Alpha Hemolytic Streptococci
Viridans Group Streptococci & Pneumococci.• Department of Microbiology
• College of Medicine
• University of Baghdad
• Lec3, 2013-2014
• Dr.Sarmad M. Zeiny
Objectives: Upon completion of this lecture, the student will:
• Analyze the diseases & pathogenicity for viridans & pneumococci.• Demonstrate the epidemiology/transmission for viridans & pneumococci.
• Outline the laboratory diagnosis for viridans & pneumococci.
• State the drug of choice and prophylaxis where regularly used.
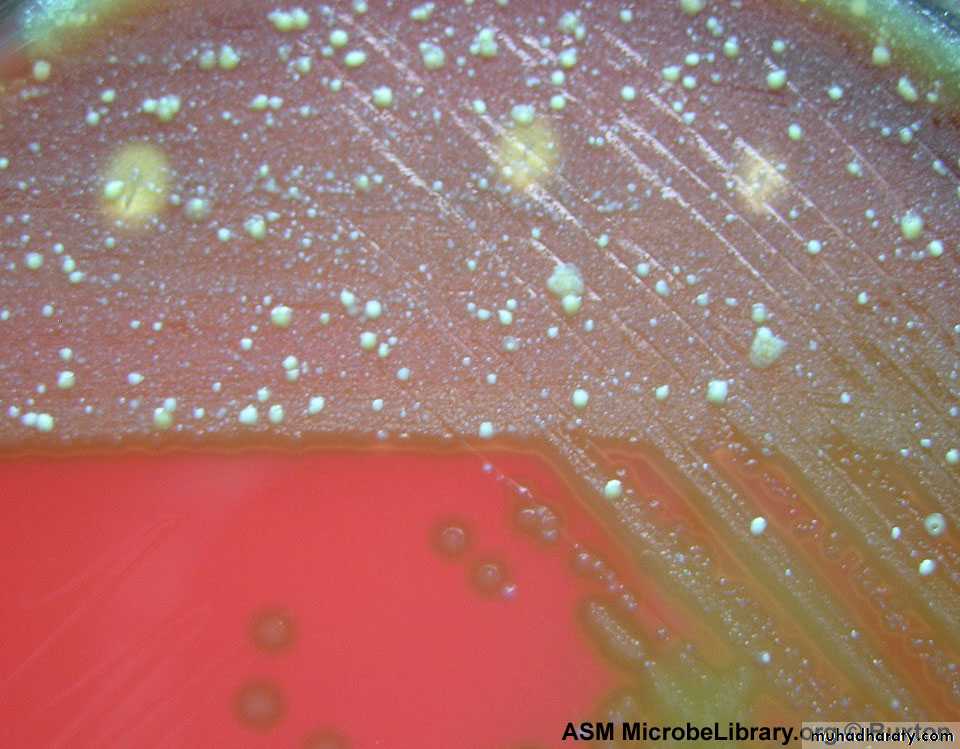
Alpha hemolysis (green discoloration)
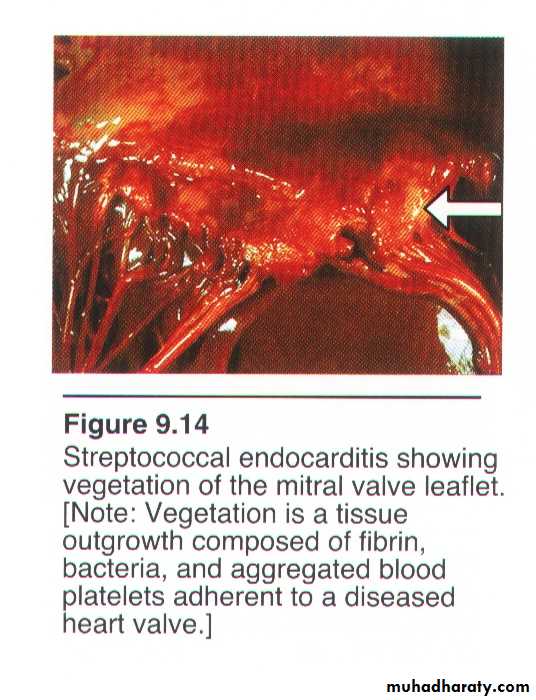
Viridans Streptococcus• Viridans Streptococcus is eating heart valves slowly, while Staphylococcus aureus is eating fast .
• Question?
• Why patient with abnormal heart valve should take antibiotic prophylaxis before tooth extraction?S.pneumoniae (Pneumococci, Diplococcus pneumoniae)
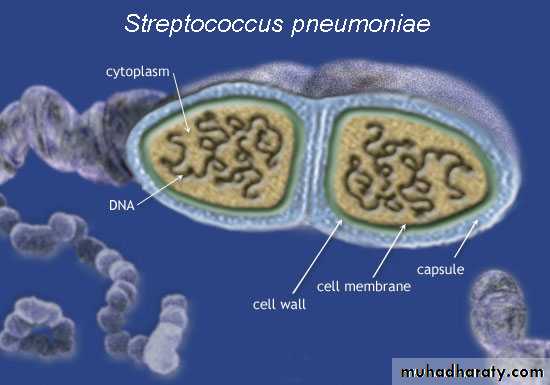
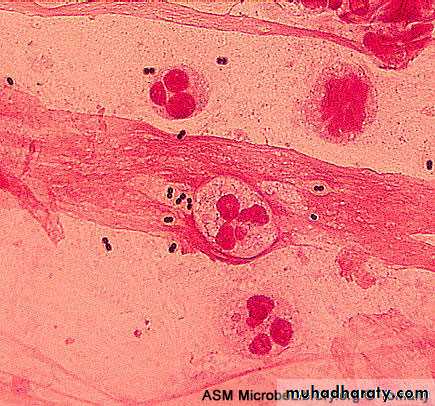
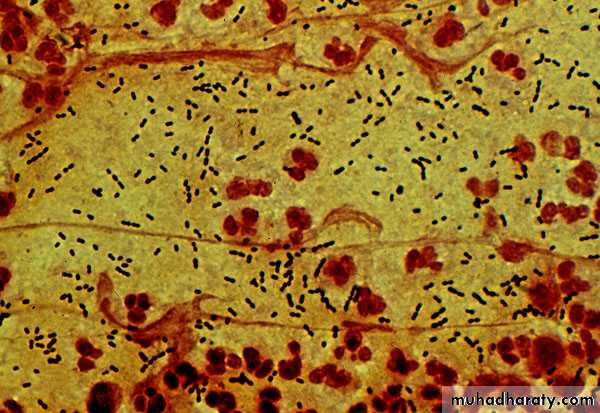
Distinguishing Features:α-hemolytic, capsulated G+ve diplococci.
Lancet-shaped diplococci (cat’s eye).
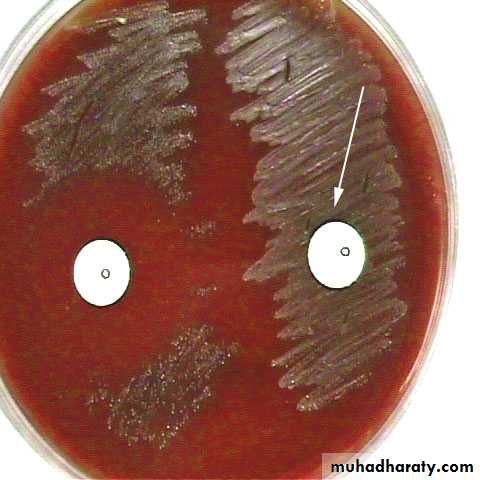
Optochin sensitive.
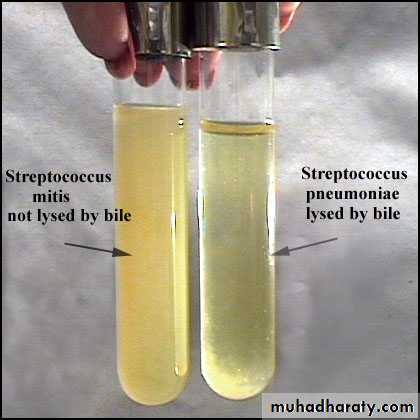
Lysed by bile.
Typed to 84 serotypes according to the nature of capsular polysaccharide antigen.
Capsular polysaccharide
Gram +VE diplococcusReservoir: human upper respiratory tract.
Transmission:By respiratory droplets:
- Not considered highly communicable.
- Often colonizes the nasopharynx without causing disease.
Predisposing Factors:
• Antecedent influenza or measles infection.
• Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
• Congestive heart failure (CHF).
• Alcoholism.
• Asplenia.
Virulent factors & Pathogenesis:
Polysaccharide capsule is the major virulence factor anti-phagocytosislgA protease Breakdown IgA
Teichoic acid. Rigid cell wall
Pneumolysin O: hemolysin/cytolysin
- Damages respiratory epithelium
- Inhibits leukocyte respiratory burst and
- Inhibits classical complement fixation
• The "pneumococcal warrior." He is a mighty foe, with "capsule" armor, a lung emblem on his shield, and a lancet-shaped diplococcus lance. The lung emblem on his shield shows the severe lobar pneumonia caused by this organism.
Diseases:
TYPICAL PNEUMONIA:- Most common cause (especially adult & elderly)
Shaking chills, high fever, lobar consolidation, blood-tinged, "rusty" sputum.
Pneumococcus is to Parents while group B streptococcus is to Babies.
ADULT MENINGITIS:
- Common cause.
- CSF reveals high WBCs (neutrophils), low glucose and high protein.
OTITIS MEDIA AND SINUSITIS IN CHILDREN:
• - most common cause
Prevention: by Vaccine
- Pediatric (PCV, pneumococcal capsular vaccine):
Seven of the most common serotypes
Conjugated to diphtheria toxoid
- Adult (PPV, pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine):
23 of the most common capsular serotypes
Recommended for all adults >65 years of age and any at-risk individuals
CHARACTER
PNEUMOCOCCIVIRIDANS STREPTOCOCCI
Morphology
Ovoid or lanceolate diplococci
Rounded cocci in short or long chains.
Capsule
Present
Absent
Optochin sensitivity
+ve
-ve
Bile solubility
+ve
-ve
Capsular swelling test (Quelling reaction)
+ve
-ve
Virulence in mice
+ve
-ve
Differences between Viridans & Pneumococci
Q: Answer with true or false
• Pneumococci is uncapsulated.
• Pneumococci is α-hemolytic.
• No vaccine for pneumococci.
• Pneumococci is bile soluble.
• Pneumococci can’t be differentiated from viridans streptococci.
Lab Dx
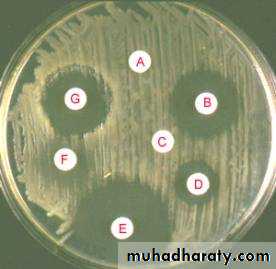
Optochin disc for S.pneumococci
India ink slide, see the Quelling reaction
Gram slide, see the diplococciQuestion? Name this test
summary• Alpha haemolytics streptococci causing greenish discoloration on chocolate agar.
• Viridans causes SBE in suspected individuals. AB prophylaxis needed.
• Pneumococci is capsulated and typed accordingly to 84 serotyped.
• Pneumococci is the leading cause of adult pneumonia.
• Pneumococci present in carrier state in 40-70% of healthy humans.
• Pneumococci & viridans can be differentiated by Optochin sensitivity, arrangement, bile solubility, Capsular swelling test (Quelling reaction) and serologically.
• Pneumococci can be prevented by a Vaccine causing Ab against capsular Ag.