
Surgery
Urinary Incontinence
Dr. Hasanain Farhan
Lec. 34
Definition
Is the involuntary loss of urine that is objectively demonstrated with social and
hygienic problem.
Classification
Anatomic or genuine urinary stress incontinence
Urge incontinence
Neuropathic incontinence
Congenital incontinence
False (overflow) incontinence
Iatrogenic incontinence
Fistulous incontinence
Stress incontinence
Is an involuntary loss of urine that occurs during physical activity, such as
coughing, sneezing, laughing, , sudden changes of position or exercise.
Bet. 15-30% of women over age 65 yr have urinary incontinence &stress
incontinence is the most common type
30%to 50% of women with stress incontinence also complain of urinary
frequency, urgency, and/or urge incontinence
Types
Classic or genuine stress incontinence is caused by pelvic prolapse, urethral
hyper mobility or displacement of the urethra and bladder neck from their
normal anatomic alignment(also called anatomic stress incontinence)
Surgery
Urinary Incontinence
Dr. Hasanain Farhan
Lec. 34
Stress incontinence can also occur as a result of intrinsic sphincter
deficiency, in which the sphincter is weak because of neurologic insult ,
previous surgery, estrogen deficiency , radiation damage or trauma.
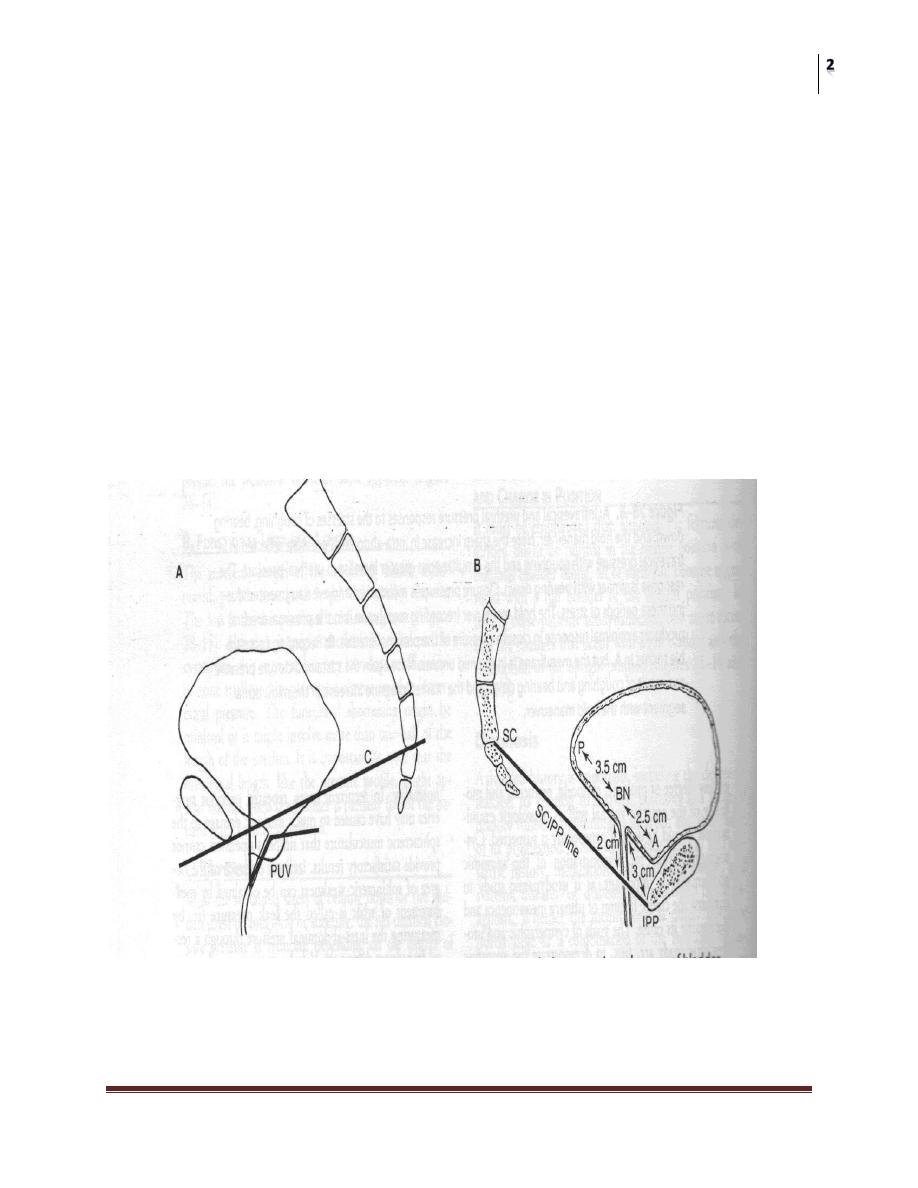
Anatomy:
The anatomic feature is that of hypermobility or a lowering of the
position of the VU segment
Various relations between the urethra, bladder, and bony landmarks
have been studied
Posterior vesicourethral angle
Axis of inclination (urethral line vs. vertical plane)
UV junction and the SCIPP
Surgery
Urinary Incontinence
Dr. Hasanain Farhan
Lec. 34
Risk Factors
1) Gender:urinary incontinence is much more common in women than men.
2) Genetics:several studies suggested genetic predisposition for stress
incontinence.
3) Race, culture, and environment—stress incontinence was reported to be
more common in whites than blacks.
4) Overweight: causes more pressure on pelvic floor.
5) Pregnancy&Childbirth: increasing weight of baby puts extra stress on pelvic
floor , the hormone relaxin softens the muscles of the pelvic floor ready for
the birth, In vaginal delivery the nerves around pelvic floor become
stretched and bruised ,women who'd had a tear or episiotomy had a three-
fold risk of developing urinary incontinence.
6) Smoking: a chronic cough puts pressure on the pelvic floor and makes SUI
worse.
7) Age: stress incontinence is not a normal part of aging ; physical changes
associated with aging as the weakening of the muscles make elderly more
susceptible to stress incontinence

Surgery
Urinary Incontinence
Dr. Hasanain Farhan
Lec. 34
8) Medications: can affect the pelvic floor. Examples are alpha-blockers used
to treat high blood pressure, some antidepressants and sedatives, and some
muscle-relaxant drugs.
DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION
causes of transient incontinence should be ruled out
1) Drug side effects
2) Delirium or hypoxia
3) Impaired mobility
4) Urinary tract infection
5) Atrophic vaginitis
6) psychological problems
7) Excessive fluid intake
8) Recent prostatectomy
9) Stool impaction.
EVALUATION include:
History
Physical examination
Urinalysis
Measurement of postvoid residual (PVR) urine volume
Micturition Diary
Pad Test
Urodynamic Evaluation
History
is important in assessing the characteristics and severity of incontinence as
well as its impact on quality of life.
It is also important in identifying risk factors and/or transient causes of
incontinence
patient history alone is not an accurate tool in the diagnosis of sphincteric
incontinence and should not be used as the sole determinant of diagnosis or
treatment

Surgery
Urinary Incontinence
Dr. Hasanain Farhan
Lec. 34
Physical Examination
Neurourologic examination begins by observing the patient's gait
The lumbosacral nerve roots should be assessed by checking deep tendon
reflexes, lower extremity strength, sensation , anal sphincter tone & genital
sensation.
The abdomen and flanks should be examined for masses, ascites &
organomegaly which can influence intra-abdominal pressure.
Rectal examination will disclose the size and consistency of the
prostate&anal sphincter tone
Cough test: the bladder full in the lithotomy position, the patient is asked to
cough in an attempt to reproduce the incontinence
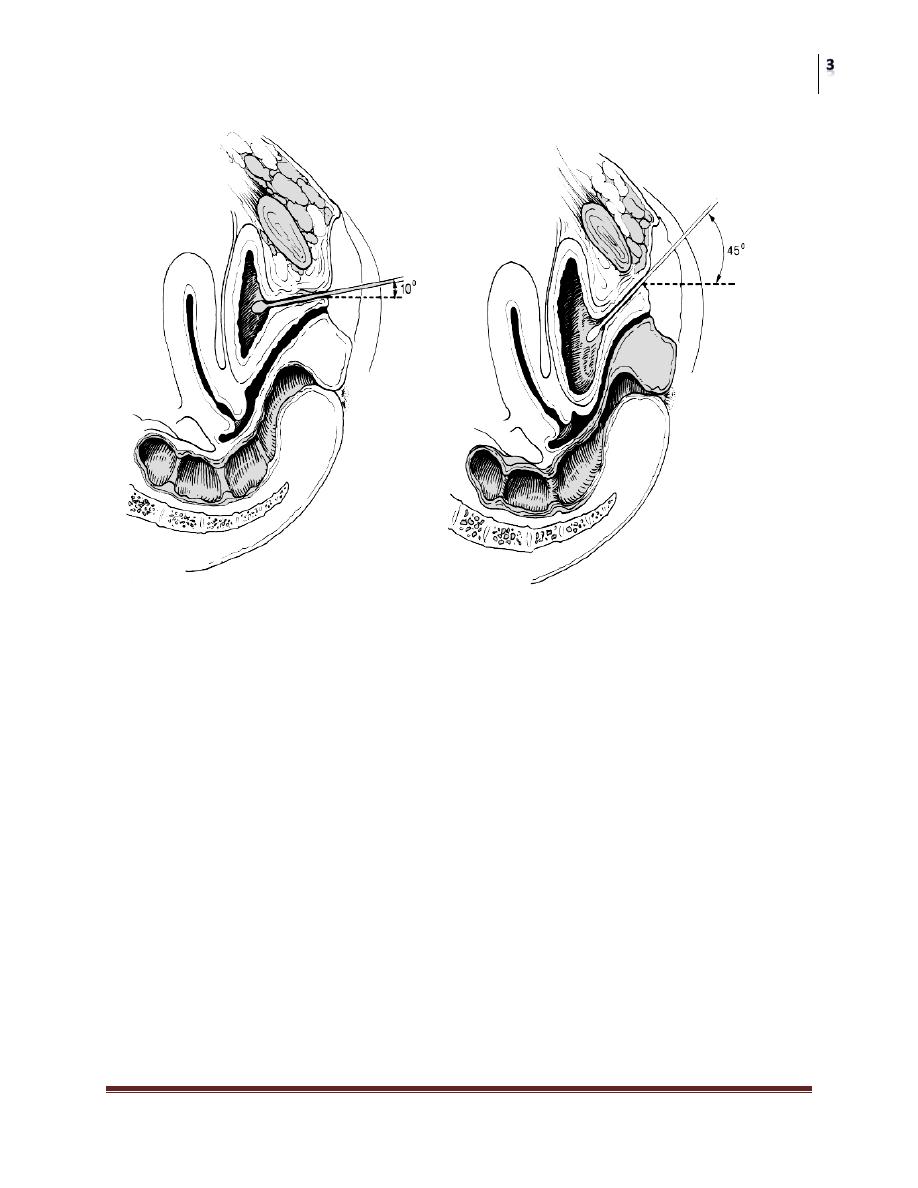
the Q-Tip test: assess the degree of urethral hypermobility by inserting a
lubricated sterile cotton-tipped applicator gently through the urethra into the
bladder,the patient is then asked to strain and the degree of rotation is
assessed. Hypermobility is defined as a resting or straining angle of greater
than 30 degrees from the horizontal.
Vaginal examination:
anterior vaginal wall is examined to assess cystocele
posterior vaginal wall and vault are examined for the presence of a rectocele
or enterocele.
Pelvic floor strength is assessed
Because the urethra and trigone are estrogen-dependent tissues. The most
common signs of inadequate estrogen levels are thinning and paleness of the
vaginal epithelium, loss of rugae, disappearance of the labia minora and
presence of a urethral carbuncle.
Urinalysis
Urinalysis can identify acute urinary tract infection ,the condition reversible with
treatment.
Residual Urine Measurement
It is usually measured by catheterization or ultrasonography. A postvoid residual of
less than 50 ml is considered normal( in Stress incontinence) , and a postvoid
residual of more than 200 ml is considered abnormal. Values between 50 and 200
ml require clinical correlation In interpreting the results

Surgery
Urinary Incontinence
Dr. Hasanain Farhan
Lec. 34
Micturition
Diary
• Micturition diaries and pad tests make it possible to document voiding
patterns in the patient's own environment and during various daily activities.
• The following measurements to be included in a micturition diary: time of
micturition, time and type of incontinence, and voided volume .
• 24-hour studies are adequate for the evaluation of lower urinary tract
symptoms.
Pad Test
a semiobjective measurement of urine loss over a given period of time.
A weight gain a sanitary towel of up to 8 g over a 24-hour pad test is
considered normal.
The simplest pad test can be done by having the patient change her or his
pads every 6 hours for one representative 24-hour period while she or he is
taking phenazopyridine (Pyridium, 200 mg tid). The amount of staining on the
pads is a rough estimate of the severity of the incontinence. Alternatively, the
pads can be weighed and the total weight, minus the weight of an unused pad,
recorded in the patient's record as an estimate of the volume of urine loss (1 g
equals approximately 1 ml of urine). A weight gain of up to 8 g over a 24-hour
pad test is considered normal
Urethral Pressure Profilometry
The classical pressure changes in stress incontinence:
1) Low urethral closure pressure.
2) Short urethral functional length
3) Weak response to stress.
Cystometry
leak with cough
Flowmetry

Surgery
Urinary Incontinence
Dr. Hasanain Farhan
Lec. 34
TREATMENT
Nonsurgical Treatment
1) Behavior Modification
2) Pelvic Floor Exercises
3) Biofeedback
4) Electrical Stimulation
have all been reported to cause improvement in 30% to 75% of patients.
5) α-adrenergic agonists ,SRI
6) Estrogens
Surgical Treatment
if hypermobility ,treatment is:
Suspension of the bladder neck & proximal urethra which is either
1) Retropubic Suspensions Marshall-Marchetti-Krantz (MMK)
and Burch colposuspension or
2) Transvaginal suspensions
if (ISD) exists
suspension alone is not adequate & treatment is:
1) Pubovaginal sling (Autologous Tissues as Rectus Fascia or
Nonautologous Tissues as pericardium or Synthetic Materials as
Monofilament Polypropylene Tape the tension-free vaginal tape
(TVT) procedure or TOT
2) Periurethral injections
3) Sphincter prostheses
Urge Incontinence
• The basic feature is detrusor instability and loss of urine while attempting to
inhibit micturition
• The bladder is described to be overactive with clinical symptoms of
urgency,frequency, and nocturia
• The bladder overactivity can be idiopathic or result from bladder
inflammation,tumour,obstruction, neurological and trauma

Surgery
Urinary Incontinence
Dr. Hasanain Farhan
Lec. 34
Urodynamic Features
• Flowmetry High flow rate
• Cystometry Detrusor hyperirritability with increase intravesical pressure
,decrease capacity and uninhibited contraction
• Urethral closure pressure Normal or high, normal response to stress and
normal urethral fuctional length
Treatment
• Behavior Modification.
• Anticholenergic drugs.
• Intravesical botulinum toxin injection.
• Surgery
SNS,augmentation cystoplasty, and diversion.
