Endodontics
Endodontia(within the tooth) is the branch of dentistry concerned with the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases of the dental pulp and its surrounding periradicular (peri =around, radi =root) tissues
Endodontics
Clinical Examinations
Clinical examinations used to diagnose the degree of pulpitis of an affected tooth may be any or all of the following:palpation: application of finger pressure to body tissues, including gingiva.
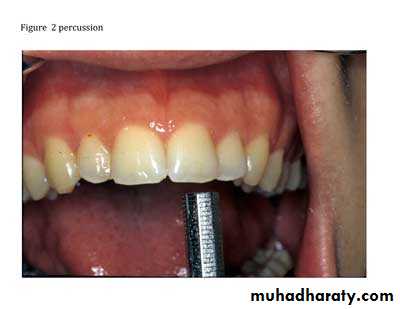
percussion ( tapping of body tissue, tooth): usually done by tapping a dental mirror handle on an affected tooth and comparing the sensation to tapping on a healthy or control tooth.mobility (capable of movement): movement of a tooth in its socket during outside force or pressure application.
thermal (pertaining to temperature): pulp sensitivity test with reaction to applications of heat and/or cold to tooth surface.
direct dentin stimulation: scratching the exposed dentin with an explorer; the presence of pain indicates inflamed or irritated pulp tissue.
laser Doppler flowmetry (LDF): to determine blood flow of pulp tissue, and pulse oximetry to assess pulp vitality.
Electric pulp testing: applying an electrical current on the enamel surface of the tooth to register the tooth’s pulpal sensitivity and presence of irritability.
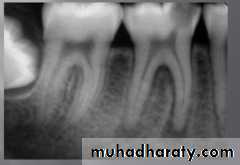
radiograph: X-ray examination with digital zoom and color contrasting ability permits a deeper insight to the pulp canal.
Periradicular Diagnosis
The principal diagnosis involving pulp tissues is to determine if the pulp is vital or nonvital. The periradicular tissue diagnosis may involve more pathologic conditionssuch as:
periodontitis( peri = around, dont = tooth,itis =inflammation): in acute apical periodontitis, a sharp, painful inflammation of tissues occurs around an affected tooth. Pain is lessened or eliminated by removal of the inflamed or necrotic pulp. A chronic apical periodontitis requires management similar to the acute symptoms.
abscess( local pus infection): an infection that may be an acute or
chronic apical abscess; also called suppurative (producing or generating pus).cyst : abnormal, closely walled fluid or exudates-filled sac in or around periapical tissues.
cellulitis : inflammation of cellular or connective tissue.
osteomylitis : an inflammation of the bone and bone marrow, usually caused by bacterial infection
Endodontic Treatment Procedures
An affected or irritated pulp may need one of several treatment procedures:pulpotomy: partial excision of the dental pulp, usually reserved for childrens
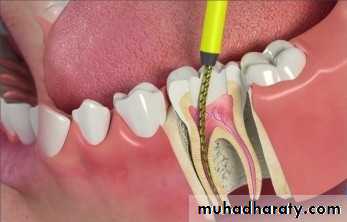
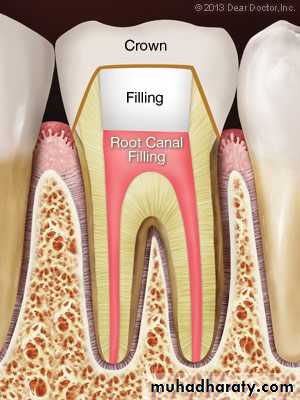
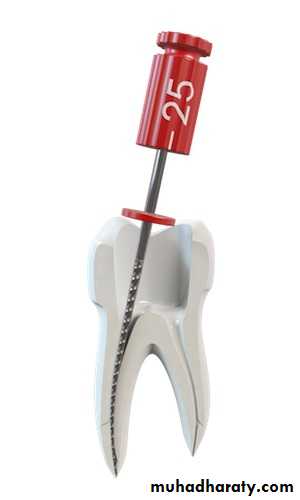
pulpectomy: surgical removal of pulp from the tooth,also known as root canal treatment (RCT)
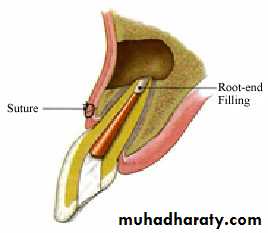
apicoectomy: surgical amputation of a root apex.
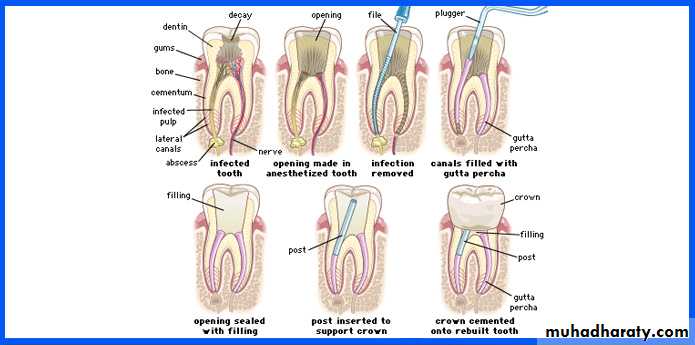
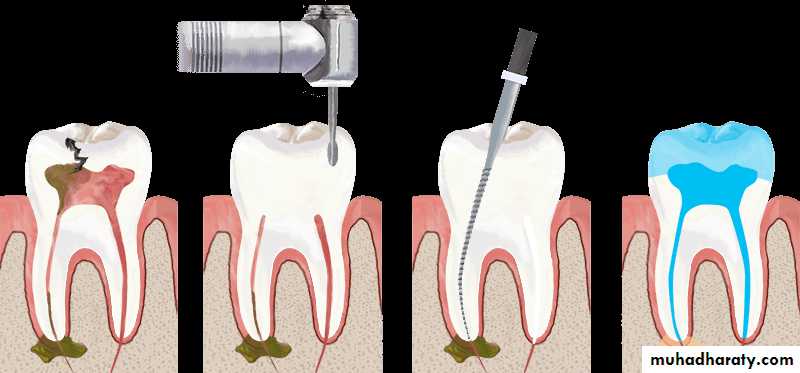
Root Canal Treatment
The standard treatment for a root canal has the following steps:1- anesthesia
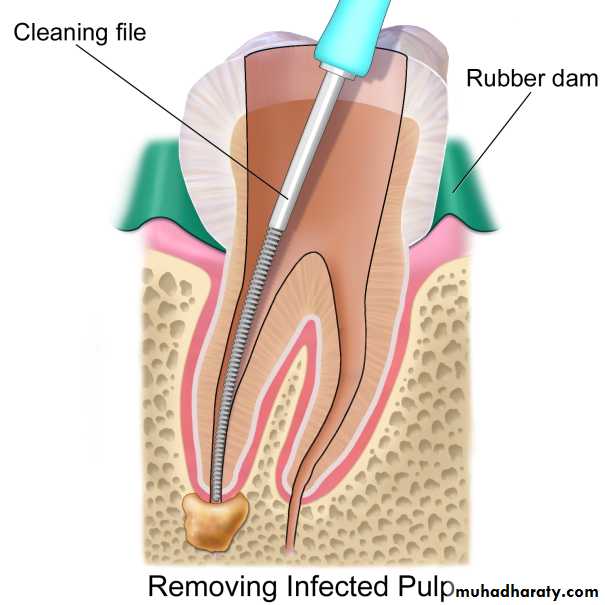
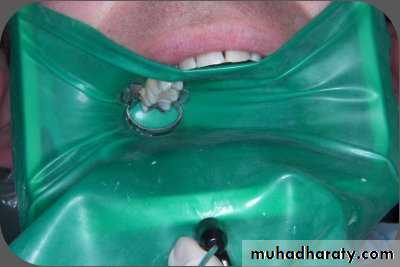
2- isolation of the operative area: accomplished to provide safety and to assure an aseptic(without disease) site.
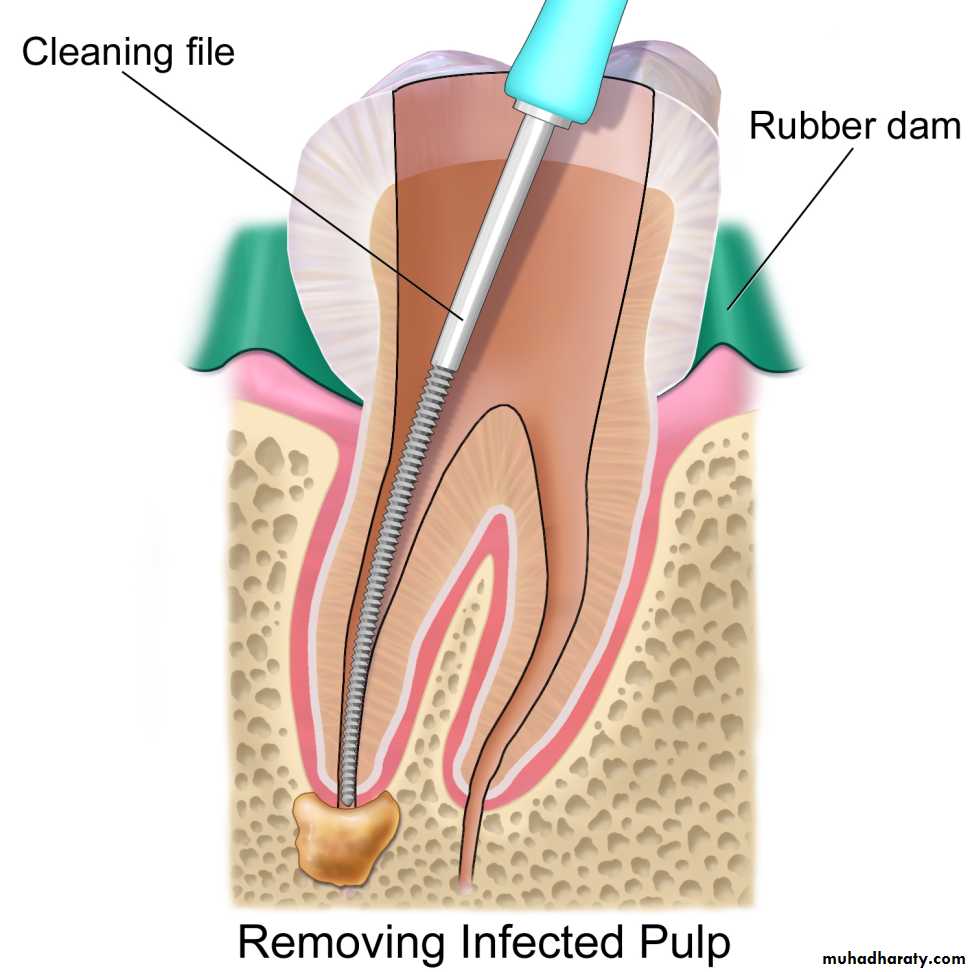
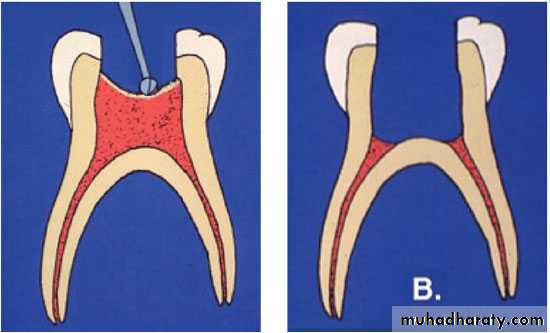
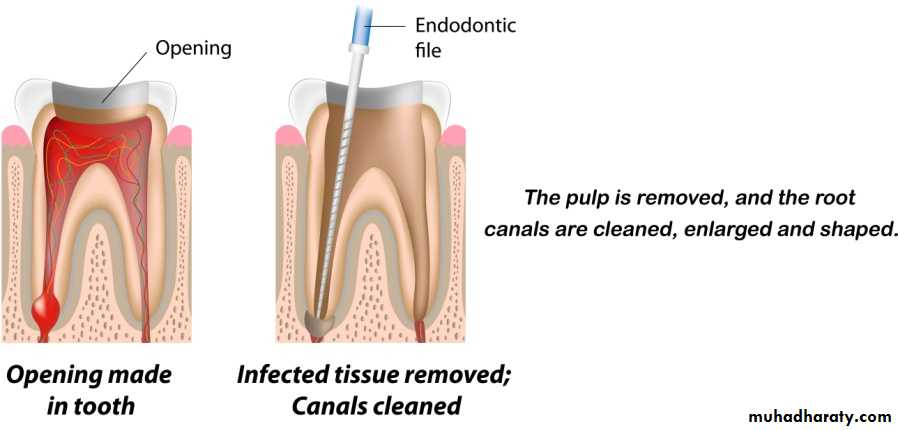
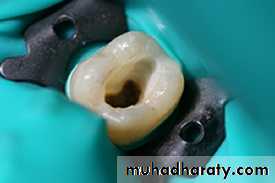
3- extirpation(to root out): removing the pulpal tissue after the pulpal opening.
4- debridement(removal of foreign or decayed matter): removing necrotic pulpal tissue and cleaning out the area.Root Canal Treatment
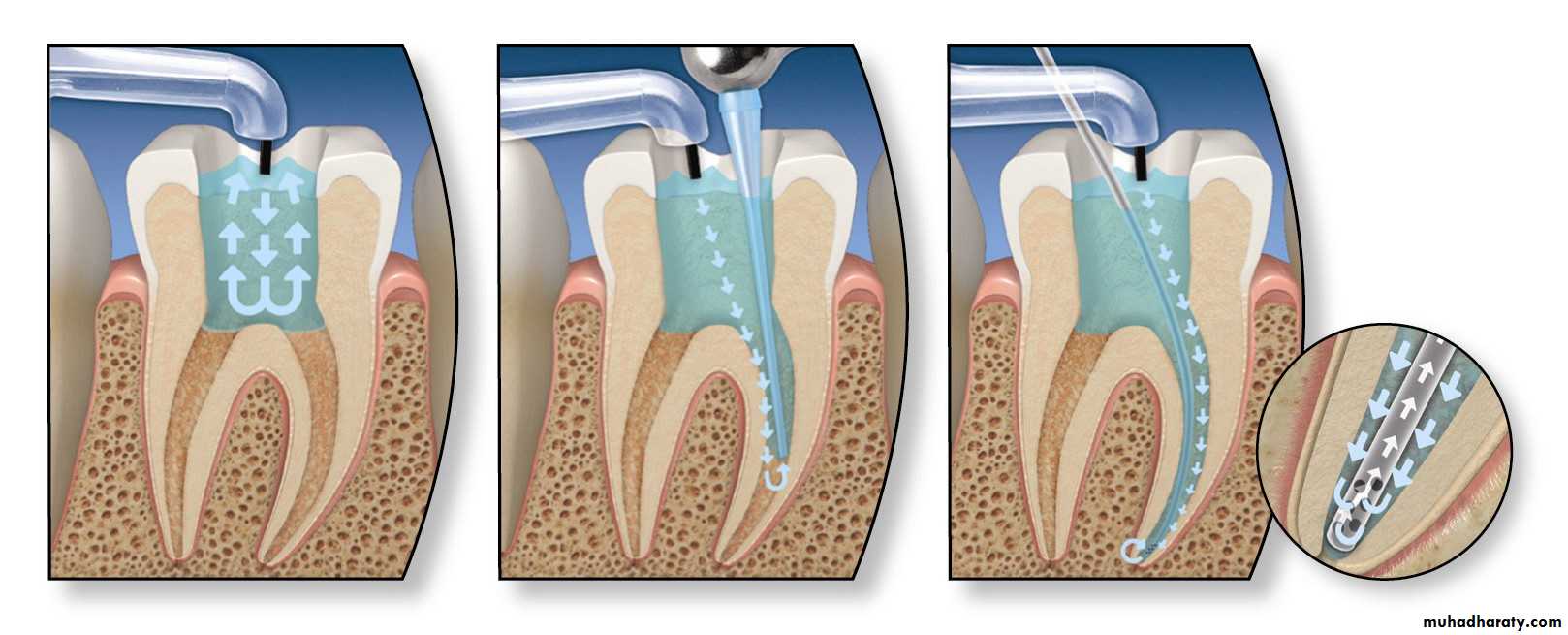
5- irrigation and cleansing:
using chemicals (sodium hypochlorite, and hydrogen peroxide are used for cleaning and sterilizing pulp canal ) and instruments to remove tissue dust and material matter from the pulp and pulp canals.Root Canal Treatment
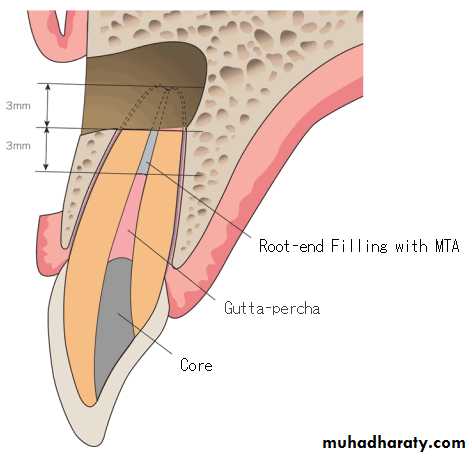
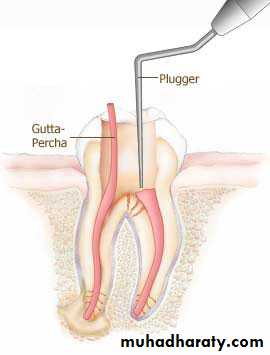
6- obturation(to close or stop up): filling and closing the canal area.
7- restoration: returning the tooth to normal function and purpose,Root Canal Treatment
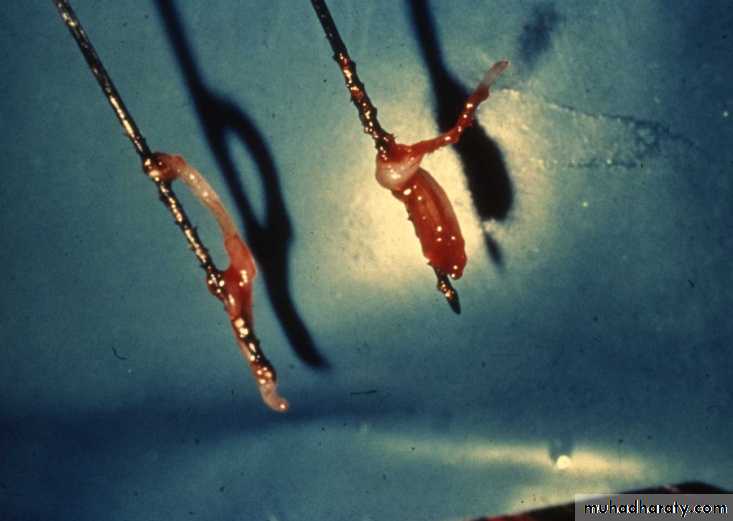
broach: a thin, barbed, wired instrument inserted into the root canal to ensnare and remove the pulp tissue and any natural or placed matter, such as paper points or cotton pellets.
Root Canal Treatment Instrumentation
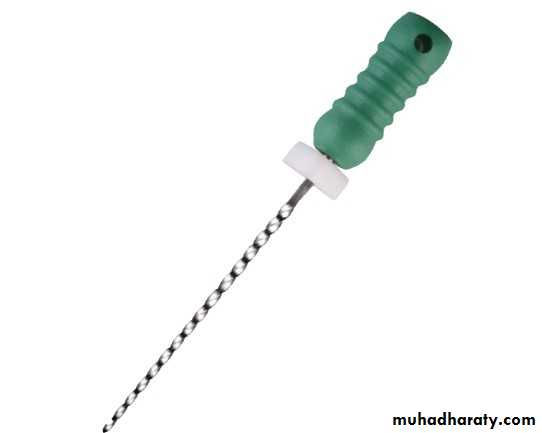
reamer: a thin, twisted, sharp-edged instrument inserted into the canal and rotated clockwise to enlarge and taper the root canal.file: a thin, rough-edged instrument used to plane and smooth pulpal walls.
Root Canal Treatment Instrumentation
paper points: small, narrow, absorbent, paper tips that may be inserted into the prepared canal; used to dry the prep site
stopper: a small piece of elastic band or commercial plug that is moved up or down the shaft of the endo instrument; used to mark and indicate the length
of penetration
stopper
gutta-percha points: tapered points made of a thermoplastic compound; similar in size to endodontic instruments, and used to fill the root canal; may be millimeter marked along length to help determinepenetration insert length.
Endodontic Materials
cement pastes and fillers: used to cement points in canal.Endodontic Materials
Not all treatments of inflamed or necrotic pulps require RCT. Some endodontic procedures involve surgical treatment that may or may not be included in the endodontic RCT. Related terms are:curettage (scraping of a cavity): scraping of the apical area; may be necessary to remove necrotic tissue.
Surgical Endodontic Treatments
apicoectomy: a procedure that may be necessary
to remove the root apex, particularly where there is a radicular cyst involvement of the affected tooth; also called root end resectionroot amputation(surgical removal of body part, root):
separating and removing molar roots of affected tooth at the junction into the crown
Surgical Endodontic Treatments
root hemisection(cutting tissue or organ in half): surgical division of multi-rooted tooth that may be performed in a lengthwise
manner
Surgical Endodontic Treatments
Besides treating the infected pulp, the endodontist performs varied procedures for traumatized( wounded) teeth, with a variety of pulp injuries:
1- luxation(dislocation): tooth movement that may be classified in one of the following ways:
Endodontic Treatment of Traumatized Teeth
A- concussion(shaken violently): tooth loosened as a result of a blow; usually recovers with minimal attention.B- subluxation(sub=under, luxation =displacement): tooth partially dislocated; evidence of bleeding but requires only minor attention.
Endodontic Treatment of Traumatized Teeth
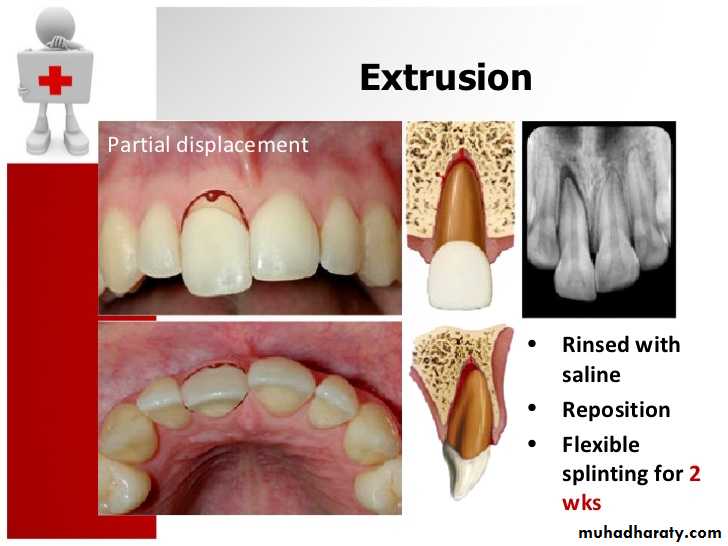
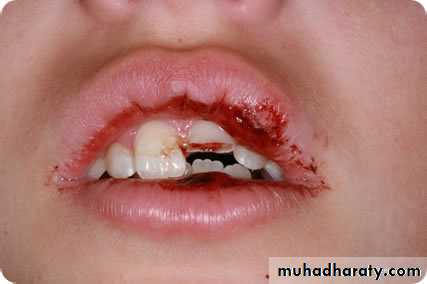
C- extruded(pushed out of normal position) luxation: tooth may be forced partially out of its socket.2-fracture: breakage; may be a broken cusp, broken crown, broken root, or a split tooth.
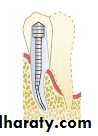
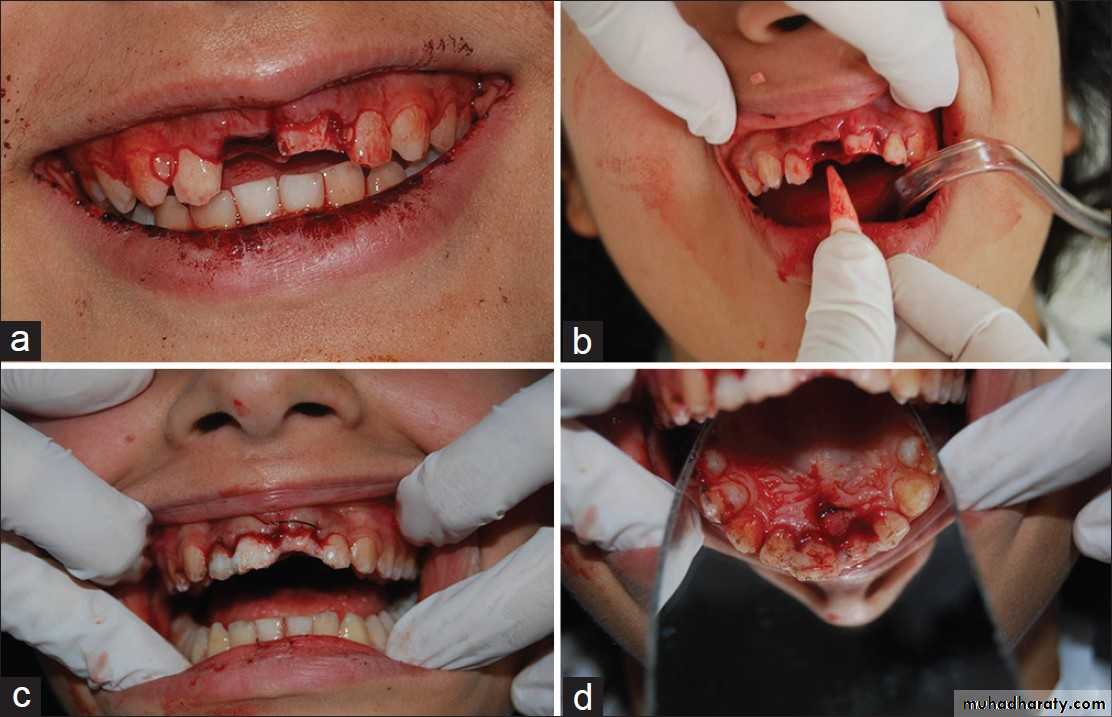
avulsion( forced or torn away)replantation(again, plant =place): of teeth that have been accidentally lost; may undergo RCT at this time or at a future appointment.
Tooth Replantation Procedures
Some additional endodontic procedures, although not common, are an essential part of pulpal therapy:replantation:replacing an avulsed tooth in its tooth socket.