
Surgery
Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction
Dr.Montadhar Al-Almadani
Lec. 39
Definition;
• A ureteropelvic junction (UPJ) obstruction can be thought of as a restriction
to flow of urine, from the renal pelvis to the ureter, which, if left
uncorrected, leads to progressive renal deterioration.
EVIDENCE
• UPJ obstruction is the most common cause of significant dilatation of the
collecting system in the fetal kidney.
• today the majority of cases are identified and diagnosed in the perinatal
period
• It has an overall incidence of 1:1500 and a ratio of males to females of 2:1
in newborns.
ETIOLOGY
• 1-Intrinsic ;
• Congenital UPJ obstruction most often results from intrinsic disease. A
frequently found defect is the presence of a peristaltic segment. Other
findings include: mucosal folds, valves…True stenosis is found rarely;
however, a thin-walled, hypoplastic proximal ureter is observed frequently.
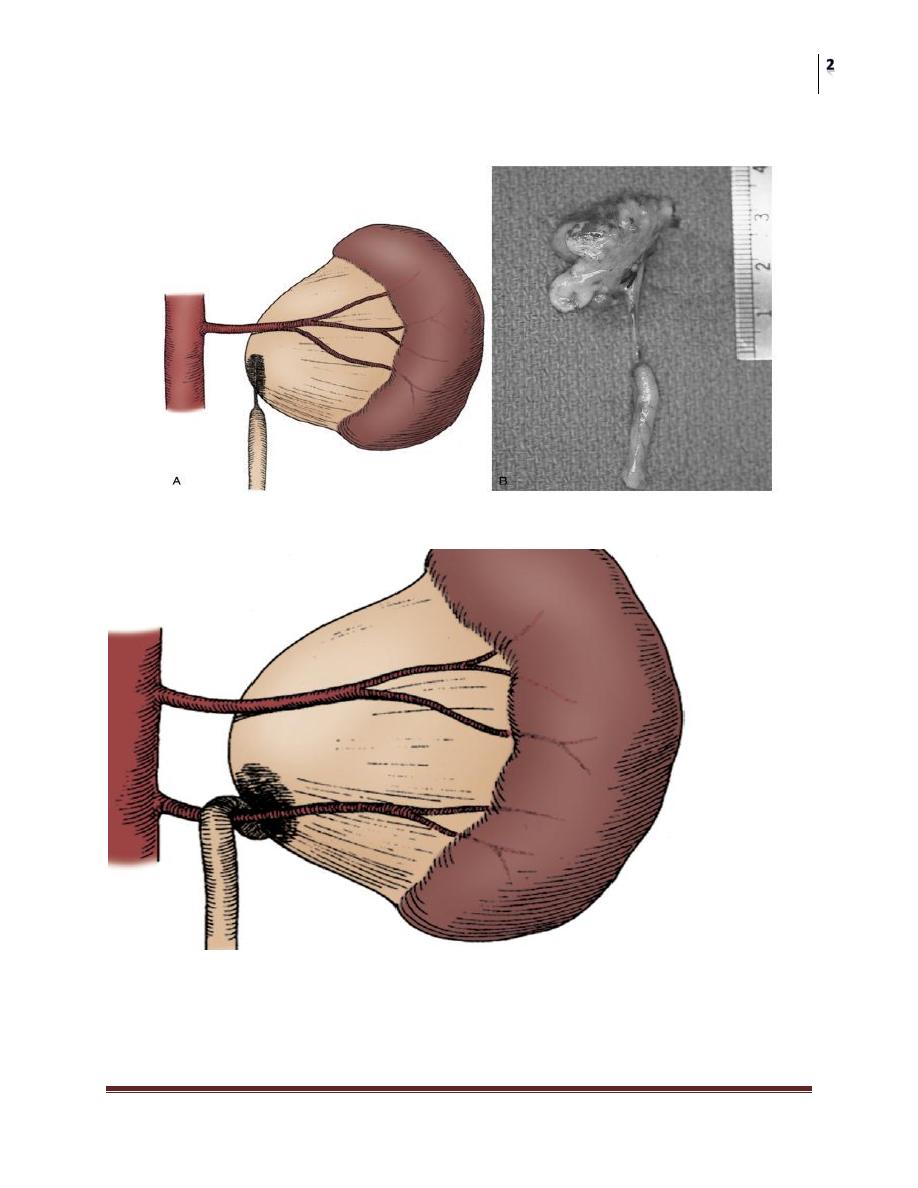
• 2-Etrinxsic; An aberrant, accessory, or early-branching lower pole vessel is
the most common cause of extrinsic UPJ .
• Secondary Ureteral Pelvic Junction Obstruction :(VUR).
Surgery
Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction
Dr.Montadhar Al-Almadani
Lec. 39
Intrinsic
Extrinsic
Surgery
Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction
Dr.Montadhar Al-Almadani
Lec. 39
Secondary PUJ Obstruction
The incidence of VUR associated with UPJ obstruction ranges from 9% to 18%
high-grade reflux being five times more likely than lower grades of reflux to be
associated with UPJ obstruction
Associated Anomalies
• UPJ obstruction is the most common anomaly encountered in the opposite
kidney; it occurs in 10% to 40% of cases.
• Renal dysplasia and multicystic dysplastic kidney are the next most
frequently observed contralaterally.

Surgery
Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction
Dr.Montadhar Al-Almadani
Lec. 39
• UPJ obstruction may also be seen with severe vesicoureteral reflux (VUR);
these conditions coexist in 10% of cases.
• Unilateral renal agenesis has been noted in almost 5% of children.
Pathology
• The response to obstruction is the development of renal pelvic hypertrophy,
in which the kidney compensates to maintain adequate urinary flow.
• Eventually, there are further changes to the renal pelvis and pressure-
induced injury that leads to irreversible renal damage.
SYMPTOMS/PRESENTATION
• Most infants are asymptomatic and most anomalies in children are
discovered because of their symptoms.
• There are still occasionally infants who present with failure to thrive,
feeding difficulties, sepsis secondary to urinary tract infection, or pain or
hematuria .
• Urinary tract infection is the presenting sign in 30% of affected children
beyond the neonatal period.
• In the older child, episodic flank or upper abdominal pain, sometimes
associated with nausea and vomiting related to intermittent UPJ obstruction,
is a prominent symptom
Diagnosis
• In neonates and infants, the diagnosis of UPJ obstruction has generally been
suggested either by routine performance of maternal ultrasonography or by
the finding of a flank mass.
• In either setting, renal ultrasonography is usually the first radiographic study
performed.
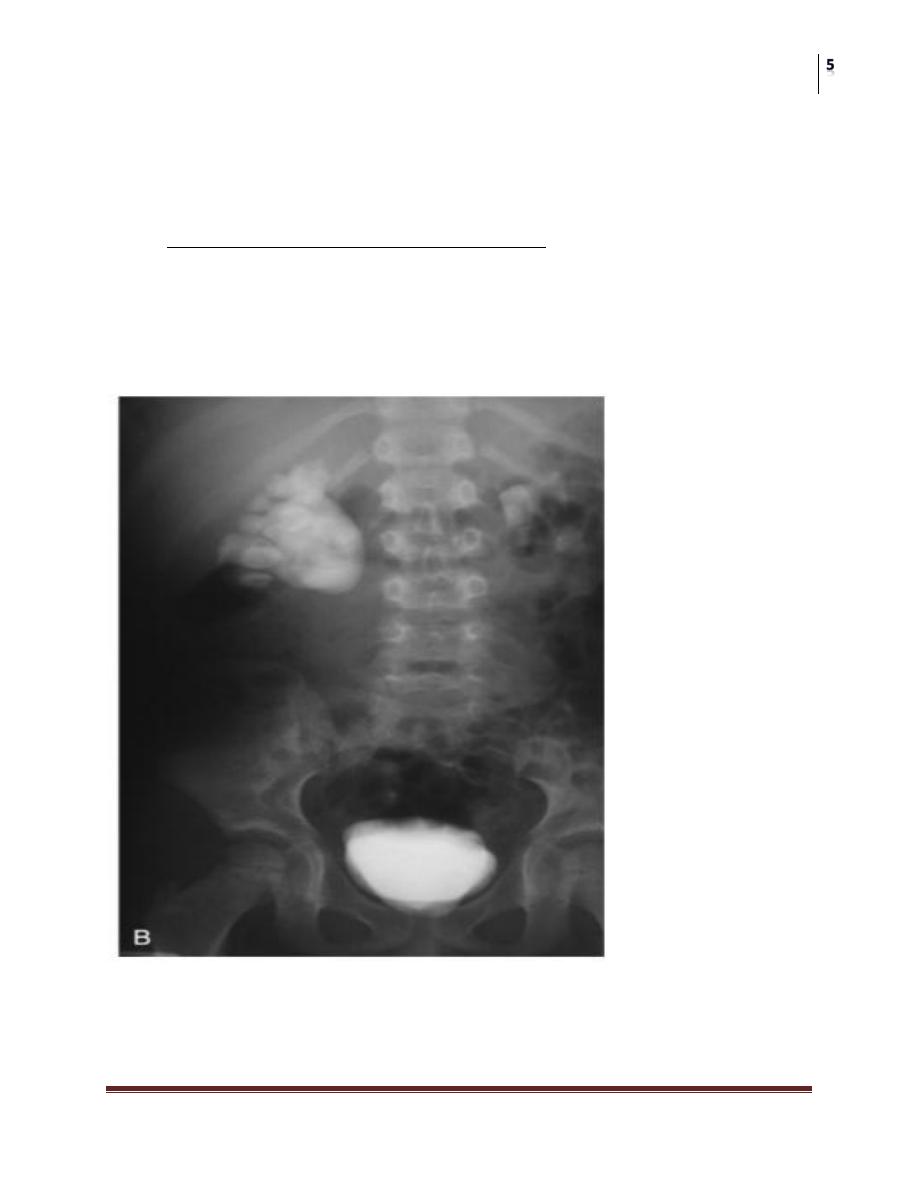
Postnatal ultrasound
• Since transitory neonatal dehydration lasts about 48 hours, imaging should
be performed after this period of postnatal oliguria.
• During ultrasound examination, the anteroposterior diameter of the renal
pelvis, calyceal dilatation, kidney size, thickness of the parenchyma, cortical
echogenicity, ureters, bladder wall and residual urine are assessed.
Surgery
Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction
Dr.Montadhar Al-Almadani
Lec. 39
Ultrasonograghy
• Ideally, u.s should be able to visualize dilatation of the collecting system, to
help differentiate UPJ obstruction from multicystic kidney, and to help
determine the level of obstruction
• Renal duplex Doppler ultrasonography ;(RI).
• RI values were much higher in the kidneys that had an obstructive pattern on
diuretic renography (RI ≥ 0.75) .
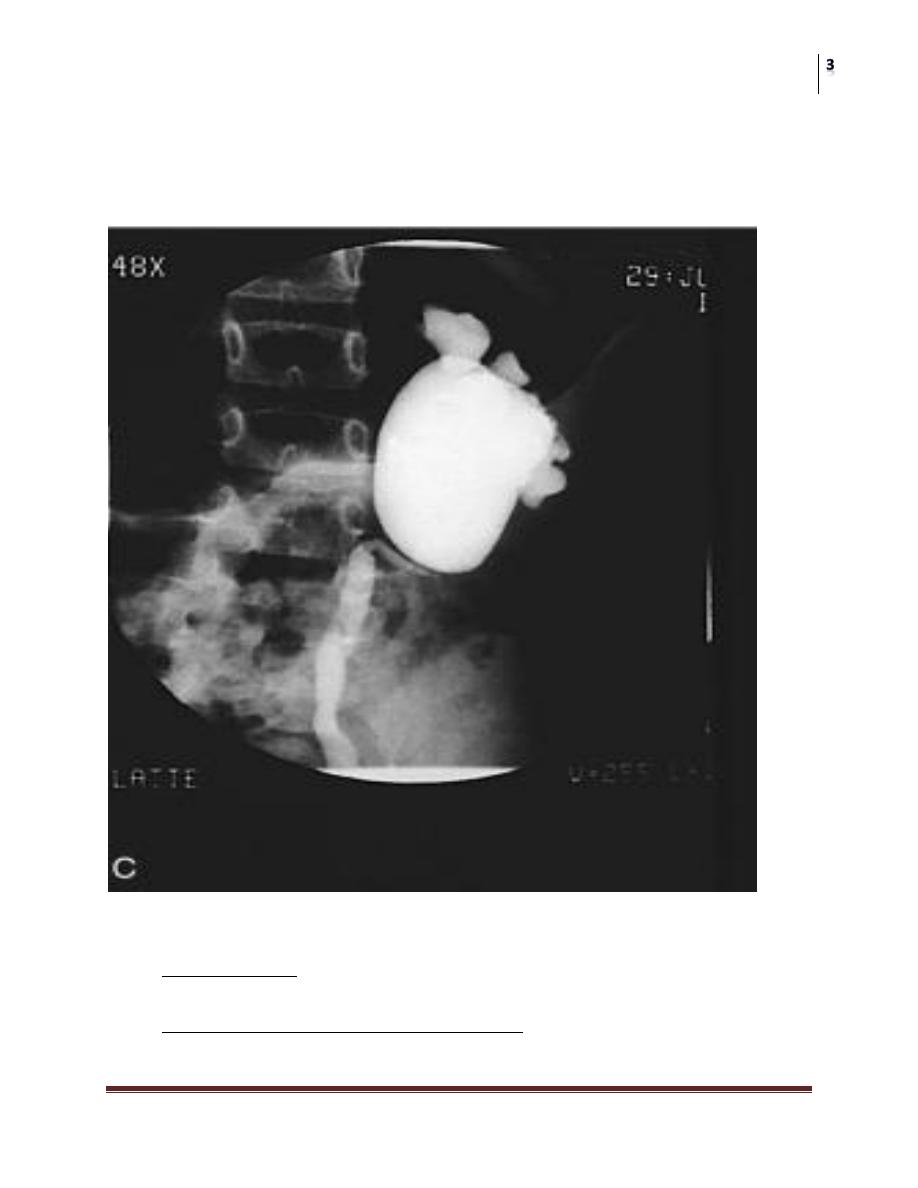
Intravenous pyelography
Is a diagnostic modality in many centers
Surgery
Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction
Dr.Montadhar Al-Almadani
Lec. 39
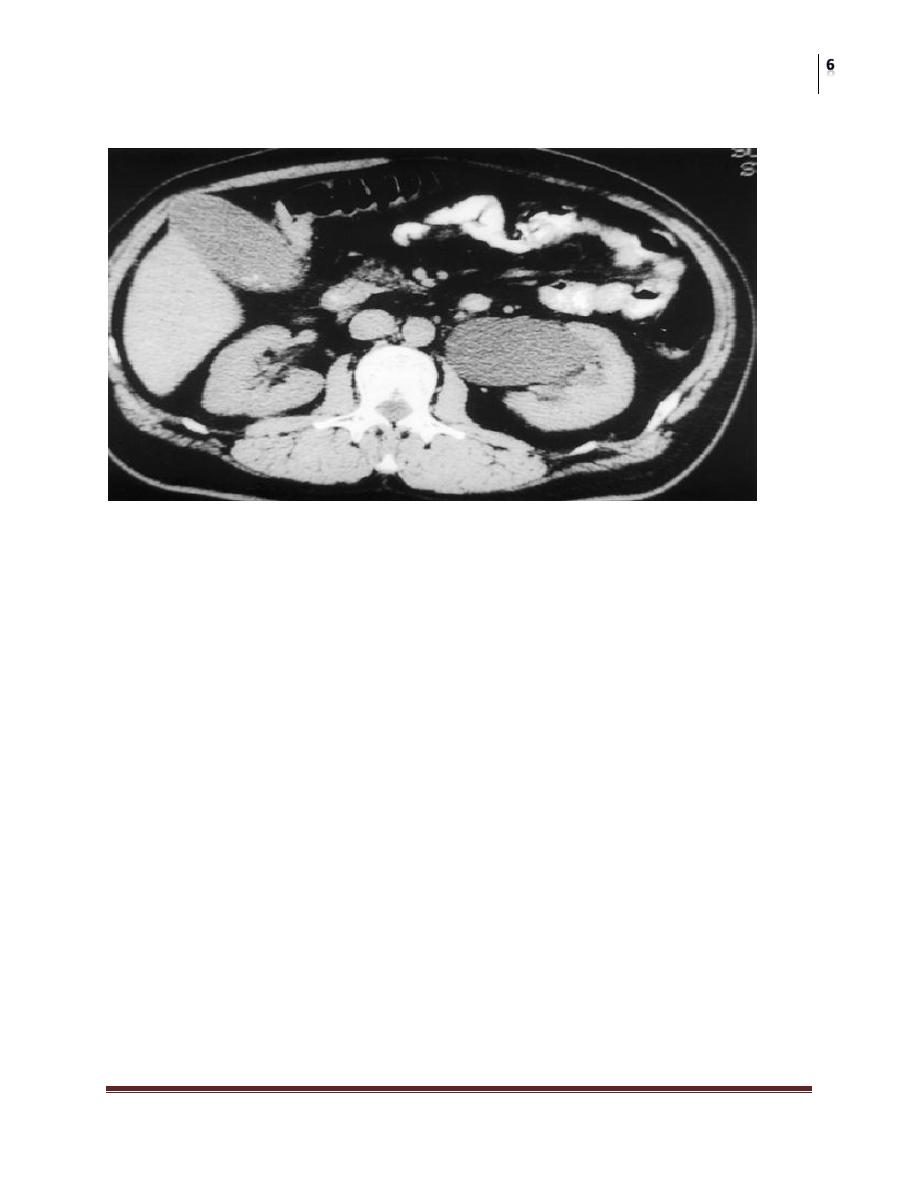
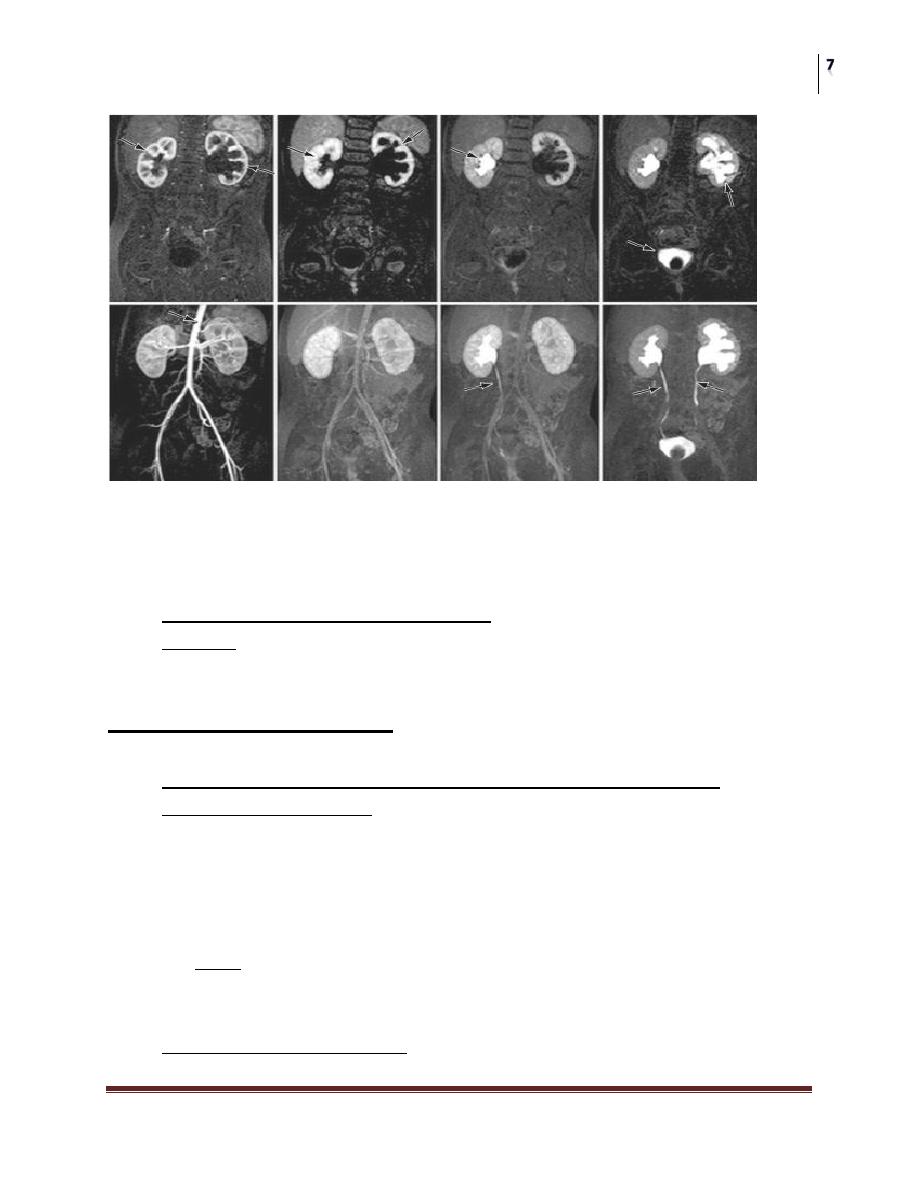
CT-Scan
Radionuclide Renography
• Nuclear renography is considered the radiographic study that best defines
the presence of a ureteropelvic junction obstruction.
• Differential renal function is quantitated along with the kidney's response to
diuretic challenge.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Surgery
Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction
Dr.Montadhar Al-Almadani
Lec. 39
Biochemical markers
• Various have been used as indicators of renal tubular injury in the setting of
obstructive uropathy. Such markers could be assessed to determine the need
for intervention, based on a detrimental change.
• N-Acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase (NAG) .
• TGF-β1: Urinary TGF-β1 : was found to be fourfold higher in bladder urine
in patients with upper tract obstruction compared with control subjects.
Indications for surgery
• Early surgery is recommended for patients who have kidneys with
diminished function, massive hydronephrosis, infection, or stones.
• Symptomatic obstruction (recurrent flank pain, urinary tract infection)
requires surgical correction using a pyeloplasty.
• In asymptomatic cases, conservative follow-up can be the treatment of
choice.
SURGICAL REPAIR
• The open techniques that have had the greatest applicability can be classified
into three main groups: the flap type, the incisional-intubated type, and the
dismembered type.
• Endoscopic and laparoscopic approaches.
Surgery
Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction
Dr.Montadhar Al-Almadani
Lec. 39
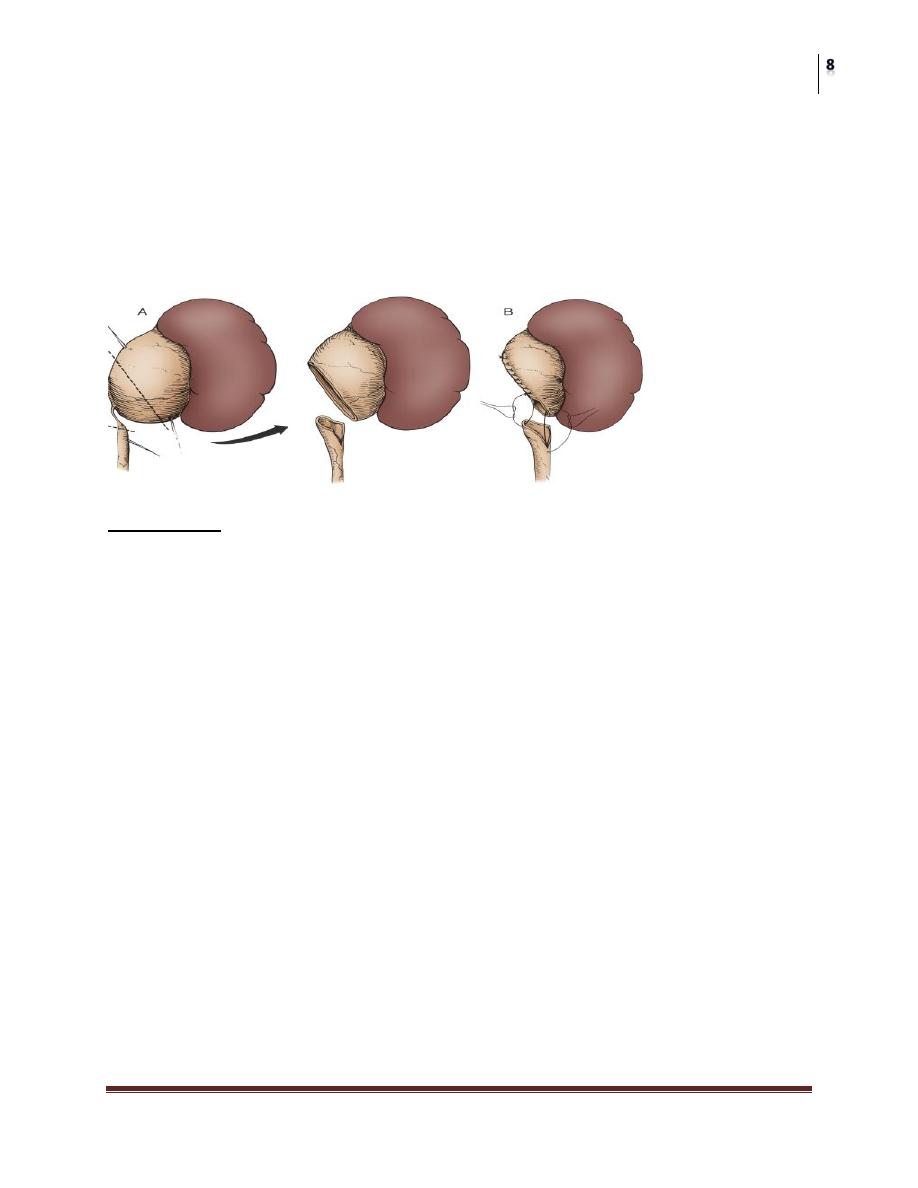
• The Anderson-Hynes pyeloplasty has become the most commonly
employed “open” surgical procedure for the repair of UPJ.
Dismembered pyeloplasty
• Incision
Surgical Technique
Endourology
• The recent explosion in the field of endourology as a subspecialty of urology
has encouraged use of percutaneous techniques for the repair of
ureteropelvic junction obstruction in selected patients
• The technique may be applied antegrade, via a nephrostomy tract, or
retrograde, using either a ureteroscope (for direct vision) or an Acusize
balloon catheter with fluoroscopic visualization.
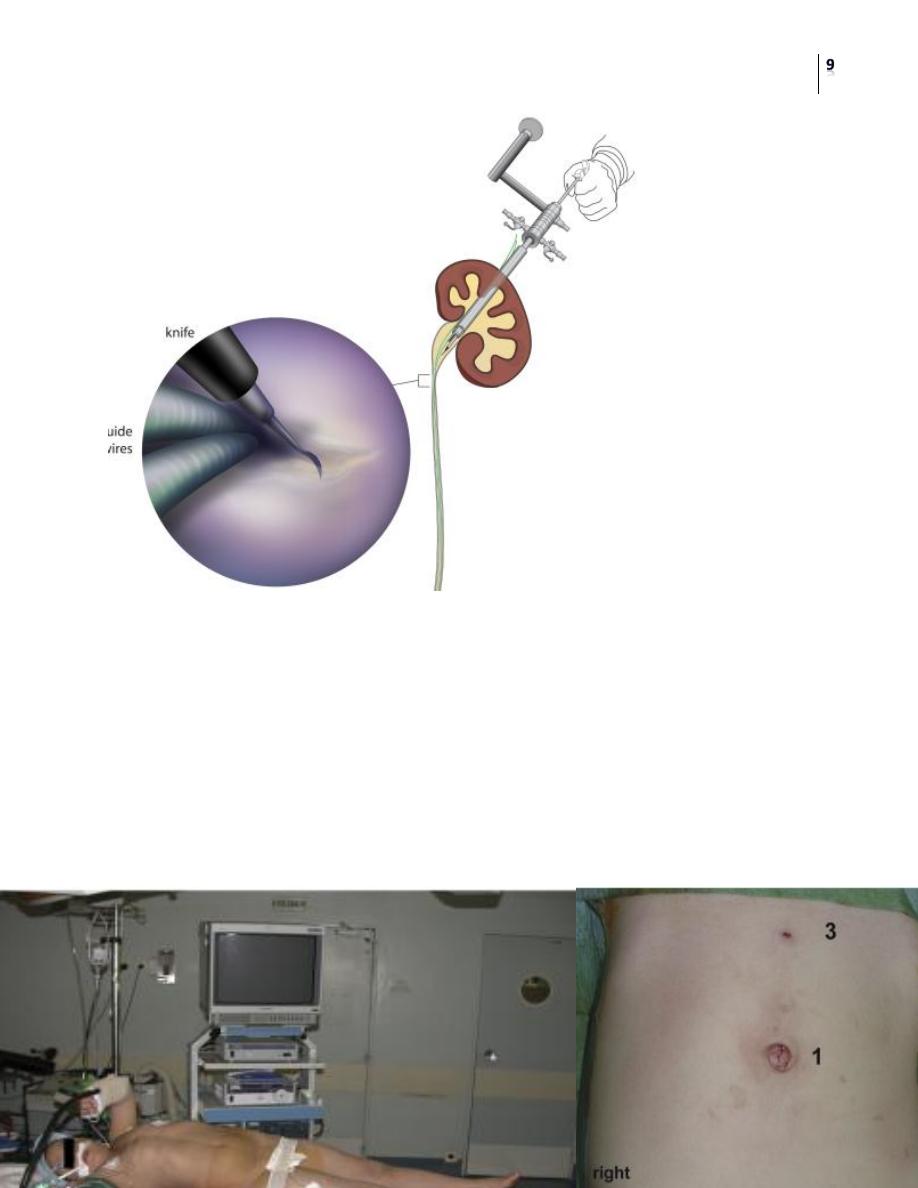
Percutaneous nephroscopic “cold knife” endopyelotomy
Surgery
Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction
Dr.Montadhar Al-Almadani
Lec. 39
The line of incision is delineated by two guide wires, which have been passed
across the UPJ in an antegrade fashion through a superior calyx using a rigid
nephroscope through a No. 30 Fr sheath.
The lateral incision is performed under direct visual control
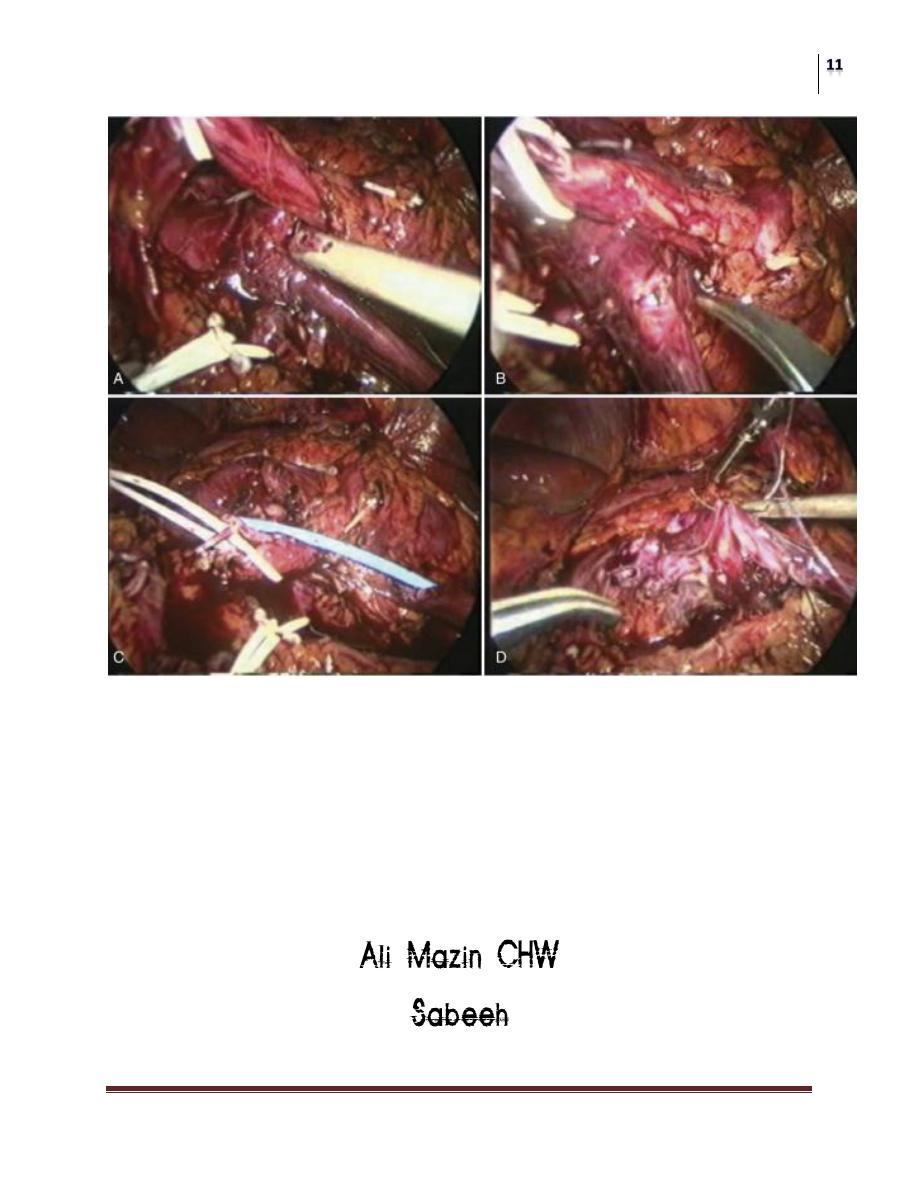
Laparoscopic Pyeloplasty

Surgery
Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction
Dr.Montadhar Al-Almadani
Lec. 39
Laproscopic Pyeloplasty
Surgery
Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction
Dr.Montadhar Al-Almadani
Lec. 39
OUTCOME
• The prognosis is generally good. In several large series, the reported
reoperation rate has been only 2–4%, but the postoperative radiographic
appearance of the area may be disappointing.
