TOXOPLASMOSIS ICD-10 B58
Dr. Nadia AzizC.A.B.C.M
Baghdad medical college
TOXOPLASMOSIS
A systemic coccidian protozoan diseaseinfections are frequently asymptomatic, or
as acute disease with lymphadenopathy only, or resemble infectious mononucleosis, with fever, lymphadenopathy and lymphocytosis persisting for days or weeks.
Development of an immune response decreases parasitaemia, but Toxoplasma cysts remaining in the tissues contain viable organisms.
TOXOPLASMOSIS
The cysts may reactivate if the immune system becomes compromised.Among immunodeficient individuals (e.g. HIV- patients), primary or reactivated infection may cause a maculopapular rash, generalized skeletal muscle involvement, cerebritis, chorioretinitis, pneumonia, myocarditis and/or death.
Cerebral toxoplasmosis is a frequent component of AIDS.
TOXOPLASMOSIS with pregnancy
A primary infection during early pregnancy may lead to fetal infection with death of the fetus or manifestations such as chorioretinitis, brain damage with intracerebral calcification, hydrocephaly, microcephaly, fever, jaundice, rash, hepatosplenomegaly, xanthochromic CSF and convulsions evident at birth or shortly thereafter.TOXOPLASMOSIS with pregnancy
Later in pregnancy
Maternal infection results in mild or subclinical fetal disease with delayed manifestations such as recurrent or chronic chorioretinitis.
Diagnosis
1- Demonstration of the agent in body tissues or fluids by biopsy or necropsy.2- Rising antibody titres are corroborative of active infection, (presence of specific IgM and/or rising IgG titres in sequential sera ).
High IgG antibody levels may persist for years with no relation to active disease.
Infectious agent
Toxoplasma gondii, an intracellular coccidianprotozoan of cats
Occurrence
Worldwide in mammals and birds.Infection in humans is common.
Reservoir
The definitive hosts of T. gondii are cats and otherfelines, which acquire infection mainly from eating infected mammals (especially rodents) or birds, probably also from oocysts acquired during natural licking/grooming.
Felines alone harbour parasites in the intestinal tract, where the sexual stage of life cycle occurs, resulting in excretion of oocysts in feces for 10–20 days, rarely longer.
Reservoir
The intermediate hosts of T. gondii include sheep, goats, rodents, swine, cattle, chickens and birds; all may carry an infective stage of T. gondii encysted in tissue, especially muscle and brain.
Tissue cysts remain viable for long periods, perhaps lifelong.
Cattle seem able to cope with natural Toxoplasma infection.
Mode of transmission
1- Transplacental infection occurs in humanswhen a pregnant woman has rapidly dividing cells (tachyzoites) circulating in the bloodstream, usually during primary infection.
2- Children may become infected by ingesting infective oocysts from dirt in sandboxes, playgrounds and yards in which cats have defecated.
Mode of transmission
3- Infections arise from eating raw or undercooked infected meat containing tissue cysts, or through ingestion of infective oocysts in food or water contaminated with feline feces.4- Inhalation of sporulated oocysts (rare)
5- Infection may occur through blood transfusion or organ transplantation from an infected donor.
Incubation period
From 5–20 daysPeriod of communicability
No direct person-to-person transmissionexcept in utero. Oocysts shed by cats sporulate and become infective 1–5 days later and may remain infective in water or moist soil for over a year.
Cysts in the flesh of infected animals remain infective as long as the meat is edible and uncooked.
Susceptibility
Susceptibility to infection is general, but immunity
is readily acquired and most infections are asymptomatic. Duration and degree of immunity are unknown but they are assumed to be permanent.
Patients undergoing cytotoxic or immunosuppressive treatment or HIV-infected patients are at high risk of developing illness from reactivated infection.
Methods of control
A. Preventive measures:1) Educate pregnant women about preventive measures:
a) Use irradiated meats or cook them to 66°C before eating. Freezing meat down to –20°C for
24 hours is a good alternative.
A. Preventive measures
b) Unless they are known to have antibodies to T. gondii,pregnant women must avoid cleaning litter pans and
avoid contact with cats of unknown feeding history.
They must wear gloves during gardening .
Preventive measures
2) Wash hands thoroughly before eating and after handling raw meat or after contact with soil possibly contaminated with cat feces.Preventive measures
3) Control stray cats and prevent their access to sandboxes and sand piles used by children for play. Keep sandboxescovered when not in use.
4) Patients with AIDS must receive prophylactic treatment throughout life with pyrimethamine, sulfadiazine and folinic acid.
B. Control of patient, contacts and the immediate environment:
• Investigation of contacts and source of infection:
In congenital cases, determine antibody titres in mother.
in acquired cases, determine antibody titres in members of the household and common exposure to cat feces, soil, raw meat or unwashed vegetables.
B. Control of patient, contacts and the immediate environment:
2) Specific treatment: Treatment not routinely indicated for a healthy immunocompetent host.Treatment routinely indicated for:
1- Initial infection during pregnancy
2- Presence of active chorioretinitis, myocarditis or other organ involvement.
Treatment
1- Pyrimethamine combined with sulfadiazine and folinic acid (to avoid bone marrow depression) for 4 weeks.2- In ocular disease Clindamycin has been used in addition to these agents.
3- Systemic Corticosteroids are indicated when irreversible loss of vision can occur from lesions of the macula, papillomacular bundle or optic nerve.
Treatment of pregnant women
1- Spiramycin is commonly used to prevent placental infection.2- Pyrimethamine and sulfadiazine ( fetal infection has occurred).
Because of concerns about possible teratogenicity,
pyrimethamine should not be given during the first 16
weeks of pregnancy; sulfadiazine may be administered alone in this case.
Treatment
Infants whose mothers had primary infections
or were HIV positive during pregnancy should be treated
with pyrimethamine-sulfadiazine-folinic acid during their 1st year of life or until congenital infection is ruled out, in order to prevent chorioretinitis and other sequelae.
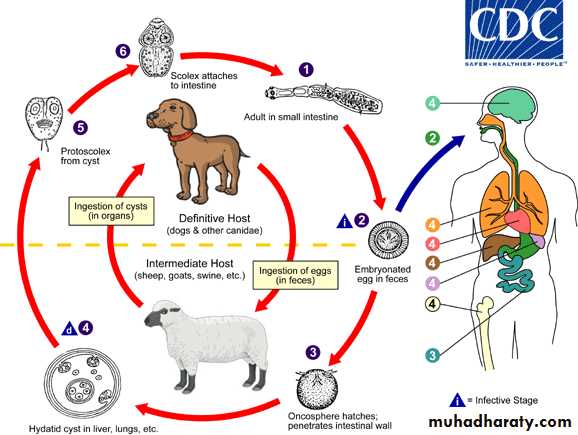
Echinococcus granulosus (Hydatid disease)
A hydatid cyst is typically acquired in childhood and may, after growing for some years, cause pressure symptoms, depending on the organ or tissue involved.In nearly 75% of patients with hydatid disease the right lobe of the liver is invaded.
In others a cyst may be found in lung, bone, brain or elsewhere.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis depends on the clinical, radiologicaland ultrasound findings in a patient who has
lived in close contact with dogs in an endemic area.
ELISA are positive in 70–90% of patients.
Reservoir
Dogs are the definitive hosts .The larval stage, a hydatid cyst, normally
occurs in sheep, cattle, camels and other animals (intermediate hosts) that are infected from contaminated pastures or water.
By handling a dog or drinking contaminated water,
humans may ingest eggs.
Infecious Agent
Tapeworm E. granulosus.
Hydatid cyst
Outer fibrous layer pericyst, laminated hyaline membrane (ectocyst) and inner germinal layers (endocyst) which gives rise to daughter cysts, or germinating cystic brood capsule in which larvae (protoscolices) develop.Over time some cysts may calcify and become non-viable.
occurrence
The disease is common in the Middle East, North and East Africa, Australia and Argentina.Prevention
Personal hygiene.Satisfactory disposal of carcasses, meat inspection and
deworming of dogs can greatly reduce the prevalence of disease.
Treatment
Hydatid cysts should be excised wherever possible.Great care is taken to avoid spillage and cavities are sterilised with 0.5% silver nitrate or 2.7% sodium chloride.
Treatment
Albendazole (400 mg 12-hourly for 3 months) should
also be used.
The drug is now often combined with PAIR
(percutaneous puncture, aspiration, injection of scolicidal
agent and re-aspiration).
Praziquantel 20 mg/kg 12-hourly for 14 days also kills protoscolices