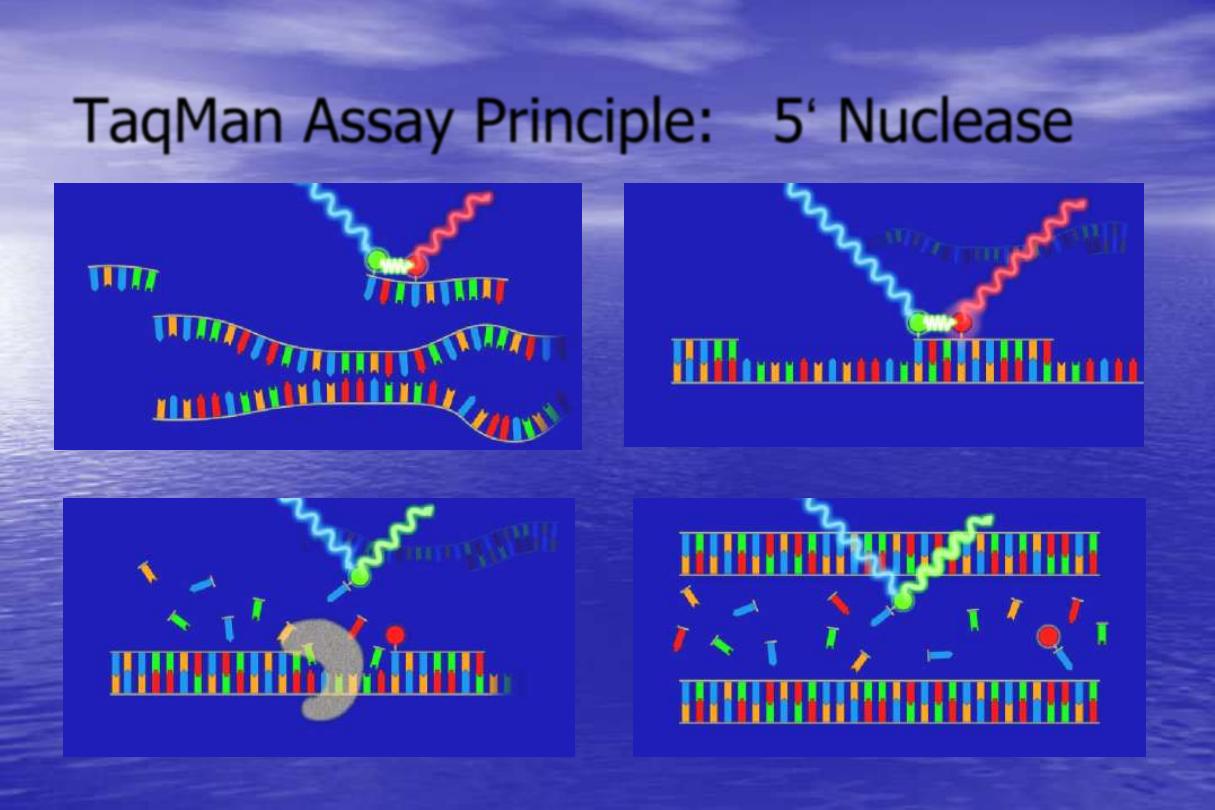
TaqMan Assay Principle: 5„ Nuclease
1
2
3
4

time PCR
-
real
TaqMan
Data analysis:
•
The detected fluorescence is captured and displayed as an amplification
plot.
•
Critical threshold line or assigned fluorescence level (AFL)
: is the
point at which a reaction reaches a statistically significant increase of
fluorescence over background.
•
Threshold cycle (CT) or Elbow
: is the cycle at which the sample
reaches the threshold level.
•
The CT is inversely proportional to the copy number of the target
template ,the higher the template concentration, the fewer the CT
measured.
•
Quantitation standard (QS)
: is a synthetic DNA or RNA designed to
closely resemble the actual target, is included in a known amount in each
and every test.
•
Quantitation of the target nucleic acid is accurately accomplished by
comparing the amplification plot values of the standard with the target.
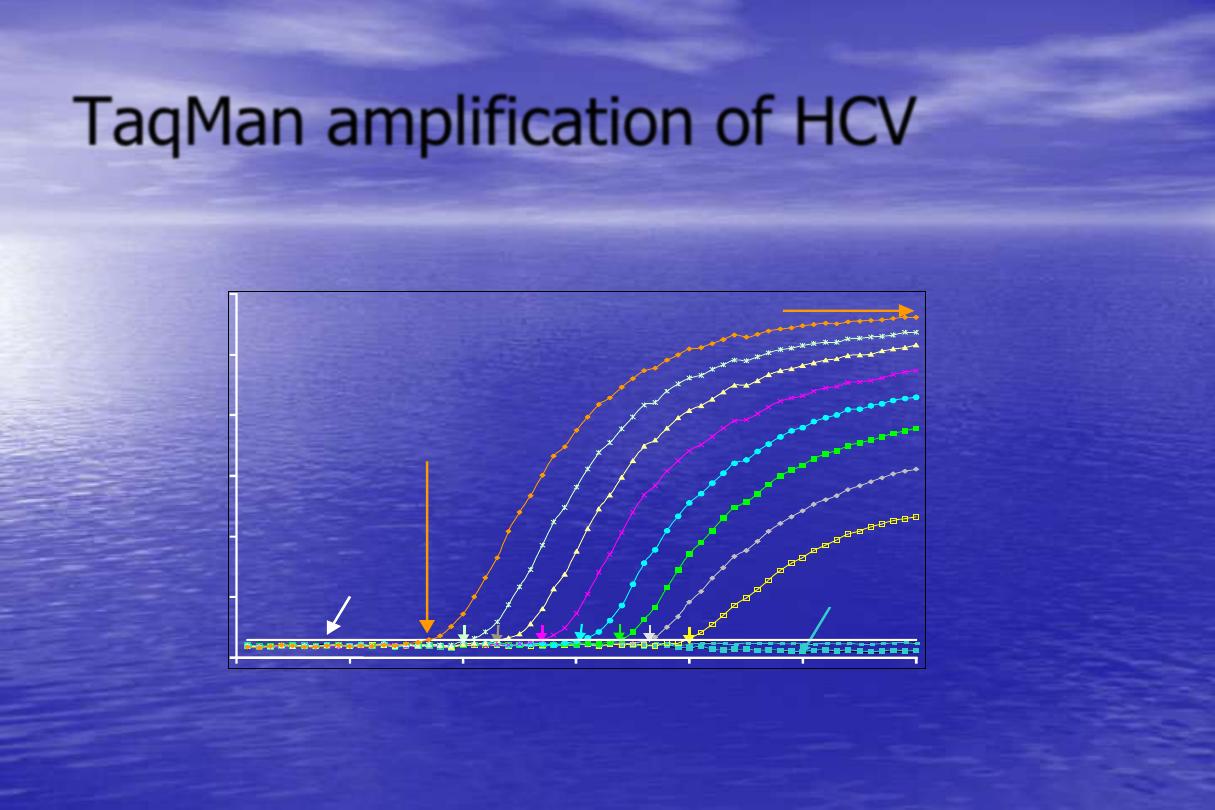
TaqMan amplification of HCV
HCV-RNAlog copies/PCR
Cycle threshold (Ct)
for 10
8
copies/PCR
Threshold
1
2
8
7
6
5
4
3
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
10
20
30
40
50
None
Cycle Number
HCV signal from 0 to 10
8
HCV-RNA copies/mL
Relative
fluorescence
from HCV

Analyzer
48
COBAS TaqMan

time PCR
-
SYBR Green Real
SYBR Green dye binds to dDNA and emits light when
excited.
SYBR Green detection of the PCR product is monitored
by measuring the increase of fluorescence caused by
the binding of SYBR Green to the increasing amounts
of dDNA.

time PCR
-
SYBR Green Real
Advantages :
Inexpensive approach as it is not necessary to
design specific probe dyes.
Easy to use and sensitive.
Disadvantages :
SYBR Green binds to any dDNA in the reaction
and leads to false positive results.

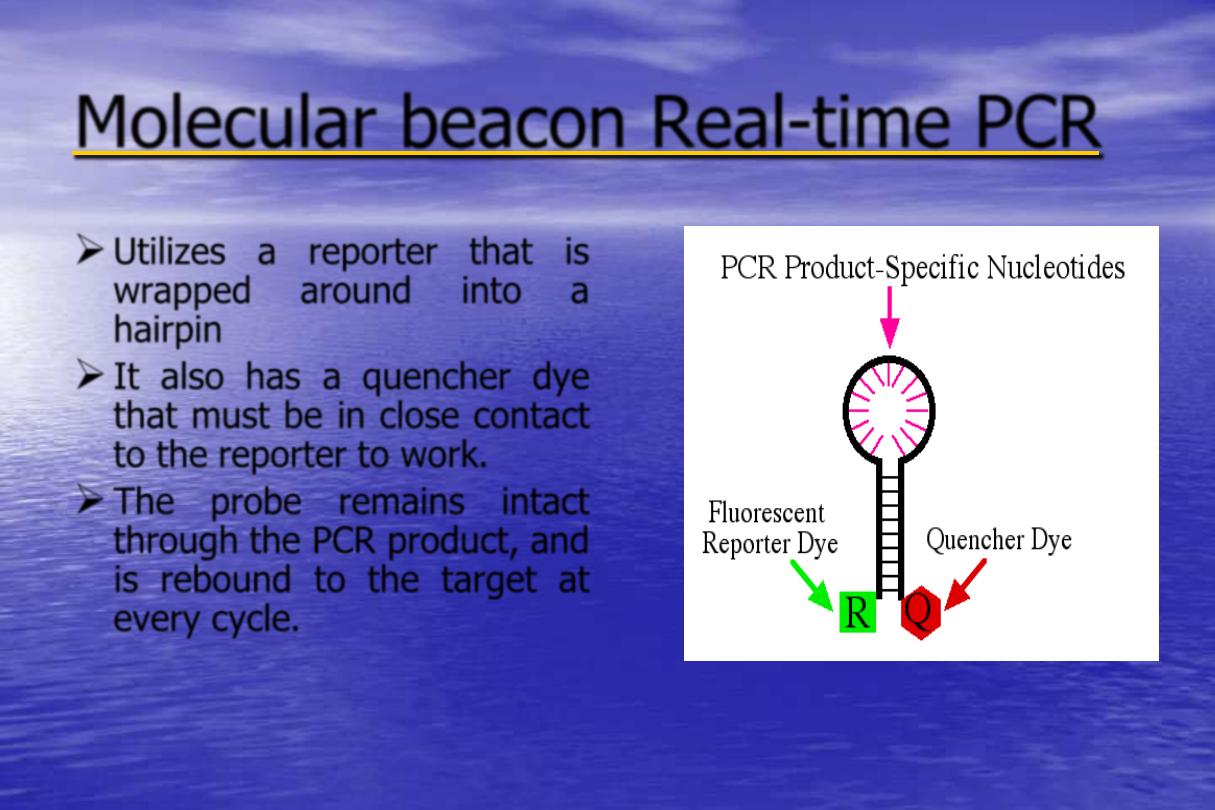
time PCR
-
Molecular beacon Real
Utilizes a reporter that is
wrapped
around
into
a
hairpin
It also has a quencher dye
that must be in close contact
to the reporter to work.
The probe remains intact
through the PCR product, and
is rebound to the target at
every cycle.
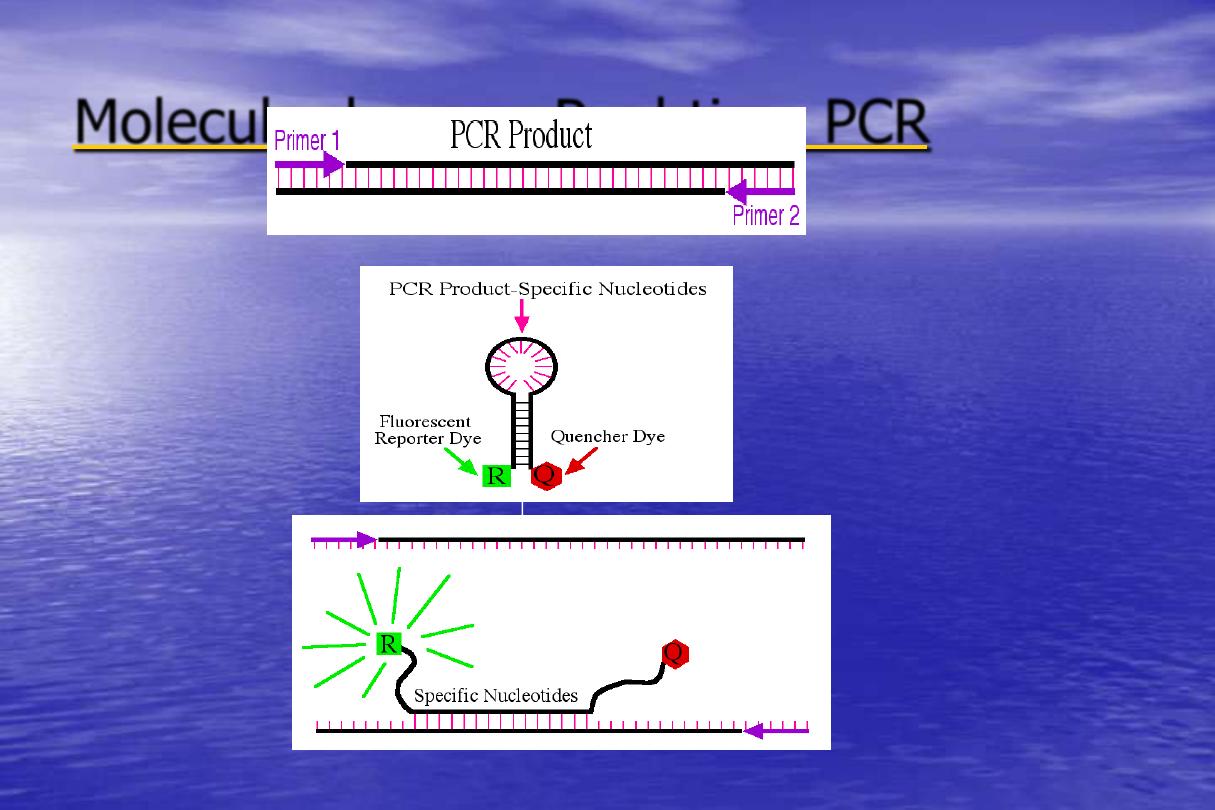
time PCR
-
Molecular beacon Real

Branched DNA assay (bDNA)
•
Branched DNA (bDNA) Signal Amplification
Assay is an alternative hybridization based
system for the sensitive and rapid detection of
agents of infectious disease. This molecular
technique amplifies the signal from a target
molecule rather than the target itself .

Branched DNA assay (bDNA)
Principle
•
This assay is a sandwich nucleic acid hybridization
procedure for the direct quantitation of nucleic acid.
The nucleic acid is captured to a microwell by specific
probes. A set of target probes hybridizes to both the
nucleic acid and the pre-amplifier probes. The amplifier
probe subsequently hybridizes to the pre-amplifier
forming a branched DNA complex.
•
Detection is by chemiluminescence using an alkaline
phosphates -specific substrate. The amount of light
detected is directly proportional to the amount of
bound nucleic acid.
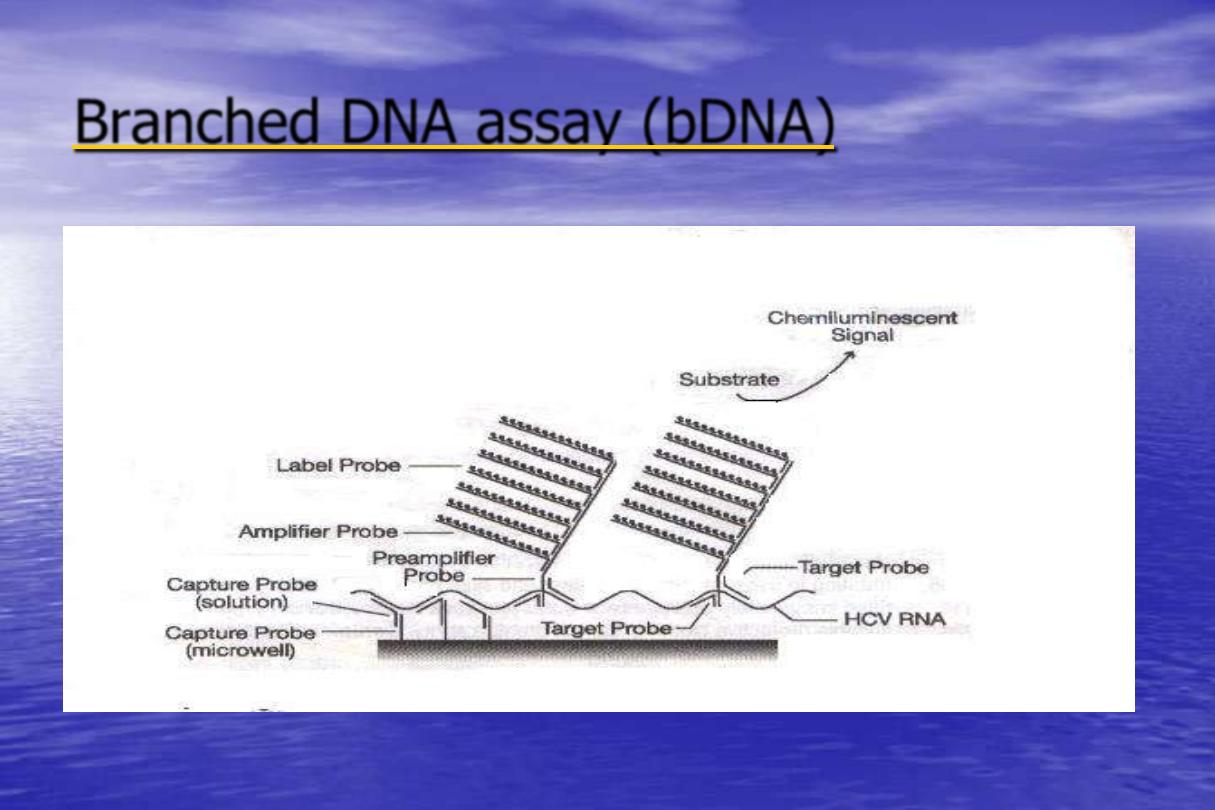
Branched DNA assay (bDNA)

Advantages of (bDNA)
One room technology.
No risk of contamination, as target is not
amplified (signal amplification).
RNA extraction not required.
High throughput of 168 samples/run.
