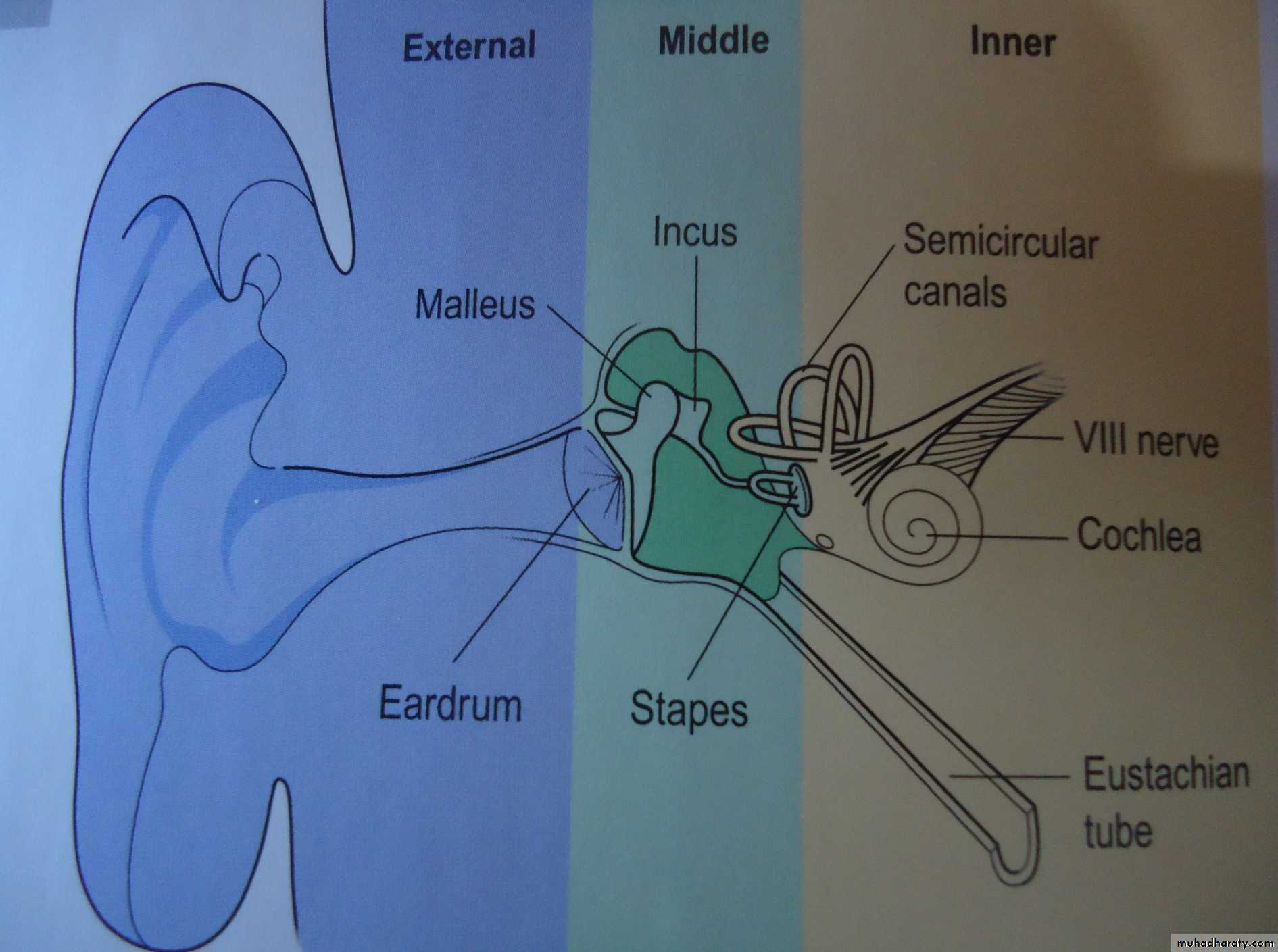
AUDITORY FUNCTION
Conductive hearing loss: there is obstruction of external auditory canal or disease of middle ear.
Sensorineural hearing loss: disease affecting cochlea or cochlear nerve.
Mixed type
Objectives:
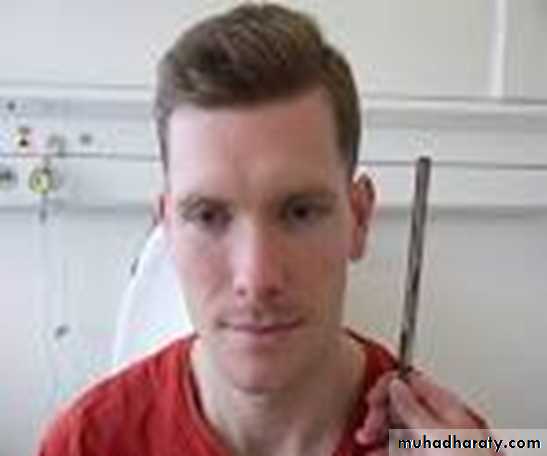
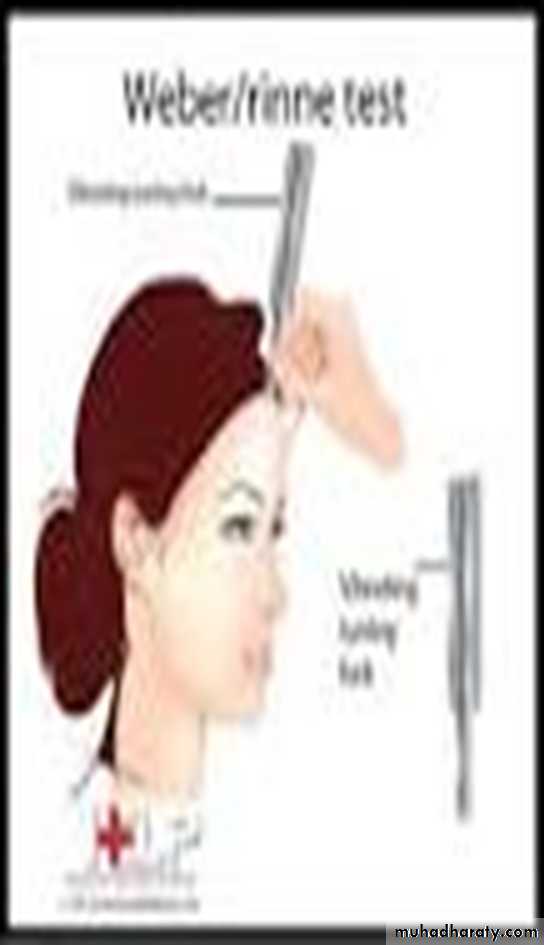
To examine and compare air and bone conduction of the subject .instruments :Vibrating tuning fork (512 Hz).
Rinne's test
Base of vibrating tuning fork placed on mastoid process until subject no longer hears sound then the vibrating top is placed one inch from the external ear canal (air).Normally : The subject hears vibrating of the tuning fork in air after bone conduction is over. This is called Rinne's positive (i.e air conduction is better than bone conduction).
In conductive hearing loss: (one ear) : patient does not hear vibration in air after bone conduction is over this is called Rinne's negative
In sensorineural hearing loss : (one ear), patient hears vibration in air after bone conduction is over.i.e Rinne's positive
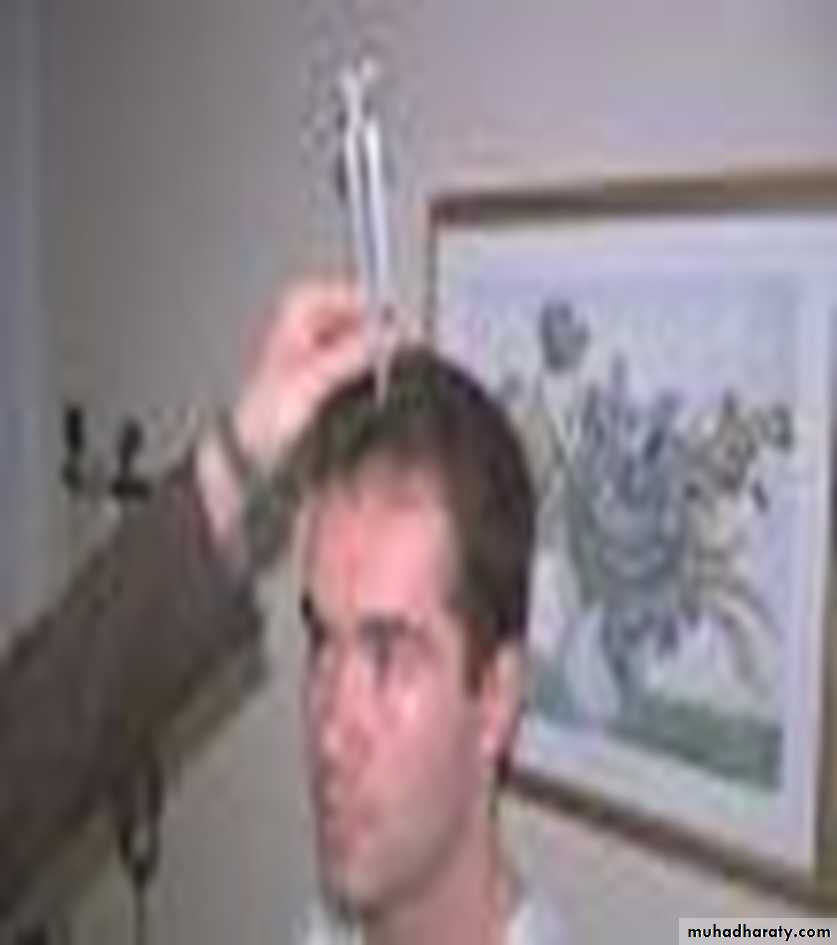
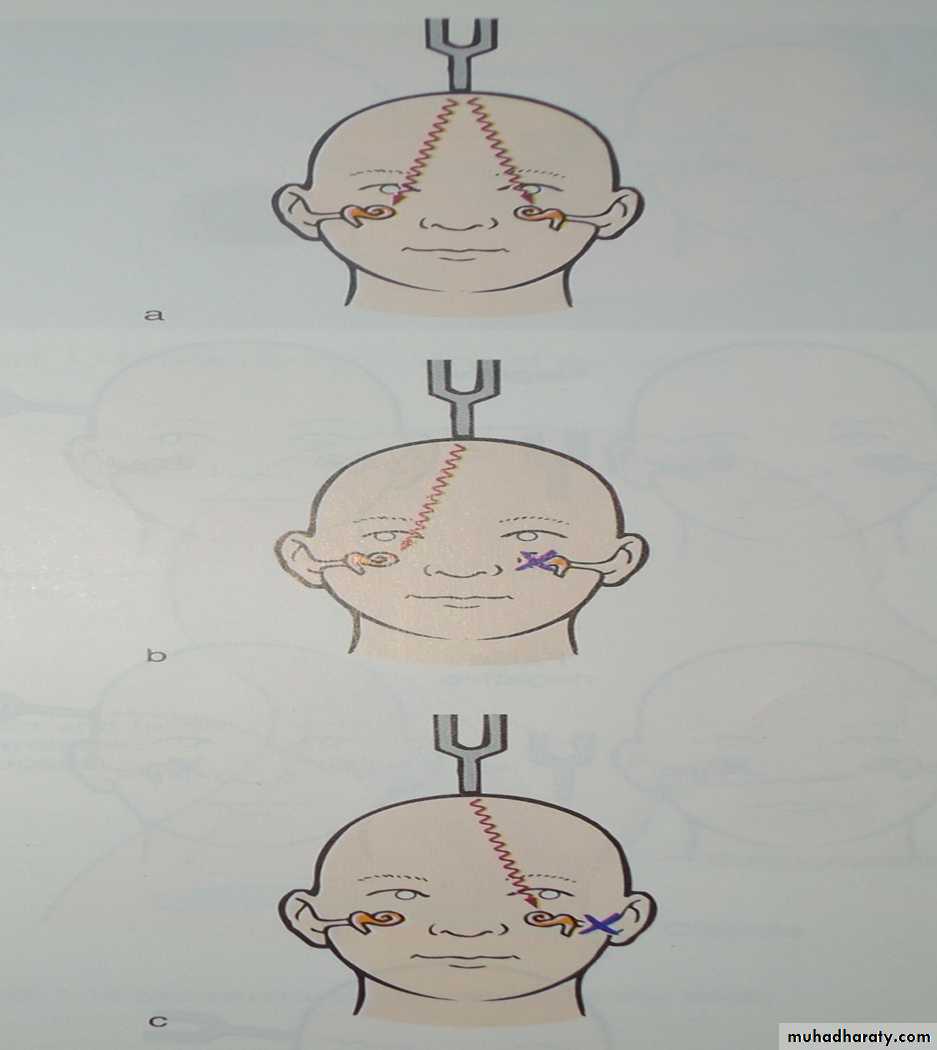
Weber's test
The base of vibrating tuning fork is placed on the patient's forehead or the nasal root exactly in the midline.Normally : Subject hears equally on both sides
In conductive hearing loss (one ear) : The sound of the vibrating tuning fork is louder in diseased ear because masking effect of environmental noise is absent in diseased side.In sensorineural hearing loss (one ear): sound louder in normal ear .
sensirineural
Normalconductive
Schwabach's test
In this test we compare bone conduction of the patient with that of a normal subject .
Normally: bone conduction is the same for examiner and patient
In conductive hearing loss: bone conduction is better than examiner.
In sensorineural hearing loss: bone conduction is less than examiner.
Rinne's test
Weber's testSchwabach's test
Normally
air conduction is better than bone conduction
hears equally on both sides
bone conduction is the same for examiner and patient
Conductive hearing loss
patient does not hear vibration
in air after bone conduction is over
Hears the sound louder in diseased ear
bone conduction is better than examiner
Partial sensorineural hearing loss
air conduction is better than bone conduction
Hears the sound louder in normal ear
bone conduction of patient is less than examiner
Complete sensorineural deafness
Hears no sound in both air and bone
Hears the sound louder in normal ear
bone conduction of patient is less than examiner
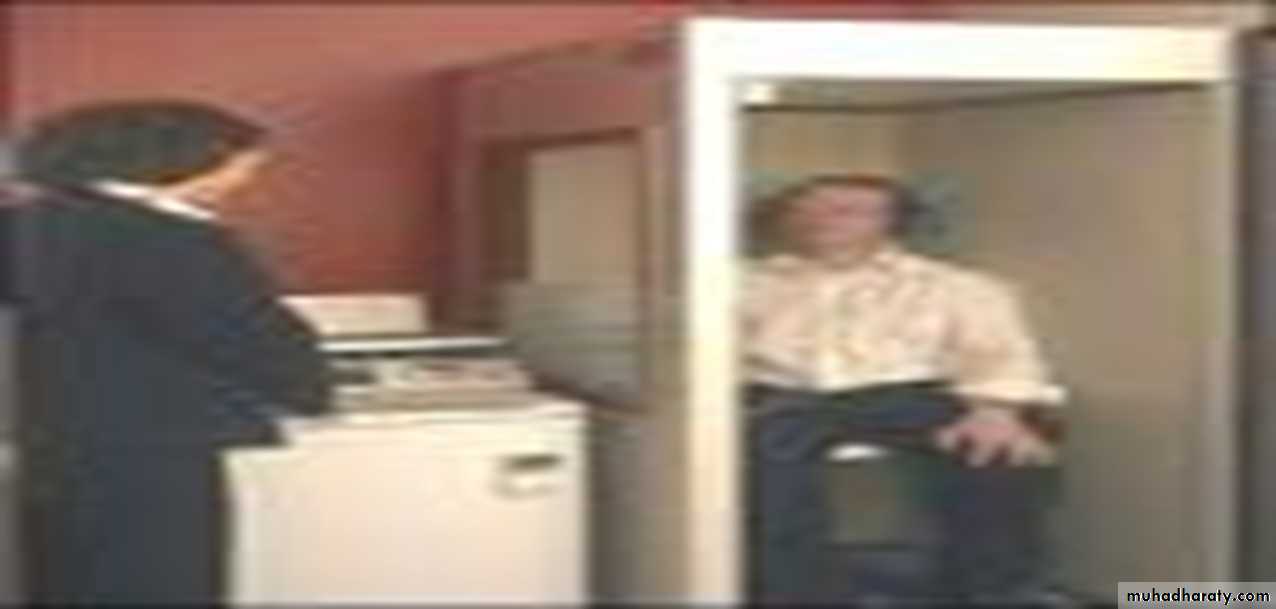
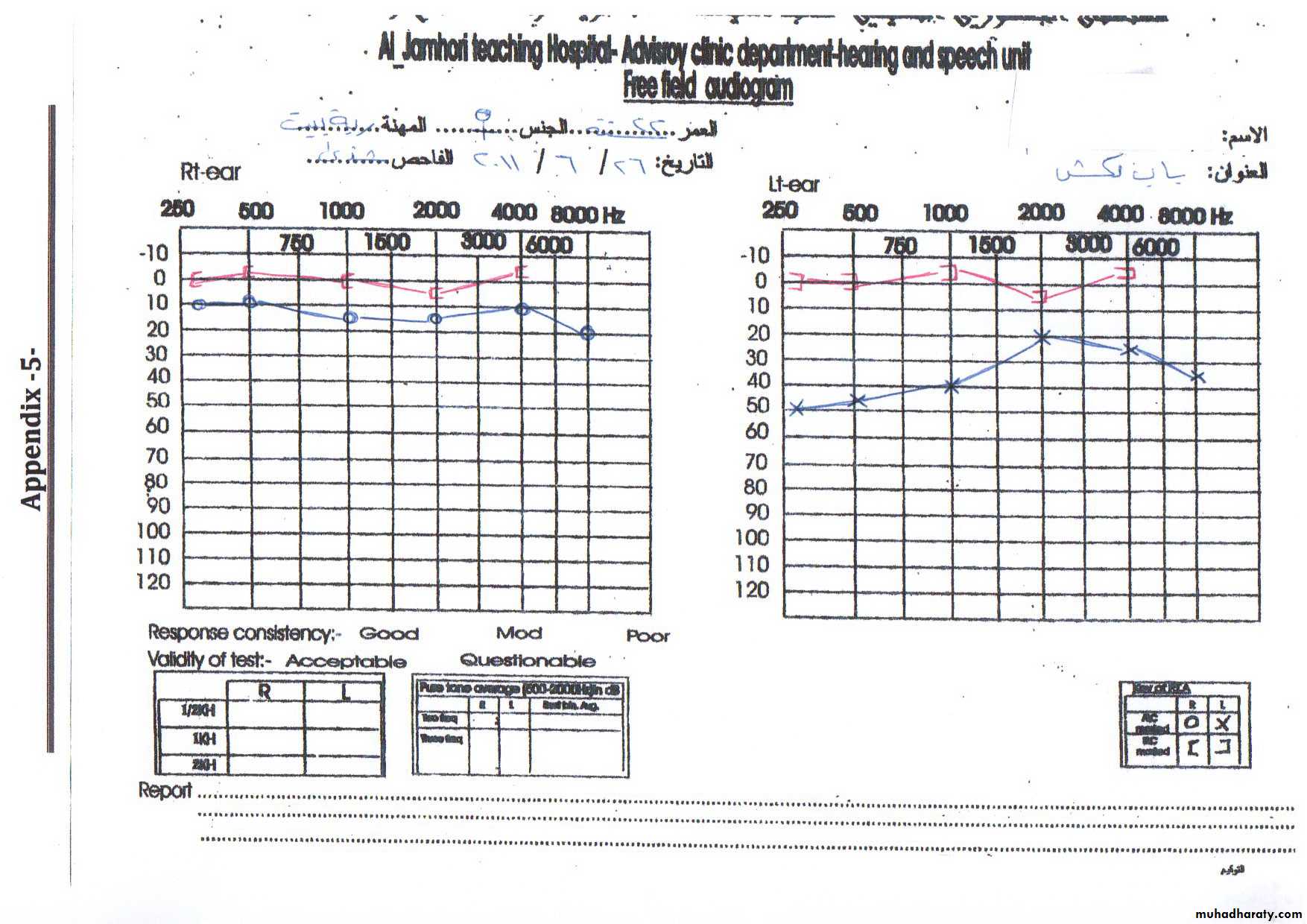
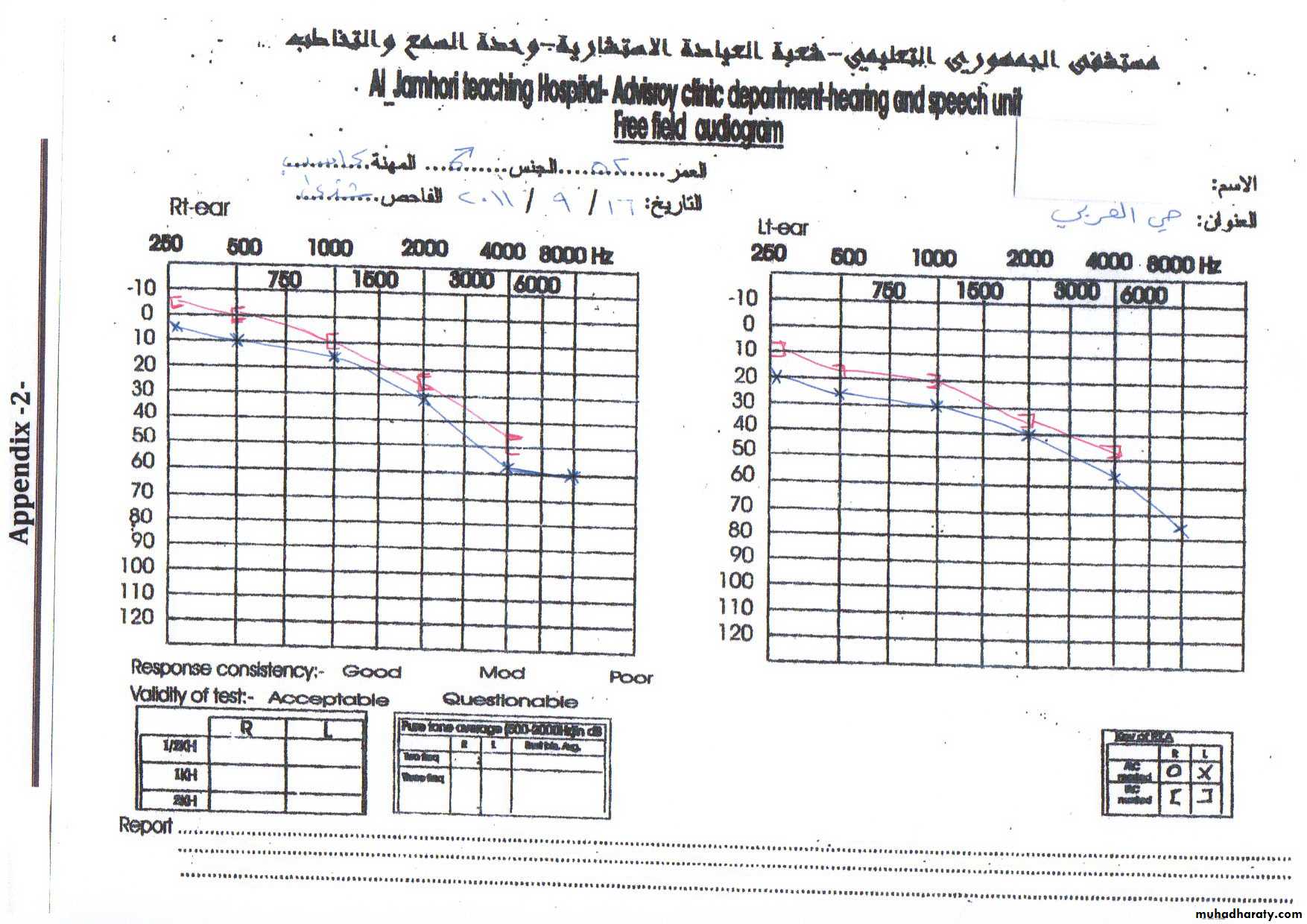
Audiometer
instrument to assess hearing in person with hearing problem.
pure tones at various frequencies are generated ,and their levels are increased and decreased until threshold are found .
Objective of the test
1-Shows whether hearing is normal or not2-If the hearing is abnormal ,it shows the severity of
hearing loss3-Also it shows type of hearing loss whether conductive or sensorineural or mixed type .
How to do the testIn isolated room first we measure air conduction by using ear phones ,we deliver sounds for each frequency we change the intensity till we get the lowest intensity which the subject hear.
The same is done for bone conduction .but we used bone vibrator instead of the ear phones.
So the graphic representation between frequency and intensity called audiogram