
connective tissues
Specialized connective tissues

Vascular connective tissue
Blood: is a specializing connective tissue
it consists of erythrocyte, leukocyte, and
the intercellular substance is the plasma,
the fibers appear as fibrin when blood is
clotted.
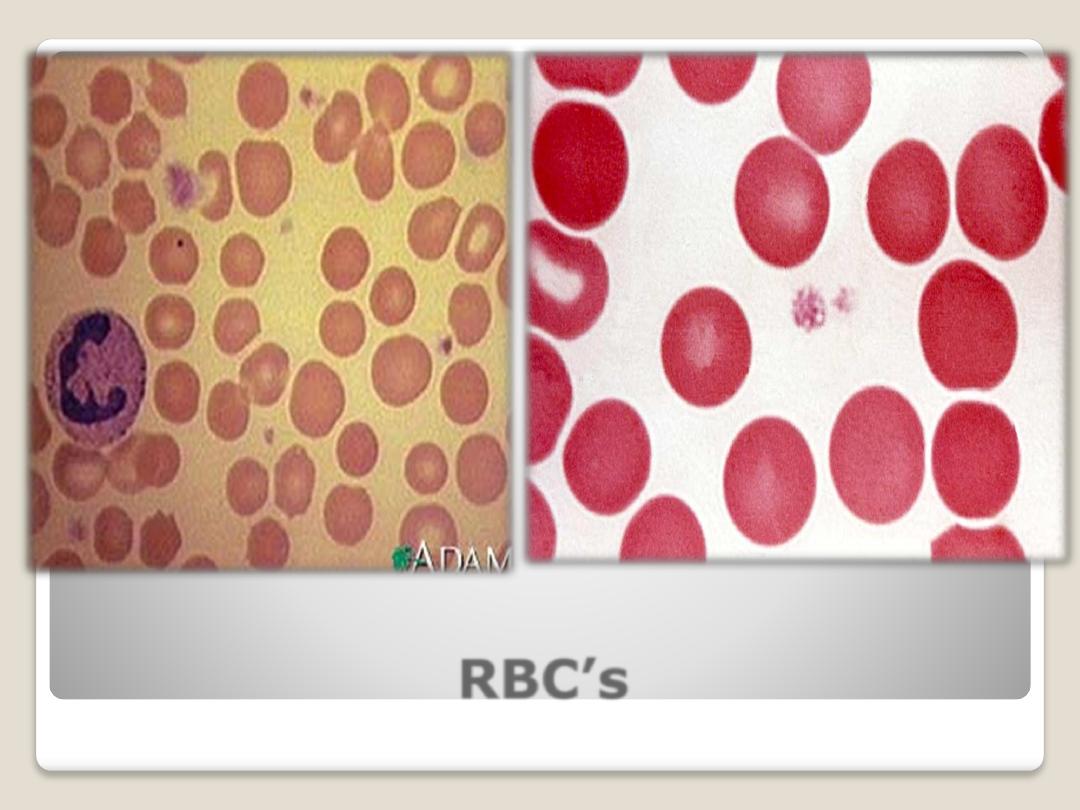
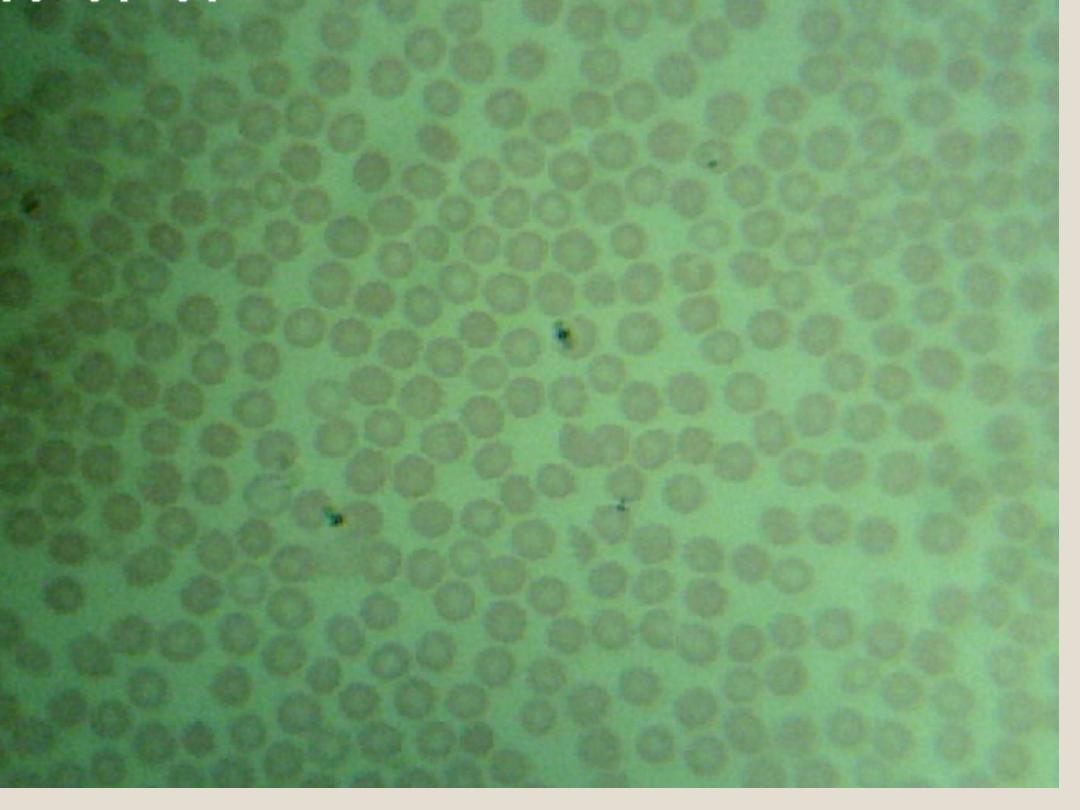
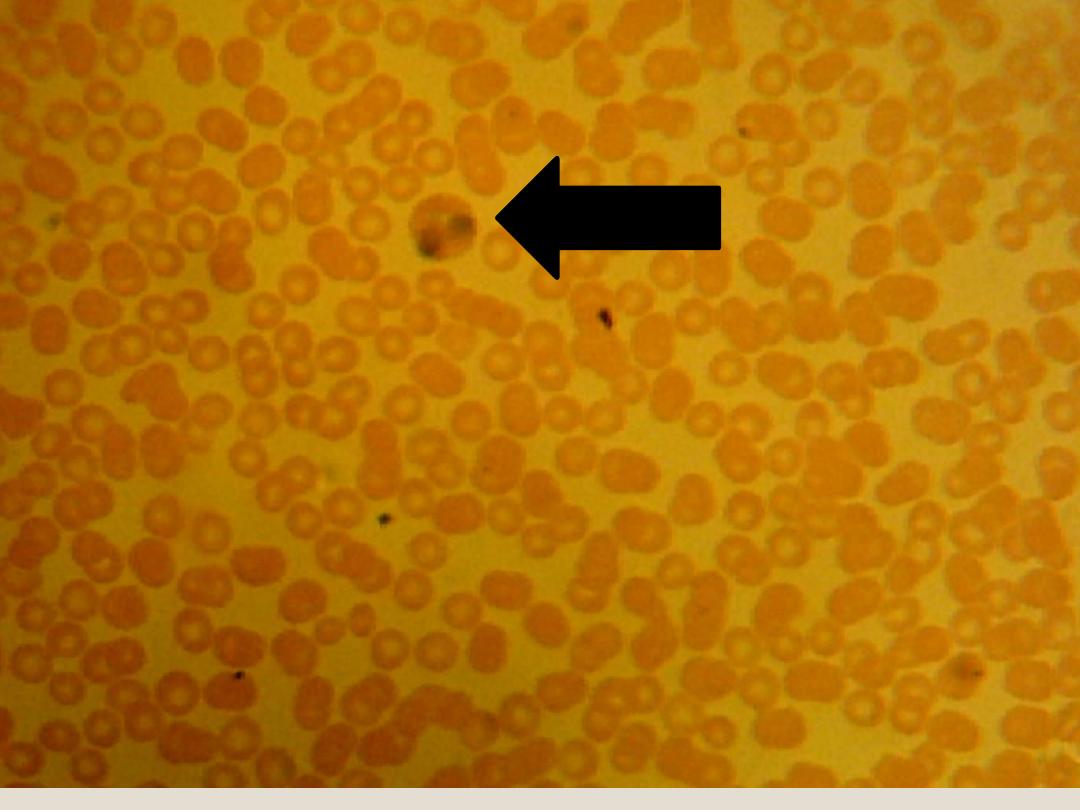
Red blood
Corpuscles
(Erythrocytes):
are biconcave disks without nuclei, When
we exam the blood smear, we can see
several amount of R.B.C’s.

RBC’s
White blood cells (leukocytes) : are
spherical in shape, according to the type
granules of their cytoplasm and the shape
of their nuclei, leukocyte are divided into:
1) A granular leucocytes : have
cytoplasm that appear homogenous and
nuclei are spherical shape. Include :
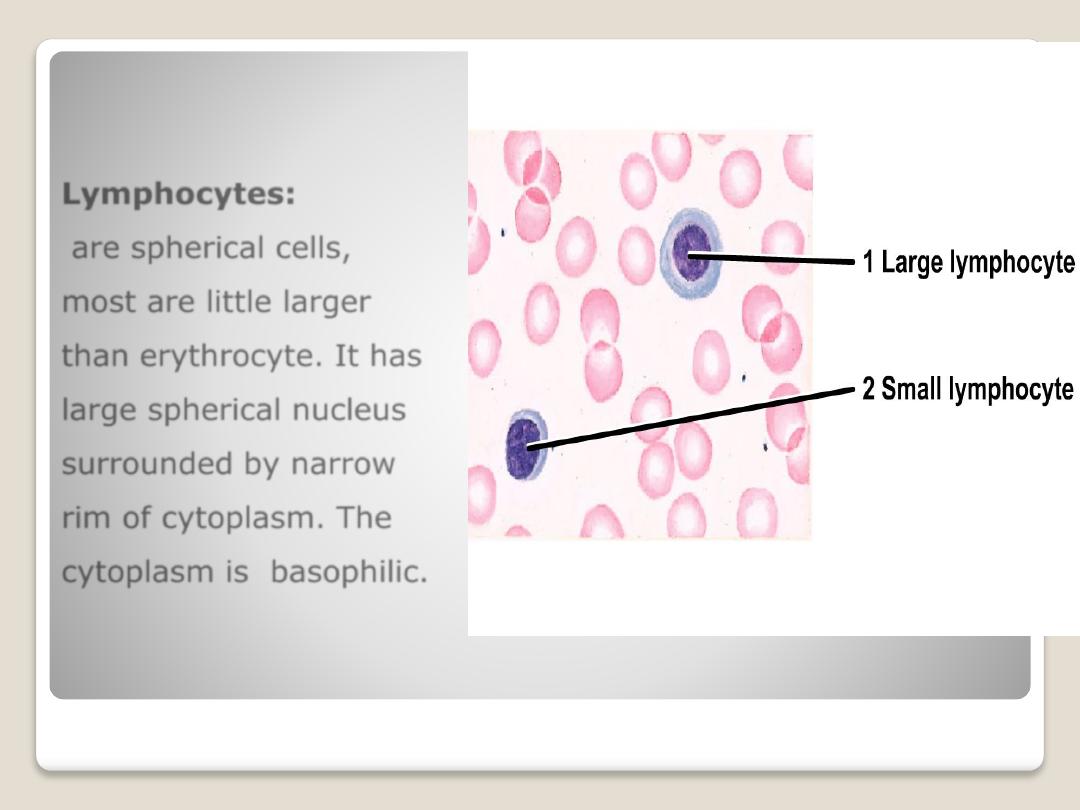
Lymphocytes:
are spherical cells,
most are little larger
than erythrocyte. It has
large spherical nucleus
surrounded by narrow
rim of cytoplasm. The
cytoplasm is basophilic.
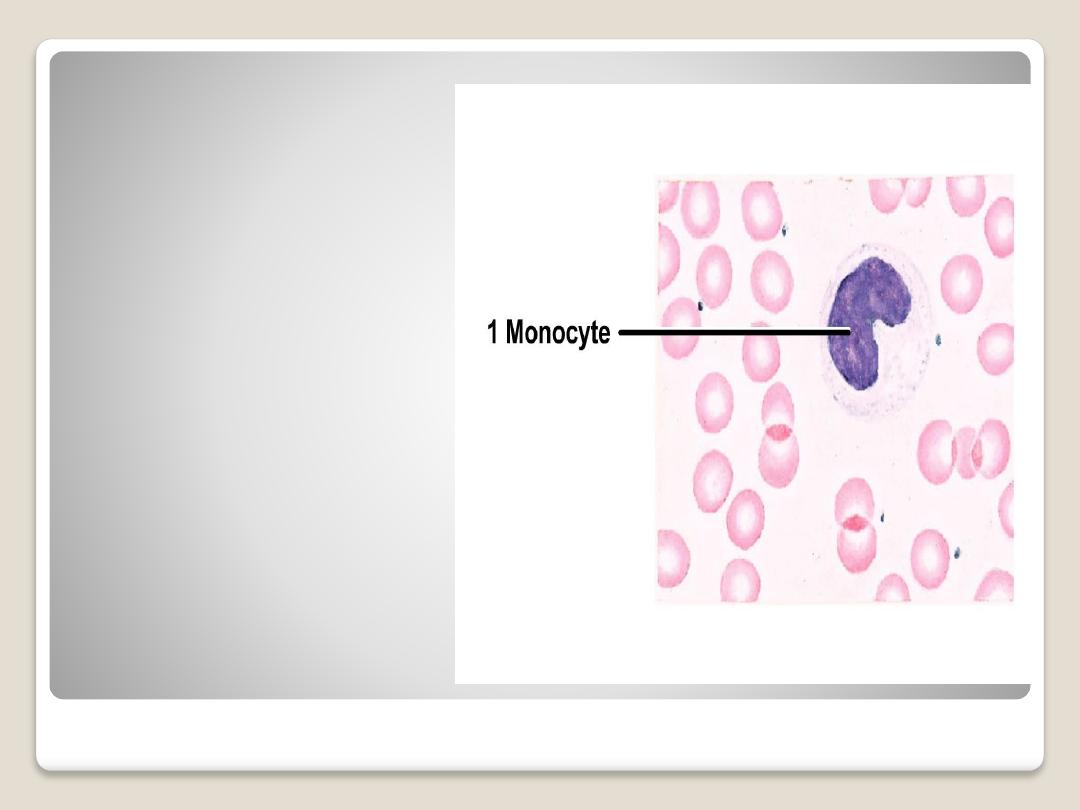
Monocytes:
are large cells, The
nucleus is oval,
horseshoe, or kidney
shaped and is generally
eccentrically placed; the
cytoplasm
is basophilic
and grayish-blue in color.
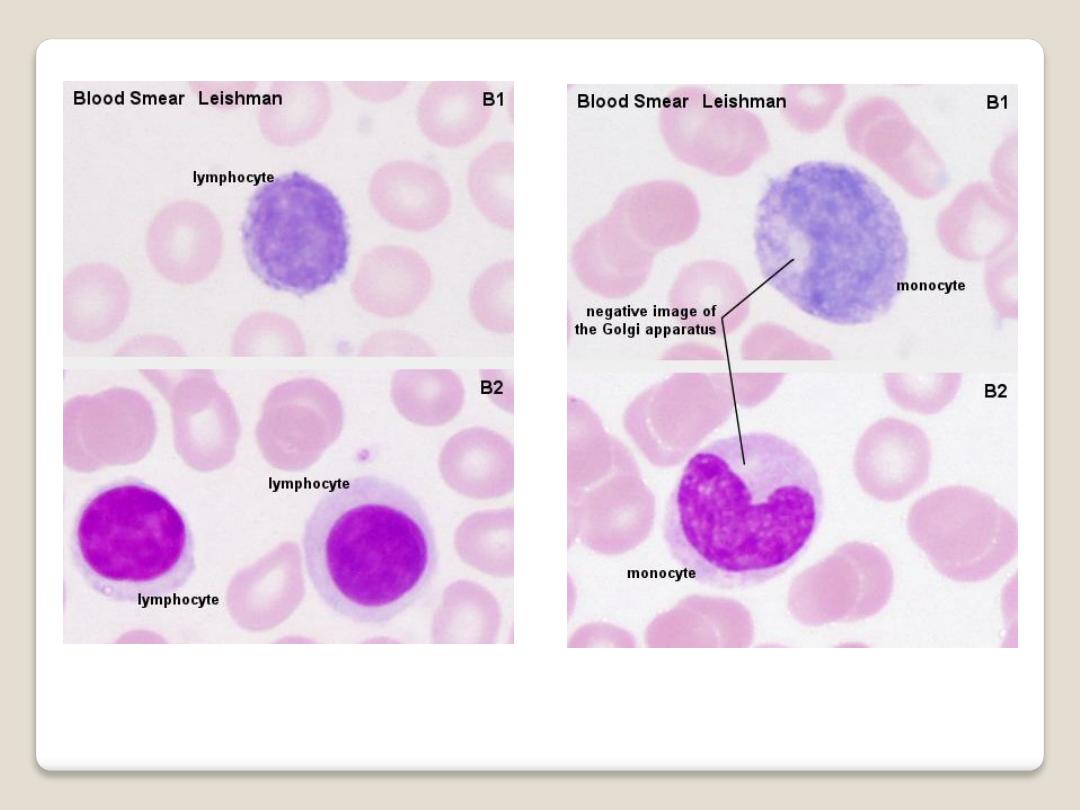
Lymphocyte & Monocyte
2)Granular leukocytes: contain specific
granules and
have nuclei with two or
more lobes . There are three types of
granular leukocytes:
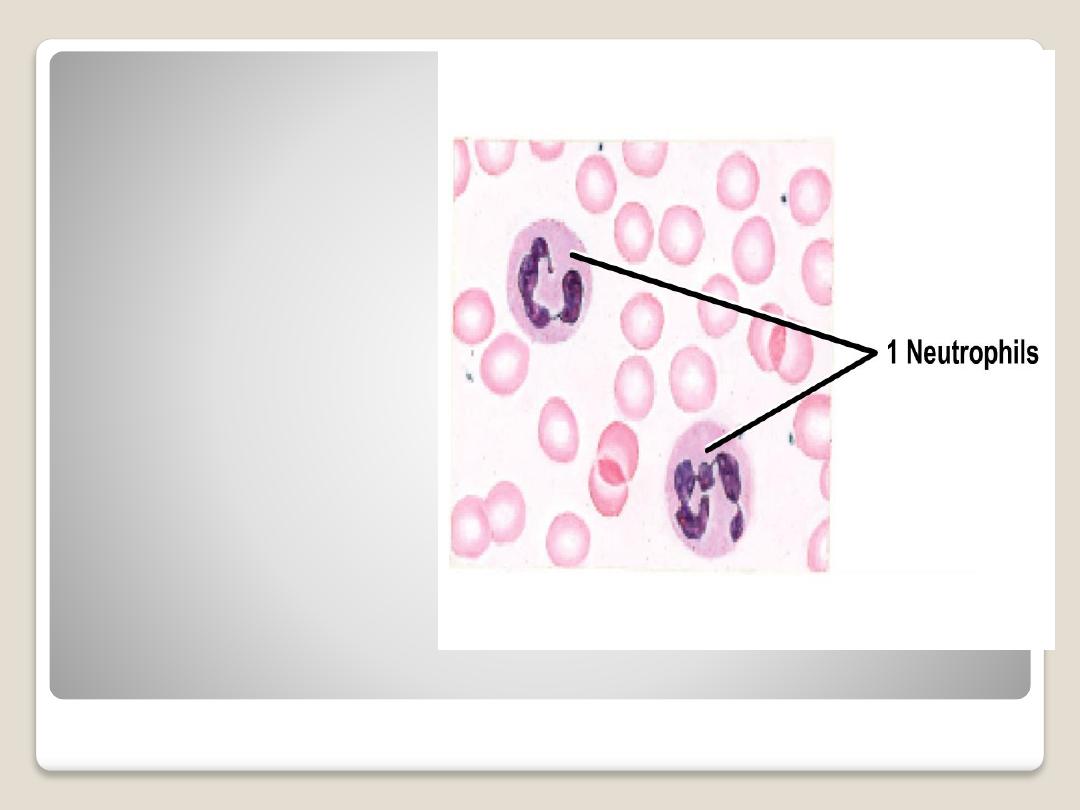
Neutrophils:
polymorphonuclear
leukocytes, nucleus
has from 3-5 irregular
ovoid lobes connected
by fine threads of
chromatin. The
cytoplasm filled with
fine
granules.
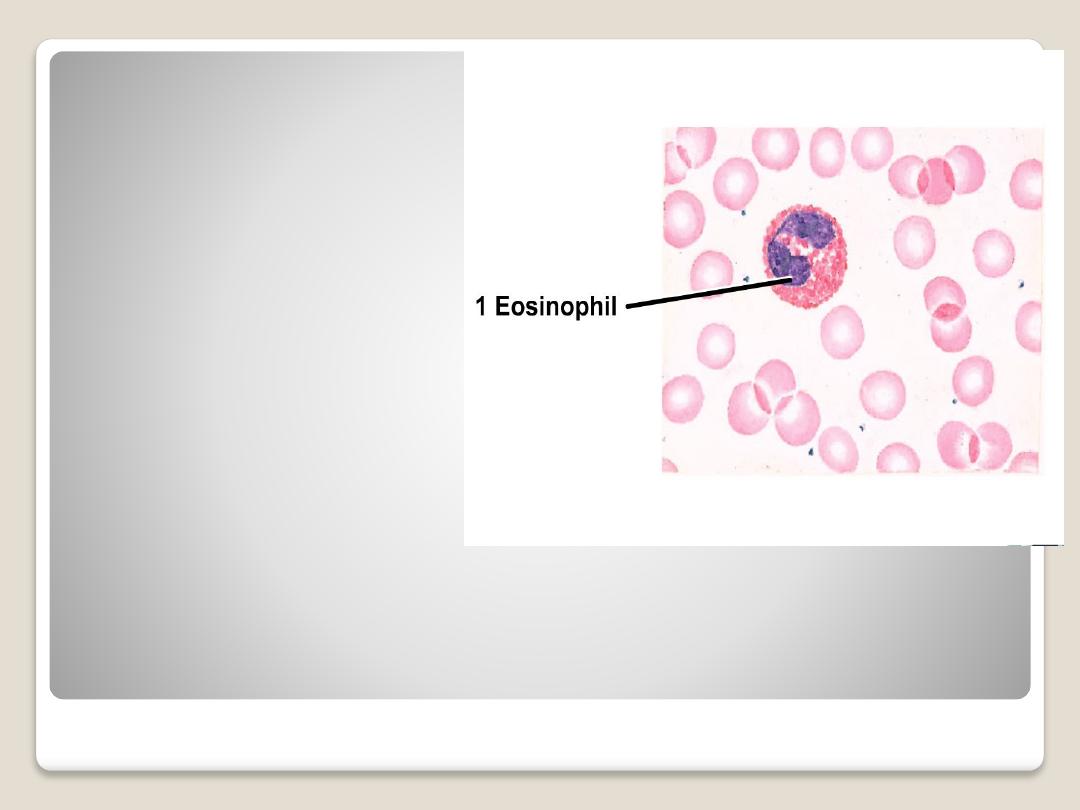
Eosinophils or
(acidophils):
are larger than
neutrophils, the nucleus
is usually bilobed. the
cytoplasm is filled with
course granules and
stain with acidic dyes.
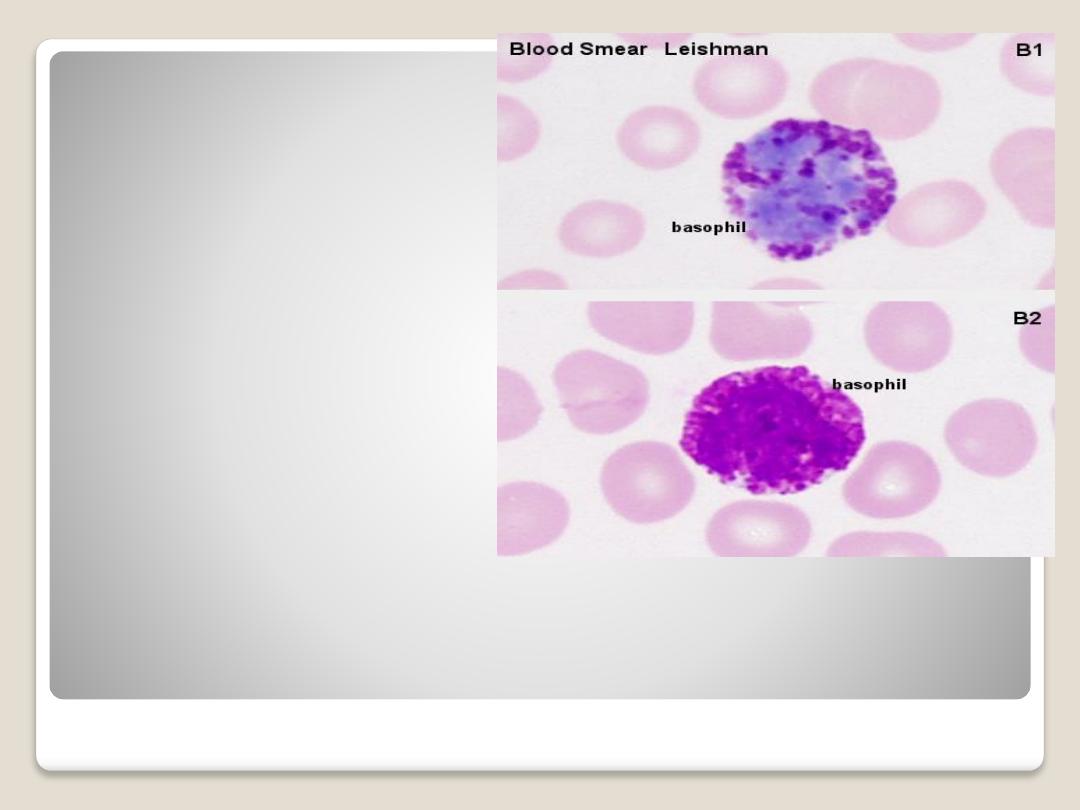
Basophiles:
are the same size as
neutrphil, nucleus usually
irregular two lobes
appearing as (S) shape.
The cytoplasmic granules
are course and variable in
size.
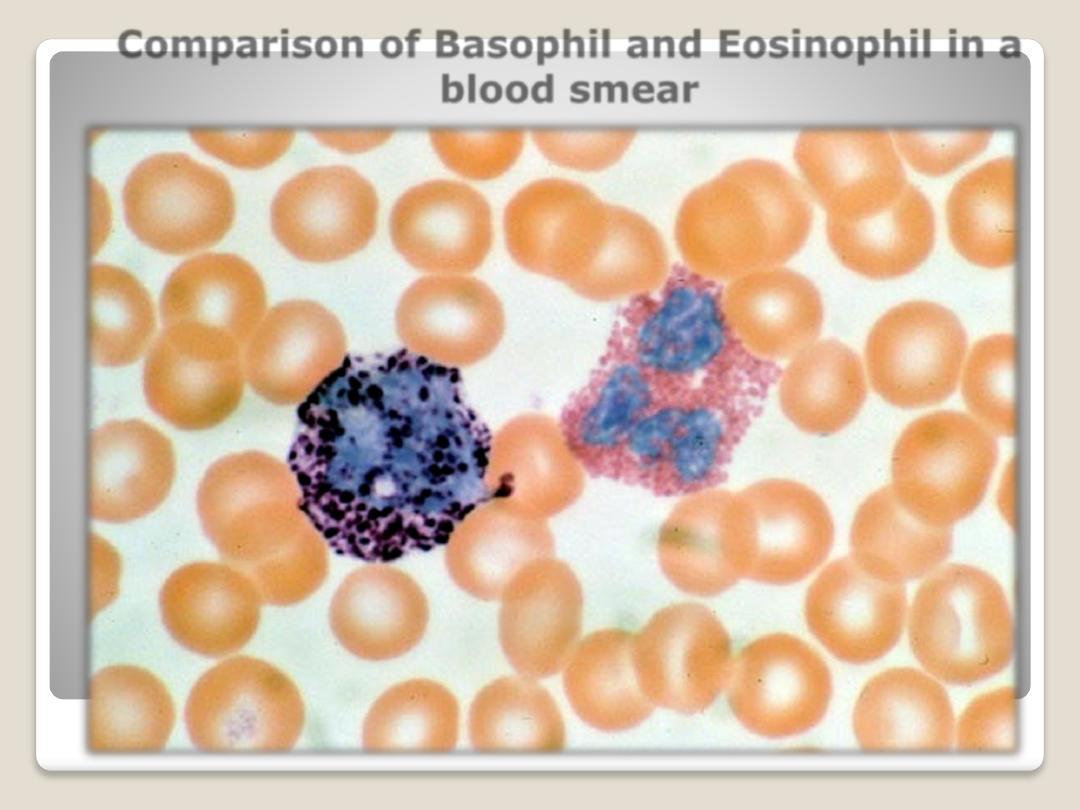
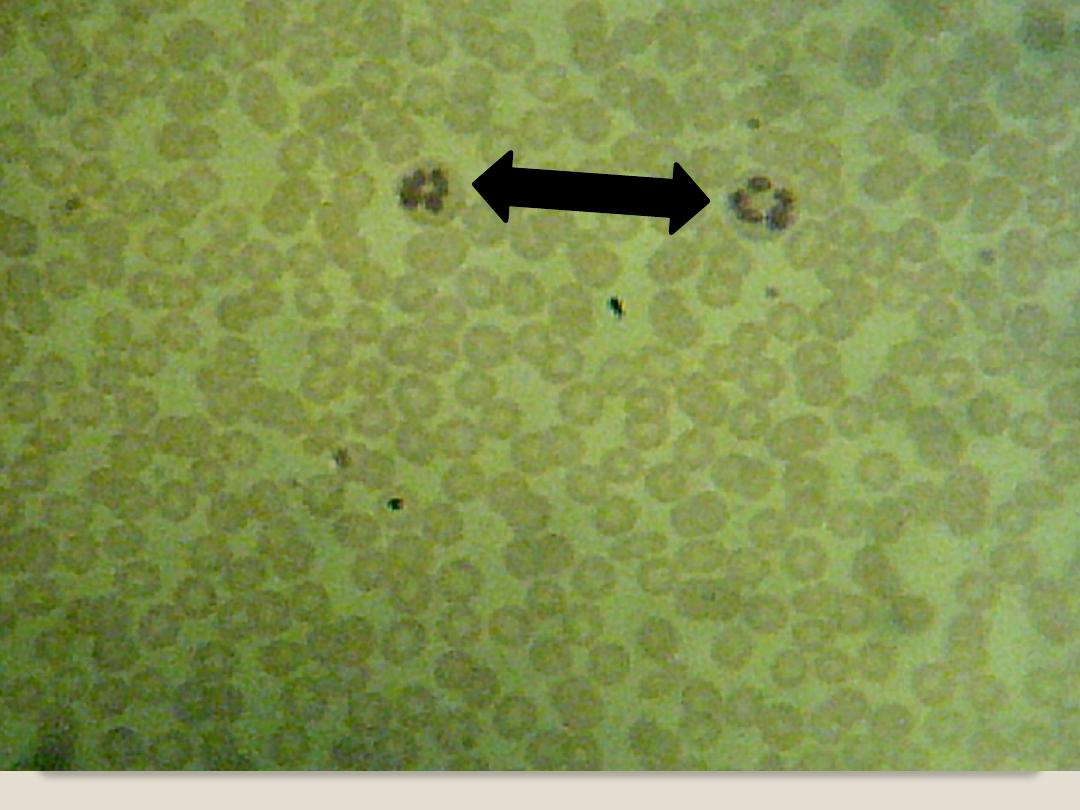
Comparison of Basophil and Eosinophil in a
blood smear
Basophil
Eosinophil
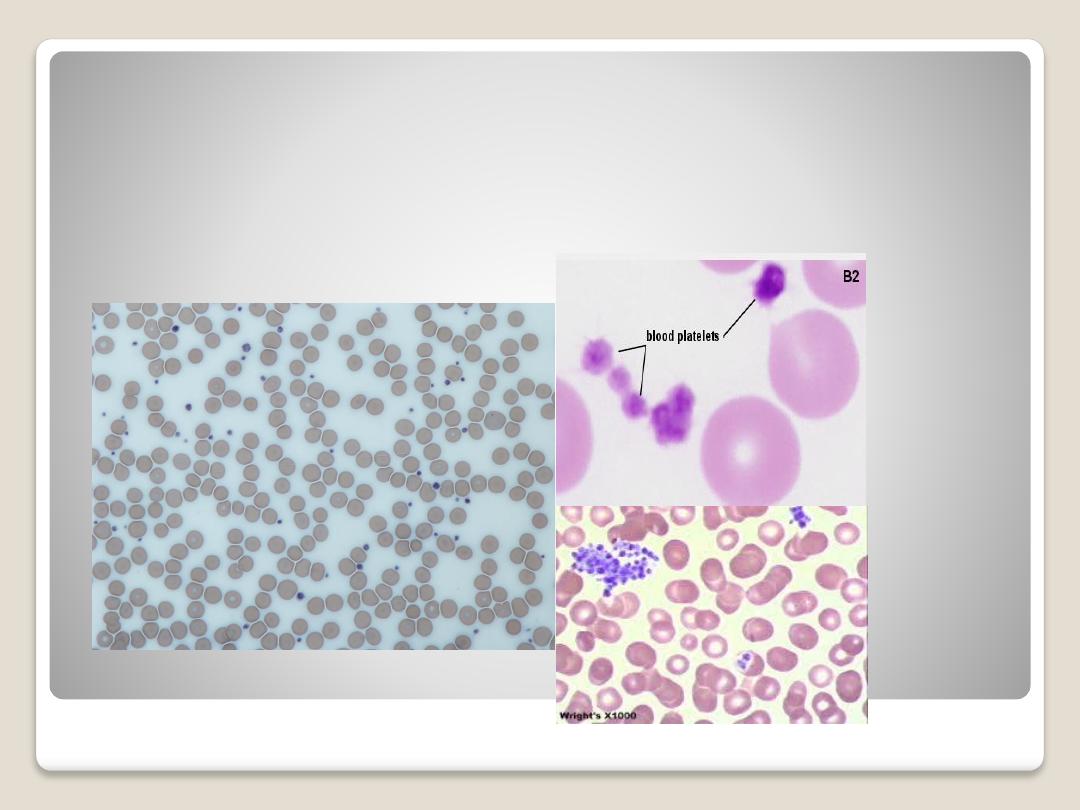
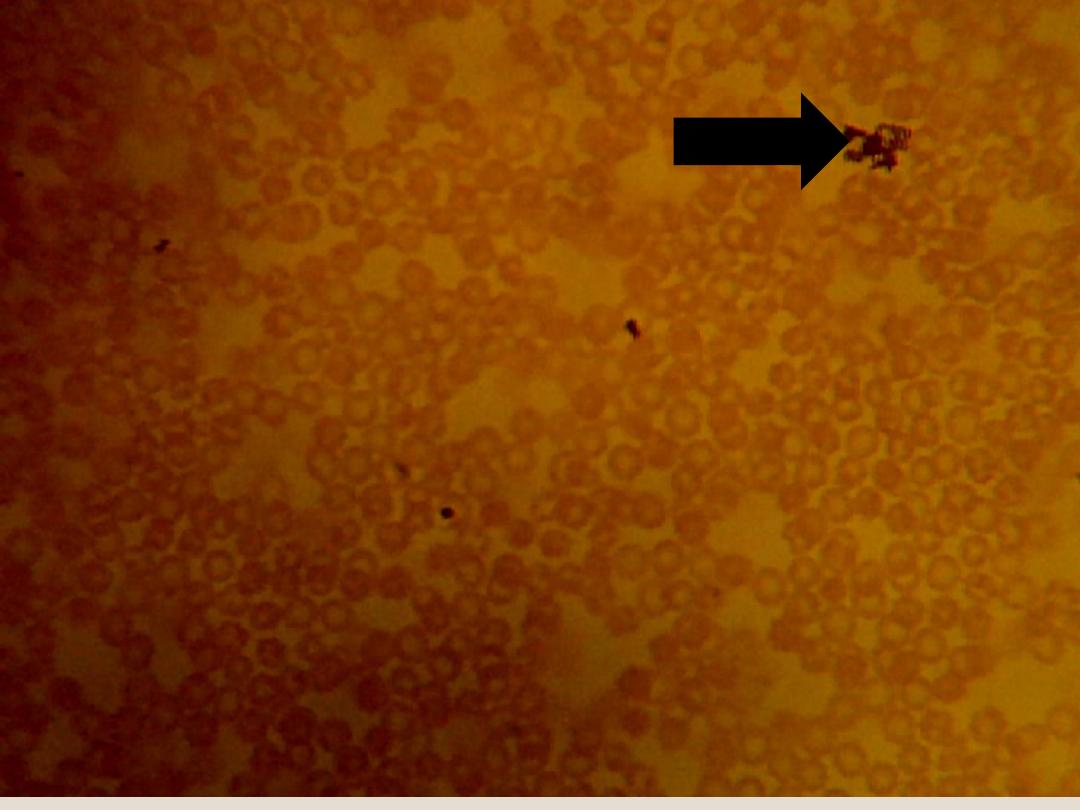
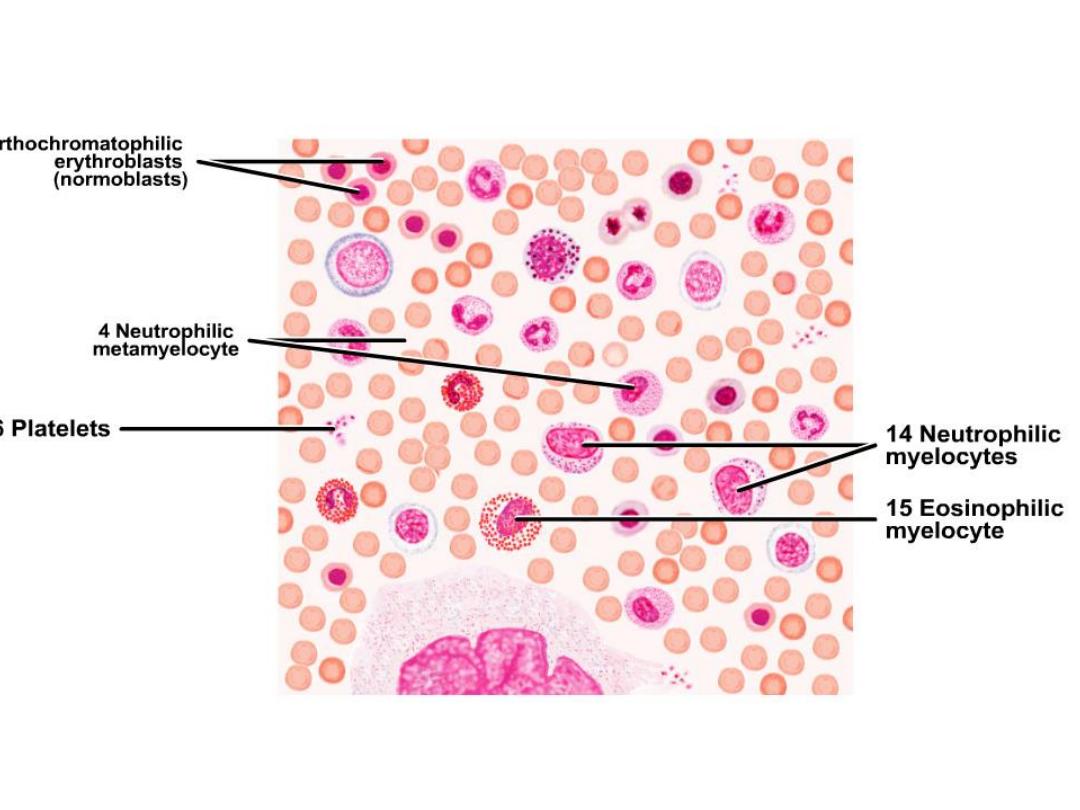
Blood Platelets:
are nonnucleated, disk-
like cell fragments. Platelets are around or
ovoid in shape and aggregate as groups.

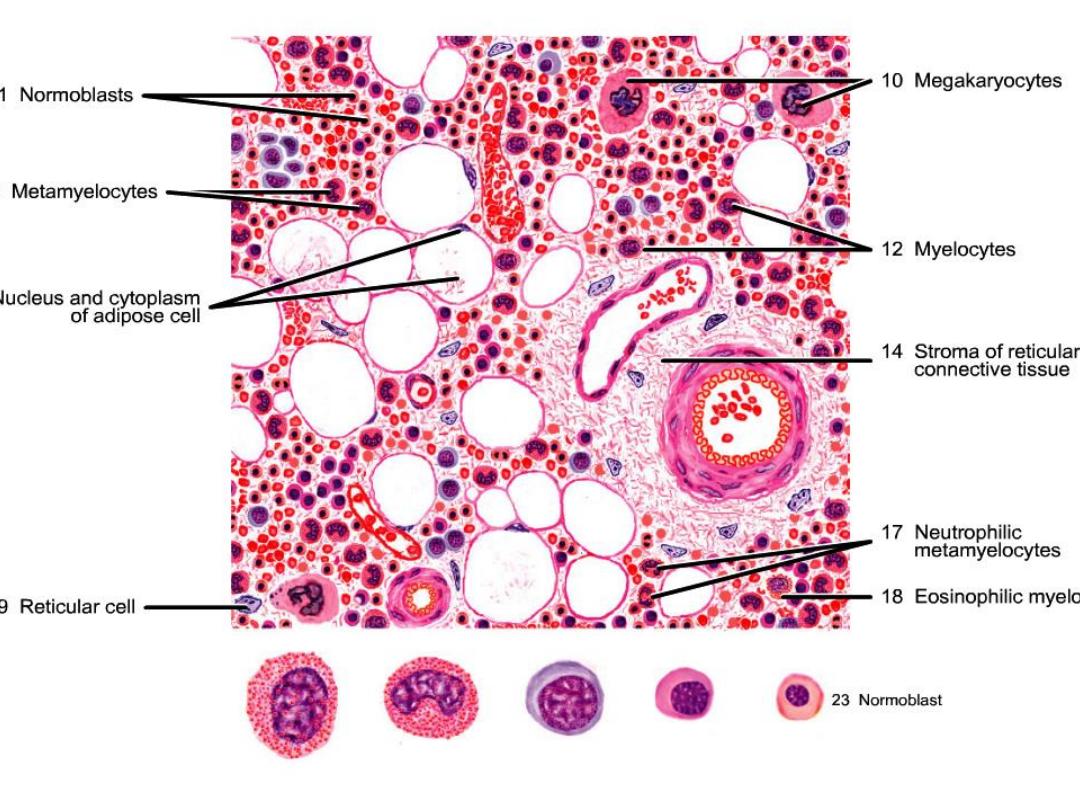
Hematopoiesis:
a proliferation and progress differentiation
from stem cell in bone marrow to mature
form found in circulatory system.
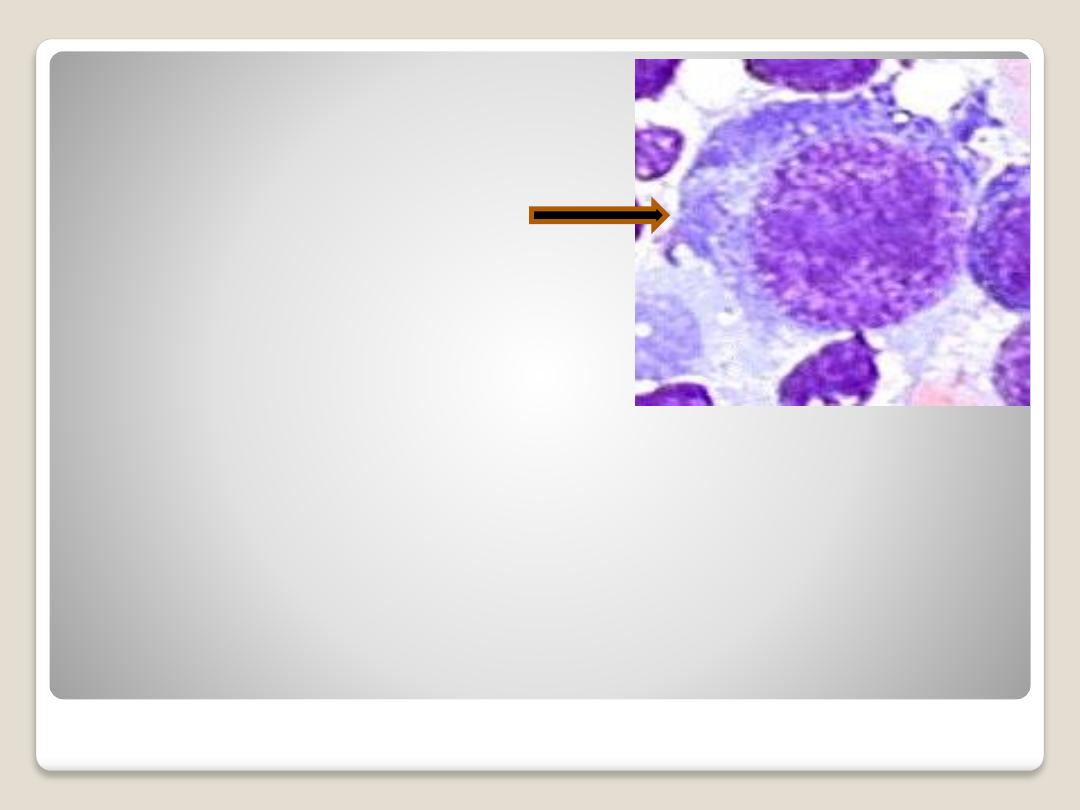
Hemocytoblast
(pluripotent stem
cell):
is large, an amoeboid
cell,
characterized by
basophilic cytoplasm
and a relatively large
nucleus with a loose
network of chromatin
and several nucleoli.
The other cells are
initiated from it.
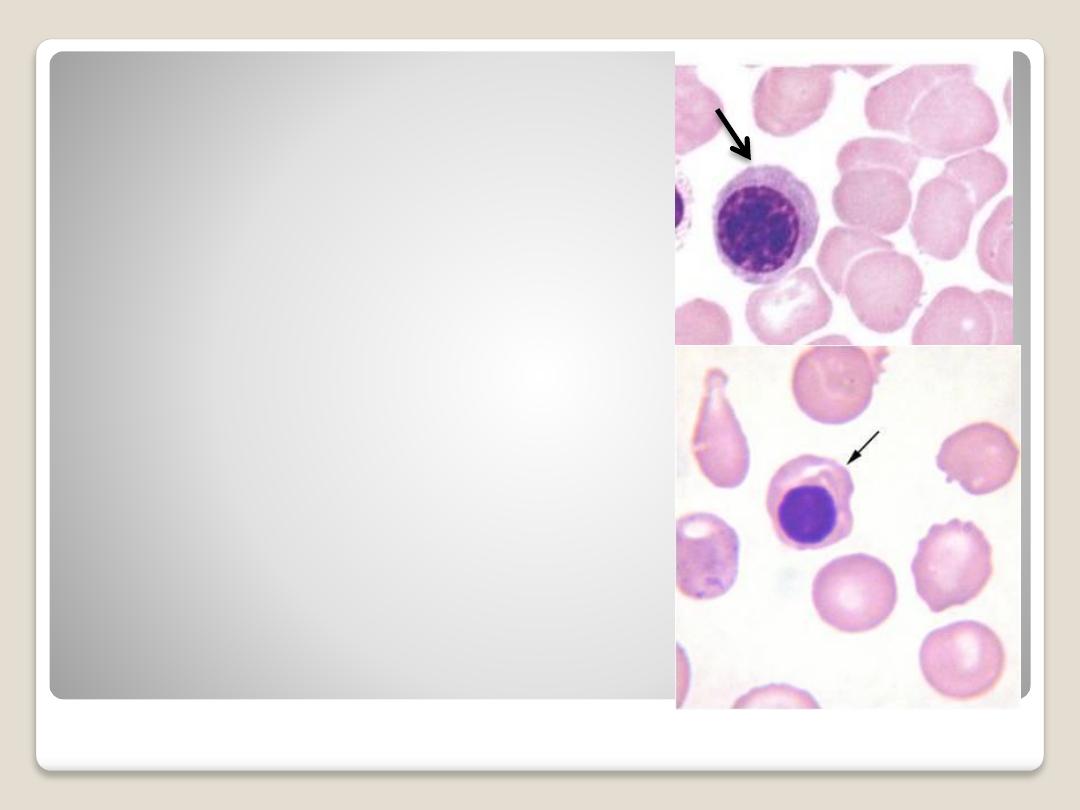
Normoblast:
The nucleus has become
pyknotic and therefore is
very dark in appearance.
The cytoplasm is
acidophilic. when it lost the
nucleus, it convert to R.B.C.
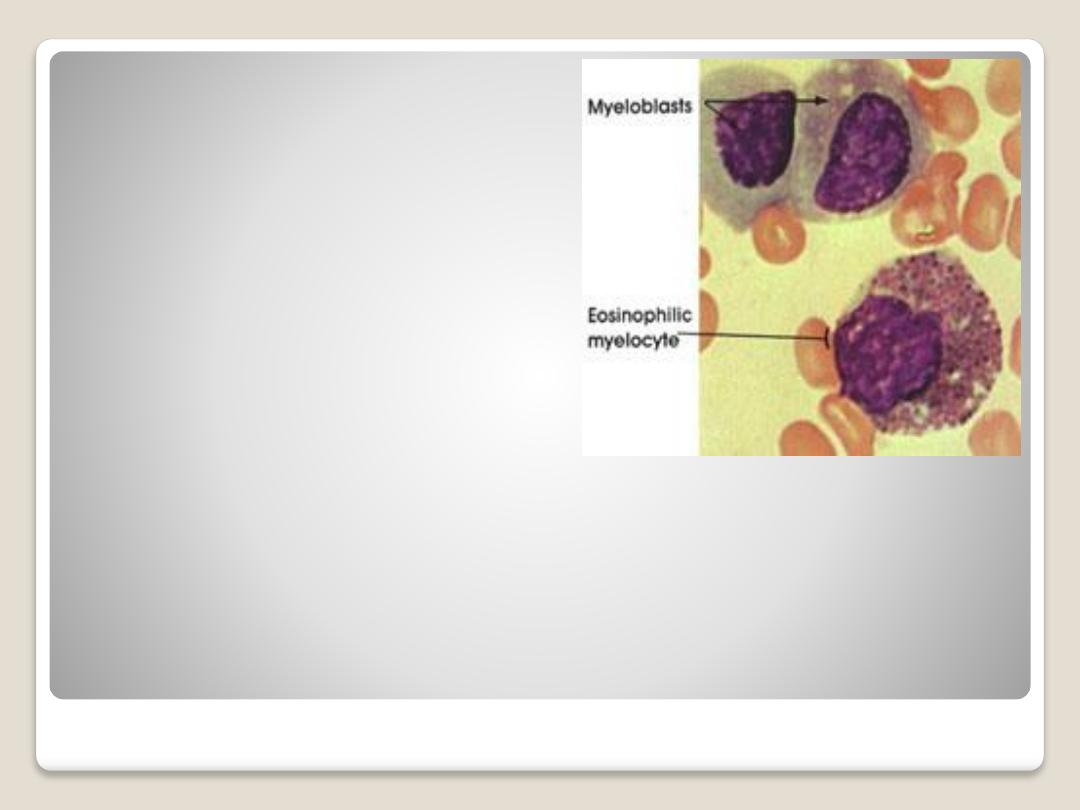
Acidophilic mylocyte:
has round or oval
nucleus, and course
granules of
cytoplasm. Its convert
to acidophil.
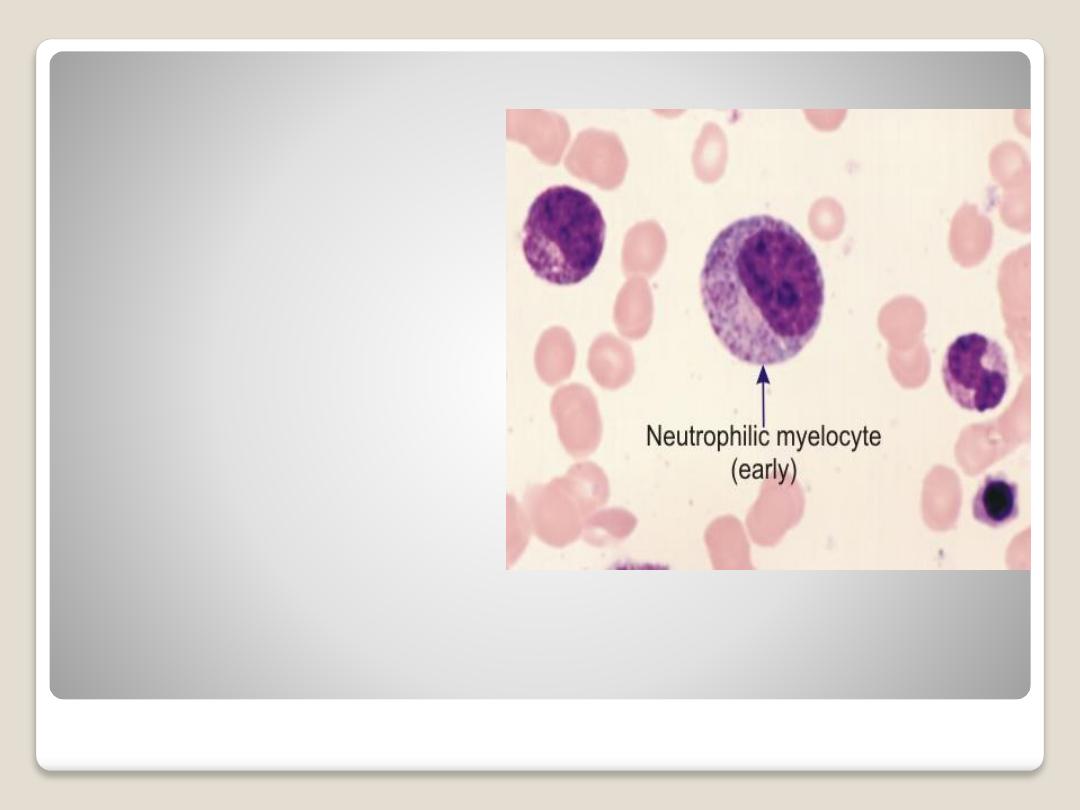
Neutrophilic
mylocyte:
it has small oval
nucleus, the
cytoplasm stains
with neutral stain.
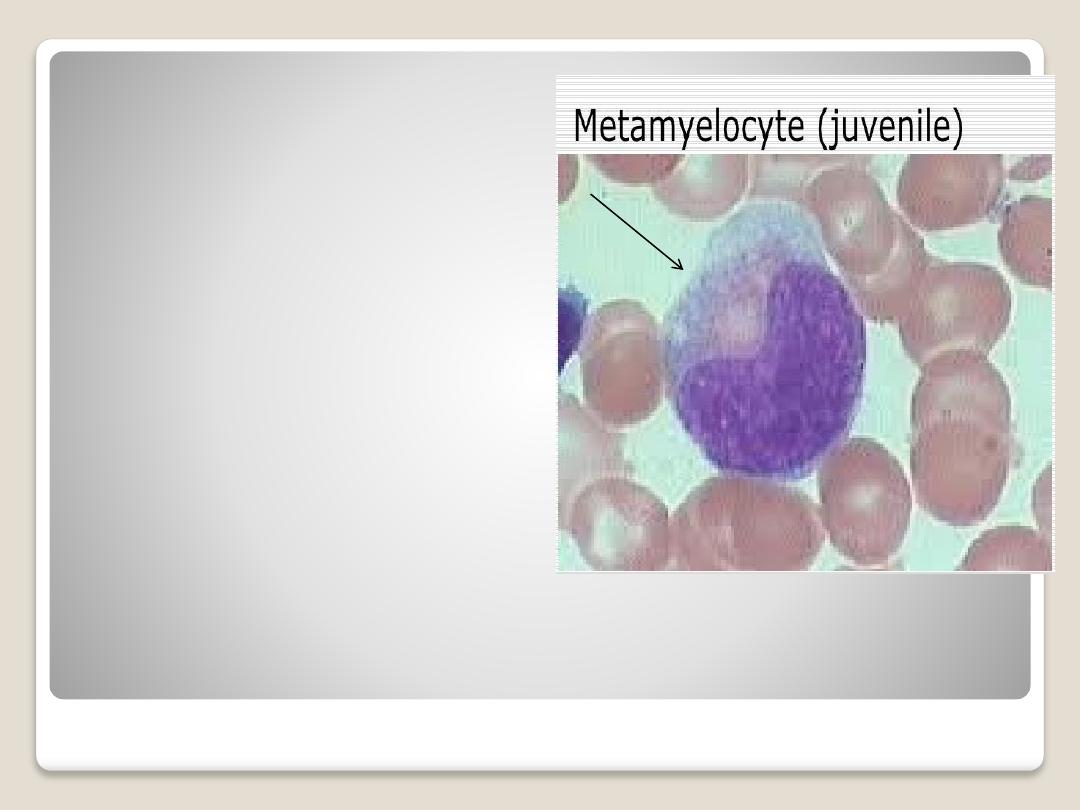
Neutrophilic
metamylocyte
(juvenile):
it's
smaller
than
myelocyte, the nucleus is
kidney shaped. The
cytoplasm filled with fine
granules. It converts to
neutrophil.
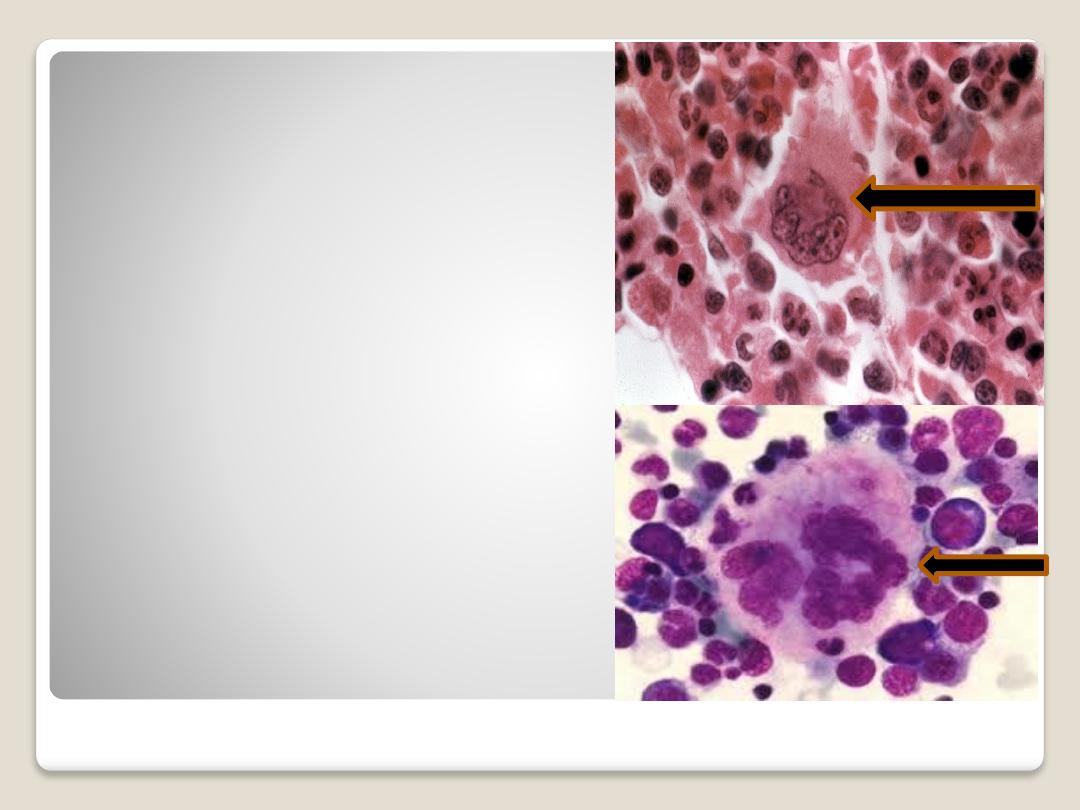
Megakaryocyte:
are giant cells with
irregularly lobulated
nucleus, with course
chromatin. The
formations of
platelets are been
from megakaryocyte.

Thank you
