د. حسين محمد جمعه
اختصاصي الامراض الباطنةالبورد العربي
كلية طب الموصل
2011
Chest x rays: a guide to interpretation
Learning bite: cavitating lung massesThe differential diagnosis of a cavitating lung mass is wide, so you must consider your clinical findings. The cause could be infective, neoplastic, vascular, granulomatous, or traumatic. Certain radiological features are important, but are not specific enough to allow a definitive diagnosis.
These include:
Wall thickness: thin walled cavities are often benign
Location and distribution: cavities associated with reactivation of tuberculosis are commonly located in the apical and superior segments of the upper lobes, and the superior segments of the lower lobes.
There are absent lung markings with a hyperlucent right hemithorax. The visceral pleura can be visualised as a curvilinear line that parallels the chest wall, separating the partially collapsed lung centrally from pleural air peripherally. An expiratory chest x ray aids in the detection of a small pneumothorax by decreasing the volume of aerated lung relative to the pneumothorax.
Learning bite: mesothelioma
All types of asbestos can cause mesothelioma. The mean latent interval between exposure and death is 40 years. The most common finding with malignant mesothelioma is the presence of diffuse pleural thickening. This is typically nodular and irregular in configuration.A pleural effusion is present in up to 80% of patients and, when large, may obscure the pleural tumour.
If the mediastinal pleura is involved, this may prevent the mediastinum shifting to the contralateral side, even if the pleural tumour is extensive. This feature may help you to distinguish between mesothelioma and metastatic disease.
You may also be able to see lymph node metastases, contralateral pleural metastases, and calcified liver metastases on the chest x ray.
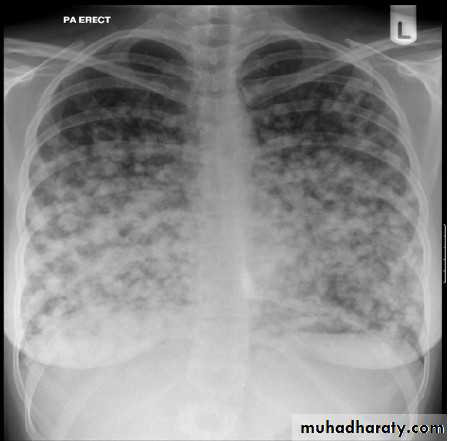
The chest x ray shows bilateral multiple nodules. Pulmonary nodules can be benign or malignant. Common benign causes include infectious granuloma, bronchial adenoma, and benign hamartoma. Malignant causes include primary lung cancer and metastases.