Diuretic Drugs
1-Overview2-Classification
3-Indiviual drugsLecture 1
1-Indications of Diuretics.
2-Adverse effects.3-Manitol and Carbonic Anhydrase inhibitors.
Lecture 21- Oedema States
Sodium overload
“Cardiac, Renal, Hepatic”
“Acute pulmonary edema”
Indications of DiureticsOedema
2-HypertensionReduction of:
Intravascular volume and peripheral vascular resistance.Indications of Diuretics
3-Hypercalcaemia
Furosemide reduces calcium
re-absorption in ascending limb of loop of Henle.
Indications of Diuretics
4-Idiopathic Hypercalciuria.
A cause of renal stone disease, treated by ThiazideIndications of Diuretics
5- The syndrome of inappropriate secretion of anti-diuretic hormone
(SIADH)May be treated with Furosemide.
Indications of Diuretics6-Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.
My be paradoxically treated with diuretics by contracting vascular volume, increase salt and water reabsorption in proximal tubule.Indications of Diuretics
7-Congestive cardiac failure.
Reduction of oedema ,relief of dyspnea
Should avoid overtreatment !
Dizziness tiredness, postural hypotensionMonitor body weight !
Indications of Diuretics
Acute Pulmonary Oedema
Potent Loop Diuretic ex Furosemide (Lasix)Used intravenously with combination of other drugs and oxygen
8-Hepatic ascitesPortal hypertension
Decrease in colloid pressure and hyperaldosteronism.“Spironolactone”
Indications of DiureticsVigorous diuresis can cause encephalopathy!
Paracentesis
Indications of DiureticsIn secondary hyperaldosteronism of Nehrotic syndrome
Spironolactone (Aldactone) is preferred.Indications of Diuretics
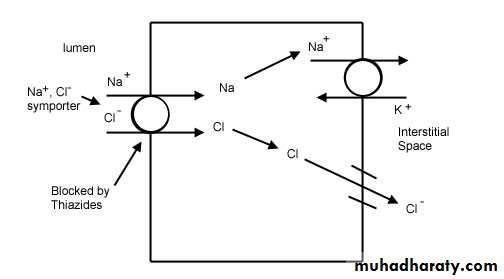
1-Potassium depletion:Increasing the sodium which reaches the exchange at the DCT and collecting duct.
“Na exchanged for K”Adverse effects
This can lead to Arrhythmia especially in patient receiving Digoxin
Safe lower limit of K = 3.5 mmol/LAdverse effects
Loop diuretics cause smaller loss in K than Thiazides:
“For the same amount of diuresis”But as loop is more potent
They cause more diuresis they cause more hypokalemia !Adverse effects
Hypokalemia is more prone to occur in hyperaldosteronism whether primary or:
More commonly Secondary to liver disease congestive cardiac failure or nephrotic syndrome.Adverse effects
Prevention of K depletion:
1-Good dietary intake.
Vegetables and fruits2-K depleting drug with sparing diuretic.
3-Intermittent diuretics.
“Drug holidays”
Adverse effects
4-Potassium supplementation
KCLbecause Cl is the principle ion excreted
All K preparations are irritant to GIT and esophageal ulceration can result.
Cupful of liquid preferably upright
Adverse effects
2-Hyperkalemia in potassium sparing diuretics
ACE Inhibitors
And can cause dangerous hyperkalemia if combined with K sparing diuretic
Adverse effects
Treatment of hyperkalemia:
1-Stop any K sparing diuretic.2-Meassures to move K rapidly into the cells including:
Adverse effectsA-Sodium bicarbonate 50 ml of 8.4% solution.
B- Glucose 50 ml 50 % solution +10 units of soluble insulin.C- Nebulised salbutamol (Beta 2 Agonist) 5-10 mg.
Adverse effects
Calcium Gluconate 10 ml of 10 % solution. IV
oppose the myocardial effects of raised serum KAdverse effects
3-Hypovolaemia in overtreatment:
Postural hypotension
DizzinessLethargy
Somnolence
“Usually Insidious”
Adverse effects
4-Urinary retention:Sudden vigorous dieresis especially in elderly
Adverse effects5-Hyponatremia
especially in patient who drinks a lot of water.Large quantities of water.
*Increase in ADH could be a mechanism.
Adverse effects
In HyponatremiaDiscontinue diuretic and water restriction.
Elderly are more predisposedAdverse effects
6-Urate retentionHyperuricaemia
Increase in uric acid
Thiazide and loop diuretics
NOTAmiloride or Spironolactone
Adverse effects
Mechanism of Hyperuricaemia could be:
1-Volume depletion and decrease in GFR.
2-Diuretics are organic acids that competes with the site of transport
Adverse effects7-Magnesium deficiency in loop and Thiazides
Loss of magnesiumK sparing diuretics leads to Magnesium retention
Cardiac arrhythmiaAdverse effects
8-Carbohydrate intolerance:Intracellular potassium is necessary in the formation of insulin
Can change latent diabetes into overt diabetes.Adverse effects
9-Calicium homeostasis
Loop diuretics Increases renal calcium loss.Furosemide can be used to treat hypercalcaemia.
Adverse effectsThiazides decrease renal excretion of calcium
Decreasing the risk of hip fracture in elderly!Adverse effects
10-IV loop diuretics potentiate ototoxicity of aminoglycoside antibiotics
and nephrotoxicity of cephalosporinsAdverse effects
Small molecular weight substancesFiltered by glomerulus but:
NOT Reabsorbed
Increases osmolarity and prevent
re-absorption of water and sodium
“Proximal convoluted tubule”
Osmotic diureticsMannitol is a polyhydric alcohol
Given intravenously.1-Reduction in intracranial pressure.
2-Maintain urine flow to prevent acute tubular necrosis and renal failure.
Increase urine volume*Contraindicated in CHF and Pul Oedema
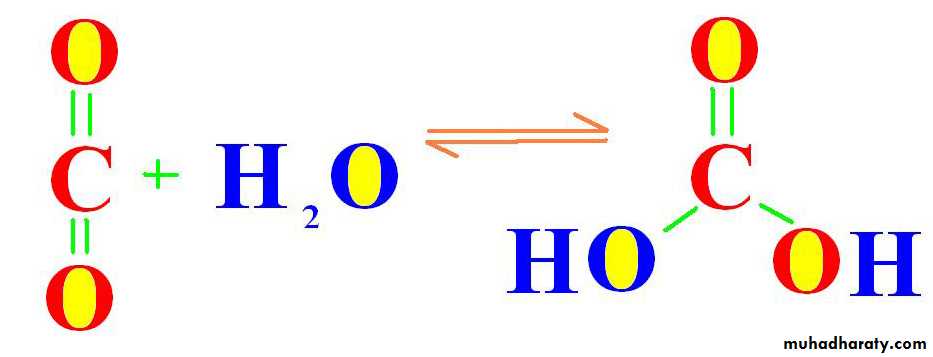
Osmotic diureticsCO2 + H2O → H2CO3
(CA)Carbonic Anhydrase enzyme
THEN BREAKDS DOWN TO
H ion + HCO3
Carbonic Anhydrase is present in:
“GIT, Eye, Pancreas, kidneys”Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors
Carbonic Anhydrase
C. A.Enzyme
Reduced hydrogen in PCT
Na loss and diuresisReduced HCO3 absorption
“Metabolic Acidosis”
*Not used as diuretic
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
Acetazolamide is the most commonly used.(Diamox)
*Reduction in intraocular pressure(IOP)(Glaucoma)
Hypokalemia and Acidosis
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitorsUsed also in treatment of mountain sickness
High altitudeOver 300 meters
Nausea
Lassitude
Headache
Pulmonary and cerebral edema
Carbonic Anhydrase inhibitors
High altitude
Mountain SicknessAcetazolamide
*Hypoxia*Hyperventilation
*AlkalosisCarbonic anhydrase inhibitors
AcetazolamideAcidosis
Increases respiratory drive
125-250 mg bid (Twice Daily)
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitorsDrowsiness
FeverRash
Paresthesia
Blood dyscrasia
Adverse effects
The Relation of serum creatinine with:1-Renal function
2-GFR***Final Remarks
A patient with ascites was receiving Thiazide & was stable until he developed hypersensitivity.
His treatment was changed to Furosemide 40 mg every other day and the dose was tittered to produce the same previous clinical efficacy.
By this the risk of K depletion and hypokalemia is:
A-Increased.
B- Decreased.C- Remained the same.
D- Unpredictable.
MCQs
A patient with oedema was receiving hydrochlorothiazide but his oedema did not resolve & that is why the treatment was changed to Furosemide tab. 40 mg /day which caused dramatic improvement.
By this the risk of K depletion and hypokalemia is:
A-Increased.
B- Decreased.C- Remained the same.
D- Unpredictable.
MCQs
60 years old lady with osteoporosis was in need for diuretic therapy and was prescribed Thiazide.
she was worried about the effect of the drug on her bone density and likelihood of fractures.
Your reply would be:
A-It has no effect.
B- It could be protectiveC- It could be harmful.
D- Unknown effect.
MCQs
A patient with congestive heart failure was receiving Furosemide diuretic every other day.His GP advised him that he could take the dose daily when he feels shortness of breath.
He consulted you complaining of severe fatigue, dizziness, dryness of the mouth, and somnolence.
The most likely cause of this could be:
A-Hypokalemia.
B-Hyperkalemia.C-Hypocalcaemia
D- Dehydration and Overtreatment.
MCQs
A patient with gout was prescribed some form of diuretic therapy which cause elevation of his serum uric acid and caused acute attack of gouty arthritis.
This diuretic could be:
A- Amiloride.
B- Spironolactone.C- Triamterene.
D- Bendrofluazide.
MCQs
A patient with hypovolaemic shock & severe hypotension has developed oliguria & was in need for drug to maintain adequate renal function and increase his urine output, the best choice for this would be:A-Furosemide.
B- Mannitol.C- Thiazide.
D- Acetazolamide.
MCQs
Which one of the following drugs increases the calcium loss in the urine?
A-Hydrochlorothiazide.
B- Amiloride.
C- Furosemide.
D- Triamterene.
MCQs
Acetazolamide is known to cause:
A- Metabolic AcidosisB-Metabolic Alkalosis.
C- Hypokalemia & Metabolic Acidosis.
D- Hypoglycemia.
MCQs