SKIN TUMORS
Dr. Ihsan Al-Turfy
Consultant Dermatologist
College of Medicine/Baghdad
MBChB,DDV,FICMS,CABD

Tumor
Definition
: Is an
abnormal growth of tissue.
This
abnormal growth usually but not always forms a
mass.
They can be
benign or malignant
Any cellular element of the skin can produce tumors

Benign
tumors of the skin
1.Hemangioma-. From bv
2. Lymphangioma.- Lymphatics
3.Neuroma. -Nerves
4.lipoma. Adipose tissue
5.Fibroma-- fibrous tissue
6. Epidermal cell tumors(Including its appendages):
(Keratinocytes & Melanocytes-mainly)

A. Pigmented nevi.( Melanocytes)
Melanocytic nevi
: are benign neoplasms or
hamartomas
(Hamartoma is Abnormal Collection of
normal tissue consituents)composed of melanocytes,
{the pigment-producing cells that constitutively
colonize the epidermis} ( Melanocytes are present in
the
basal layer of the epidermis
) Melanocytes are
derived from the neural crest and migrate during
embryogenesis to selected ectodermal sites
(primarily the skin and the CNS), but also to the
eyes and the ears.

Melanocytic nevi…..
They are divided into
congenital and acquired
types.
Conventional or common
acquired
melanocytic nevi
are generally less than 1cm in diameter and evenly
pigmented. They are of three types:
Junctional ,compound, and dermal

Melanocytic nevi….
Congenital
:
are thought to represent an anomaly in
embryogenesis and, as such, could be considered,
at least in a sense, malformations or
hamartomas
.
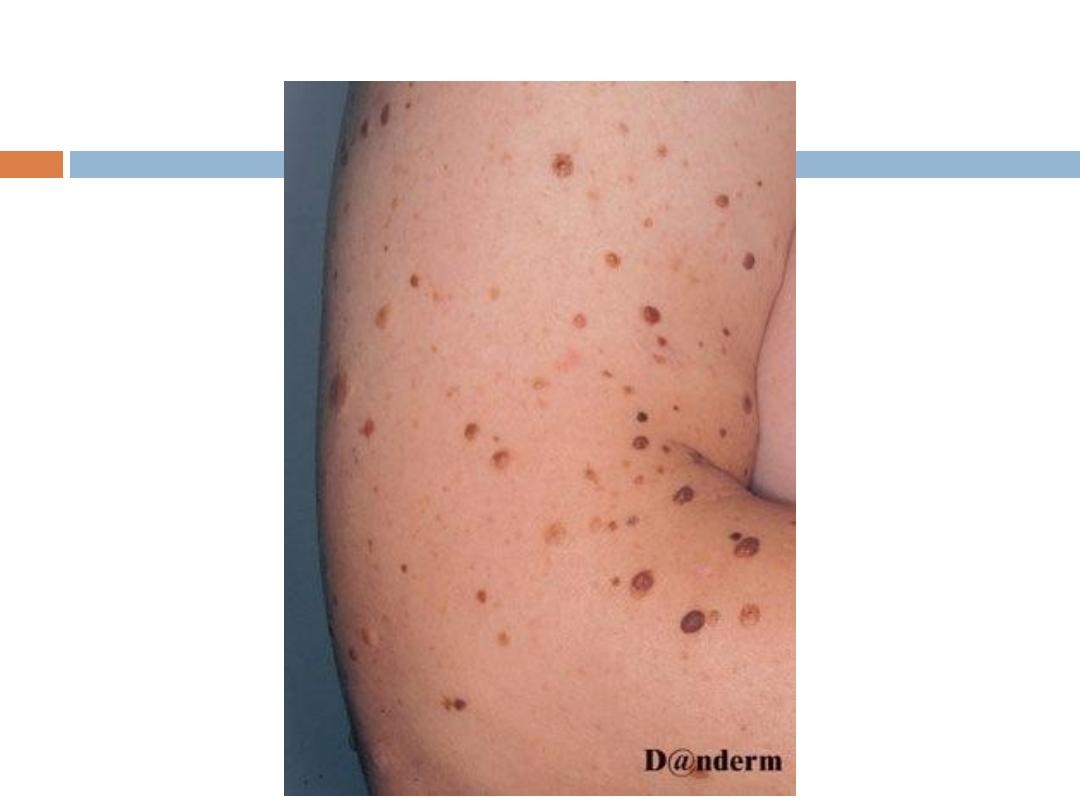
Melanocytic nevi
are
common
lesions that can be
found on the integument of almost all individuals.
Some patients present with few lesions, while others
have hundreds .Melanocytic nevi represent
proliferations of melanocytes that are in contact
with each other,
forming small collections of cells
known as nests.

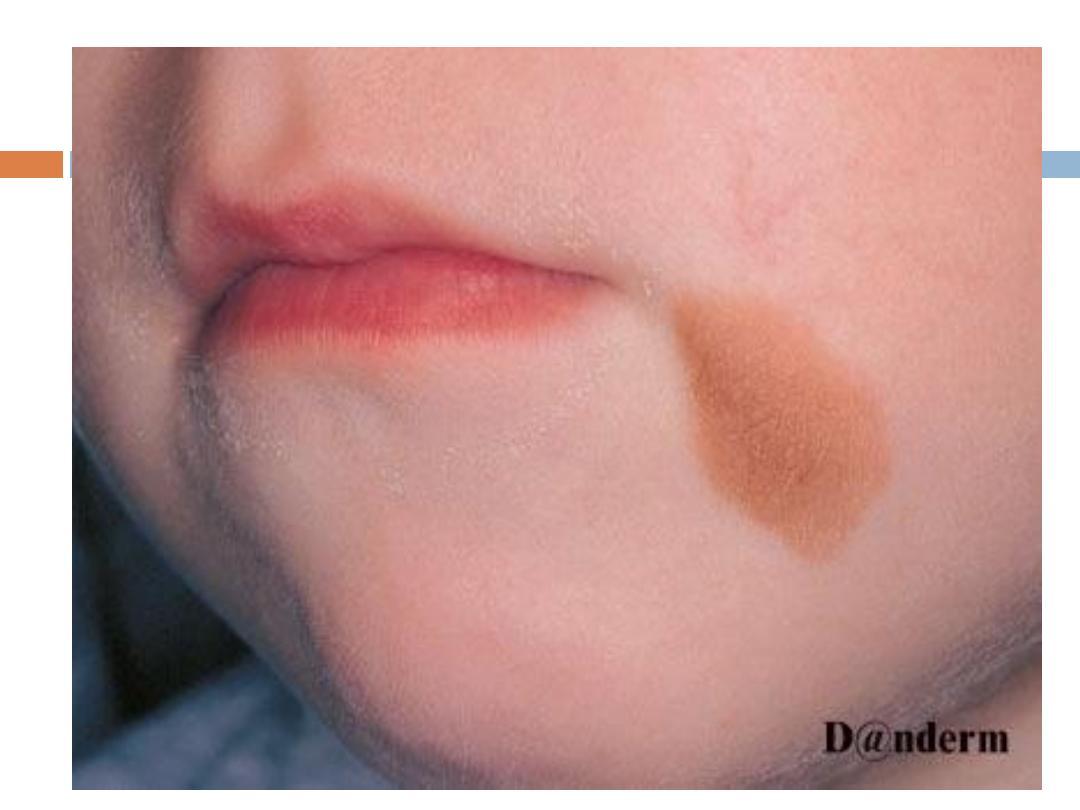
Congenital
melanocytic nevi
They are present
since birth
( that is why they are
called" congenital") Are of 2 types; small
and large (
bathing trunk
), that have deep
color(usually ) with irregular border and covered by
hair.
Larger ones do have a malignant potential.

Types
of melanocytic nevi
1.
Junctional
melanocytic nevi (directly attached to
the basal layer)
are macular or thinly papular. Junctional lesions
typically range from
brown to brownish-black
. The
darker coloration of junctional melanocytic nevi
stems from the fact that the surface epidermis is
often simultaneously hyperpigmented.

2 & 3 .
Compound and intradermal
melanocytic nevi
display
elevation
relative to surrounding uninvolved
skin. Compound melanocytic nevi are often
lighter
in
color than junctional nevi and range from tan to
light brown. Some compound melanocytic nevi have
areas of dark pigmentation, particularly those that
have been recently irritated or traumatized. Many
wholly
intradermal
melanocytic nevi display
no
significant pigmentation.

NB
Compound nevi have both junctional and dermal
elements. While dermal nevi have no junctional
element.

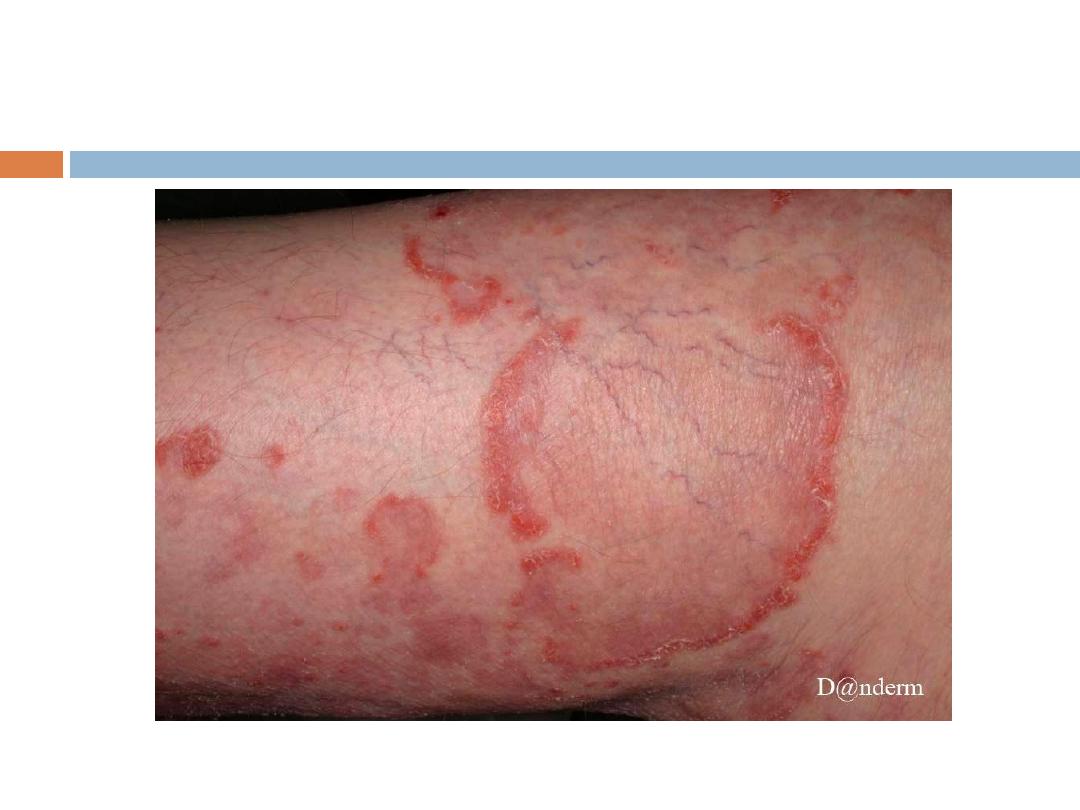
The development of a
new area of pigmentation
within a long-standing nonpigmented or lightly
pigmented compound or intradermal melanocytic
nevus,is a cause for
concern.
While pigmentary
changes could be due to incidental inflammation or
recent
irritation or trauma,
the possibility of evolving
melanoma
is also a consideration in the differential
diagnosis.

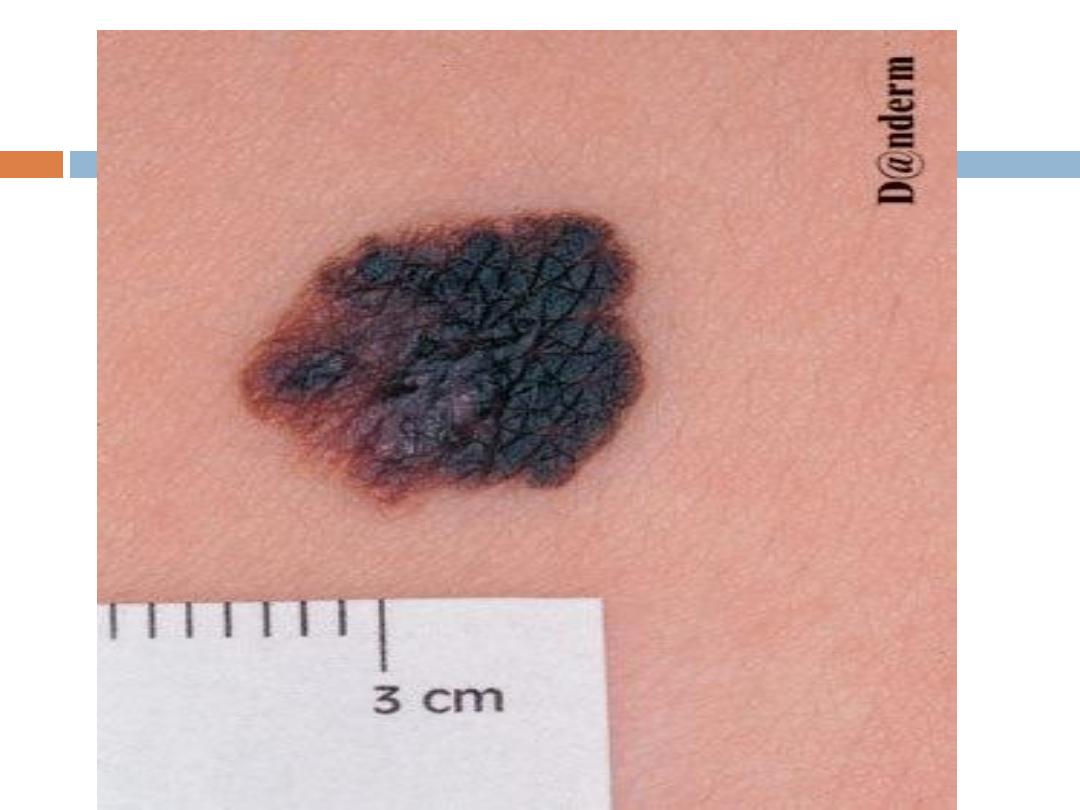
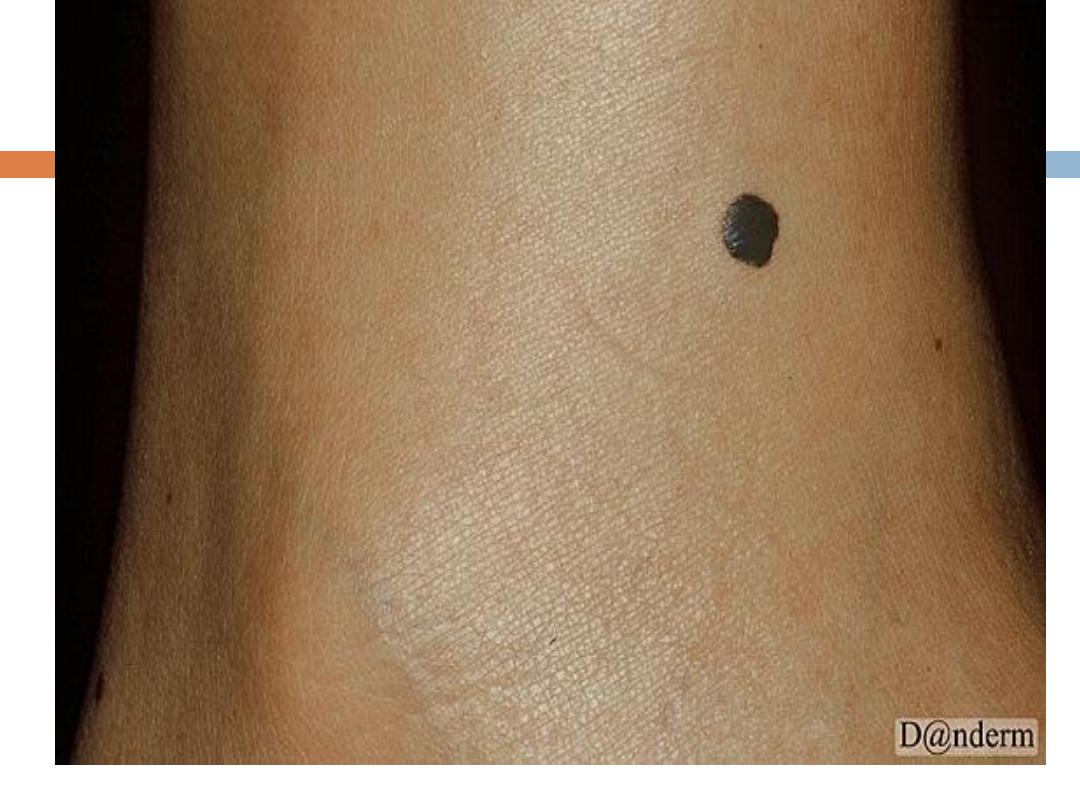
Nevi & MM
Signs of suspicion of MM
in any pigmented skin lesion
(ABCDE):
A:
A
symmetry in shape, one half of the lesion is
unlike
the
other half.
B:
B
order is
irregular
C:
C
olor is
not uniform
; mottled, different shades of black,
grey red and white.
D:
D
iameter more than
0.6 cm
E: In addtion to increase in size of the lesion( which usually
brings the patient to hospital
).-Enlargement

Note
Melanocytic nevi never become malignant because of
manipulation and trauma.
The risk of malignant transformation is very small .
Management
( of melanocytic nevi): None ,but they
can be removed for
cosmetic
purposes

Epidermal cell tumors-
(keratinocytes)
B.
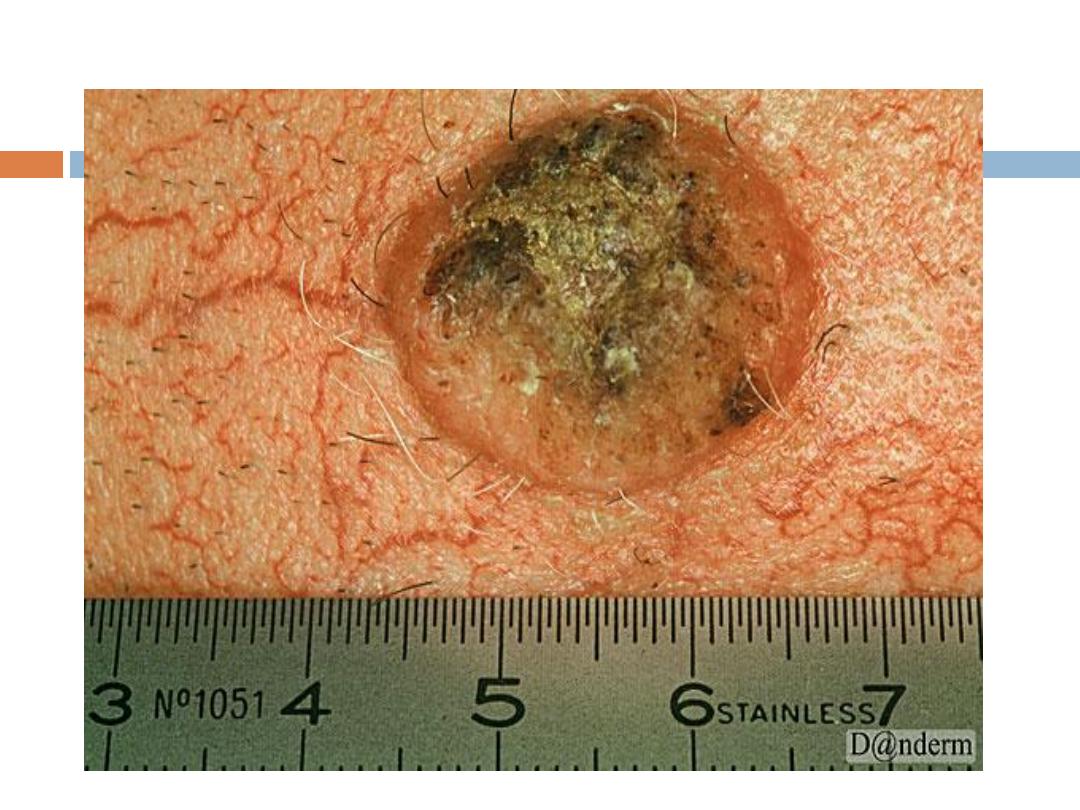
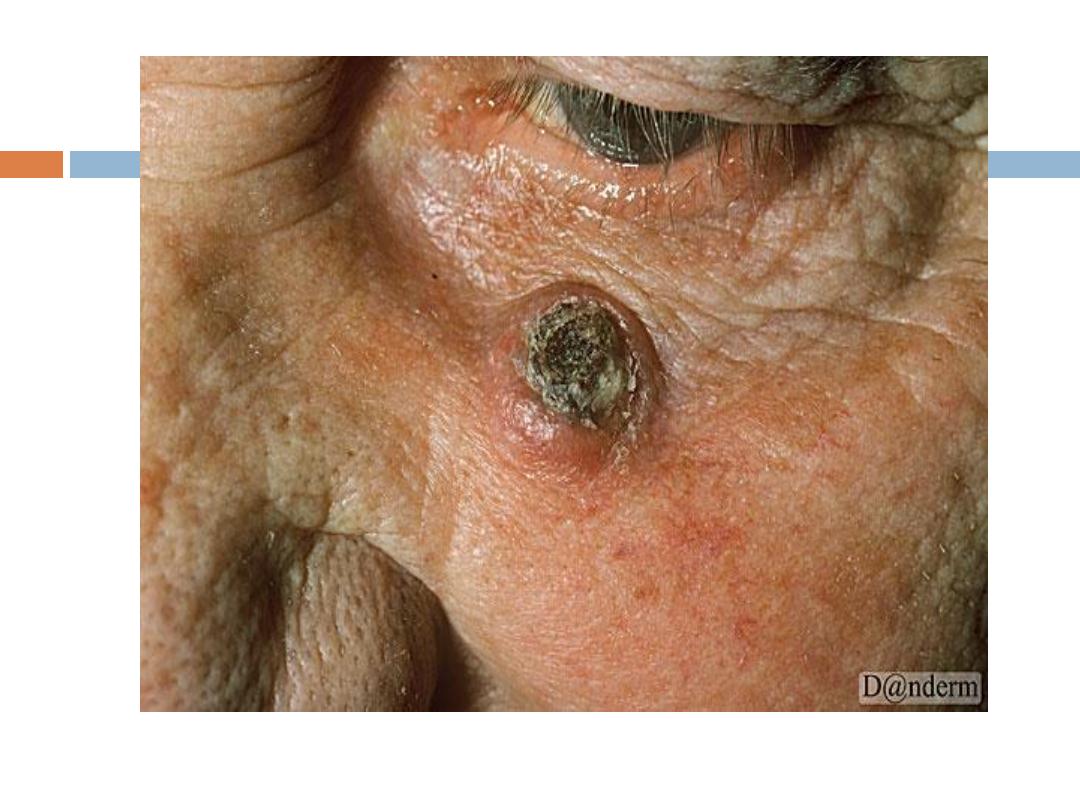
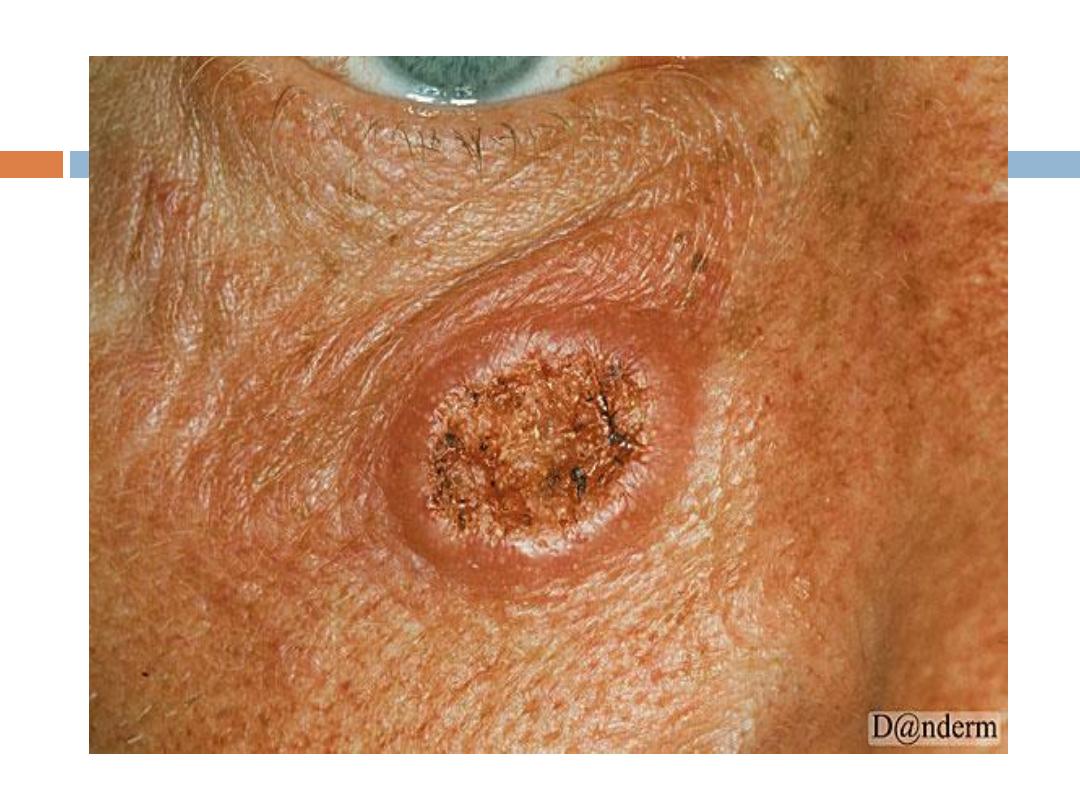
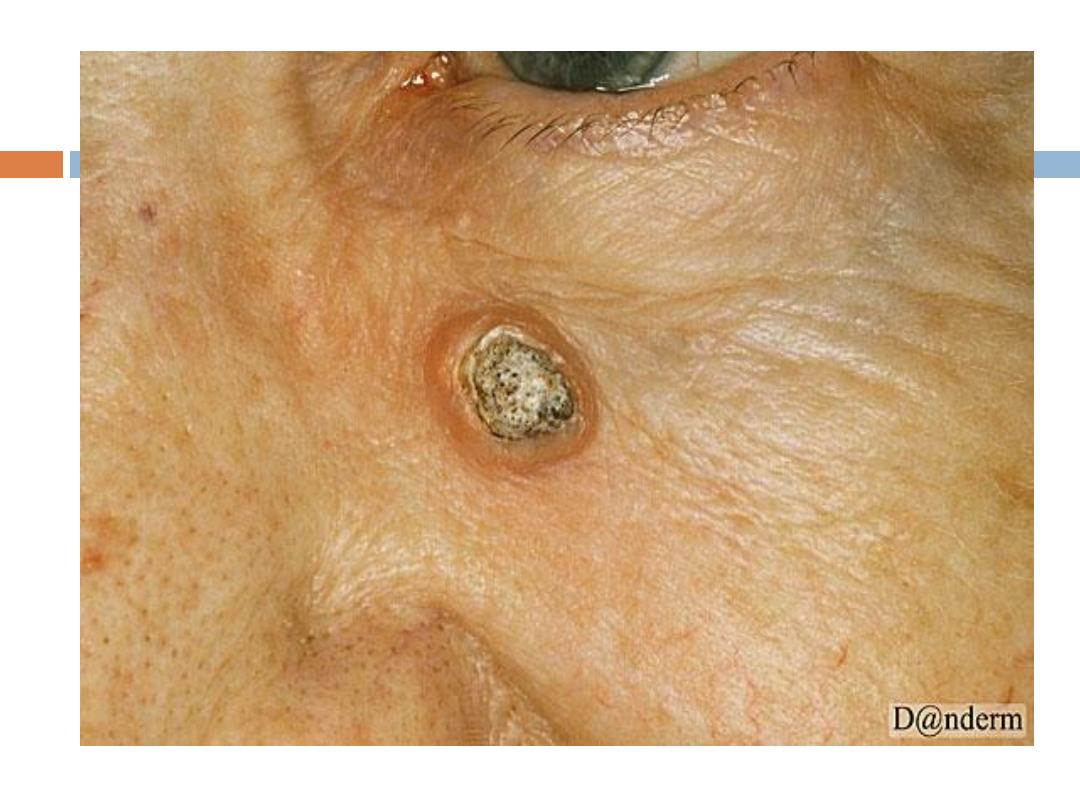
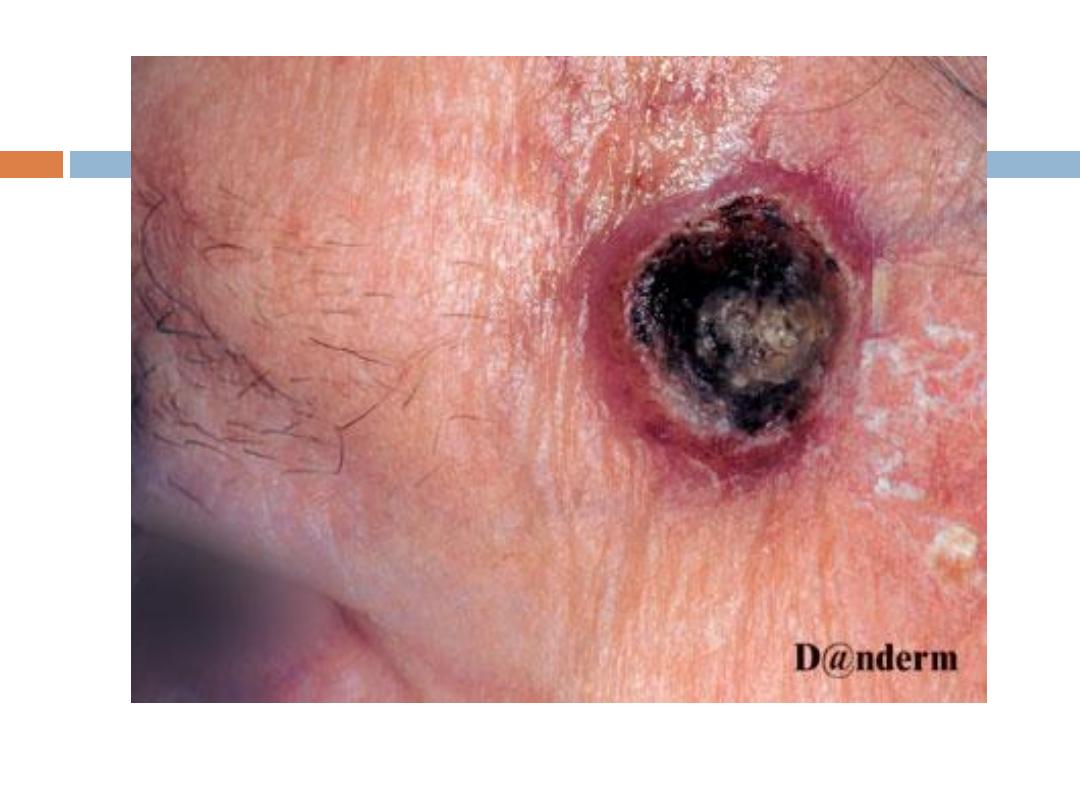
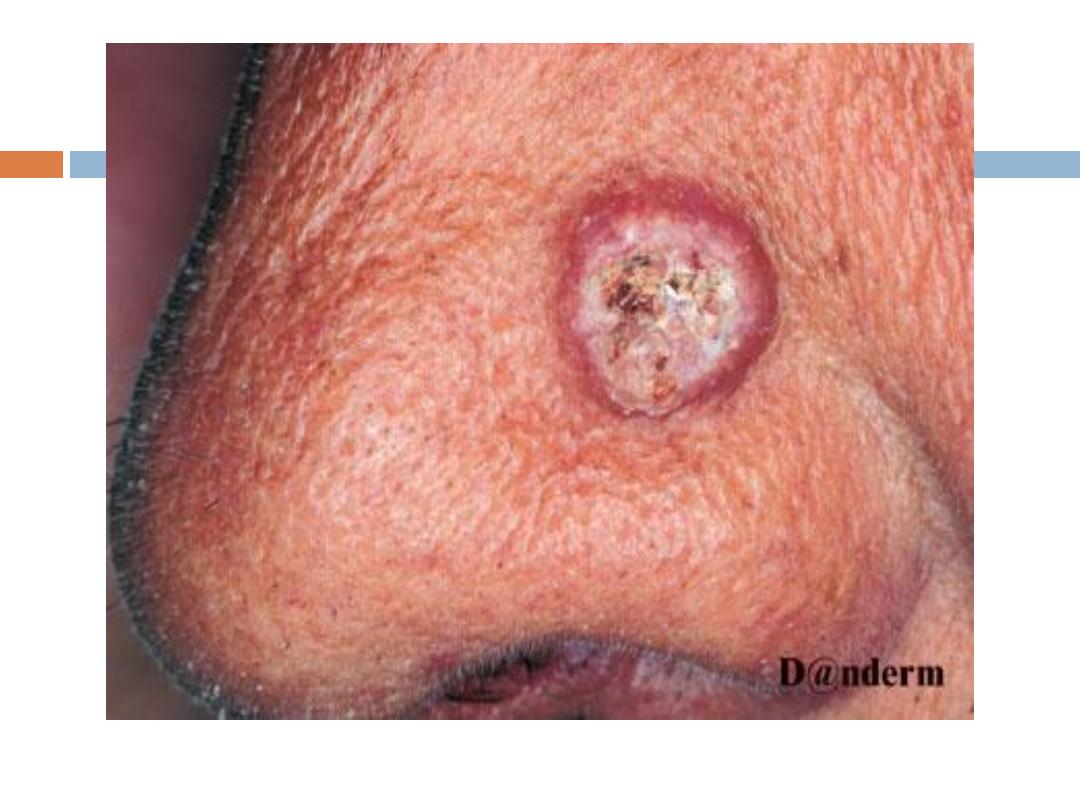
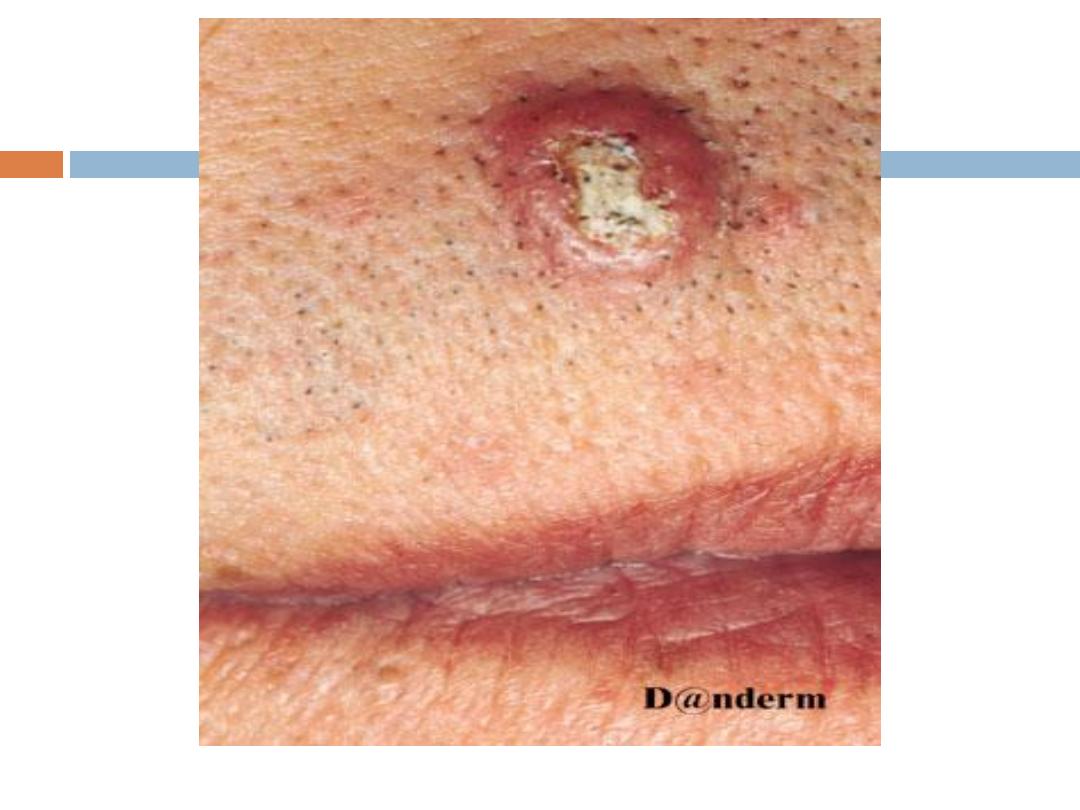
Keratoacanthoma
( KA):
is a relatively
common
low-grade tumor that
originates in the pilosebaceous glands and closely
& pathologically resembles squamous cell
carcinoma(SCC). Keratoacanthoma is characterized
by
rapid growth
over a few weeks to months,
followed by
spontaneous resolution
over 4-6 months
in
most
cases.

KA…..
It typically
grows rapidly
, reaching 1-2 cm within
weeks, followed by a slow
involution
period lasting
up to one year and leaving a residual
scar
if not
excised. Typically are
solitary
skin-color or red
papules(or nodules) with smooth shiny surface and a
central
crateriform
ulceration or keratin plug.
Sites
:face,neck, and dorsum of the hands.

Treatment of KA
Many consider surgical treatment of KA to be
equivalent to treatment of SCC.

Other benign tumors(keratinocytes)
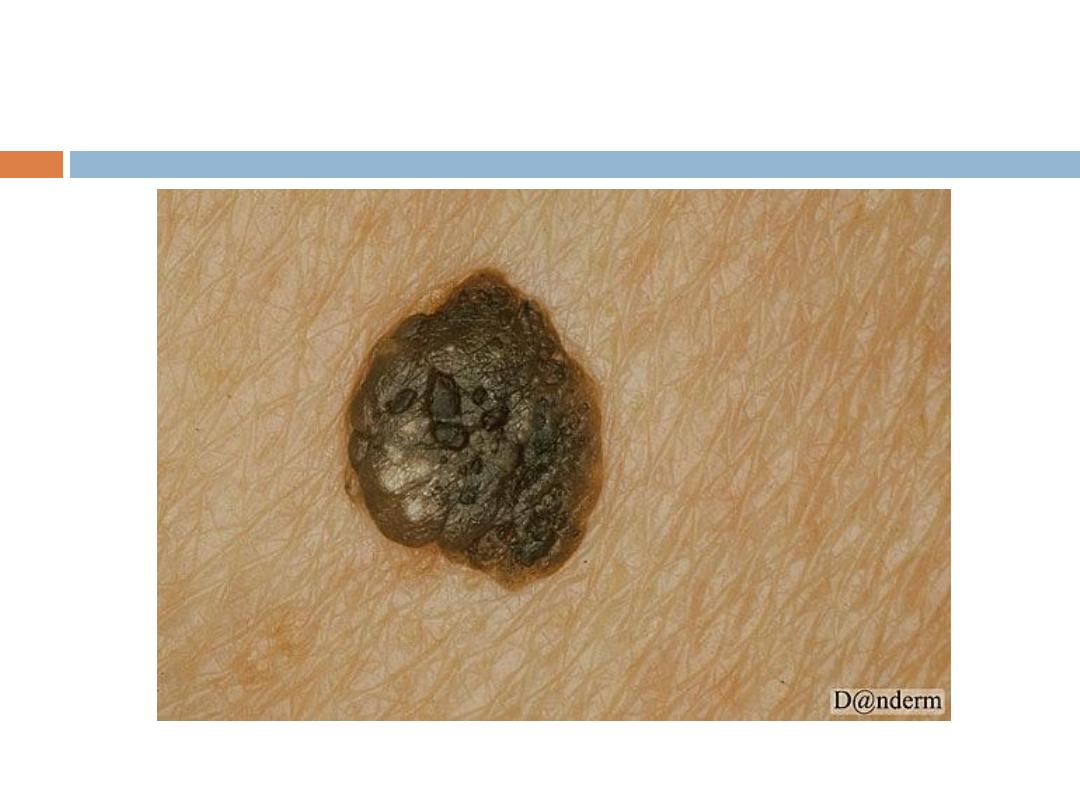
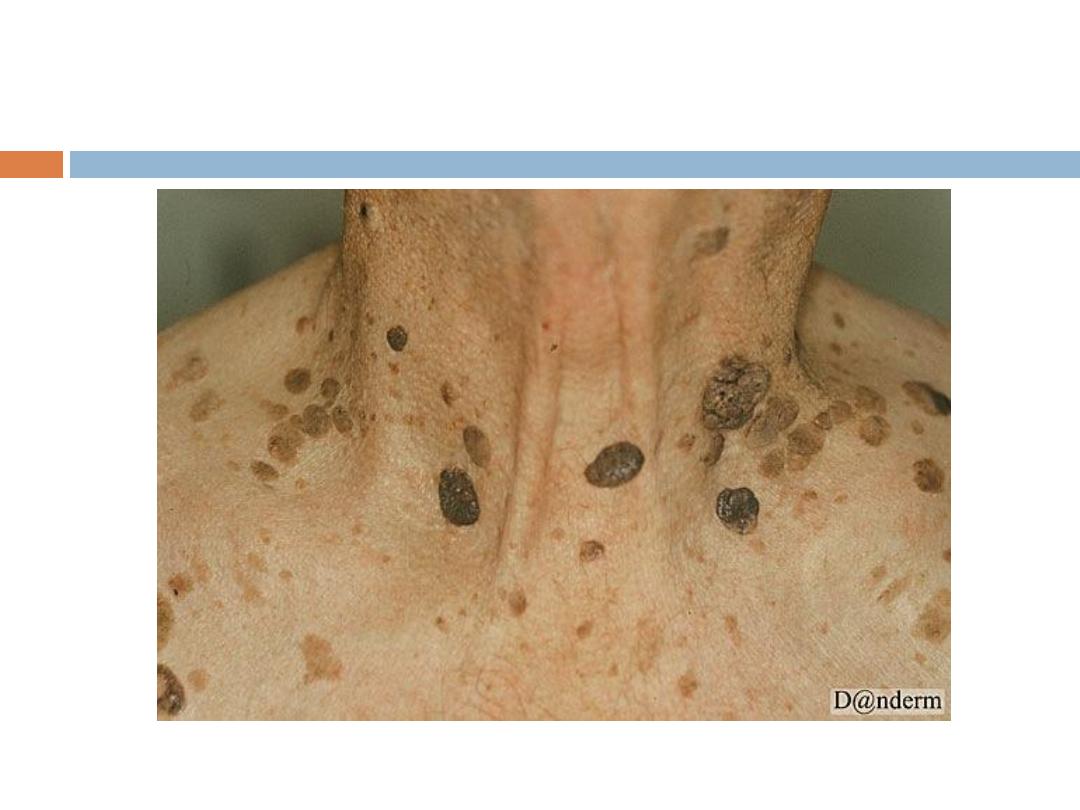
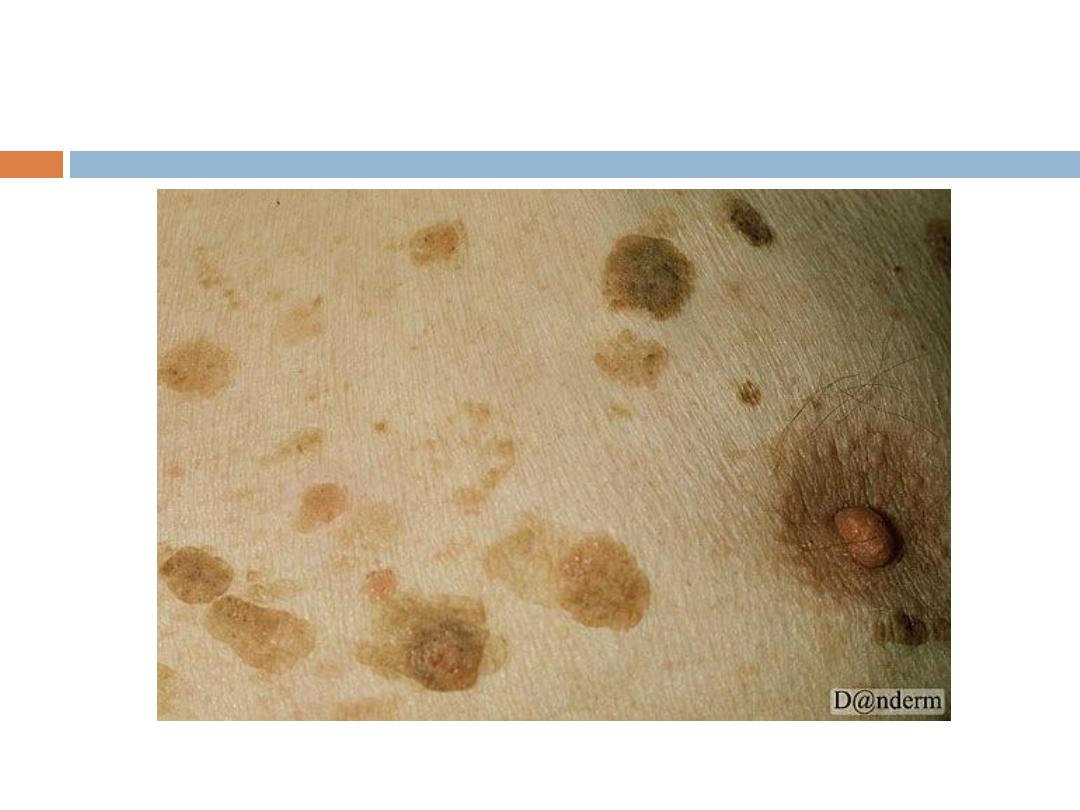
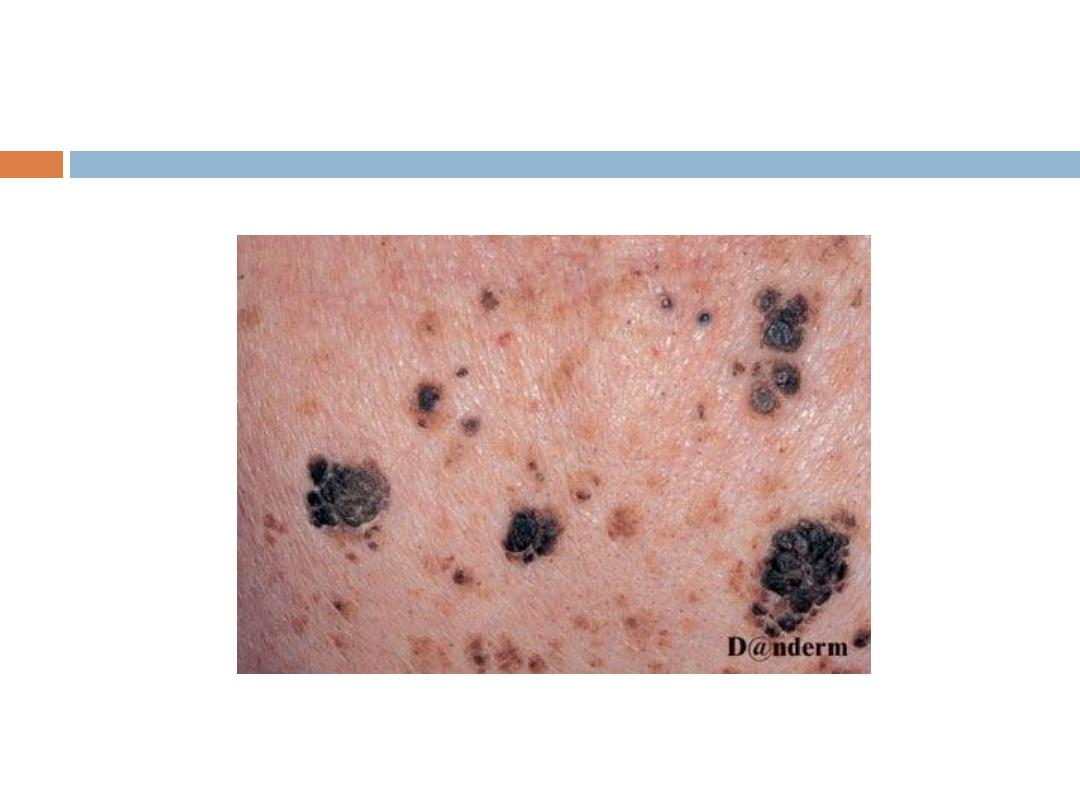
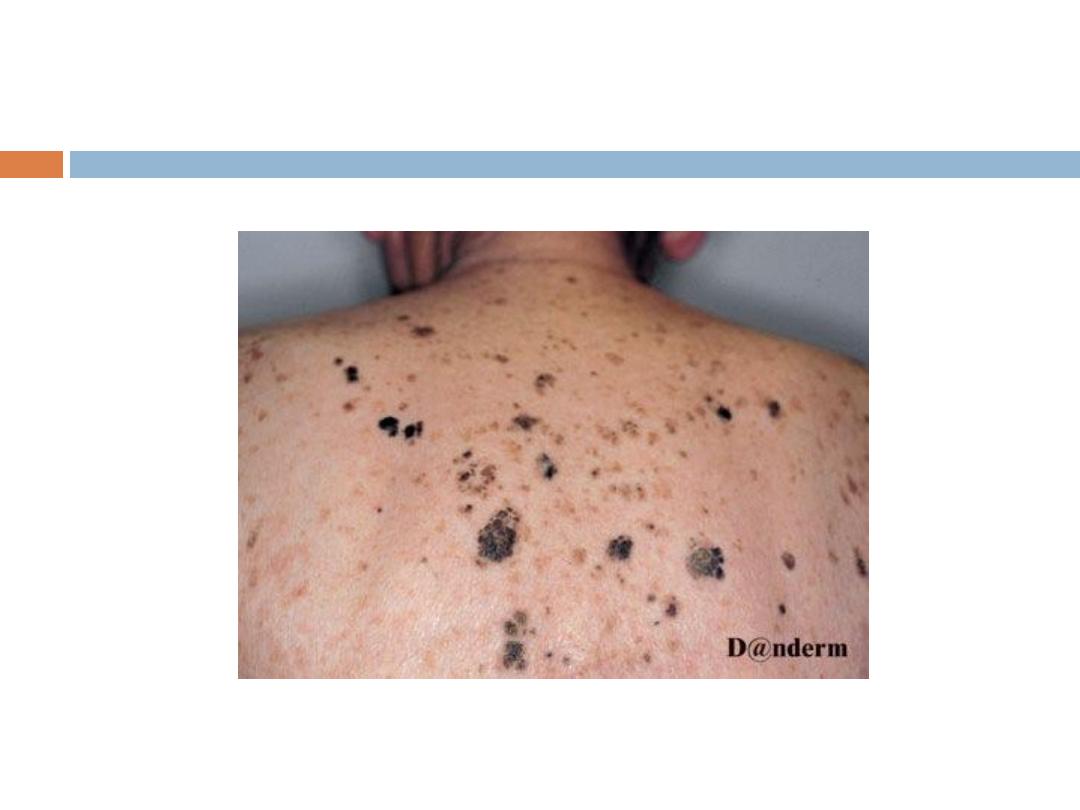
C. Seborrheic keratoses
are the
most common
benign
tumor in older individuals (usually never appear
before the age of 30). Seborrheic keratoses have a
variety of clinical appearances
that begin with the
appearance of one or more
sharply defined, light
brown, flat macules.
The lesions may be sparse or
numerous, asymptomatic or itchy .

SK…
The color May become
dark
brown to black with
warty stuck on appearance
Sites:
face, upper trunk & scalp are the commonest
They are
NOT premalignant
that is why treatment
should be simple like curettage or cryotherapy. We
can apply topical AHA or Retinoids.
NB being colored they should be differentiated from
malignant melanoma(ABCDE).

Histopathology of Seb K.
Epidermal proliferating cells with
basaloid
appearance. The lesions are raised above skin
surface with
papilomatosis
and
horn cyst
formation.
No tendency toward malignancy.

Treatment of seb. keratosis
Can be removed easily by curettage,cryotherapy or
electrodessication
Others :AHA, TCA,Tazarotene cr.

Other benign tumors
D.
Trichelemmal cysts(pilar cyst)-
- from hair(External
Root sheet):Arise on the
scalp
,
similar to sebaceous
cyst
but has no opening( punctum) may be single or
multiple( usually familial),surgical removal is easier
than that for sebaceous cysts.
E.
sebaceous gland
tumors--- benign seb
hyperplasia,and seb.cyst

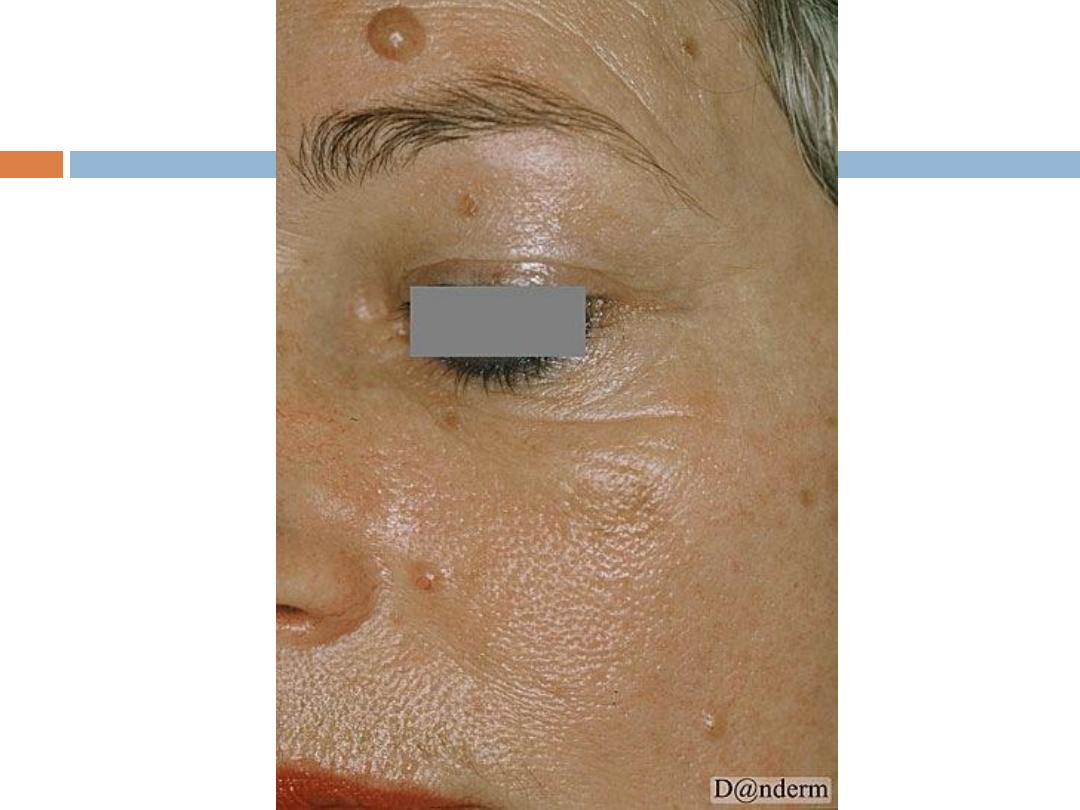
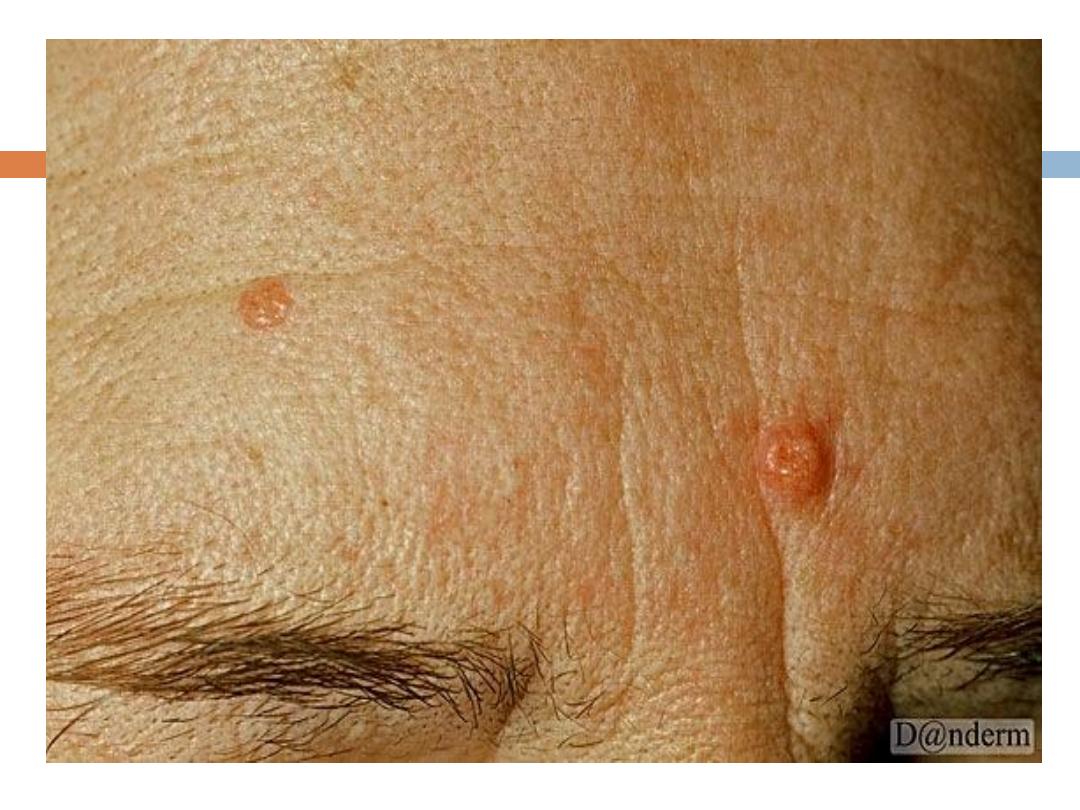
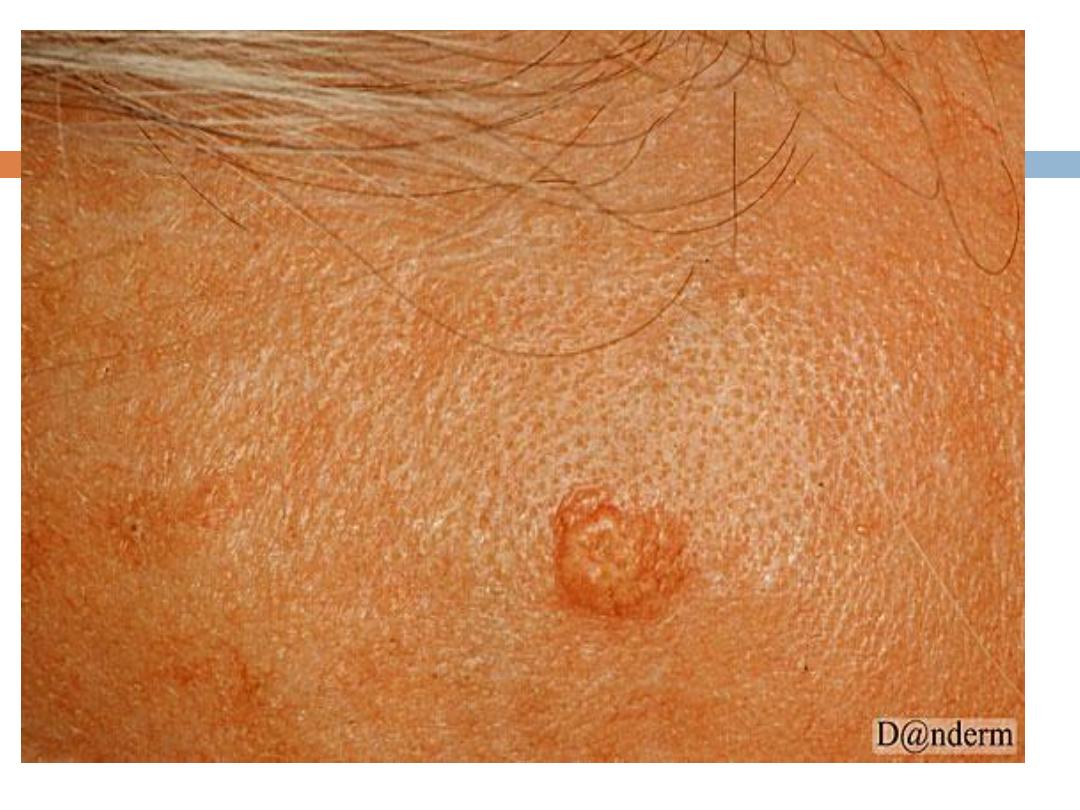
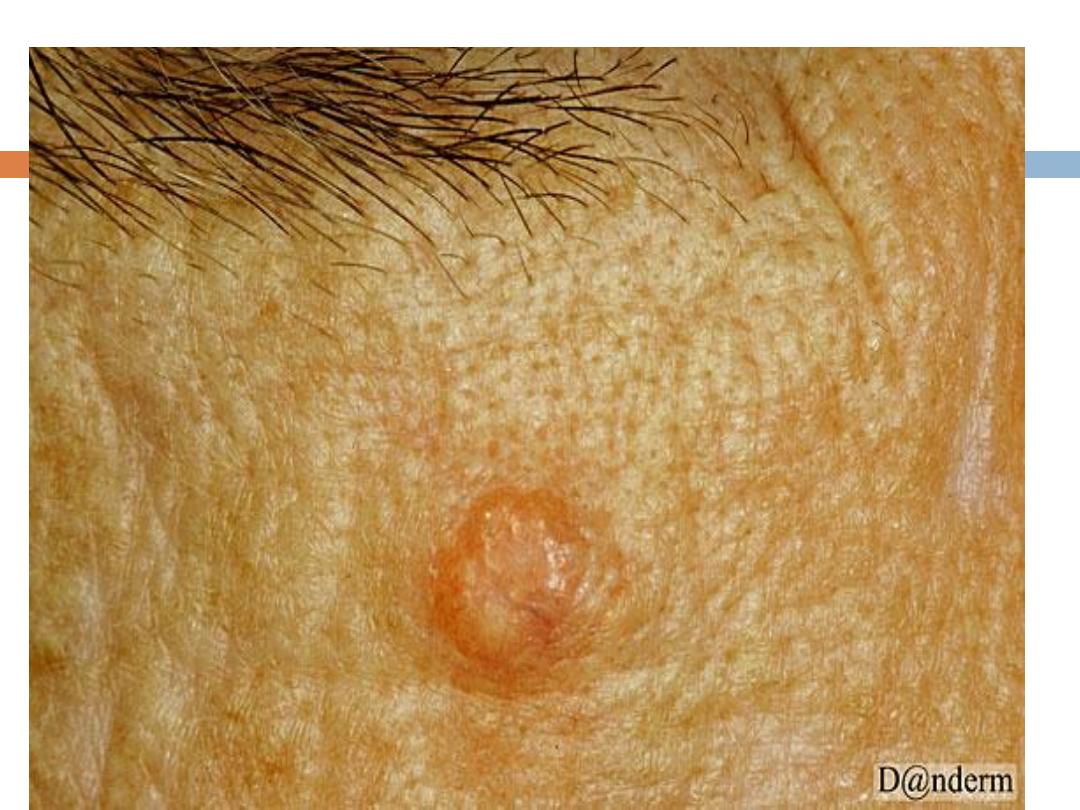
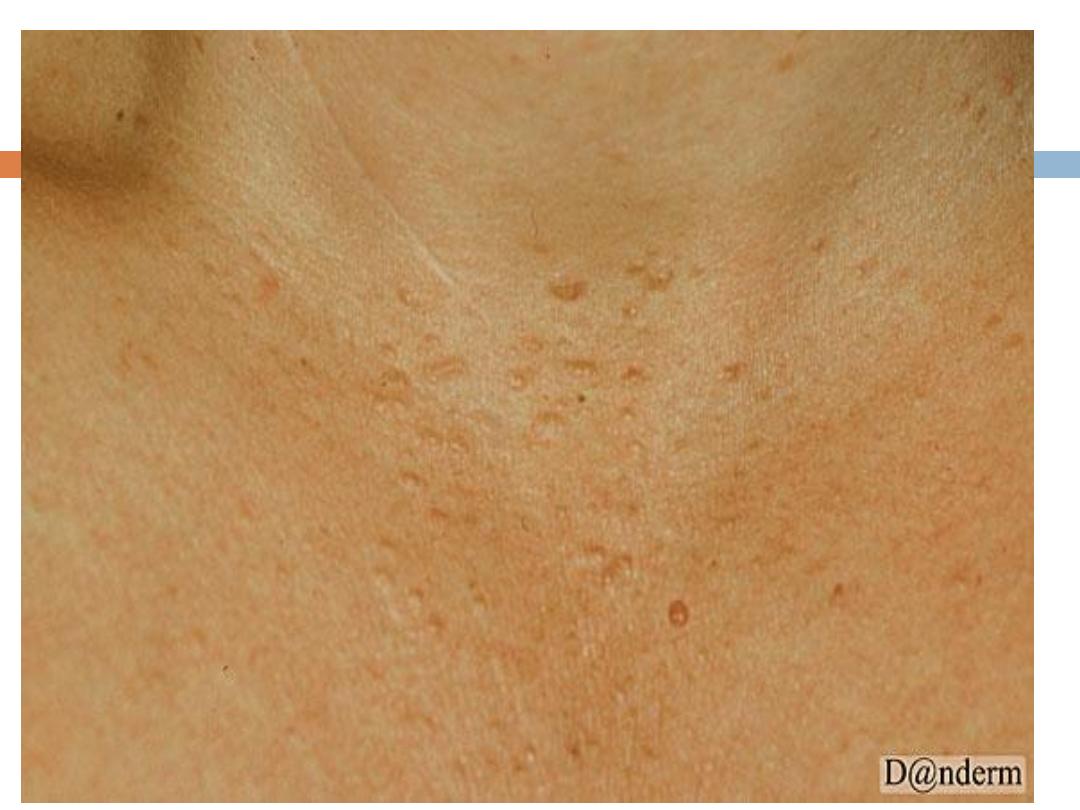
Benign sebaceous hyperplasia
:
Is a
common
,
benign
condition of sebaceous glands in
adults of middle age or older. Lesions can be single
or multiple and manifest as
yellowish, soft, small
papules on the face
(particularly nose, cheeks, and
forehead).often with an umblicated center.
It may occasionally be confused with BCC
Can be removed by simple shave excision

Benign sebaceous hyperplasia..
NB occasionally oral isotretinoin may be needed for
wide spread disfiguring lesions.

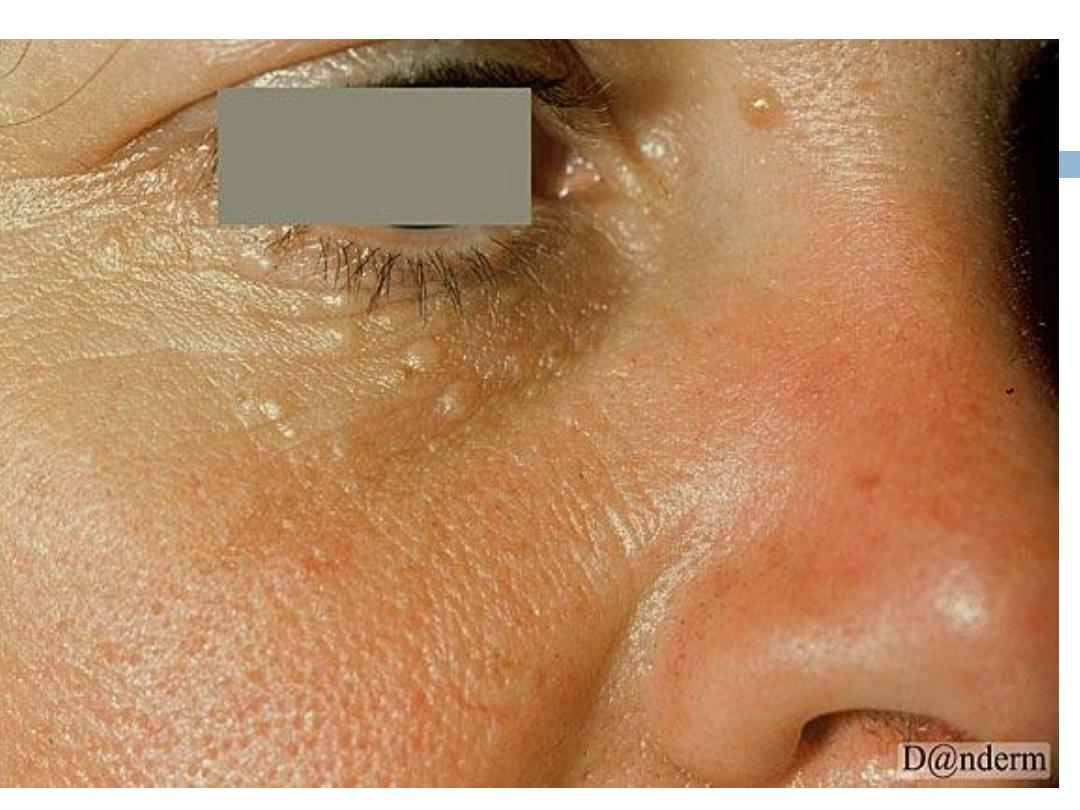
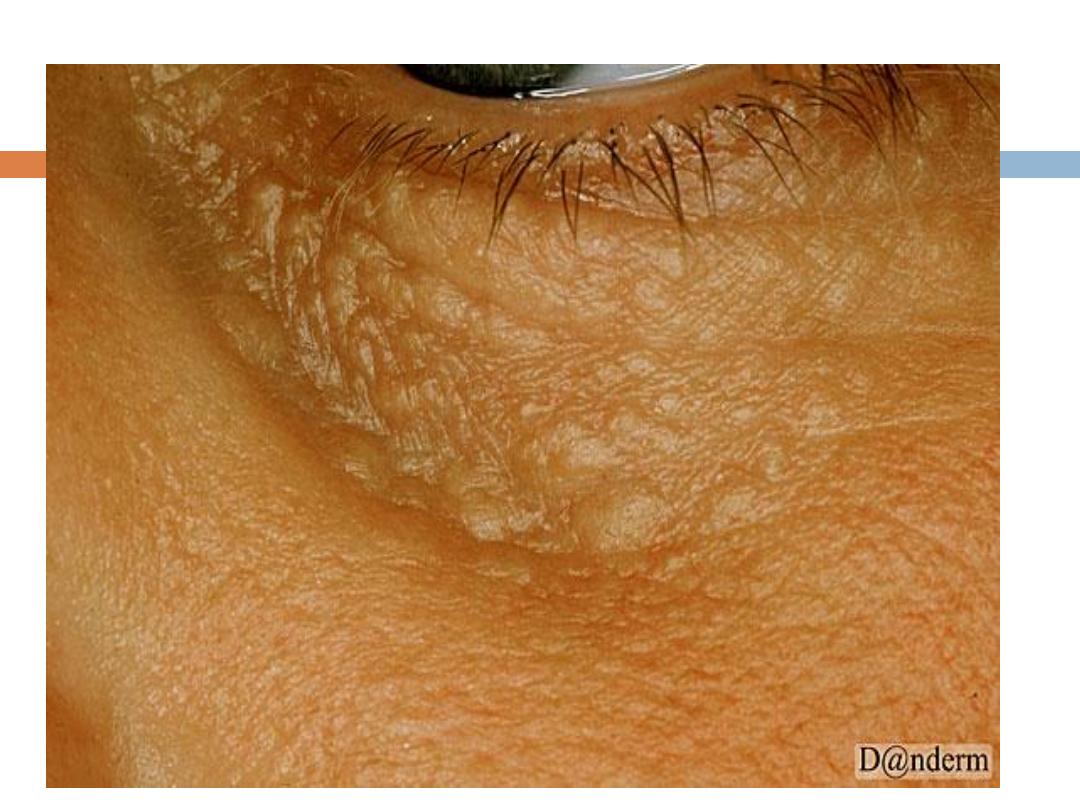
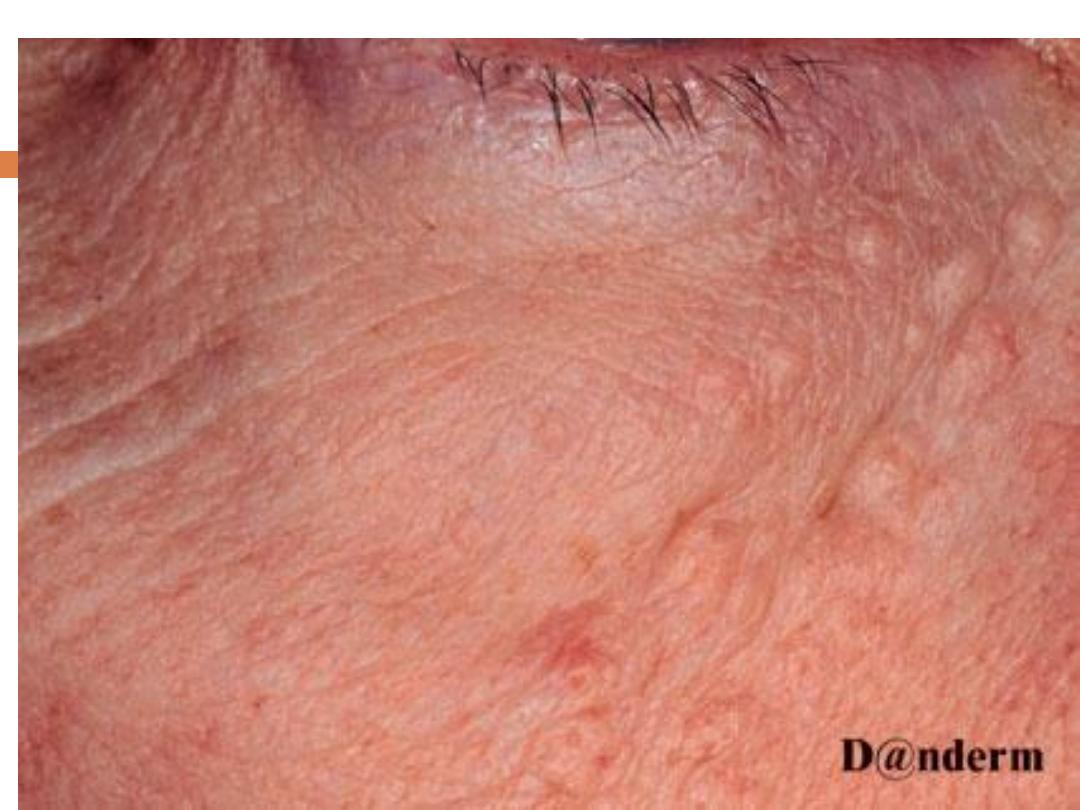
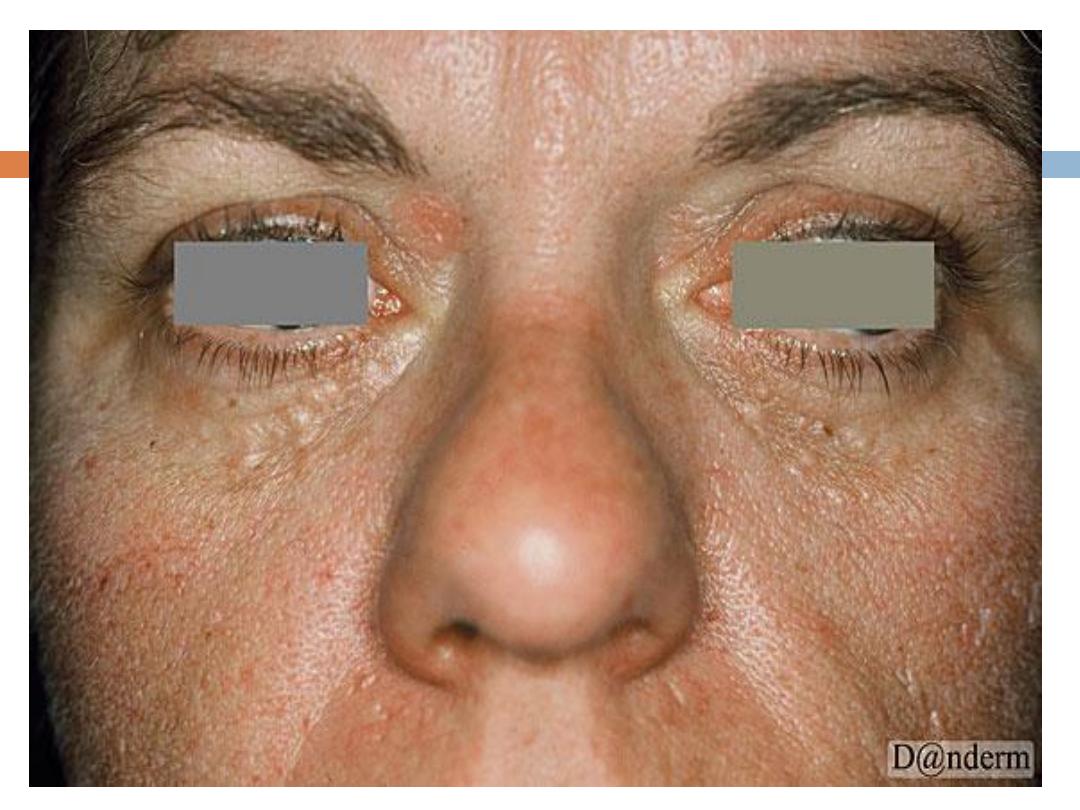
F.
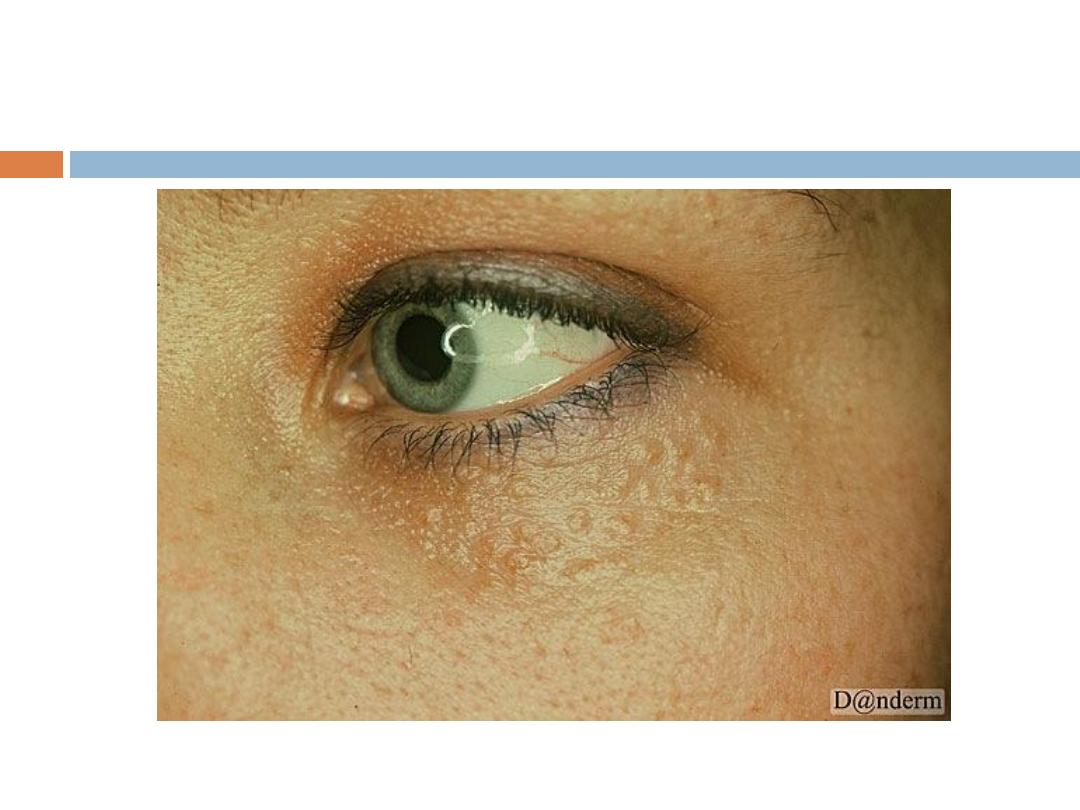
Syringoma
Is a
sweat duct tumor
:
are
skin-colored or yellowish
, generally small, dermal
papules Most commonly, syringomas are limited to
the upper parts of the
cheeks and lower
eyelids
.They are only of cosmetic importance

Premalignant
skin conditions
Any skin condition that will lead ultimately to frank
malignancy if left untreated.
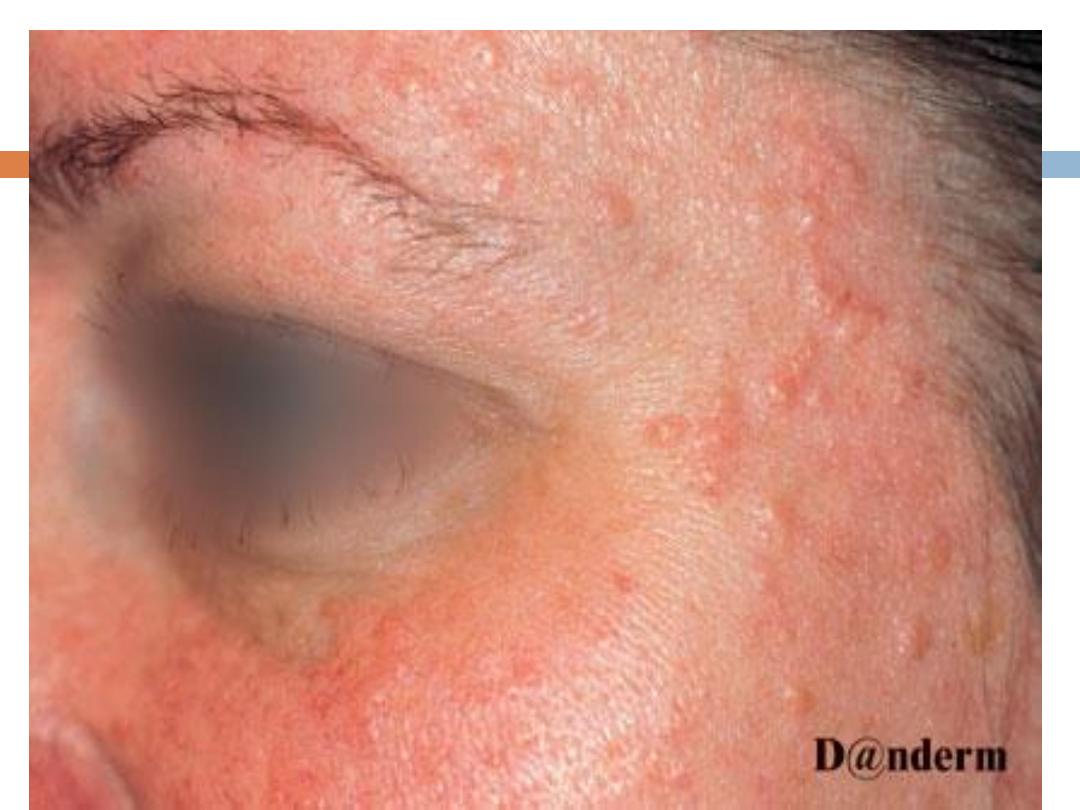
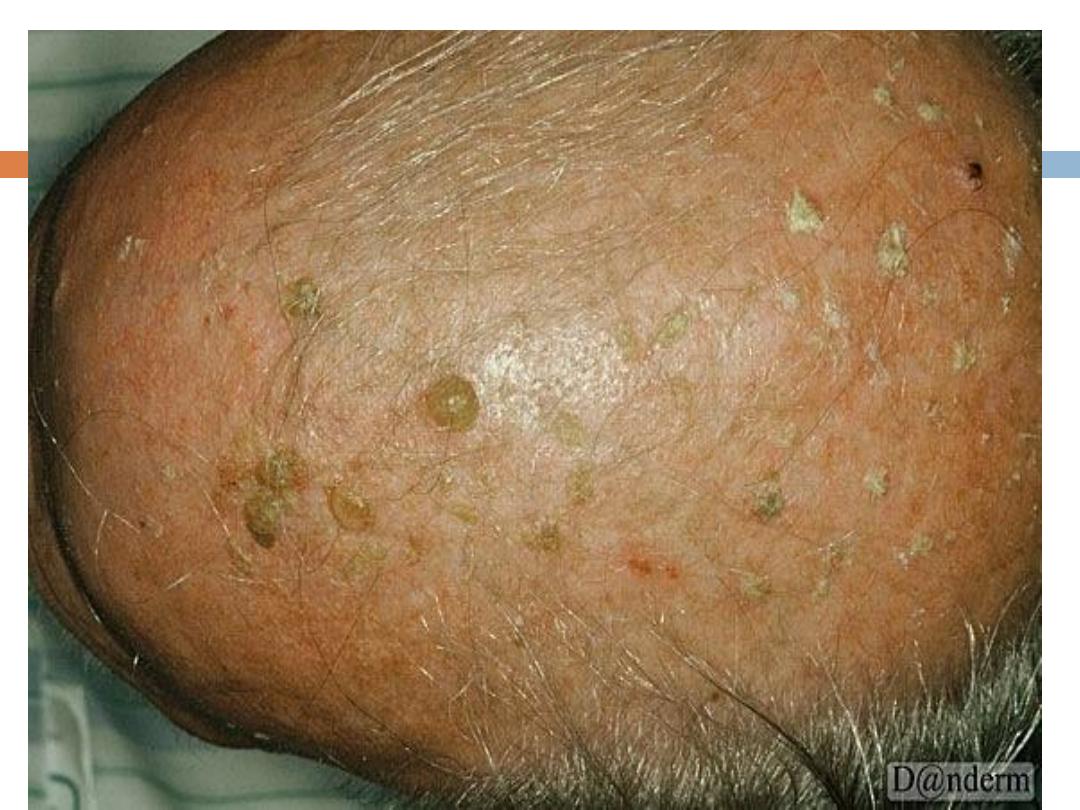
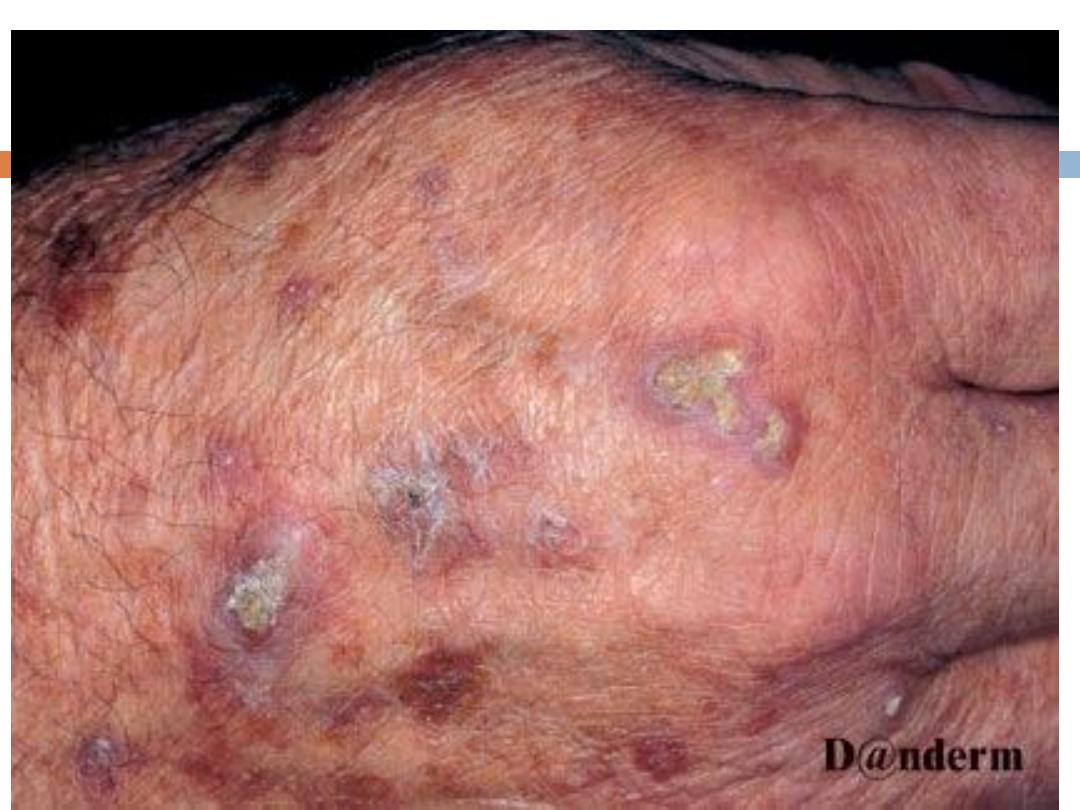
The classic example is
actinic (senile,solar)
keratosis(AK)
-AKs are amongst the most
frequently
encountered
skin lesions in clinical practice. They
present on
sun-damaged skin of
the head, neck,
upper trunk and extremities. Individuals at higher risk
of developing AKs include the elderly, lighter skin
phototypes and history of chronic sun exposure.

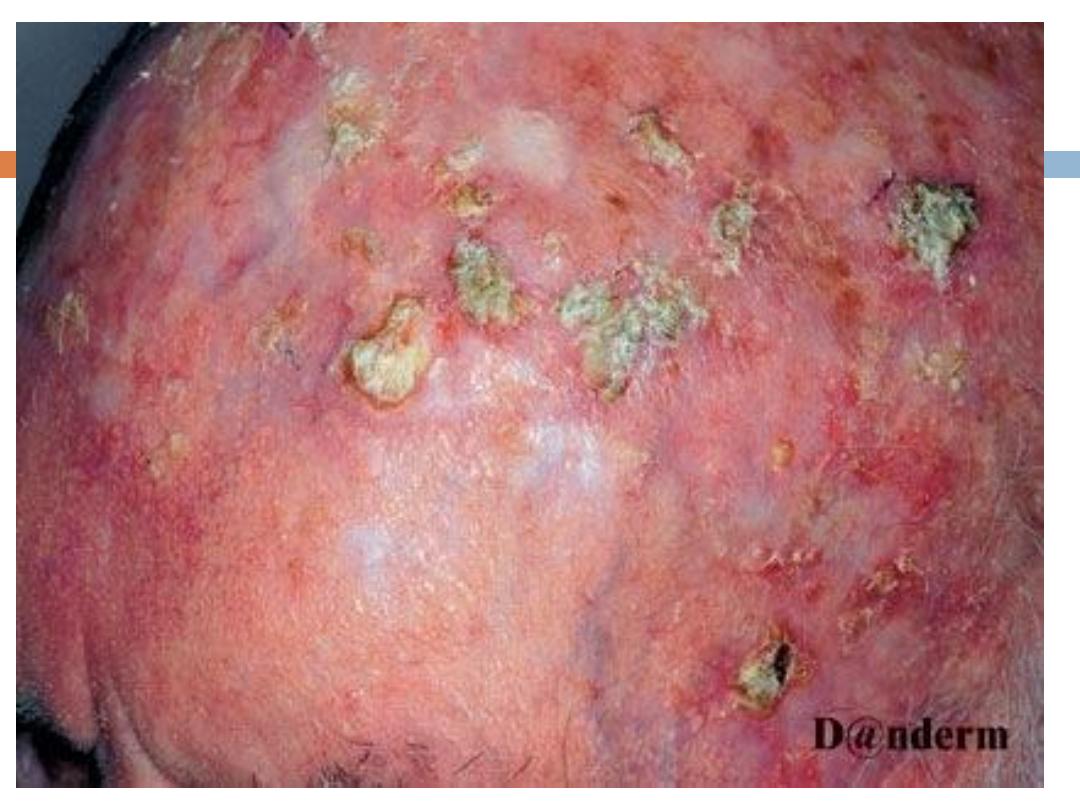
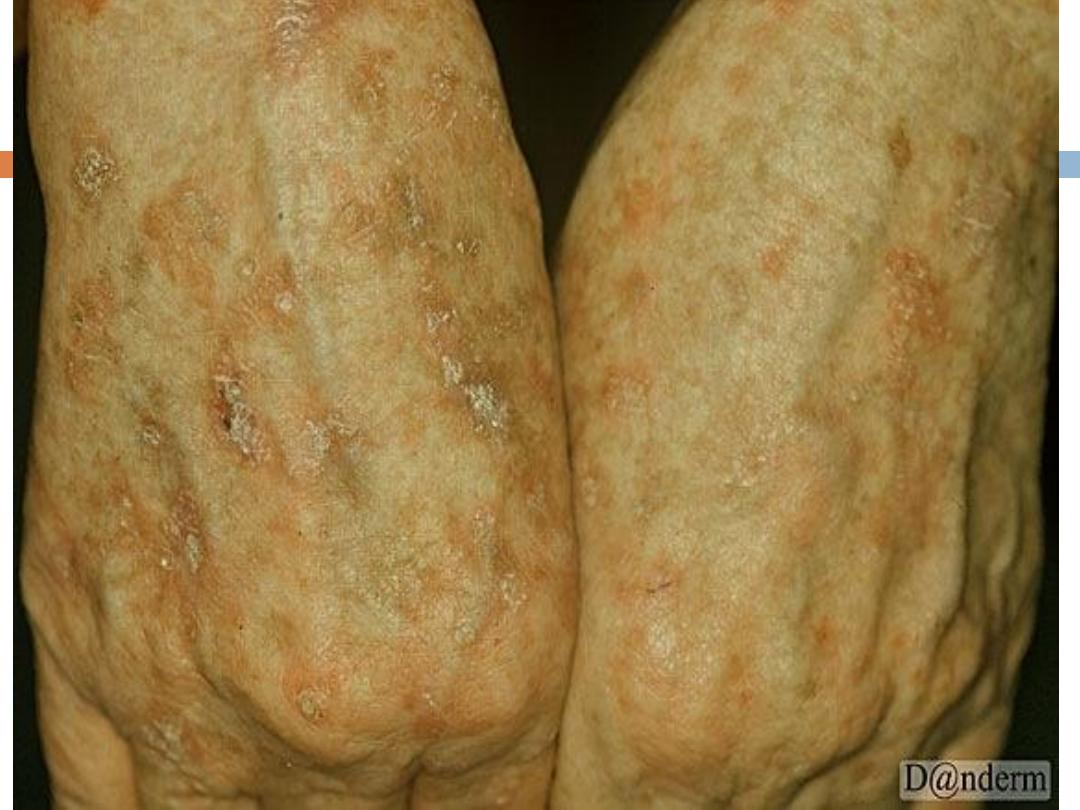
AK….
They present with
rough
erythematous
papule with
white to yellow scale
. size from a few millimeters
to large confluent patches several centimeters in
diameter surrounded by
photodamaged
skin
(wrinkled, telangiectatic with dyspigmentation)
Sites
: face,ears,bald scalp, and dorsa of hands.

Treatment
1.5-FU– TOPICAL.
2. Topical imiquimod.
3.Topical diclofenac.
4. PTD with topical delta-aminolevulinic
acid(generation of oxygen free radicals).

Important
malignant
tumors of the skin
1. Related to basal cells.--
BCC
2. Originating from keratinocytes.--
SCC
3 Originating from melanocytes--
MM
4. Mycosis fungoides
(MF
) originating from T cells( T
cell lymphoma)
NB: recently kaposi’s sarcoma(malignant vascular
tumor) is raising concern in our country .

General
causes
of malignant tumors
1.
Sun
exposure.
2.Chronic skin disease or
irritation
Including old burns
3.
X rays
and ionizing radiation.
4.
Genitic
diseases like xeroderma pigmentosa-- in ability
to repair Sundamaged DNA
5. Exposure to Some
chemical
s Like arsenic.
6. The presence of some
immune defects
(Genitic ,
Aquired"HIV" ,and drug induced"For organ
transplants")
7.
HPV
(Human papIlloma virus" certain types")

NB:
susceptibility
to UVR damage
Well-known markers for UVR vulnerability
include the following:
Fair skin
(or a history of repeated sunburns)
Hazel or
blue eyes
Blonde or
red hair
Albinism
(NOT Vitiligo)

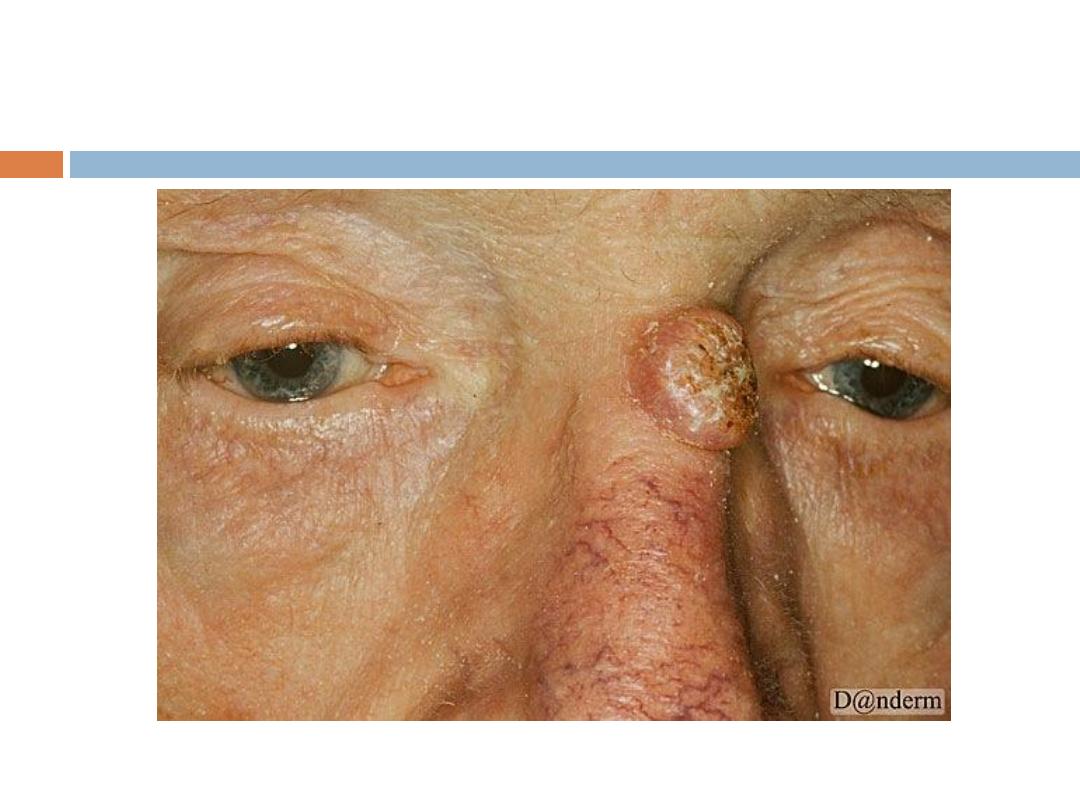
Basal cell carcinoma (
BCC
)
a nonmelanocytic skin cancer (ie, an epithelial
tumor) that
arises from basal cells
( small, cuboidal
cells found in the lower layer of the epidermis)--???.
The
prognosis
for patients with BCC is
excellent,
but
if the disease is allowed to progress, it can cause
significant morbidity
.
NB: Many believe that BCCs arise from
pluripotential
cells
in the basal layer of the epidermis or
follicular
structures.

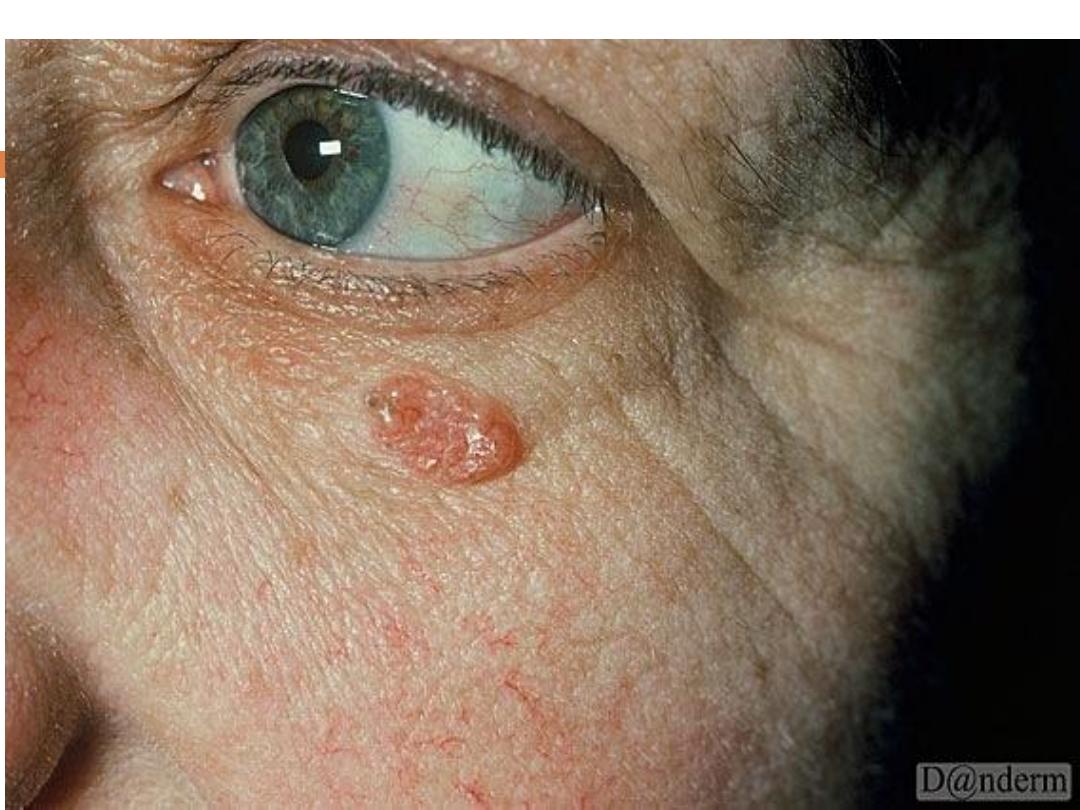
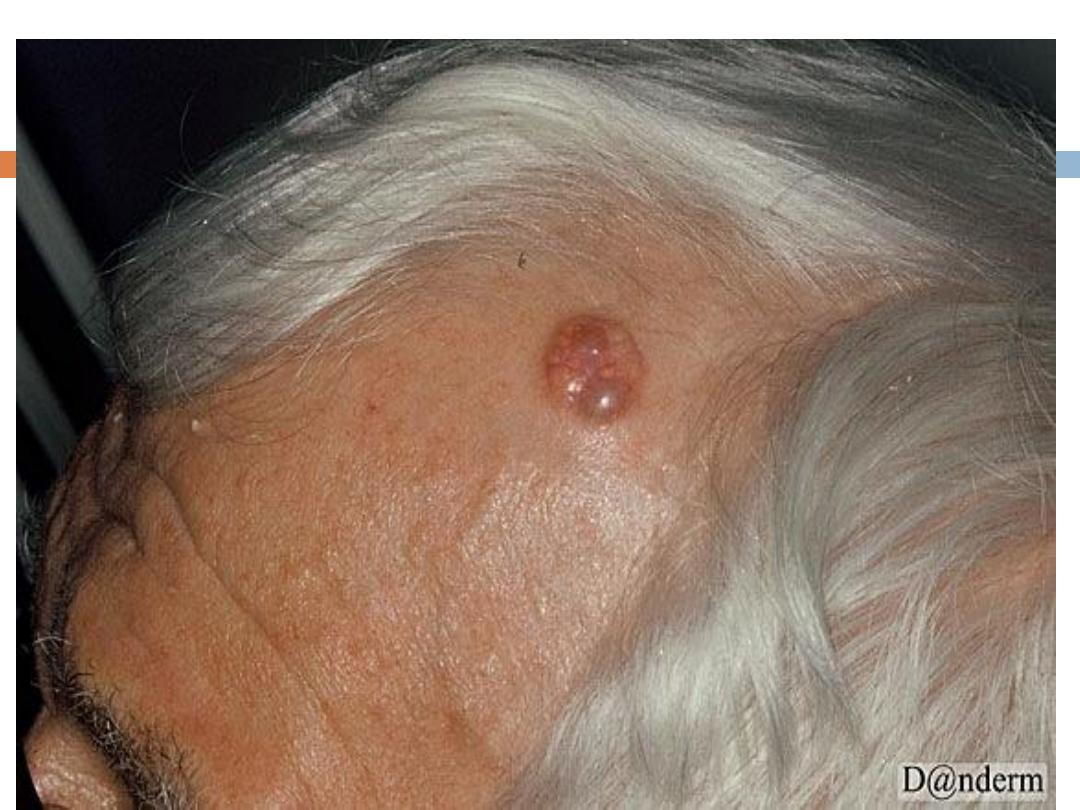
BCC..
Signs and symptoms
BCC occurs mostly on the
face, head
(scalp included),
neck, and hands.Other characteristic features of
BCC tumors include the following:
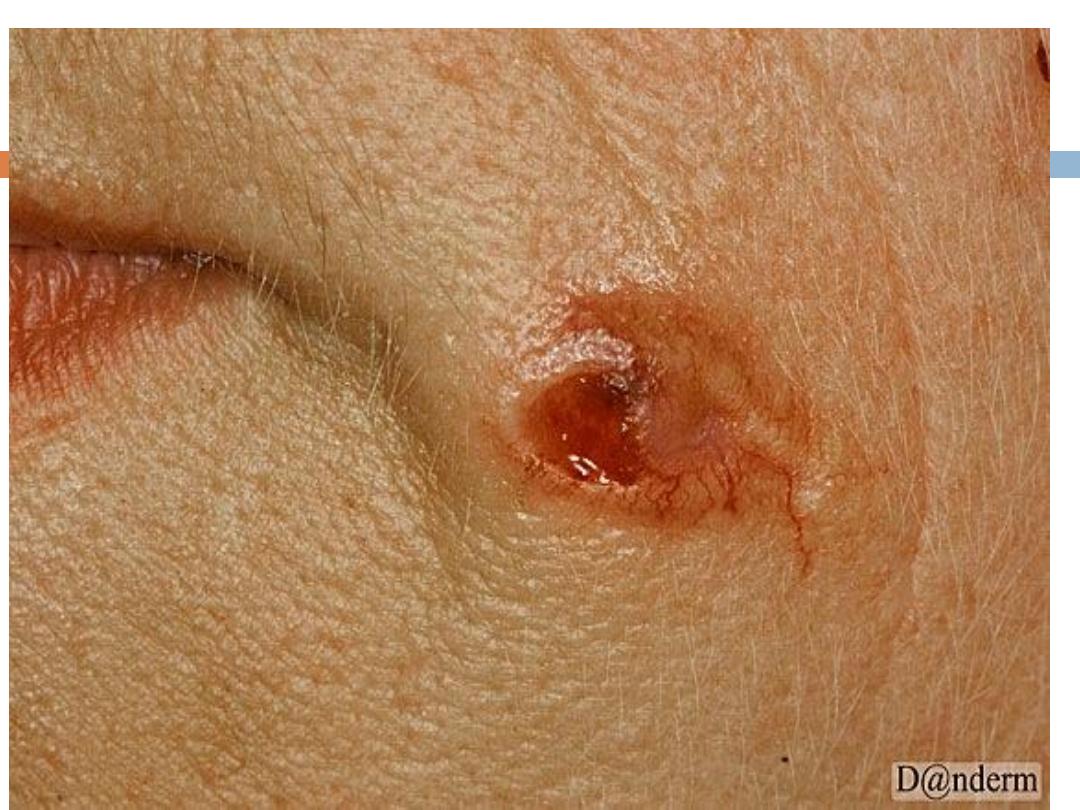
Waxy
papules with central depression
Pearly
appearance Erosion or ulceration: Often
central and pigmented
Bleeding: Especially when traumatized

BCC features…
Oozing or crusted areas: In large BCCs
Rolled (raised) border
(often inetrrupted)
Translucency
Telangiectases
over the surface
Slow growing: 0.5 cm in 1-2 years
Black-blue or brown areas

Clinicopathologic
types
of BCC
Each of which has a distinct biologic behavior,
include the following:
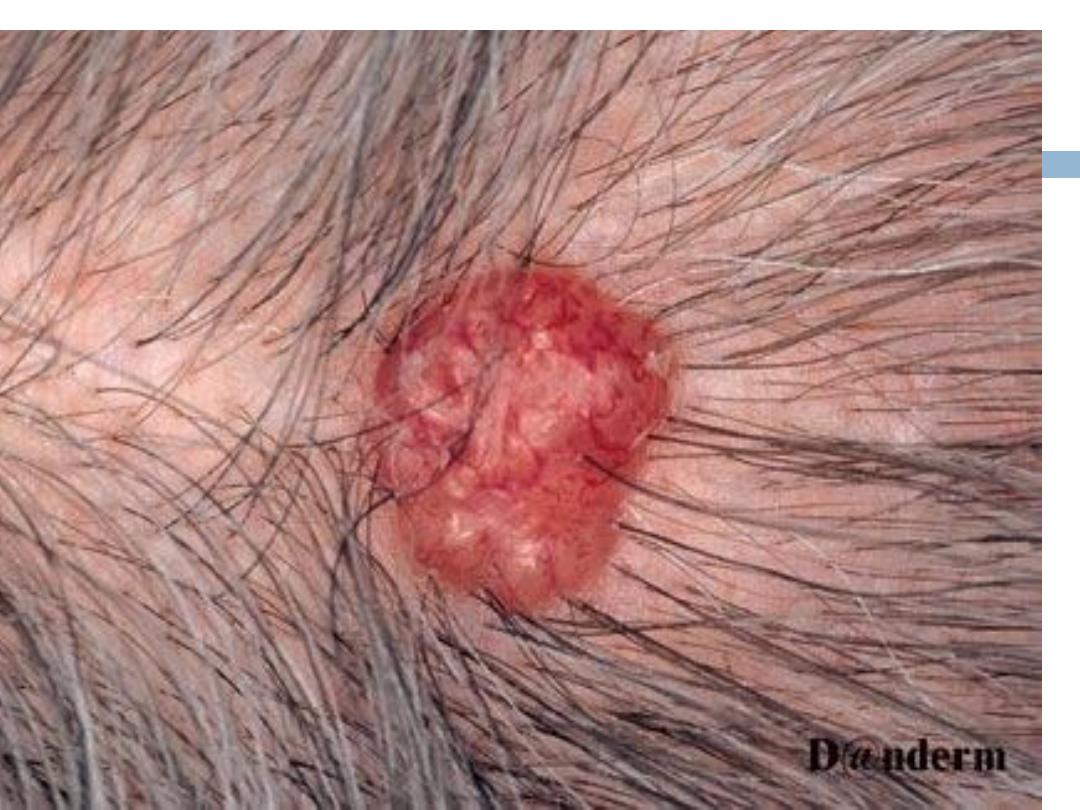
Nodular,morpheaform, superficial, Cystic, pigmented,
keratotic
.The most common type of BCC; usually
presents as a round, pearly, flesh-colored papule
with telangiectases
Infiltrative: Tumor infiltrates the dermis in thin strands
between collagen fibers,
making tumor margins less clinically apparent

OTHER TYPES of BCC
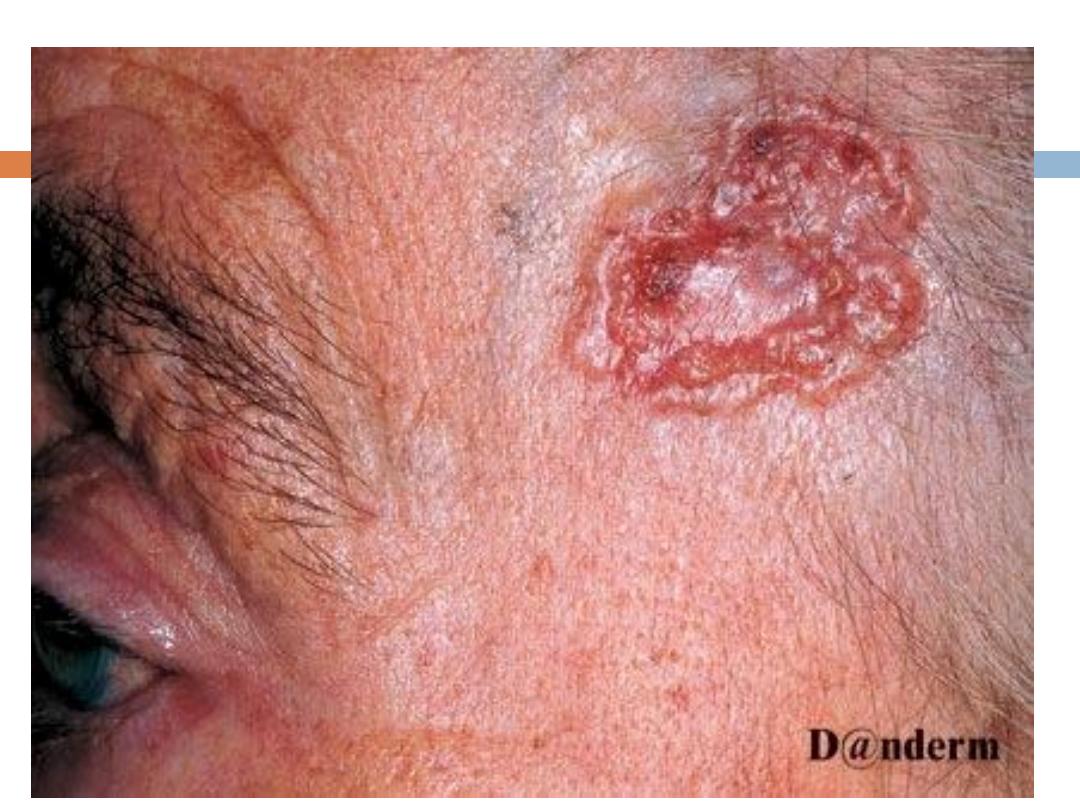
Morpheaform:
Appears as a
white or yellow
, waxy,
sclerotic plaque that rarely ulcerates; is flat or
slightly depressed, fibrotic, and firm.
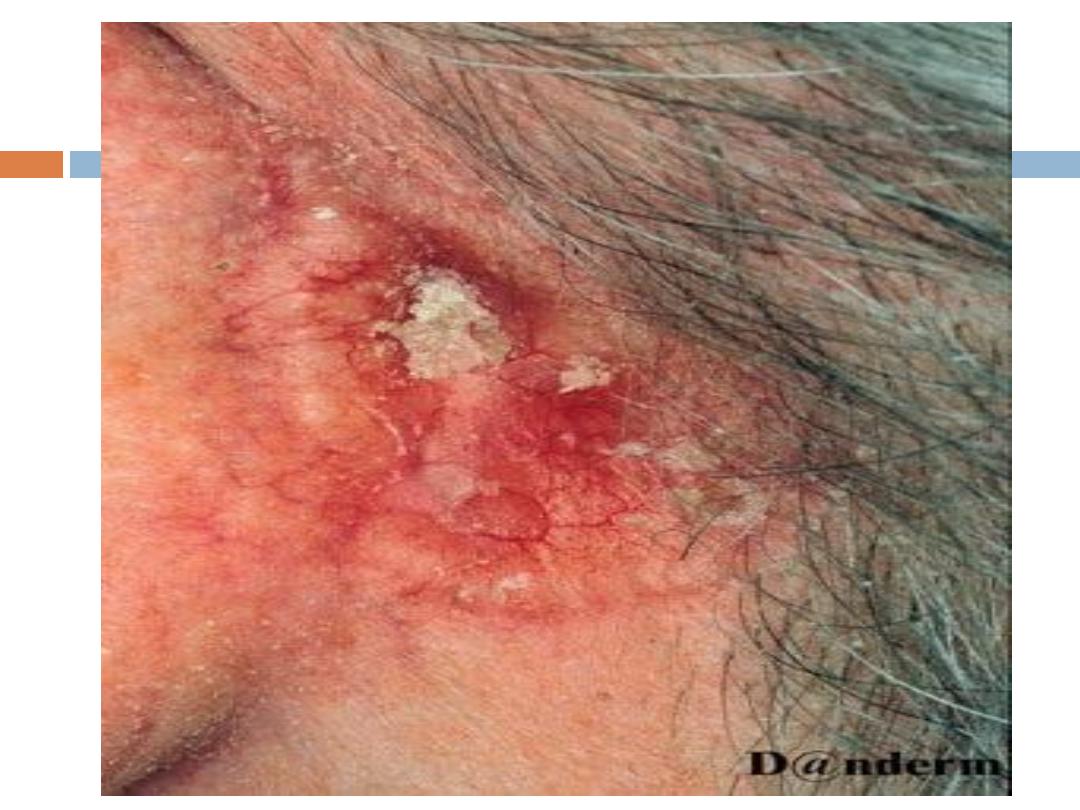
Superficial
: Seen mostly on the upper trunk or
shoulders; appears clinically as
an erythematous,
well-circumscribed patch or plaque
, often with a
whitish scale

Diagnosis
Clinical plus histopathological.
Given that BCC rarely metastasizes, laboratory and
imaging studies are not commonly clinically
indicated in patients presenting with localized
lesions.
Imaging studies may be necessary when involvement
of deeper structures, such as bone, is clinically
suspected. In such cases, computed tomography
scans or radiography can be used.

Biological behavior according to
type
Nodular, Cystic, pigmented, keratotic; the most
common type of BCC; usually presents as a round,
pearly, flesh-colored papule with telangiectases
Infiltrative: Tumor infiltrates the dermis in thin strands
between collagen fibers, making tumor margins less
clinically apparent
Micronodular: Not prone to ulceration; may appear
yellow-white when stretched,…

is firm to the touch, and may have a seemingly well-
defined border
Morpheaform: Appears as a white or yellow, waxy,
sclerotic plaque that rarely ulcerates; is flat or
slightly depressed, fibrotic, and firm.
Superficial: Seen mostly on the upper trunk or
shoulders; appears clinically as an erythematous,
well-circumscribed patch or plaque, often with a
whitish scale.

Biopsy
Types of skin biopsy that may be used to confirm the
diagnosis and determine the histologic subtype of
BCC include the following:
Shave biopsy: Most often, the only biopsy that is
required

Punch biopsy: May be indicated in the case of a
pigmented lesion if there is difficulty distinguishing
between pigmented BCC and melanoma; ensures
that the depth of the lesion can be determined if it
proves to be a malignant melanoma.

proliferation of
basiloid
( similar to basal cells) cells
within the dermis forming a peripheral
palisade
appearance( like a fence), presence of
tumour
retraction
and
stroma
are the main features. It can
be undifferentiated or differrentiated (towrd
hair, sebaceous gland or tubular glands).
Histology of BCC

Management
1.Surgery
In nearly all cases of BCC, surgery is the
recommended treatment modality.
Techniques used include the following:
a.Electrodesiccation and curettage
b.Excisional surgery
c.Mohs micrographically controlled surgery

2.Cryosurgery-freezing the skin to about 180 c
3.Radiation therapy
BCCs are usually radiosensitive; radiation therapy
(RT) can be used in patients with advanced and
extended lesions, as well as in those for whom
surgery is not suitable. Postoperative radiation can
also be a useful adjunct when patients have
aggressive tumors that were treated surgically or
when surgery has failed to clear the margins of the
tumor.

RX….
4.Photodynamic therapy (PDT)(( application of a
photosensitizer plus UV light ))
is a reasonable choice in Certain conditions .
5.Pharmacologic therapy:
Topical agents used in the treatment of superficial
BCC include the following :

RX….
Topical 5-fluorouracil 5%: May be used to treat small,
superficial BCCs in lowrisk areas
Imiquimod: Approved by the US Food and Drug
Administration for the treatmentof nonfacial
superficial BCC
Tazarotene ( is a tpoical retinoid): Can also be used
to treat small, low-risk BCCs

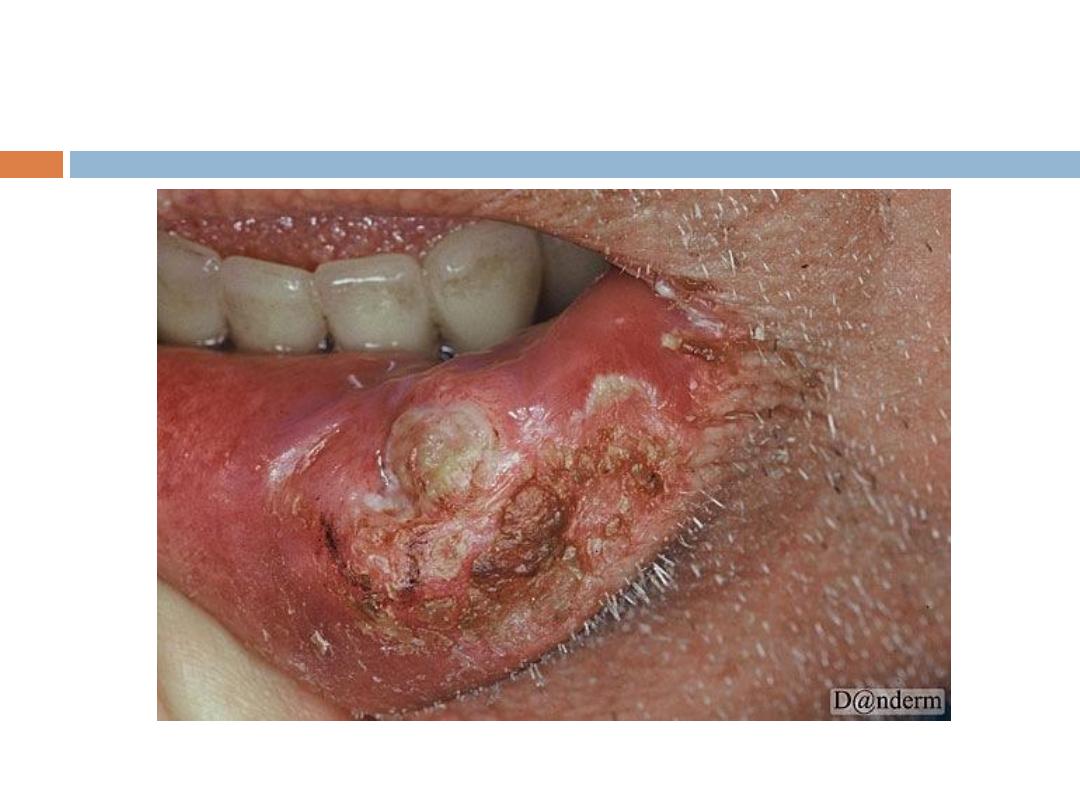
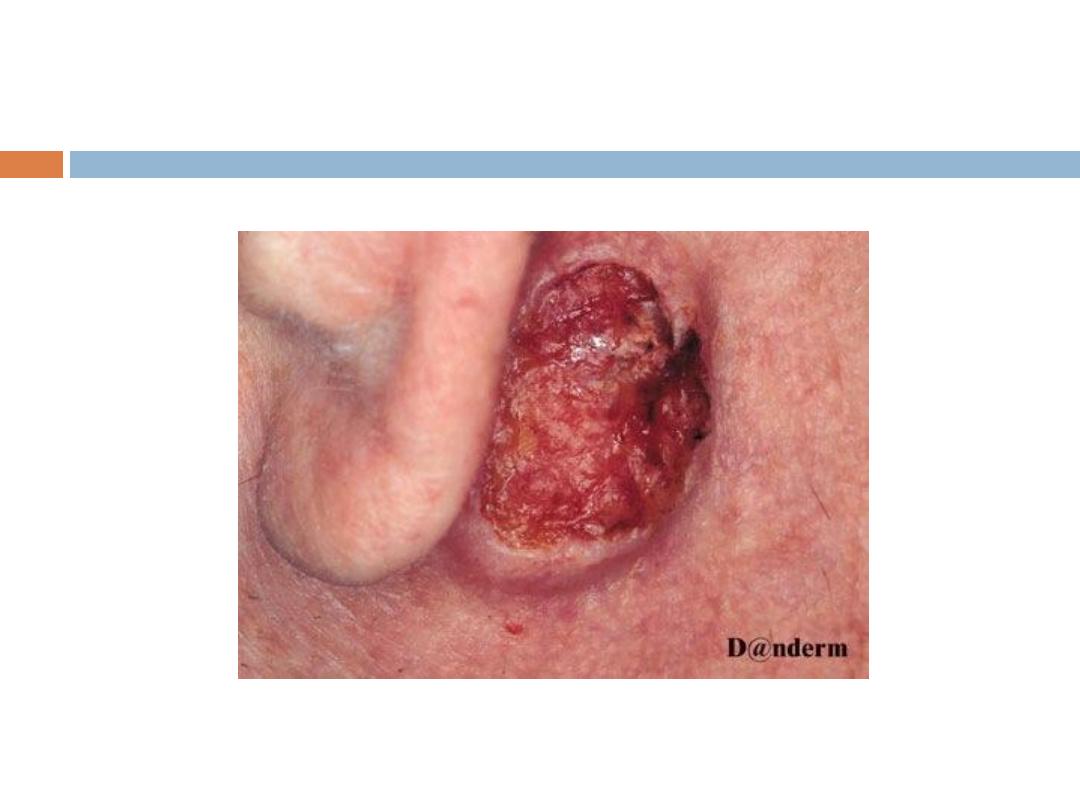
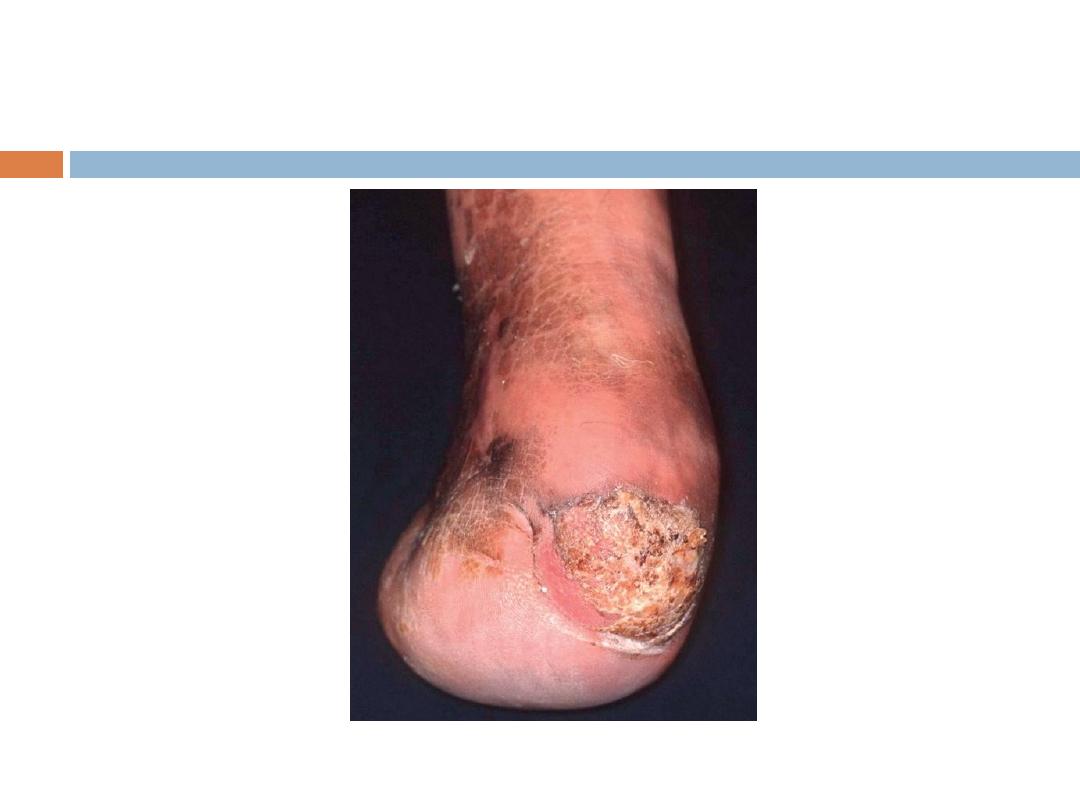
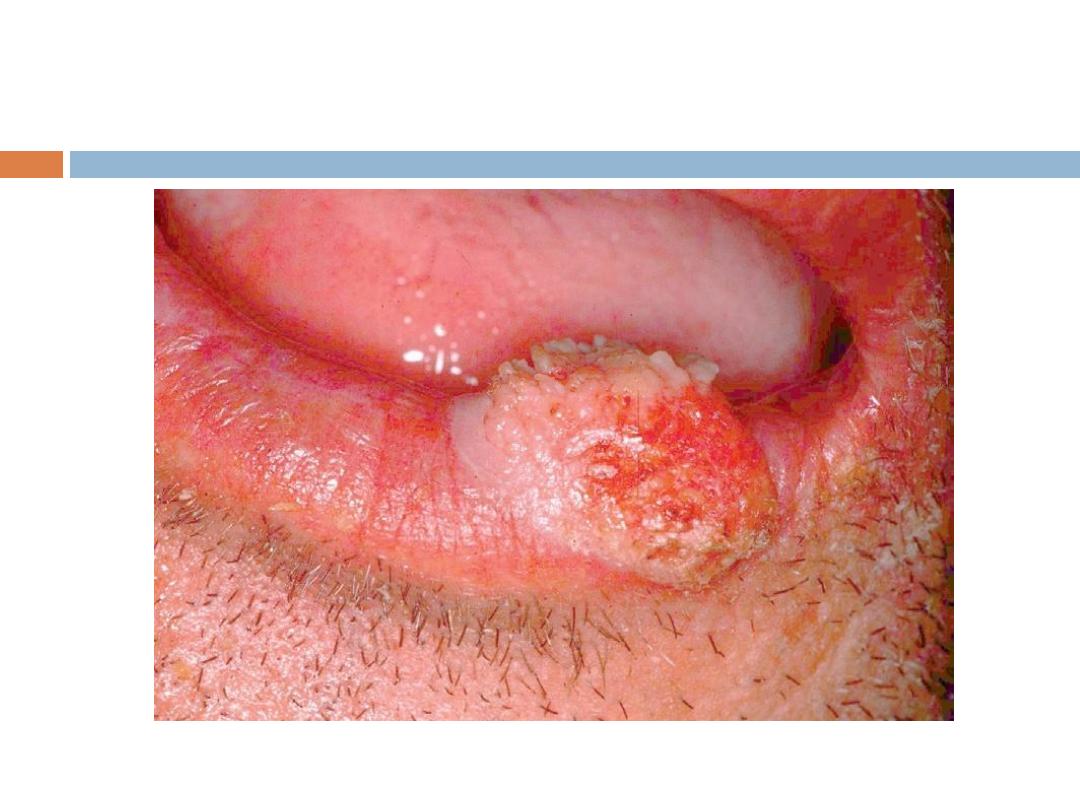
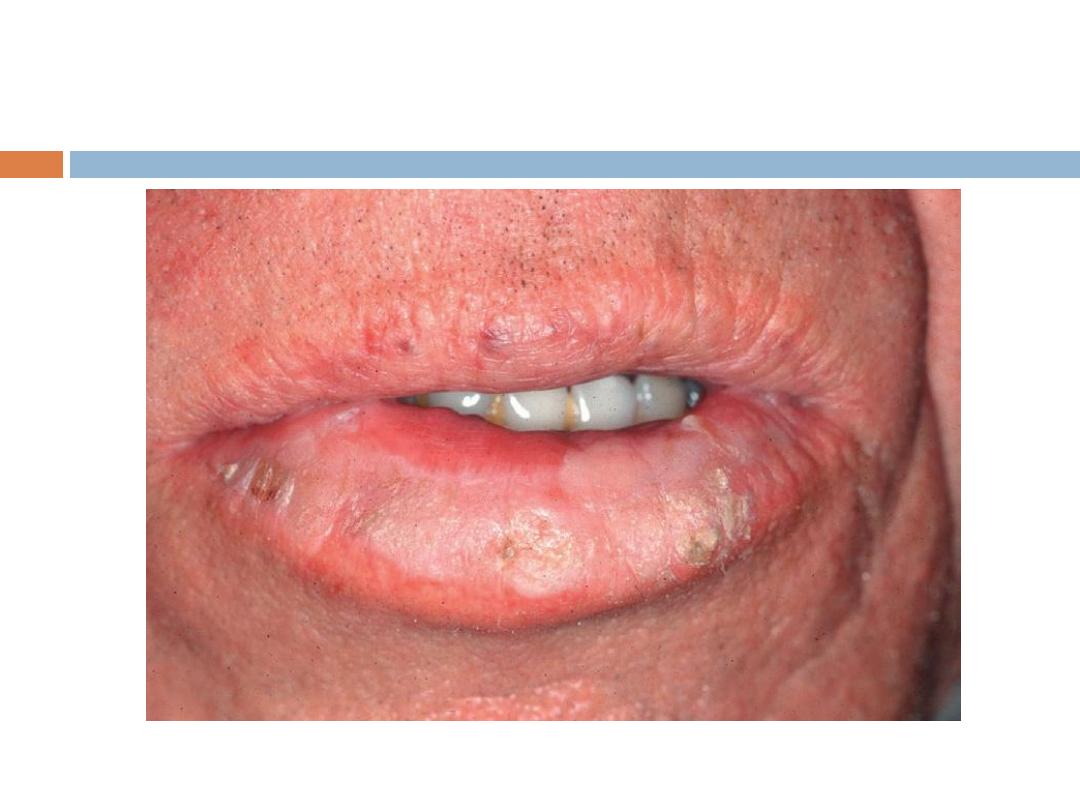
Squamous cell CA (SCC)
Squamous cell Ca (SSC) is the second most common
skin cancer, after basal cell carcinomas(BCC)
Site - mostly on head and neck ( development in non-
sun exposed skin usually follows chronic skin
inflammtion" old burn, lupus vulgaris, DLE" ).
Signs and symptoms
The classic presentation of a SCC is that of a shallow
ulcer with heaped-up edges, often covered by a
plaque, usually in a sun-exposed area.

SCC …
Typical
surface changes may include the following:
Scaling,ulceration, crusting,and a cutaneous horn
Less commonly, SCC presents as a pink cutaneous
nodule without overlying surface changes. Regional
spread of head and neck SCC may result in
enlarged preauricular, submandibular, or cervical
lymph nodes.

Diagnosis
The workup of suspected SCC may include the
following: Biopsy: Indicated for any lesion suspected
of being a cutaneous neoplasm
Computed tomography (CT) scanning: To evaluate for
bone or soft tissue invasion and cervical lymph
nodes at risk for metastasis
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): Preferred for
evaluation of perineural invasion and orbital or
intracranial extension.

Pathology
Nuclear atypia Frequent mitoses Cellula
pleomorphism Parakeratosis and hyperkeratosis.
A disorganized progression of cells from the basal to
apical layers of the epidermis. When cells break
the basal layer and invades the dermis it is called
invasive SSC With invasive SCC, nests of atypical cells
are found within the dermis, surrounded by an
inflammatory infiltrate.

Pathology…
The presence of malignant appearing
cells.SSC can be well differentiated moderately
differentiated or poorly differentiated.( The first
one has better prognosis).
Squamous cell carcinoma in situ (CIS){ malignant cells
are still within the epidermis}, sometimes referred to
as Bowen disease, is a precursor to invasive SCC.

Management
Treatment options include the following:
1.Electrodessication and curettage: Low-risk SCC on
the trunk and extremities 2. Mohs micrographic
surgery: Invasive SCC
3.Radiation therapy: As an adjuvant to surgery, to
provide improved regional control, or as primary
therapy in patients who are unable to undergo
surgical excision

Rx..
Oral 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and epidermal growth
factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitors: Adjuvant therapy
for select highest-risk cases
Systemic chemotherapy: A consideration for
metastaticSCC

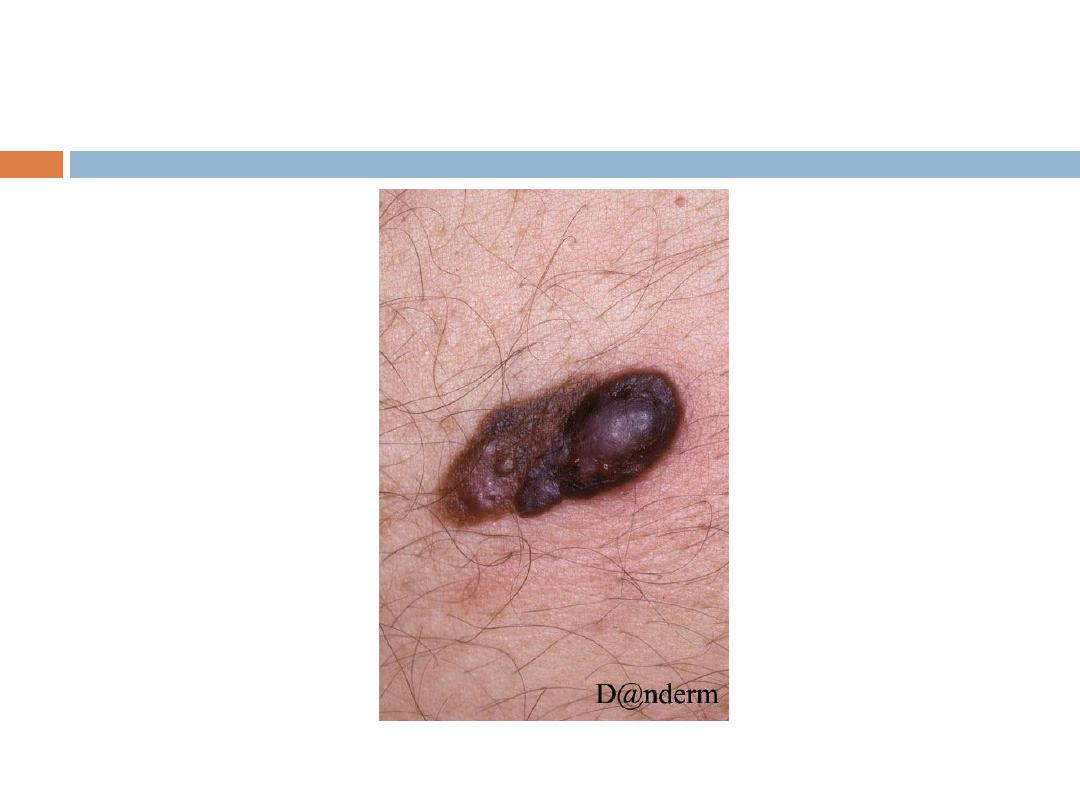
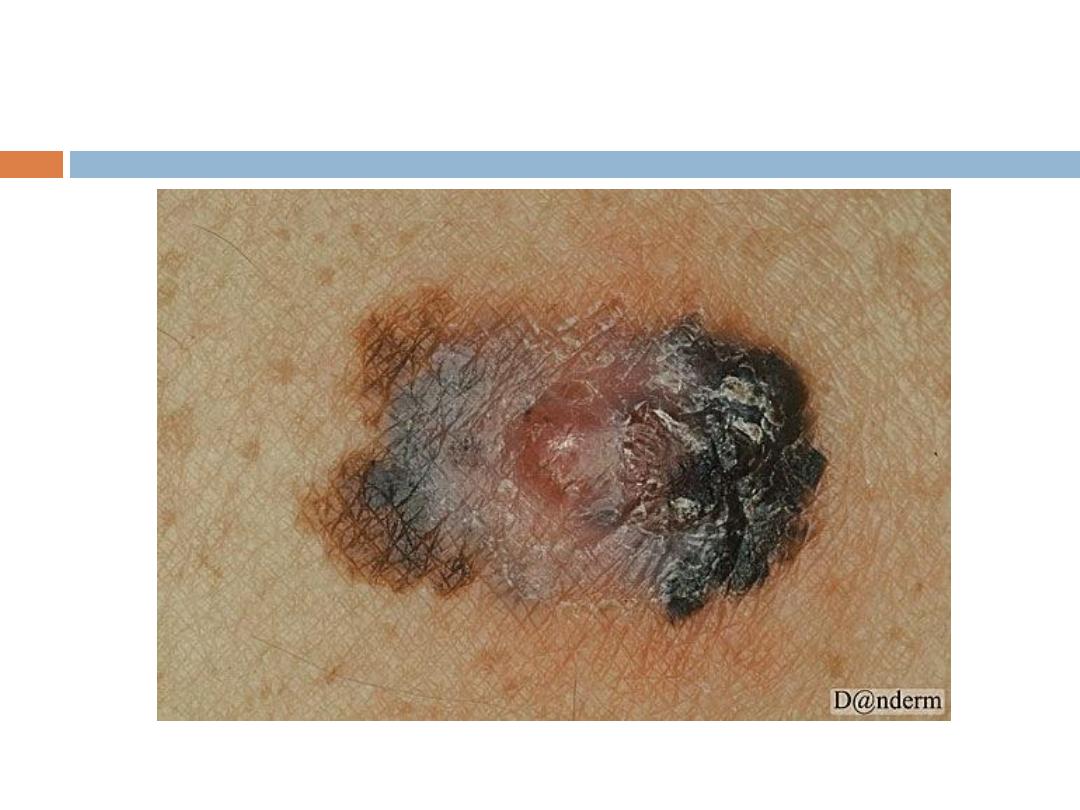
Malignant melanoma
is a neoplasm of melanocytes or a neoplasm of the
cells that develop from melanocytes. Although it
was once considered uncommon, the annual
incidence
has increased dramatically over the past few
decades. Surgery is the definitive treatment for
early-stage melanoma, with medical management
generally reserved for adjuvant treatment of
advanced melanoma.

History
The history should address the following:
Family history of melanoma or skin cancer
Family history of irregular, prominent moles
Family history of pancreatic cancer or astrocytoma
Previous melanoma (sometimes multiple; patients have
reported as many as 8 or more primary
melanomas)

History…
Previous sun exposure
Changes noted in moles (eg, size, color, symmetry,
bleeding, or ulceration)
History or family history of multiple nevus syndrome

Physical examination includes the following:
Total-body skin examination, to be performed on
initial evaluation and during all subsequent visits
Serial photography, epiluminescence microscopy,
dermoscopy ,and computerized image analysis, to
be considered as adjuncts
Skin examination involves assessing the number of
nevi present

and distinguishing between typical and atypical
lesions. Early melanomas may be differentiated
from benign nevi by the ABCDs, as follows:
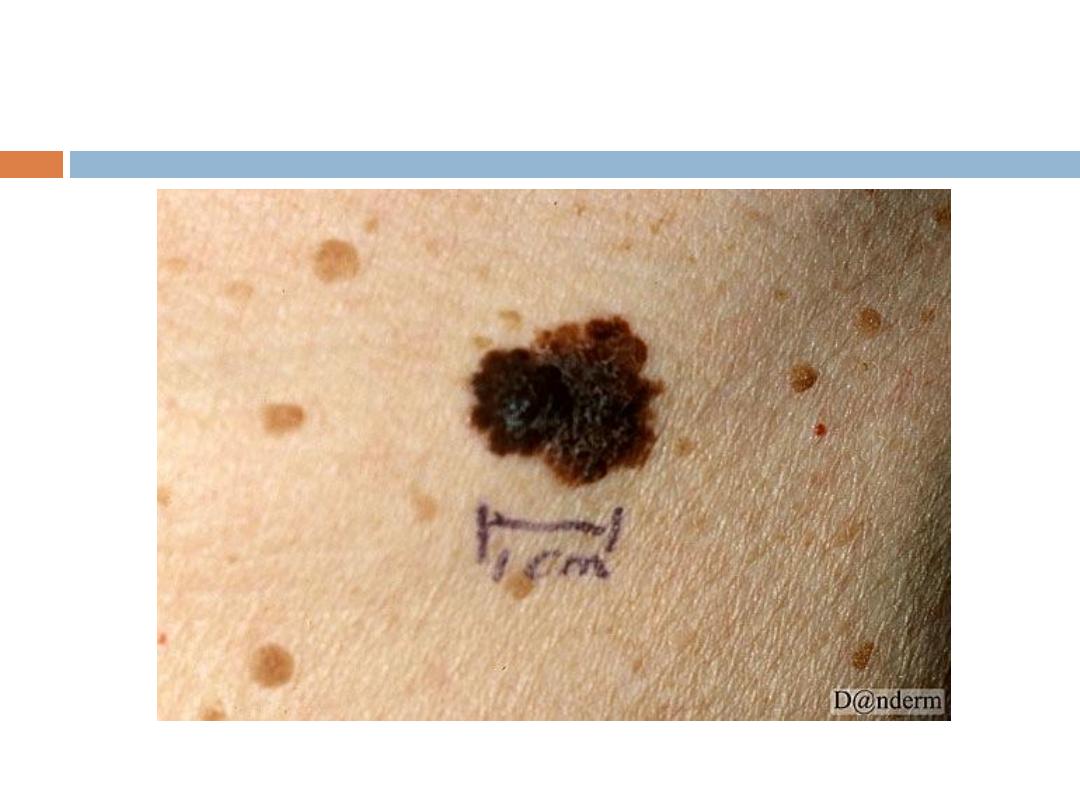
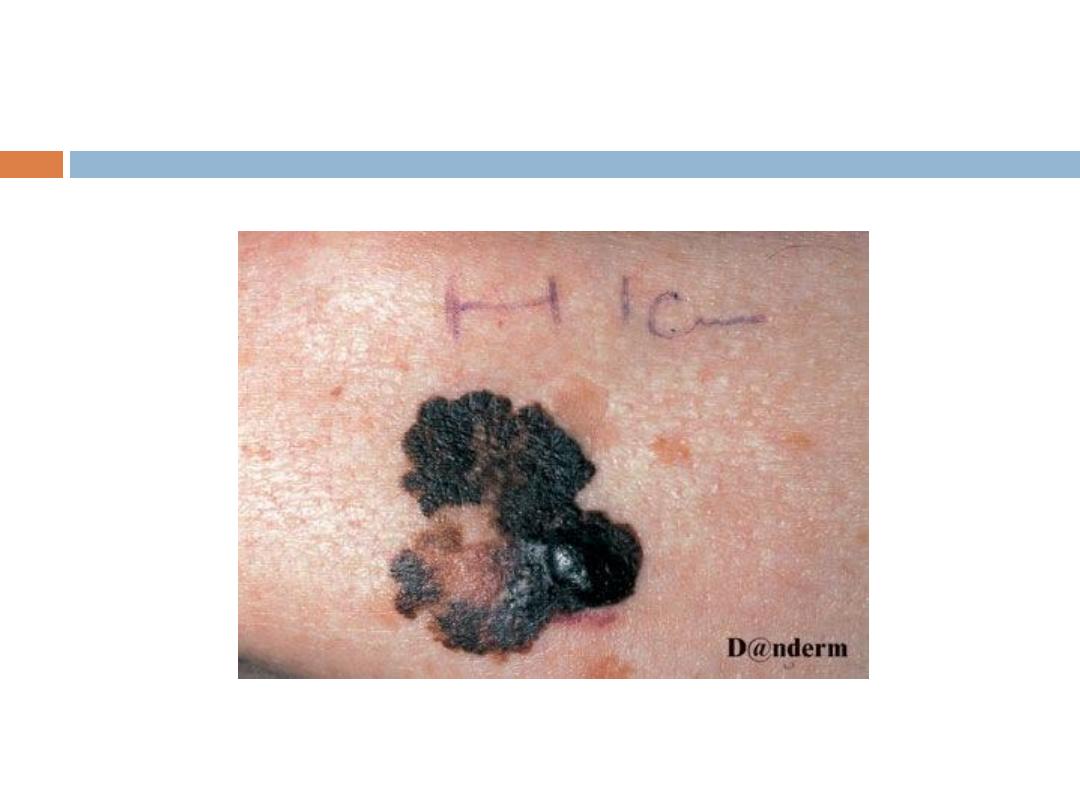
A - Asymmetry
B - Border irregularity
C - Color that tends to be very dark black or blue
and variable
D - Diameter ≥ 6 mm

If a patient is diagnosed with a melanoma, examine
all lymph node groups.
NB: Dermoscopy: (a hand held device for the
examination and differentiation of pigmented
lesions Including MM) may be a useful tool.

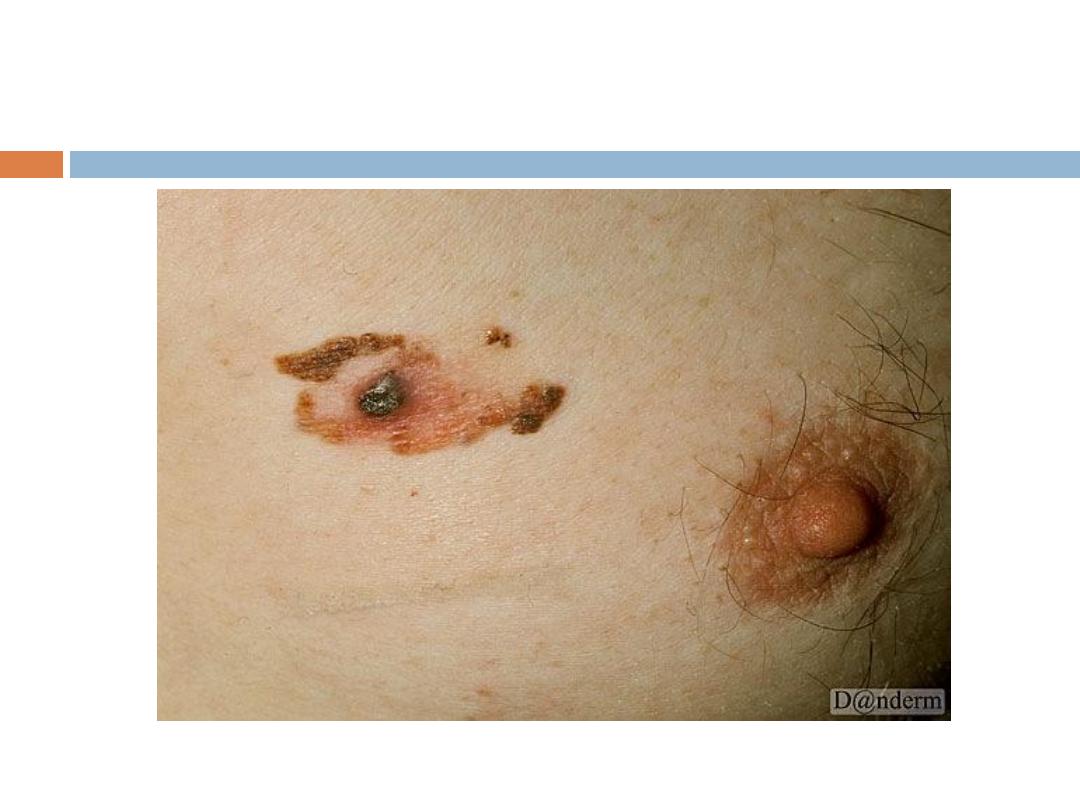
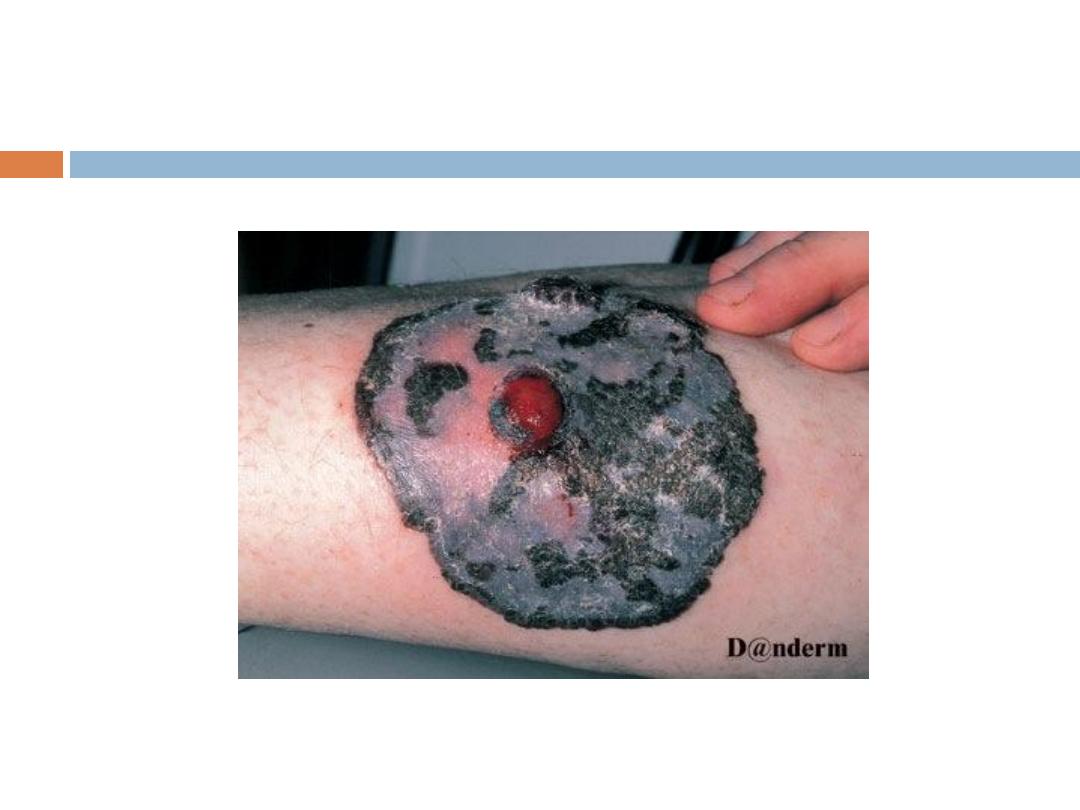
Clinical types:
1- Lentigo maligna melanoma:
Affects the face in elderly people, irregular in shape
and pigmentation grows for
years in situ before invasion.
2- Superficial spreading melanoma:There is a radial
growth phase into the epidermis before invading
the dermis.

Clinical types…
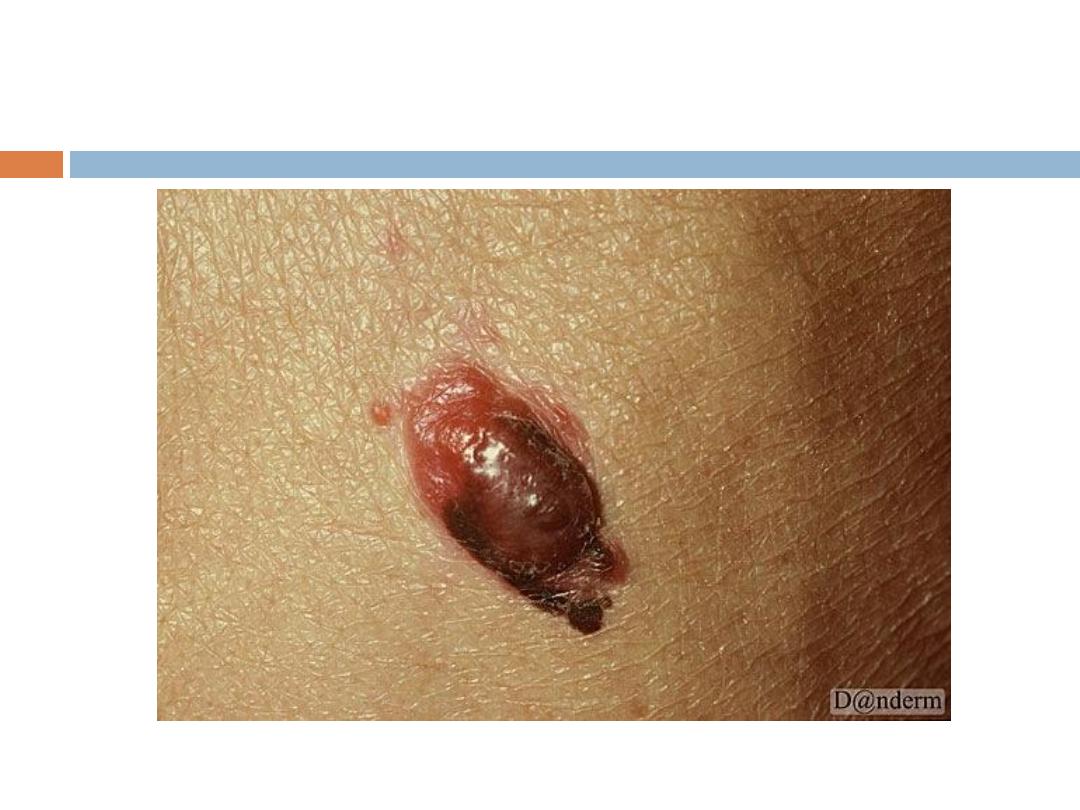
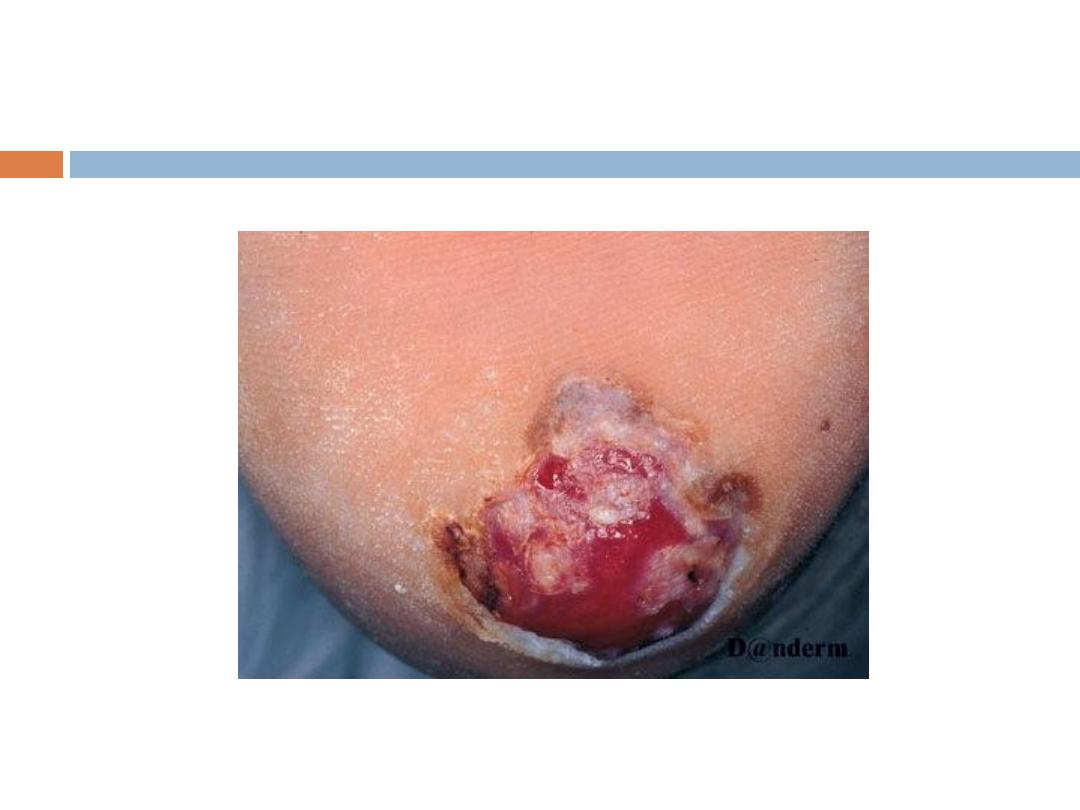
3- Nodular melanoma: No radial growth phase, early
invasion, very aggressive.
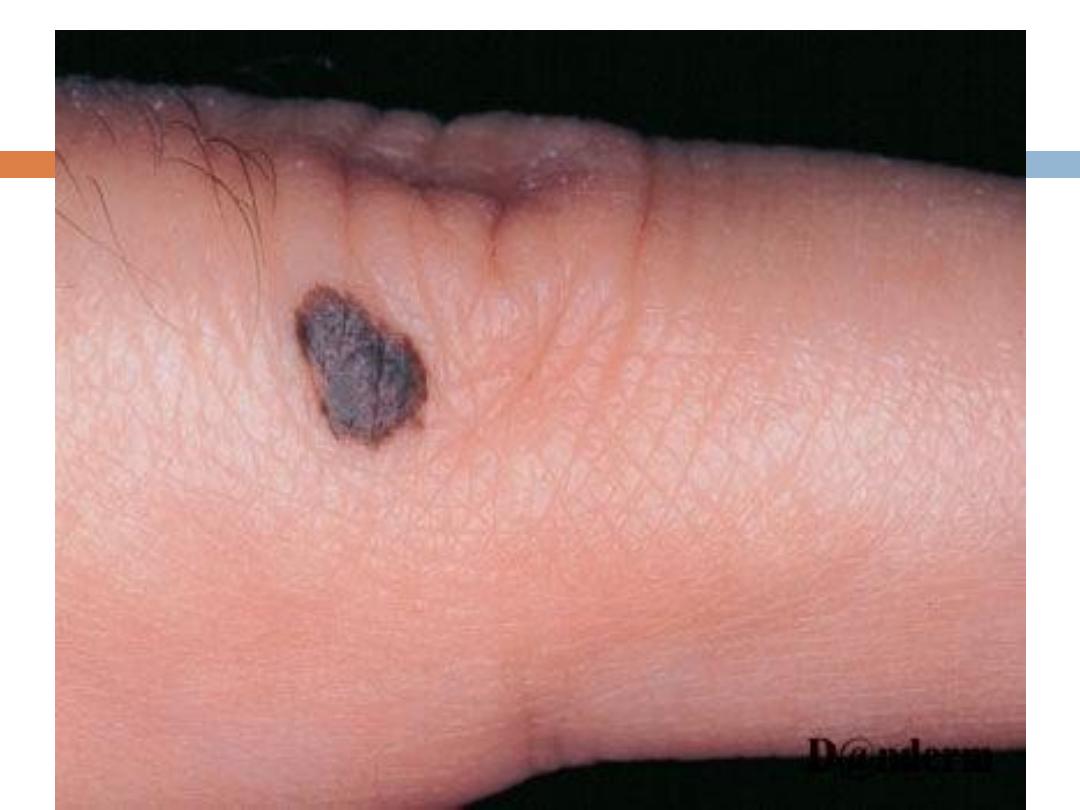
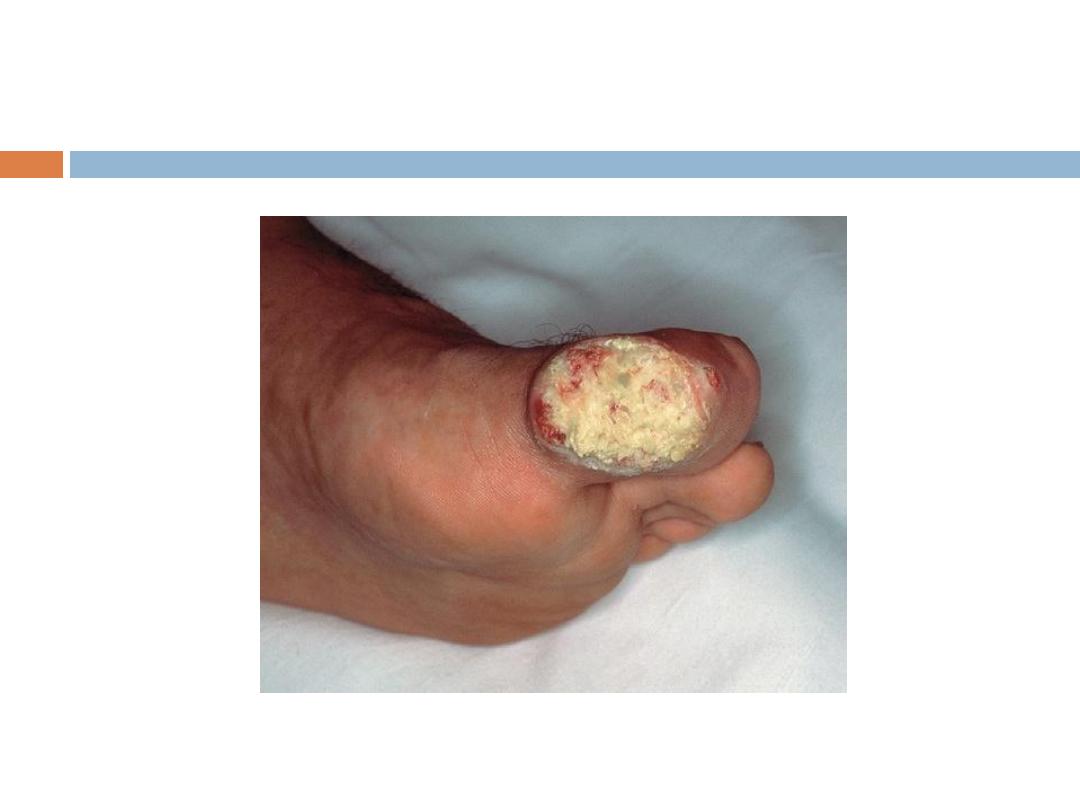
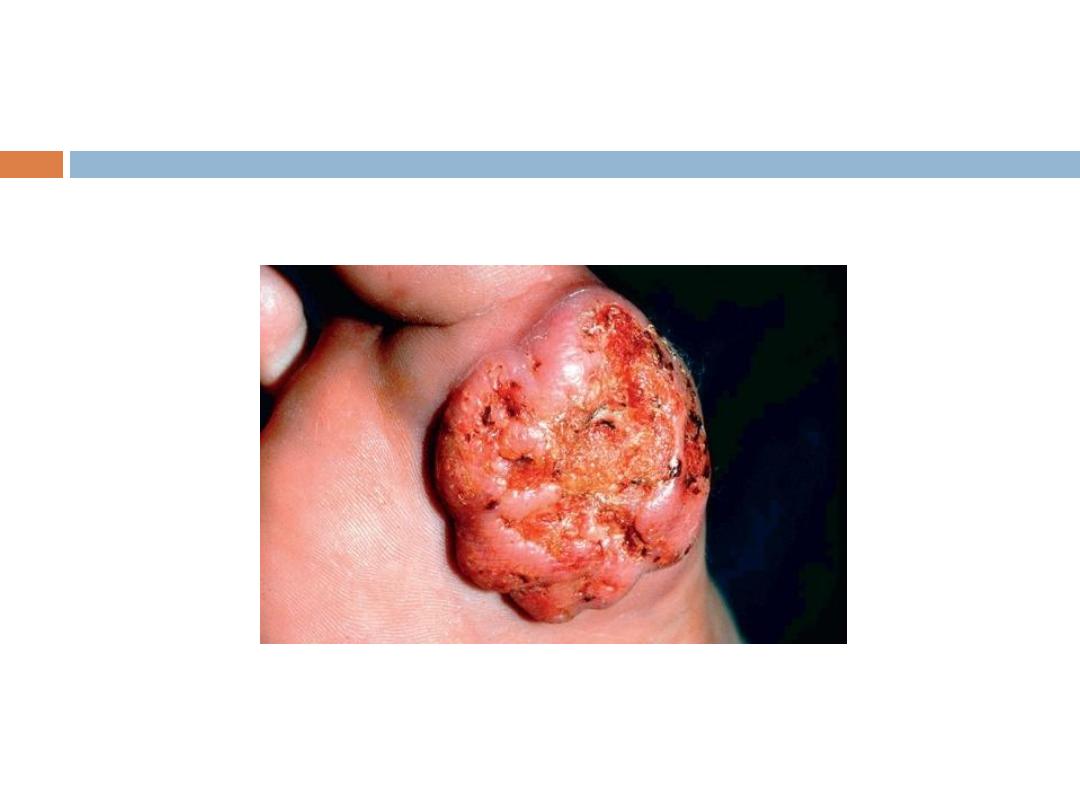
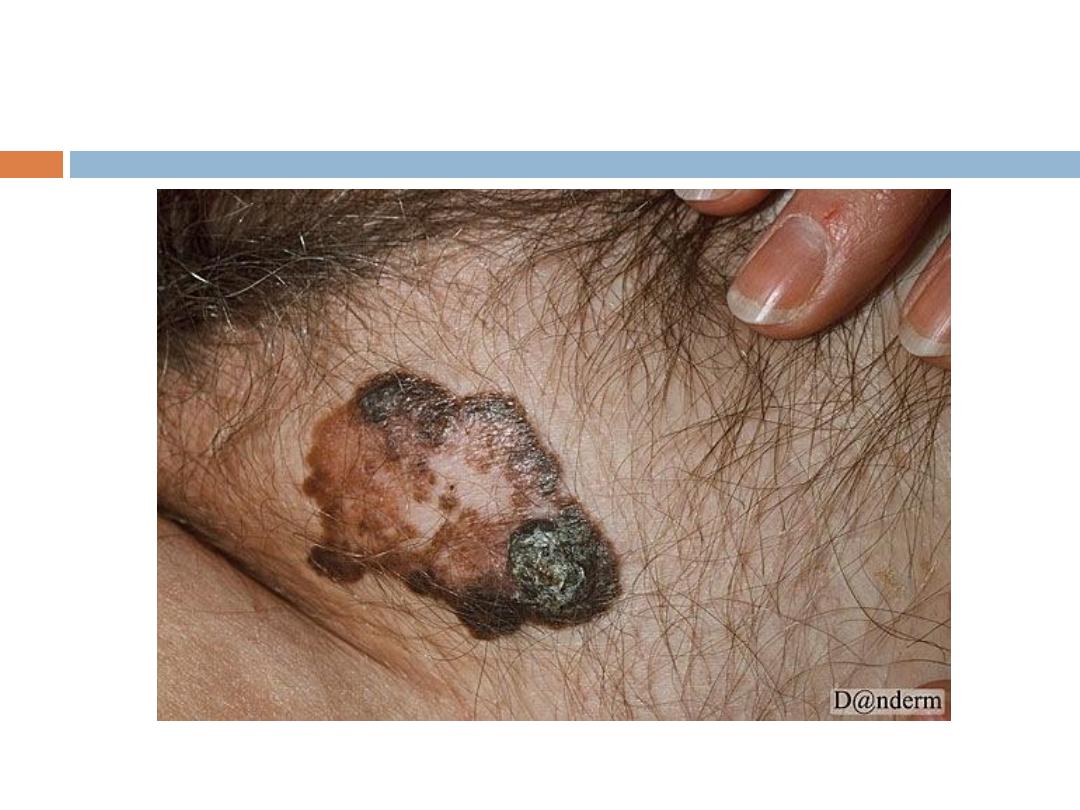
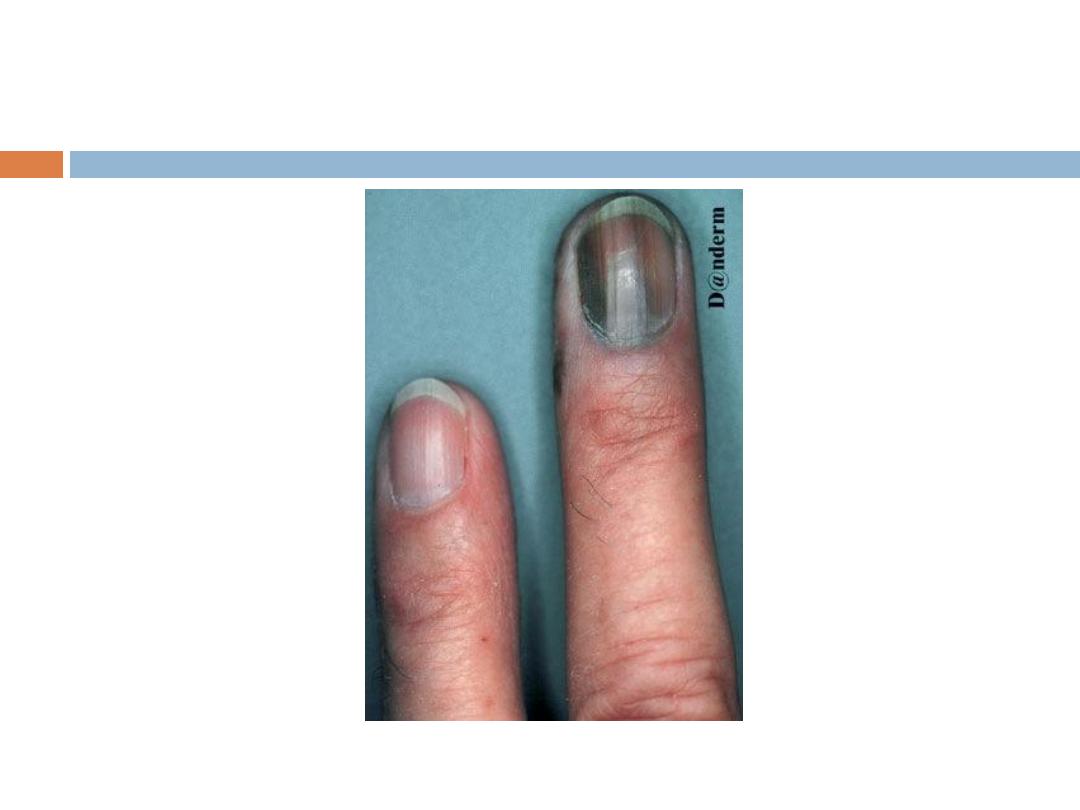
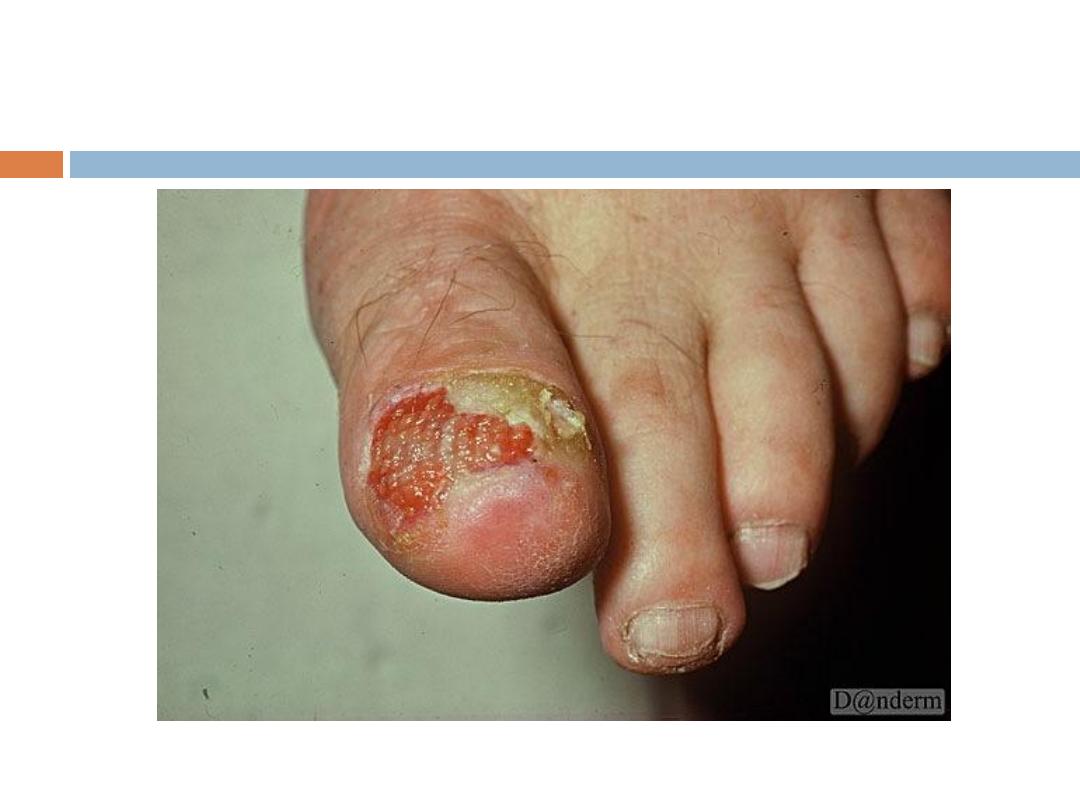
4- Acral lentigenous melanoma: Most common type in
Iraq, affects the palms and soles, presents as
irregularly pigmented macule or patch. presence of
nodule indicates invasion

laboratory studies
The following laboratory studies are indicated:
Complete blood count
Complete chemistry panel (including alkaline
phosphatase, hepatic transaminases, total protein,
and albumin)
Lactate dehydrogenase

imaging modalities
Chest radiography
Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain
Ultrasonography (possibly the best imaging study for
diagnosing lymph node involvement)
Computed tomography of the chest, abdomen, or
pelvis
Positron emission tomography (PET; PET-CT may be
the best imaging study for identifying other sites of
metastasis)

Histopathology
Characteristic histologic findings include the following:
Cytologic atypia, with enlarged cells containing
large, pleomorphic, hyperchromic nuclei with
prominent nucleoli
Numerous mitotic figures
Pagetoid growth pattern with upward growth of the
melanocytes

Procedural management
Complete excisional biopsy of a suggestive lesion
Surgical excision or reexcision after biopsy
Elective lymph node dissection (ELND) for patients with
clinically enlarged nodes and no evidence of distant
disease
Sentinel lymph node biopsy .

Management
Surgery (wide local excision ) is the definitive
treatment for early-stage melanoma.
Medical management is reserved for adjuvant
therapy of patients with advanced melanoma.
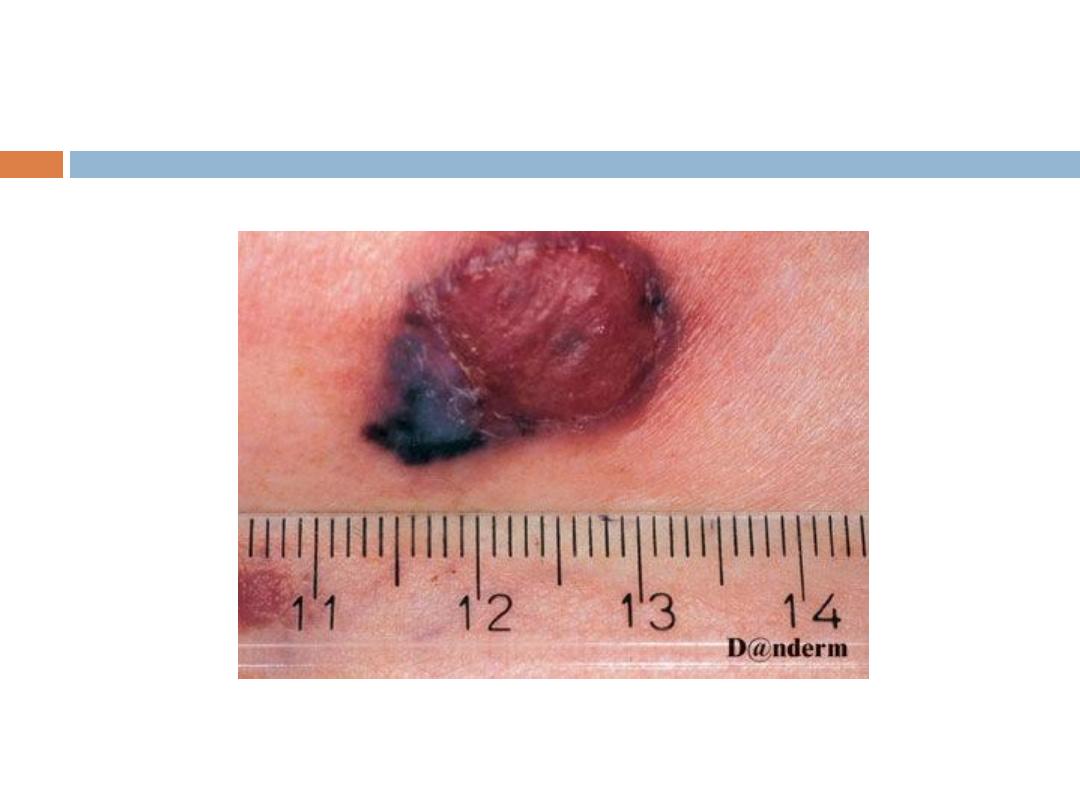

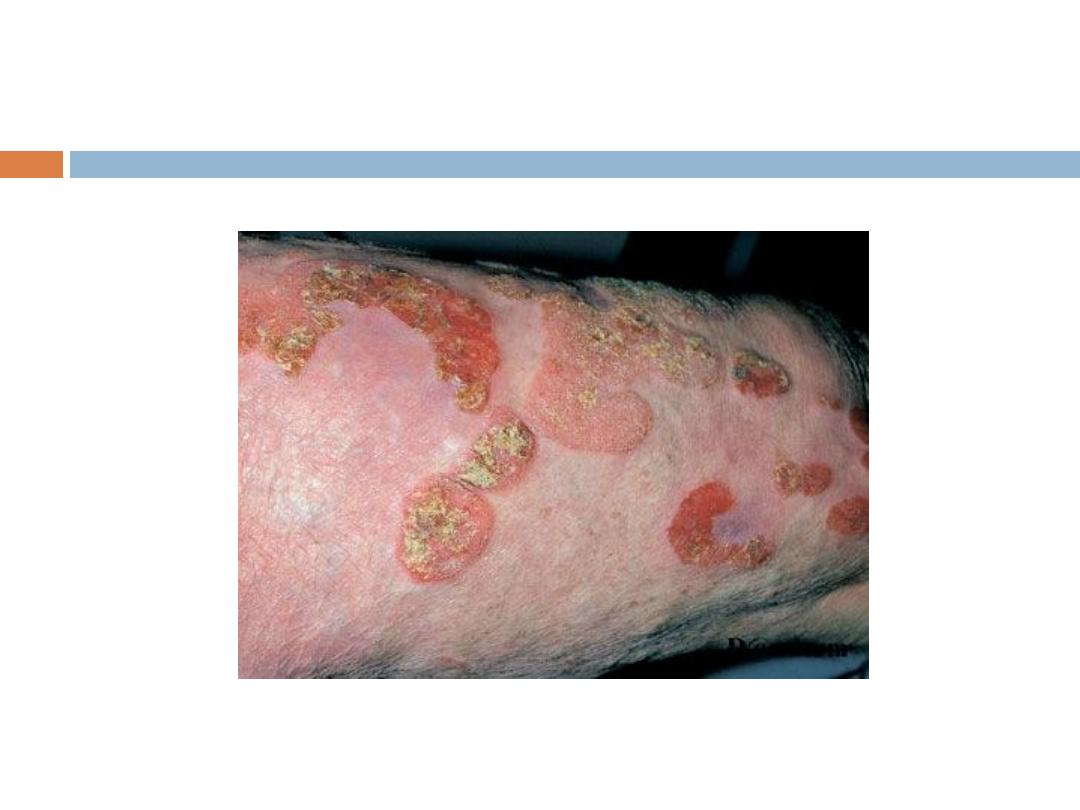
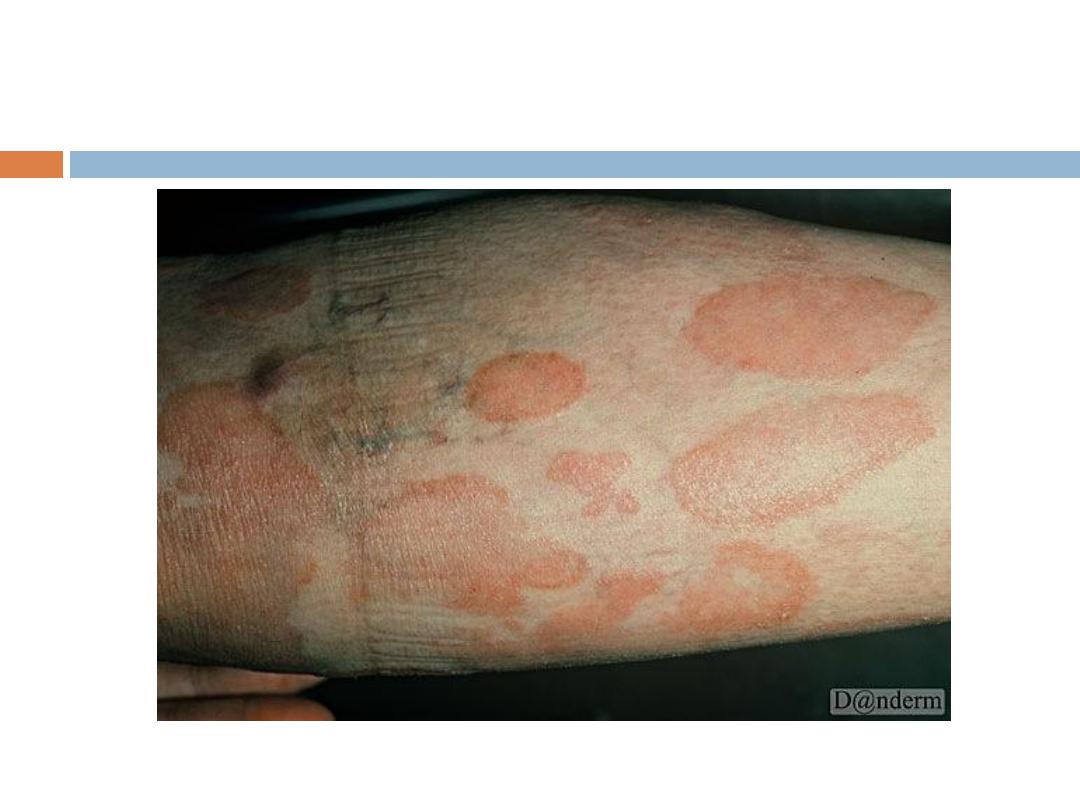
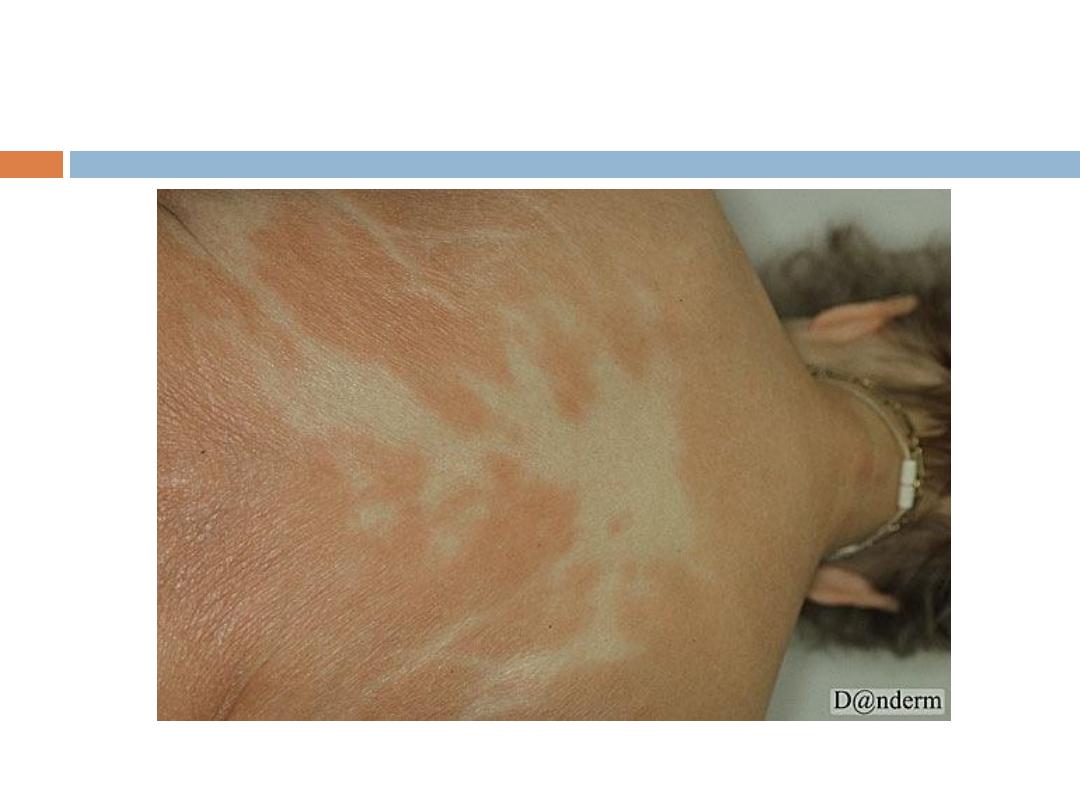
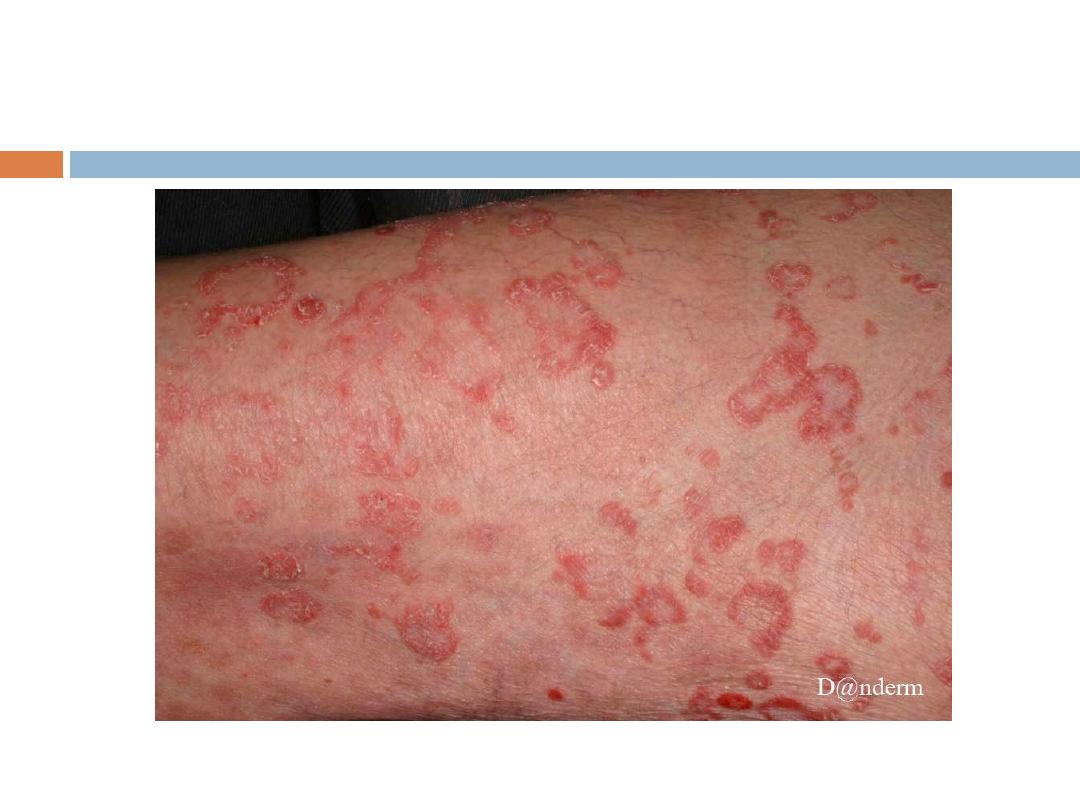
Mycosis Fungoides (MF):
It is primary T-cell lymphoma of the skin. There is
clonal proliferation of CD 4 positive T-cells while
CD 8 positive T-cells represent the antitumor
response.
Clinical manifestations:
The disease arises in mid to late adulthood.

Stages
1- Patch stage: Randomly distributed usually scaly
patches.
2- Plaque stage: Plaques of different shapes; round,
oval or bizarre-shaped, persistent and randomly
distributed.
3- Tumor stage: tumors arise sometimes with
ulceration.
4- Erythroderma: Generalized erythema and scaling
that involves most of the skin surface.

Symptoms
pruritus
, which may be severe.

Dermatopathology
Atypical lymphocytes with large
cerebriform(Convoluted) nuclei are gathered in
the dermis at the dermo-epidermal junction. Some of
these cells invade the epidermis in collections called
Pautrier's micro-abscesses.
Staging: TNM

Treatment
According to the stage
Topical steroids
Topical retinoids Topical chemotherapy - Eg, nitrogen
mustard or bischloroethylnitrosourea (BCNU)
Ultraviolet B (UV-B) light treatment or UV-A light
treatment enhanced with psoralen (PUVA)

RX..
Total-body electron beam radiation
These modalities are also used in combination with
systemic modalities (eg, PUVA plus interferon) for
higher-stage disease.
Course and prognosis:
The course is slow. The prognosis depends on the
stage
Survival May be for 10 to 15 years.