1
Forth stage
Surgery
Lec-3
د
.أ
ح
م
د
ا
ب
ر
ا
ه
ي
م
3/4/2016
Tongue Cancer
It is the sixth most common cancer.
Etiology : male > female (both smoker)
Age >60y old
Geographical: India 40% because tobacco chewers and spicy food.
Predisposing factors: chronic irritation (smoke, spirit,sepsis) but not necessary to lead to
cancer
Precancerous lesions:
Erythroplakia
Leukoplakia
Chronic hyperplastic candidiasis
Oral submucous fibrosis
Oral lichen planus
Discoid lupus erythematosis
Discoid keratosis congenital
2
Pathology of tongue cancer
Lateral margin of anterior 2/3 of the tongue (45-55%) ,
Posterior 1/3 20% and
Less common site the ventral 9%, dorsal 6%.
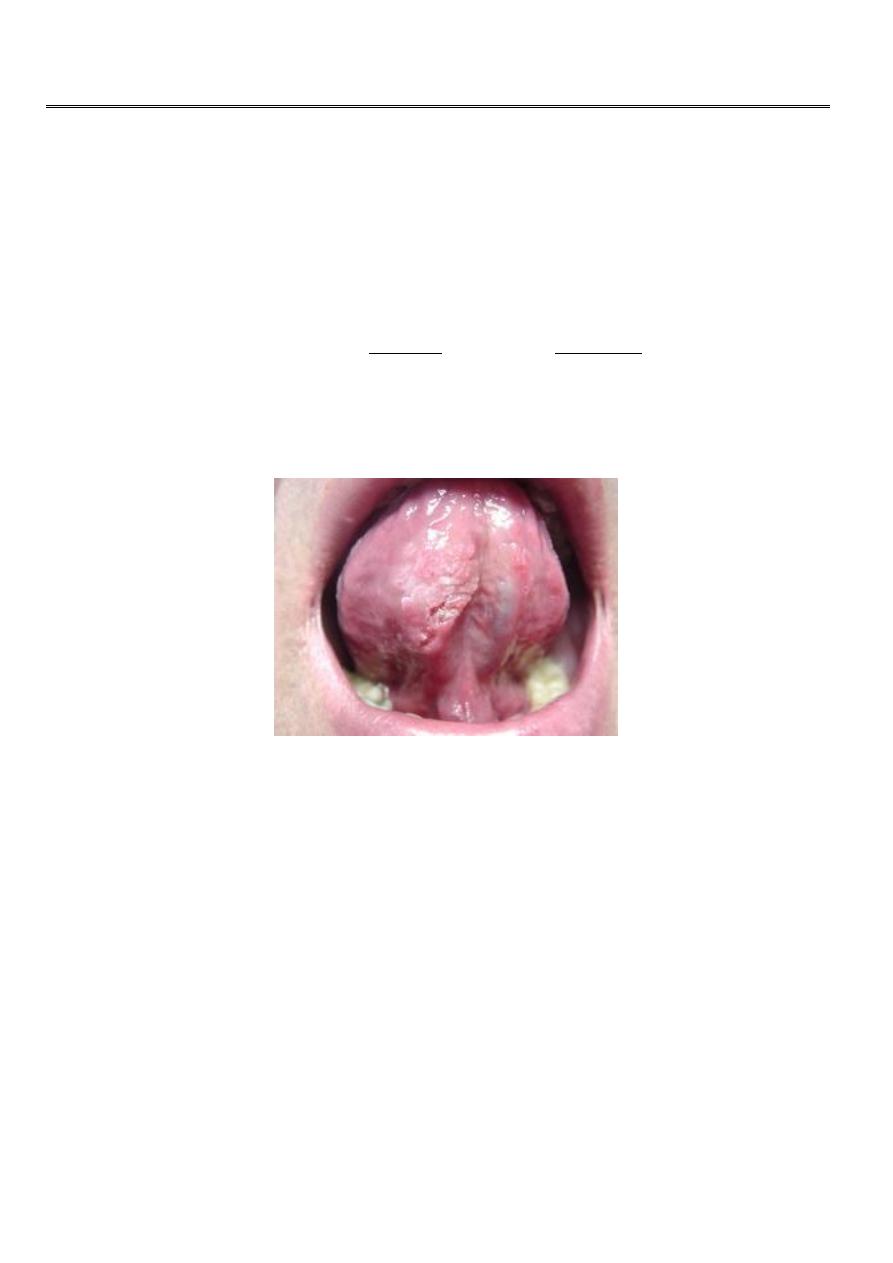
Grossly
Malignant ulcer raised, deep, irregular with necrotic floor and everted edge
Or raised oval white plaque that fungating, central necrosis or hard submucous
nodule or diffuse infiltrative (rare).
Microscopically
Ant 2/3 well differentiated SCC >95%.
Post 1/3 less differentiated
BCC and adenocarcinoma of minor salivary gland (rare
).
Spread
Direct: to nearby structure
(ant 2/3 to lat) and
(the post 1/3 to tonsil , pharynx ,larynx)
Lymphatic: to LN of the neck
lat 1/3 to submandibular and then to deep cervical LN .
Posterior 1/3 upper deep cervical directly.
Blood: rare mainly in the post 1/3
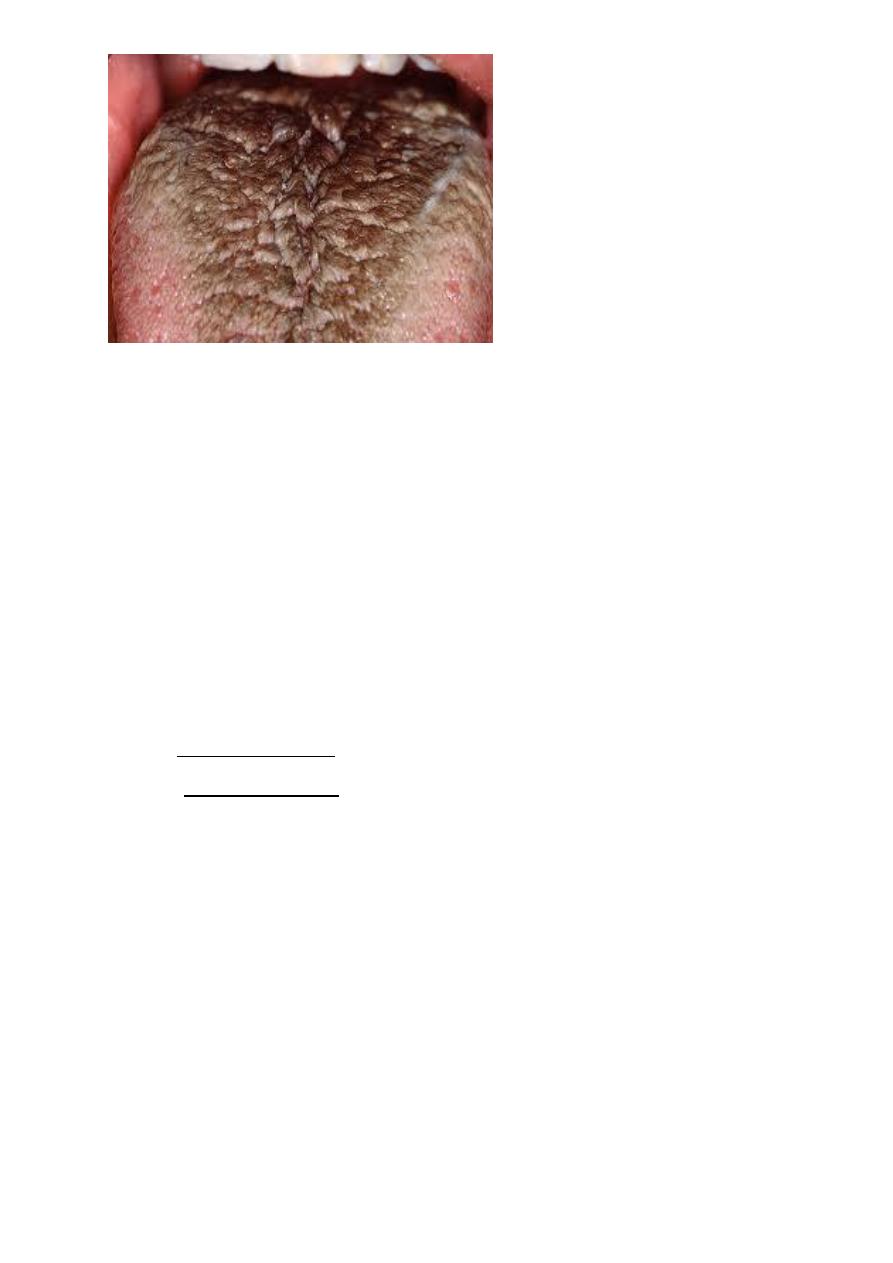
Hairy tongue

3
Clinical presentation
Symptomless.
Or persistent ulcer >4weeks
Or deep indurated fissure
Or oval raised papillated plaque and white keratin
Or lobulated mass with overlying yellow patch of submucous necrosis.
Late stage
Sore tongue the pain first due to infection then due to invasion of lingual n. it may
refer to ear.
Salivation due to pain and decrease tongue movement may be blood stained and bad
smell.
Enlarged cervical LN (usually painless).
Complications:
1. Inhalation of necrotic tissue lead to bronchopneumonia
2. Cachexia due to dysphagia and pain
3. Bleeding due to invasion of lingual vessels or ICA in post 1/3 tumor
4. Asphyxia due to enlarged LN or glottic edema .

4
Investigations
Incisional biopsy for lesion >4weeks UGA or LA
FNAC
MRI or CT to see the invasion
Treatment
Lines of treatment: surgery and radiotherapy while chemotherapy as adjuvant in some
cases.
Surgery
1. CA in situ = local excision +1 cm safety margin in extent and 0.5 cm in depth ,the defect
closed directly or flap from floor of the mouth .
2. Partial or hemiglossectomy using cutting diathermy or laser. The defect closed by radial
flap or rectus abdominis or forehead flap.
3. CA post 1/3 = either total or external radiation
4. If LN metastases so excision of tumor with neck dissection (modified or radical).
5.
Mandible invasion = hemiglossectomy +hemimandibulectomy +neck dissection
(commando operation
)
Radiotherapy
Tumor <4 cm equally benefit from RT or surgery
Palliative treatment
Radiotherapy
Palliative resection of 1ry to comfort the patient
Analgesia+NG feeding,trachistomy
Chemotherapy
Radiofrequency thermal ablation(minimal invasive therapy)
Gene therapy new treatment gene manipulation to change genetic code in persons
cells.
A.L.Y
