Surgery
Scrotal Disorders
Dr. Saad Dakhil
Lec. 51
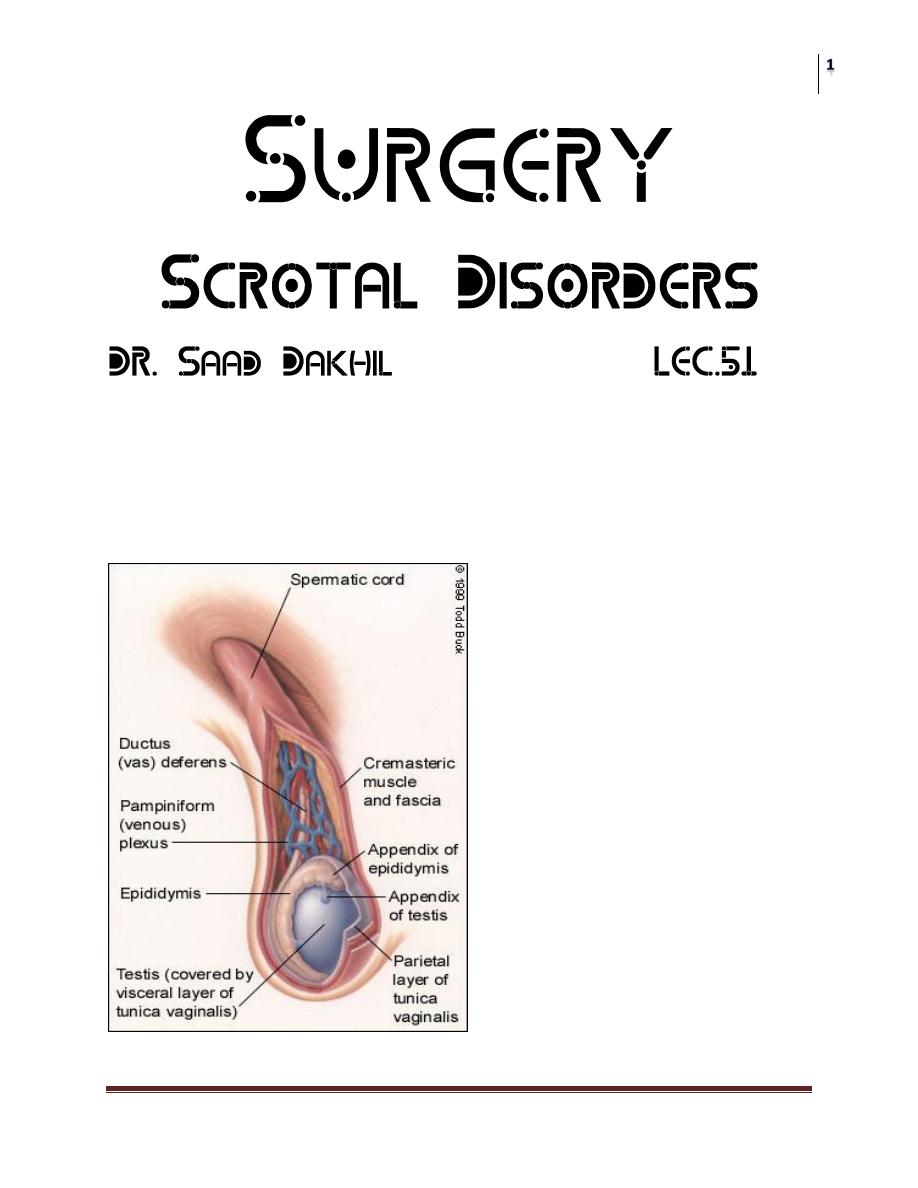
Anatomy;
Scrotum; can be considered as an outpouching of the lower part of the
anterior abdominal wall.it contains the Testis,Epididymides,lower end of
spermatic cord
Surgery
Scrotal Disorders
Dr. Saad Dakhil
Lec. 51
Spermatic cord
Structure of spermatic cord;
1. vas deferens
2. testicular artery
3. Testicular veins (pampiniform plexus)
4. testicular lymph vessels
5. autonomic nerves
6. processus vaginalis
7. cremasteric artery
8. Artery of the vas deferens
9. genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve
Surgery
Scrotal Disorders
Dr. Saad Dakhil
Lec. 51
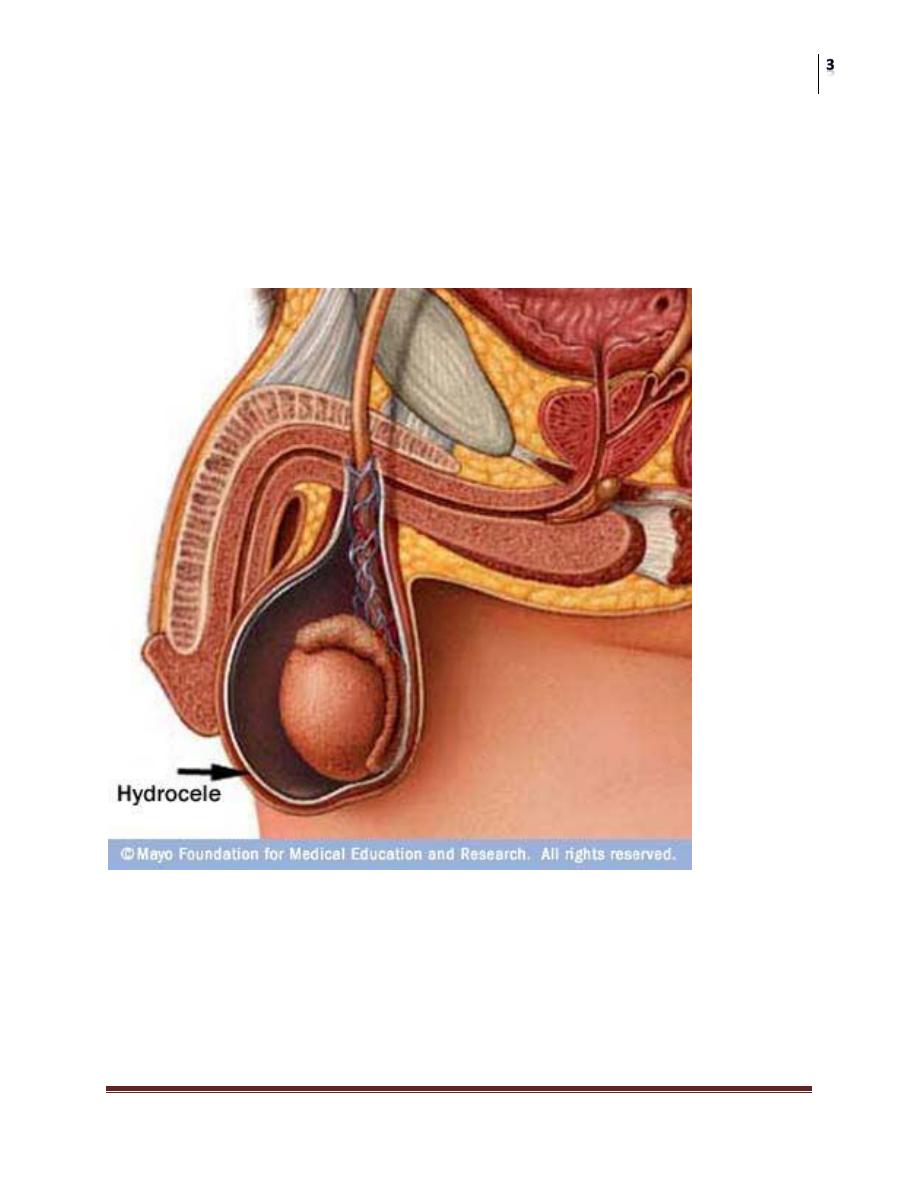
Hydrocele;
Collection of abnormal quantity of serous fluid in the tunica vaginalis.
If it contains pus or blood it is called pyocele or haematocele respectively.
Hydrocele is more common than the two other varieties.
Hernia / Hydrocele
Hydrocele: incomplete obliteration of the processus vaginalis
Hernia: large opening of the processus vaginalis which may allow
abdominal contents to enter scrotal sac.
Surgery
Scrotal Disorders
Dr. Saad Dakhil
Lec. 51
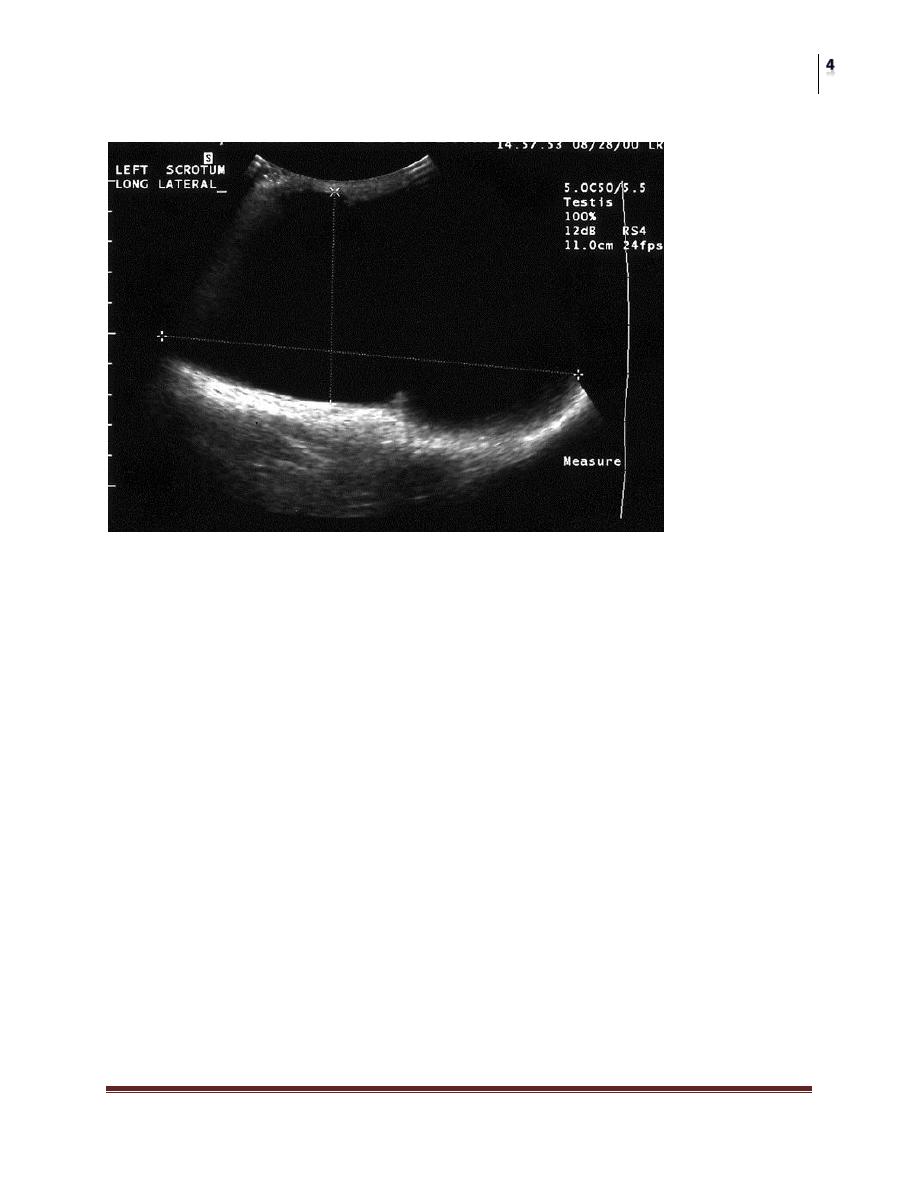
Scrotal Ultrasound
Large left hydrocele
Causes;
A- Primary; cause unknown associate with patency of proccessus vaginalis.
It classified as follows;
1-communicating;it connect with the peritoneal cavity.
2-noncommunicating; it does not connect with peritoneal cavity.
B- Secondary; where the fluid accumulate secondary to pathology inside the
testis like epididymo-orchitis,testicular tumor and trauma.
Clinical presentation;
Symptoms;
1-painless swelling
2-embarrassment
3-frequent and painful micturation may occur if hydrocele is secondary to
epididymo-orchitis
Hydrocele not affect fertility
Surgery
Scrotal Disorders
Dr. Saad Dakhil
Lec. 51
Examination;
Position; the swelling usually unilateral but can be bilateral .if
communicating cannot feel the cord above the lump.
Color and temperature; normal
Tenderness; primary are not tender but secondary may be tender
Composition; fluctuant and have fluid thrill if large enough
Reducibility; cannot reduced
Testis impalpable and transillumenate
Mangement;
Primary;
in children:
Most neonatal hydrocel resolve in first 2 year of life if persists repair
as herniotomy.(communicating).
The scrotal approach (Lord or Jaboulay technique) is used in the
treatment of a secondary non-communicating hydrocele.
In adult;
Surgical excision.
Secondary :
Treatment the underlying condition.
ACUTE SCROTUM IN CHILDREN
A child or adolescent with acute scrotal pain, tenderness, or swelling should
be looked on as an emergency situation requiring prompt evaluation,
differential diagnosis, and potentially immediate surgical exploration.
Surgery
Scrotal Disorders
Dr. Saad Dakhil
Lec. 51
Is it torsion or not
Testicular torsion
Epidimyo-orchitis
Age
Children
Adolescent
Onset
Sudden
Gradual
Fever
Absent
Present
Severity
Sever
Moderate
Irritative symptoms
Absent
Present
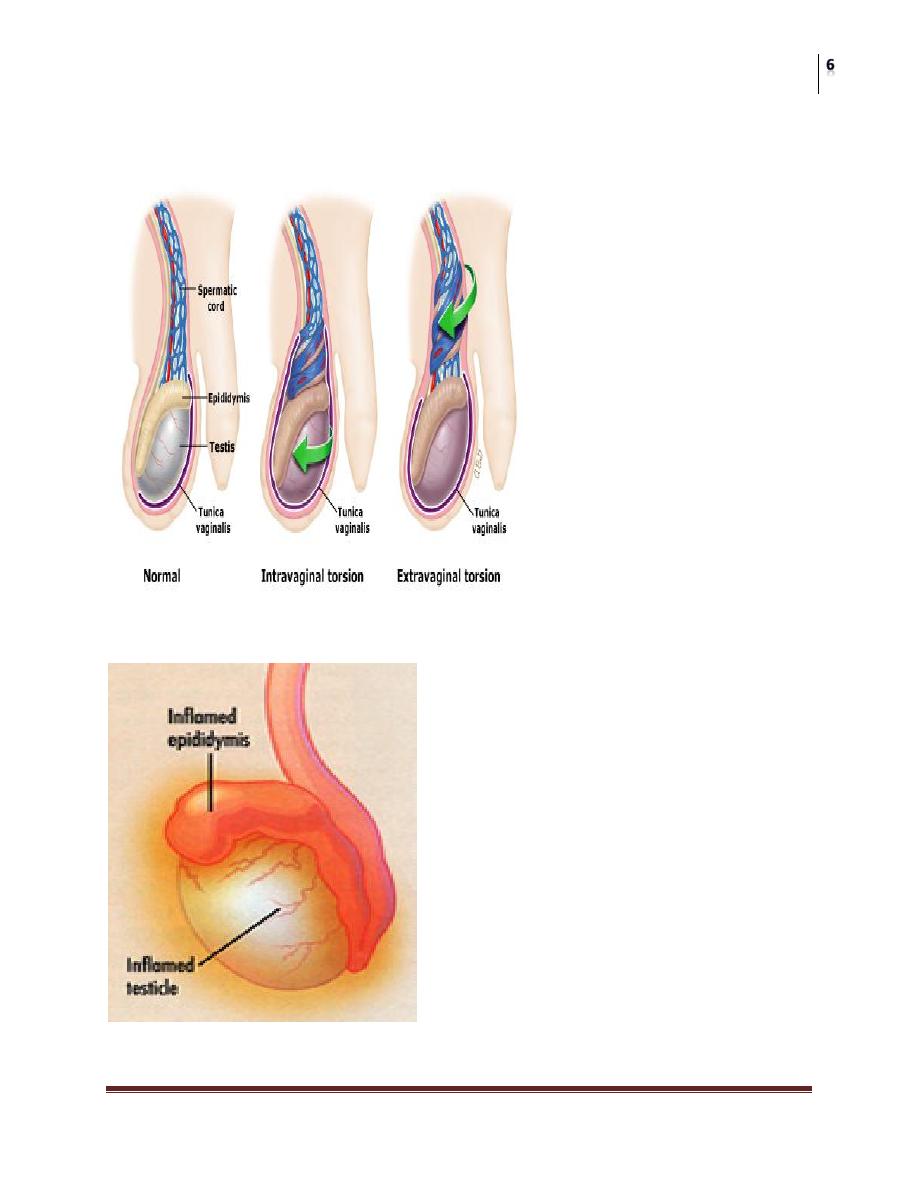
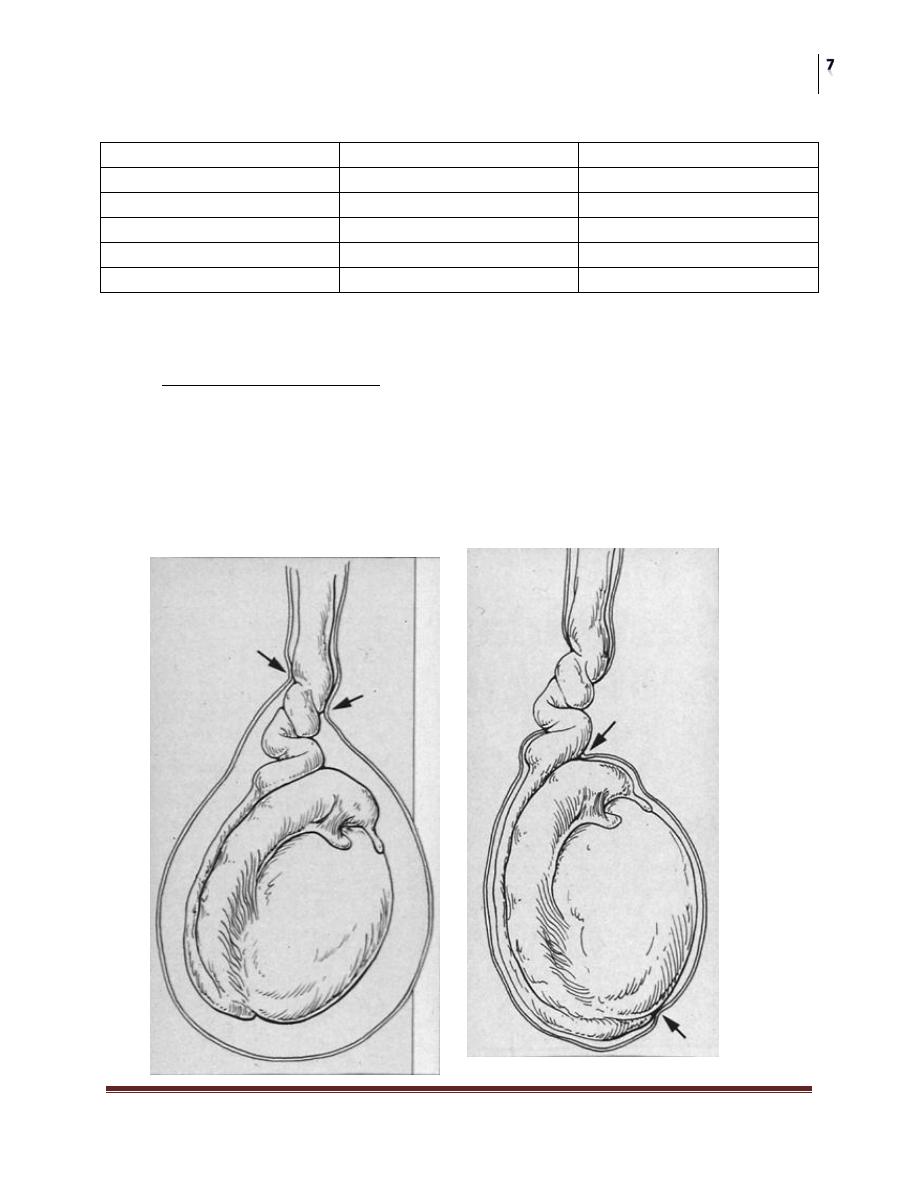
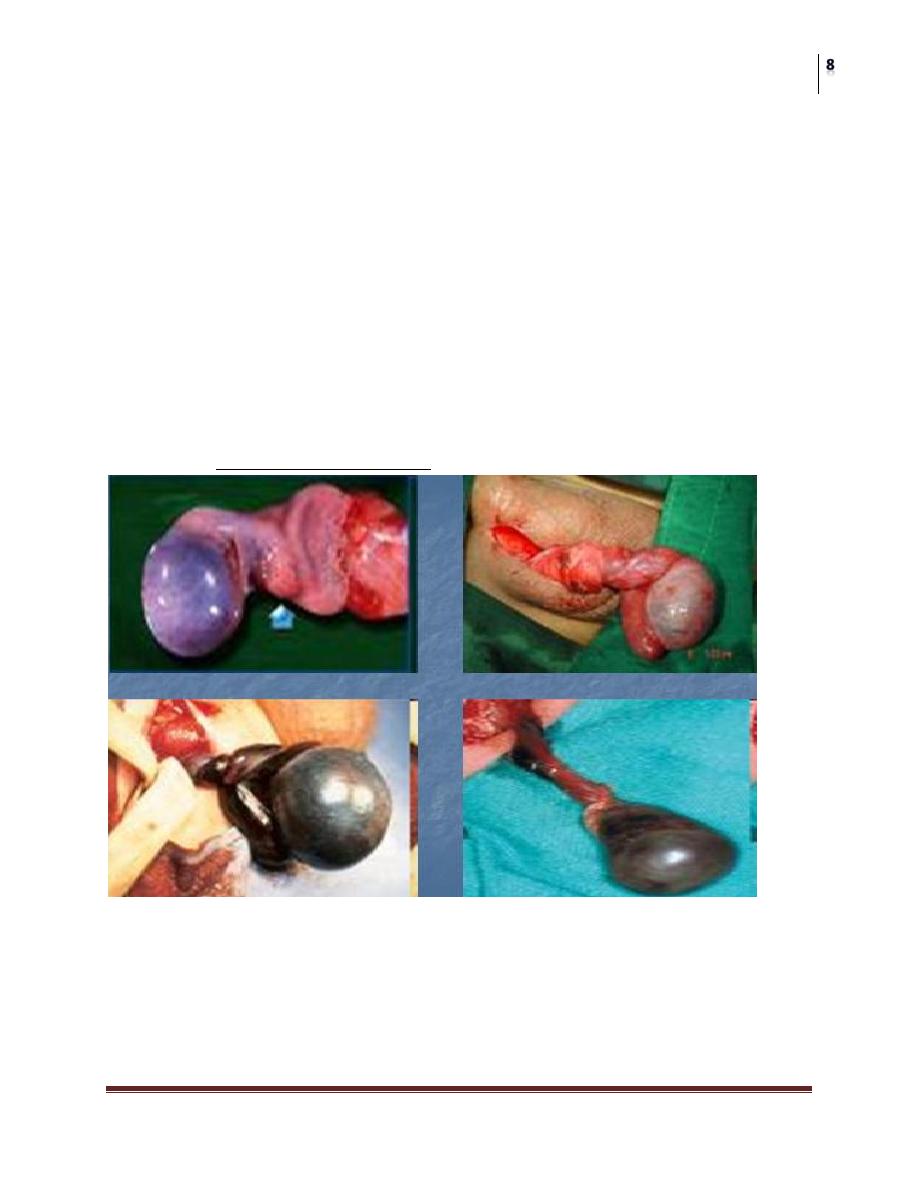
Testicular Torsion
The most urgent problem.
High risk of loss due to infarction (90%)
May have torsion of cord or appendages
Neonatal and adolescence
more common in undescended testes due to absence of fixation
Extravaginal: exclusive to perinatal
Intravaginal: 90% of adolescent age group
Surgery
Scrotal Disorders
Dr. Saad Dakhil
Lec. 51
History
Sudden onset of pain
Past history of similar pain in 50%
Physical
Cremasteric reflex may be absent
Prehn’s sign: elevation of testes does not relieve pain
Lateral testicular lie.
Diagnosis
if certain : emergent surgery
if uncertain:
Nuclear scan: not done often depending on facility
Ultrasonography: documents blood flow
PROVIDES ANATOMY
Refer Emergently!
< 6 hours, 90% salvage
> 24 hours, 100% loss and atrophy
Attempt manual detorsion- outward
“ open the book “
Some may be twisted 360, 720 degrees
Surgery
Scrotal Disorders
Dr. Saad Dakhil
Lec. 51
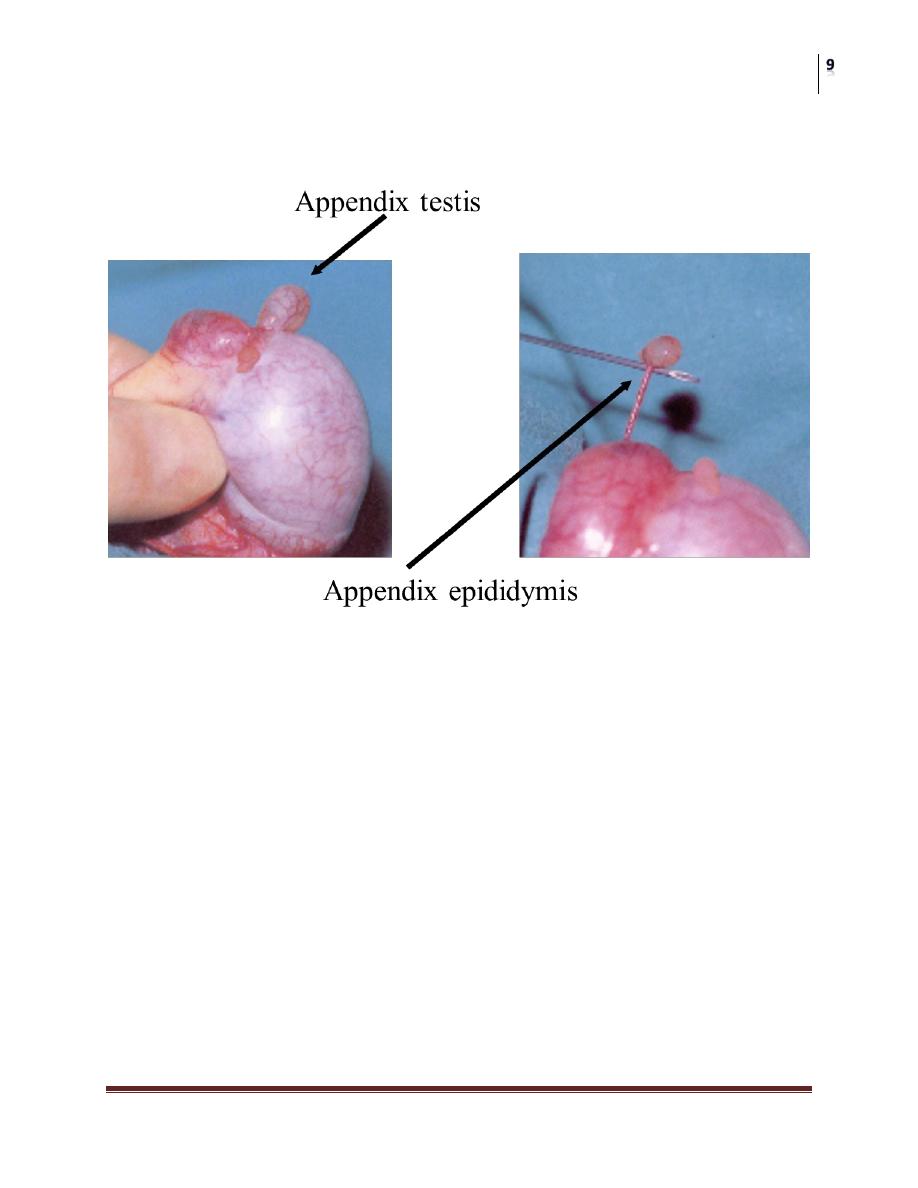
Testicular Appendages
Torsion of appendages rarely seen after puberty
Presents with pain
Physical
may develop scrotal swelling & erythema
“blue dot sign” seen early
Ultrasound required to rule out testis torsion
Treat symptomatically
Be sure of early exam before swelling makes any further exam
suspect!
Surgery
Scrotal Disorders
Dr. Saad Dakhil
Lec. 51
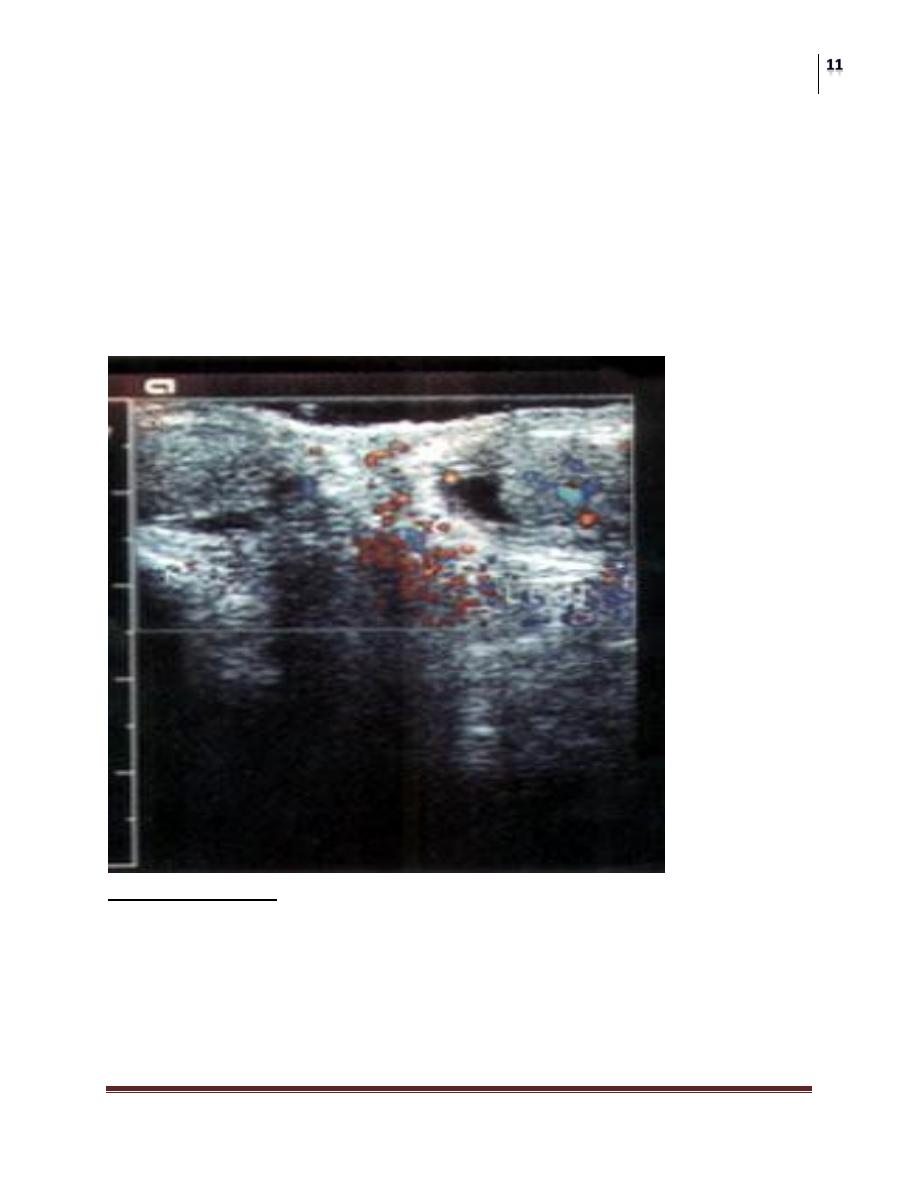
Blue dot of gangrenous appendix testis
Surgery
Scrotal Disorders
Dr. Saad Dakhil
Lec. 51
Epididymitis
Most common acute scrotum post-pubertal
Gradual onset of pain
Fever in 40% of patients
Dysuria in 50% of patients
Urinalysis may show pyuria in 50%
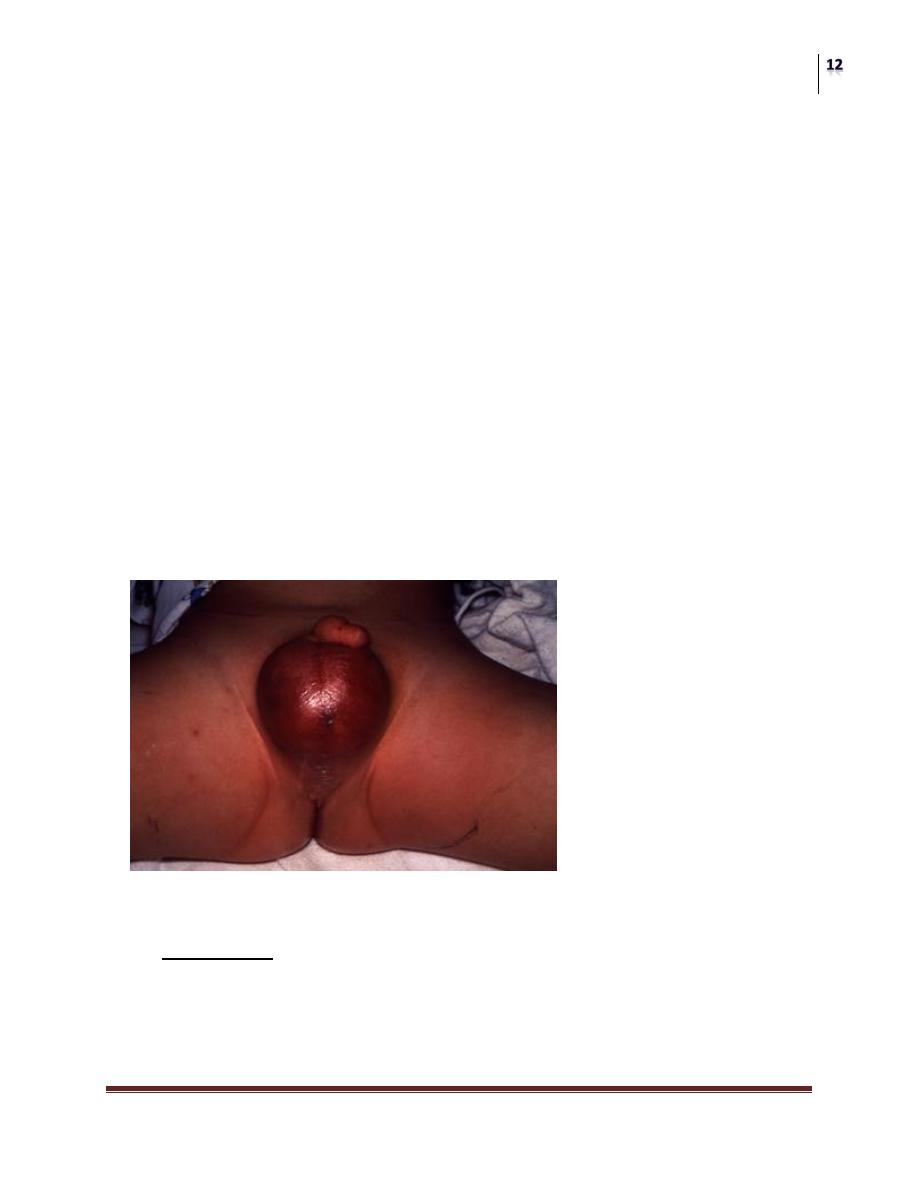
Doppler Epididymitis
Left Epididymitis Increased blood flow
Surgery
Scrotal Disorders
Dr. Saad Dakhil
Lec. 51
Confirm that torsion of testis does not exist
Treatment
scrotal elevation
Antibiotics considered: keflex, septra
Refer for persistence of pain/swelling.
Fournier’s Gangrene
Necrotizing fasciitis of the perineum
May ascend of fascial planes
Colles > Dartos > Scarpas
20% to 50% Mortality Rate
Polymicrobial infection
Treat with Gent, Pen G and Flagyl
Debridement surgically
20% to 30% related to GU source
CRYPTORCHIDISM
Background
Almost 1% of all full-term male infants are affected at the age of one year.
Premature > full term infant.
Categorisation into palpable and non-palpable testis seems to be most the
appropriate method.

Surgery
Scrotal Disorders
Dr. Saad Dakhil
Lec. 51
• Iliac fossa 3
rd
-5
th
month
• Deep inguinal ring 7
th
month
• Superficial ring 8
th
month
• Scrotum 9
th
month
Complications (THIN)
Higher incidence of:
Cancer. 25-30 times increased risk. not affected by orchiopexy.
Infertility.
50% abnormal semen in unilat. UDT
70% in bilateral.
Testicular torsion.
Trauma.
Hernia
Assessment
A physical examination is the only method of differentiating between
palpable or non-palpable testes.
Radiological imaging: 44%
There is no reliable examination to confirm or rule out an intra-abdominal,
inguinal and absent/vanishing testis (nonpalpable testis), except for
diagnostic laparoscopy.
In cases of bilateral non-palpable testes and any suggestion of sexual
differentiation problems, urgent endocrinological and genetic evaluation is
mandatory.
Treatment
To prevent histological deterioration, treatment should be undertaken and
completed before the age of 12-18 months.
Medical therapy
Medical therapy using human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) or
gonadotrophin-releasing hormone (GnRH) is based on the hormonal
dependence of testicular descent, with success rates of a maximum of 20%.
Surgery
Scrotal Disorders
Dr. Saad Dakhil
Lec. 51
Surgery
Palpable testis:
Surgery for the palpable testis includes orchidofuniculolysis and
orchidopexy, with success rates of up to 92%.
Non-palpable testis:
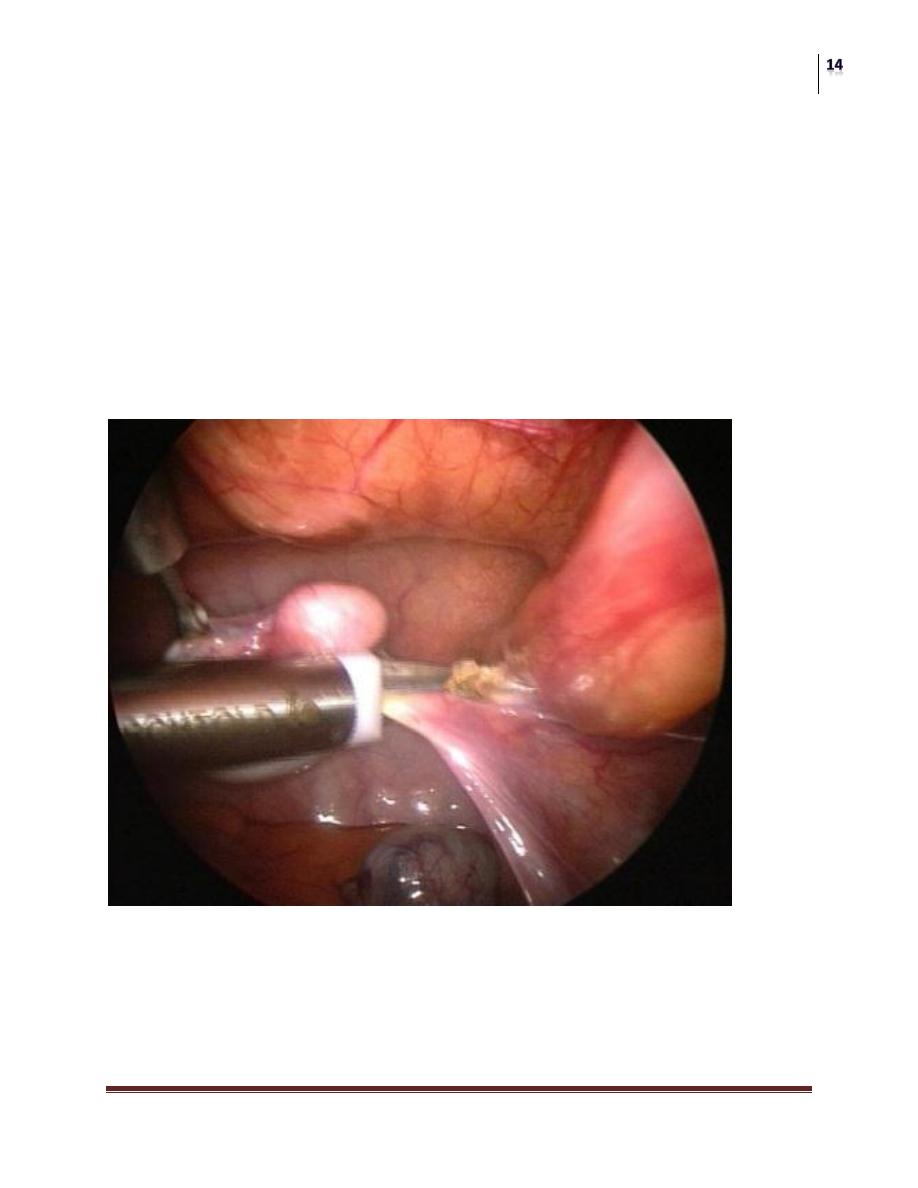
Inguinal surgical exploration with the possibility of performing laparoscopy
should be attempted. Laparoscopy is the most appropriate way of examining
the abdomen for a testis.
Microvascular autotransplantation is also an option.
laparoscopic View of abdominal testis
Surgery
Scrotal Disorders
Dr. Saad Dakhil
Lec. 51
Ectopic Testes
• perineal
• prepenile.
• Femoral.
• Inguinal pouch.
Vs undescended?
Retractile Testes
• Functions normally.
• normal size & consistency
• Scrotum well developed.
• ? Hyperactive cremasteric reflex.
• Most are normal by 12 yrs.
Atrophied Testes?
- Trauma.
- Torsion.
- Infection.
- Previous inguinal surgery.
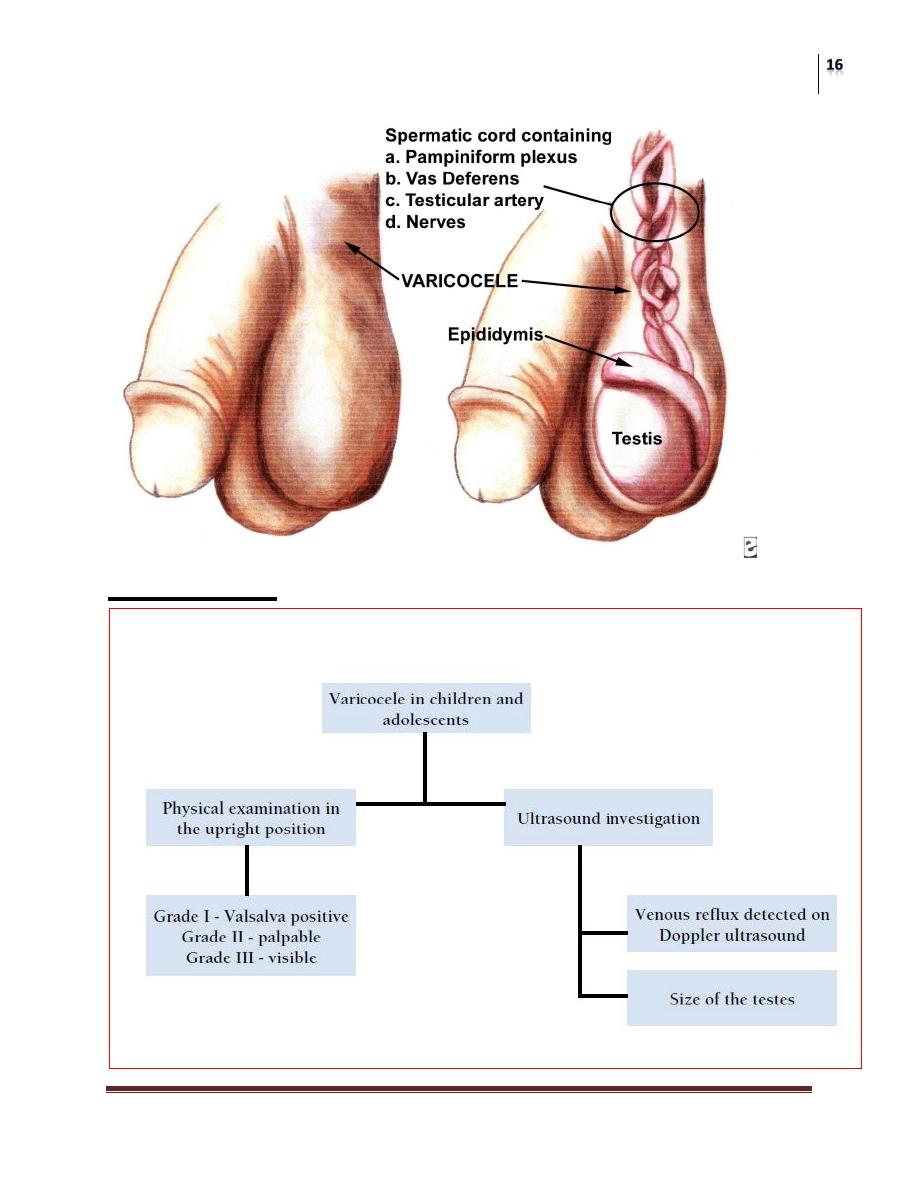
VARICOCELE IN CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS
Background
Ectatic and tortuous veins of the pampiniform plexus of the spermatic cord
are found in approximately 15% of male adolescents, with a marked left-
sided predominance .
This is unusual in boys under 10 years of age, but becomes more frequent at
the beginning of puberty.
Fertility problems will arise in about 20% of adolescents with varicocele.
The adverse influence of varicocele increases with time.
Surgery
Scrotal Disorders
Dr. Saad Dakhil
Lec. 51
Assessment

Surgery
Scrotal Disorders
Dr. Saad Dakhil
Lec. 51
Treatment
Surgery
Surgical intervention is based on ligation or occlusion of the internal
spermatic veins. Microsurgical lymphatic-sparing repair (microscopic or
laparoscopic) are associated with the lowest recurrence and complication
rate.
Follow-up
During adolescence, testicular size should be checked annually. After
adolescence, repeated sperm analysis is to be recommended.
The potential complications of varicocelectomy
Hydrocele formation, varicocele recurrence and testicular infarction
(atrophy).
Hydrocele formation is related to failure to preserve the lymphatic
vessels associated with the spermatic cord.
Testicular tumors
Commonest malignancy in men < 35 years.
Rare in african men and before puberty.
Peaks in the early twenties.
One in 10 testicular tumors occurs in association with maldescent of the
testis.
Prognosis is good particularly if there was no lymph node involvement.
Classification
According to the cells of origin, they’re classified into:
1. Primary cell tumors (90-95%), which include:
Germ cell tumors: Seminoma, teratoma,Embryonal CA, Yolk Sac Tumor.
Non-germ cells tumors: like sertoli cells tumors, Lyedig cell tumor.
2. Secondary tumors: lymphoma, leukemic infiltration of the testes.

Surgery
Scrotal Disorders
Dr. Saad Dakhil
Lec. 51
Symptoms:
Painless swelling of the testis, (sometime dull aching, dragging pain )(80%)
Heaviness in the scrotum.
Maybe history of trauma delays diagnosis.
General malaise, wasting ,loss of appetite.
Abdominal pain if lymph nodes are enlarged.
Swelling of legs caused by lymphatic or venous obstruction.
Infertility.
Secondary hydrocele.
Signs:
Can “get above it”.
Testes cannot be felt separately.
Not translucent.
Not fluctuant.
Harder than normal testis.
Dull to percussion hydrocele.
If skin is affected, it may be warm & discolored.
Usually not tender.
Irregular, different sizes.
Surface usually smooth (sometime irregular or nodular).
Examine the para-aortic & supraclavicular lymph nodes for metastasis .
The liver may be enlarged & there maybe sign of pulmonary secondaries
(collapse, consolidation or a pleural effusion).
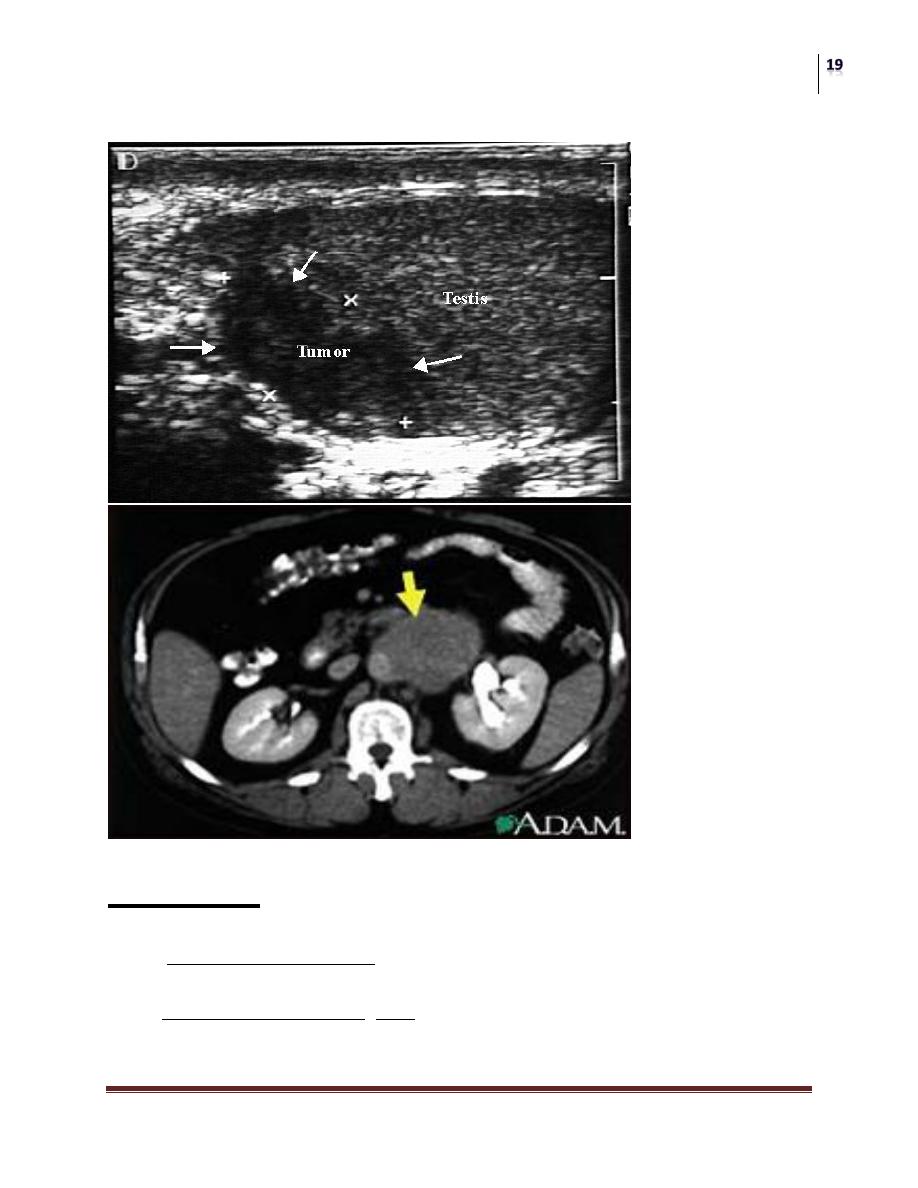
Investigation:
US testis
CXR metastasis
CT scan abdomen and chest to identify lymph nodes and pulmonary mets
Tumor Markers: AFP (yolk-sac cell), βHCG (trophoblastic cells), LDH
(lactate dehydrogenase).
Surgery
Scrotal Disorders
Dr. Saad Dakhil
Lec. 51
Treatment:
Explore testis through an inguinal incision.
Radical Orchidectomy.
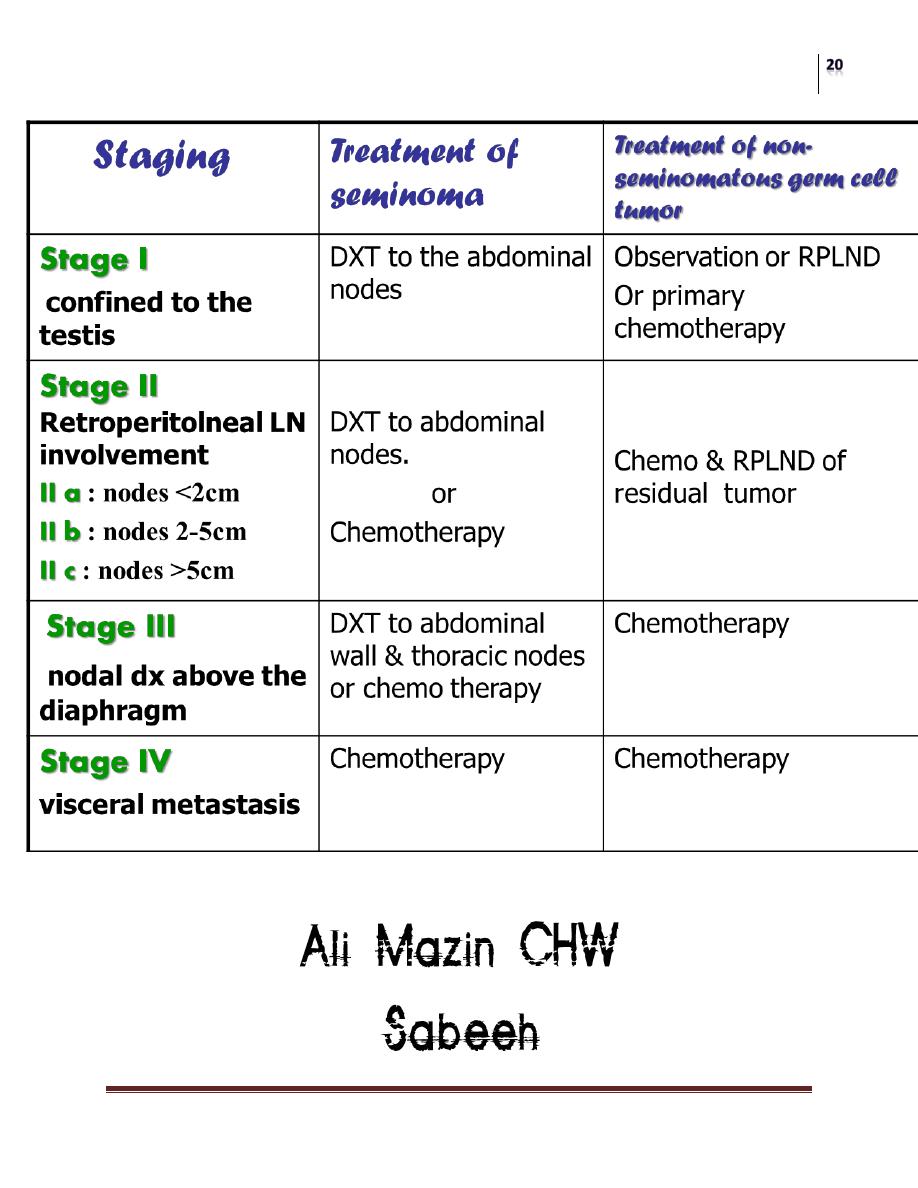
Further treatments depends on the type and stage ( see the following Table) .
Chemotherapy regimen : BEP :Bleomycine , Etopside ,Cisplatine
DXT=deep x-ray therapy, RPLND=retroperitoneal lymph node dissection
Surgery
Scrotal Disorders
Dr. Saad Dakhil
Lec. 51
The end ^_^