
Surgery
Intestinal Stomas
Dr. Haussam
Lec. 11
(1) Colostomy
Definition: It is an artificial opening made between the large bowel and skin,
to divert faeces and flatus to the exterior, where it can be collected in an
external aplliance. Effluent is usually solid.
(a)
Temporary Colostomy.
Indications:
1. Distal Obstruction.
2. Defunction a low rectal anastomosis after anterior resection of
the rectum.
3. Following traumatic injury to the rectum or colon.
4. During operative treatment of a high
fistula in ano.
5. Fulminant Colitis (IBD).
6. Complicated Diverticular disease.
Site of the colon used:
A segment which has a mesentery:
1. Transverse colon. (Disease involve Lt. side of the colon)
2. Sigmoid colon. (|Disease involve the rectum or rectosigmoid junction)

Surgery
Intestinal Stomas
Dr. Haussam
Lec. 11
Types of temporary colostomies:
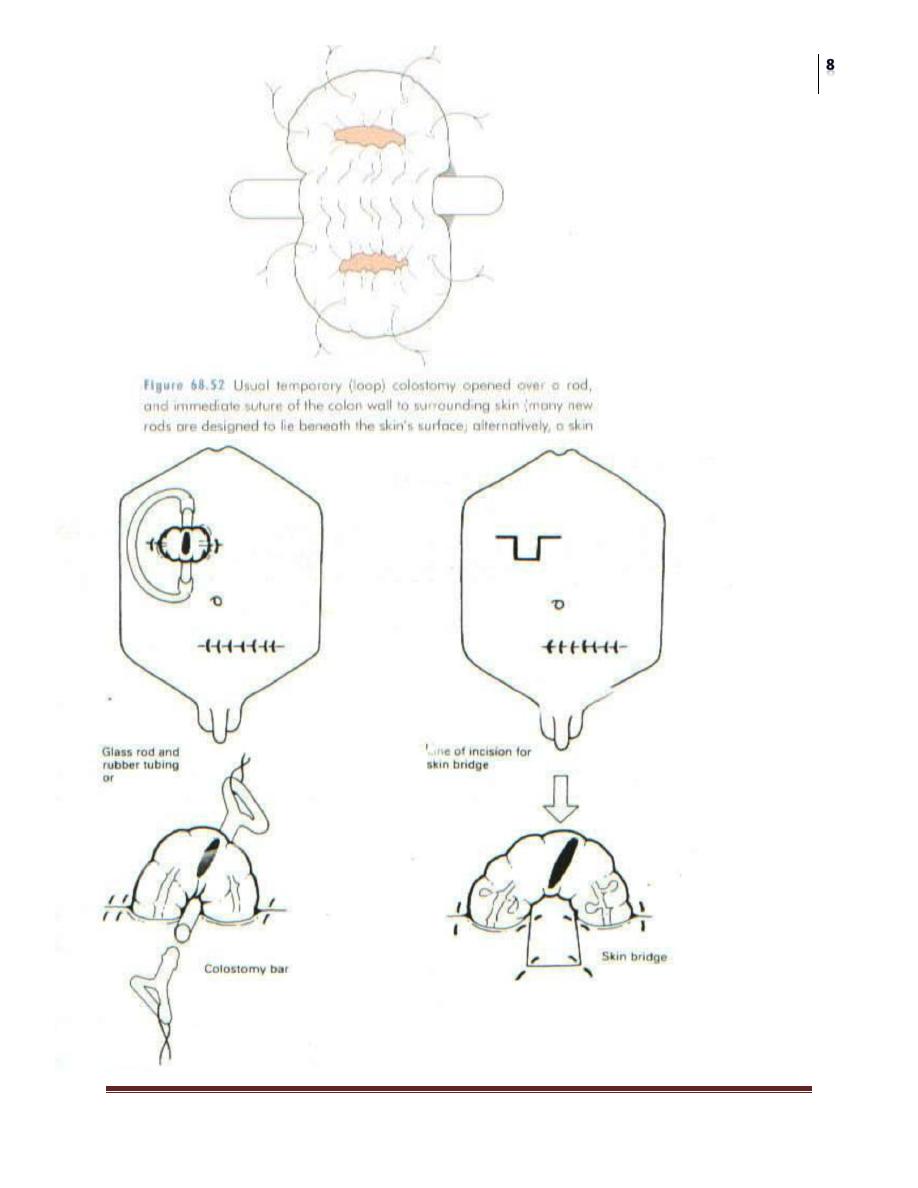
1. Loop colostomy:
bringing a loop of bowel to the surface where it is
held in place by a plastic or glass rod passed through the mesentery. Firm
adhesion of the colostomy takes place after 7 days then the bridge can be
removed.
Closure: follows the surgical cure or healing of the distal lesion for which
the temporary stoma was constructed (a distal loopogram) is best performed to
check there is no distal obstruction or any problem at the site of previous
surgery). Also the stoma should be mature (at least 2 months after
establishment of the colostomy).
Steps of loop colostomy:
GA is important since since traction on the mesentery causes pain and
nausea.
A transverse incision 8-10cm long, with removal of a disc of skin, is made
for transverse colon (in the Rt. upper abdomen midway between the
umbilicus and xiphisternum over the rectus abdominus muscle and
extending laterally to the lateral border of the rectus muscle), while for the
sigmoid colon (in the Lt. iliac fossa with a muscle cutting incision).
Cut down all layers including the rectus muscle which is divided
transversely ligating and dividing the epigastric artery.
The most proximal loop of colon is prepared by removing the omentum
from its anterior surface (only in Transverse colon), then a small hole is
made in the mesocolon through which a rubber tube is passed to fascilitate
delivery of the colon through the incision.
The laparotomy wound should be closed at this stage.
The colonic loop is held by an underlying glass rod or by a colostomy bar or
skin bridge incised initially. The colon is then opened on its antimescolic
border longitudinally (along the taenia coli).
Sutures are used to fix the colonic serosa to the abdominal wall, and colonic
mucosa to the surrounding skin.
The finished loop colostomy should allow one finger to pass down on each
side.

Surgery
Intestinal Stomas
Dr. Haussam
Lec. 11
2. Double Barrelled colostomy:
the colon is divided so that both ends can
be brought separately to the surface with a skin bridge intervening.
Advantage: ensures that the distal segment (colon, rectum) is completely
defunctioned (Absolute Rest).
3. Hartmann’s Procedure:
This includes a proximal End Colostomy with
a distal closed colonic segment. This procedure can be used when resecting a
tumour of the Lt. Site of the colon or in complicated diverticular disease.
(b) Permanent Colostomy
Indications:
1. Rectal carcinoma excision (A-P resection) ----- End
colostomy.
2. Inoperable rectal or colonic carcinoma ------ Loop
colostomy.
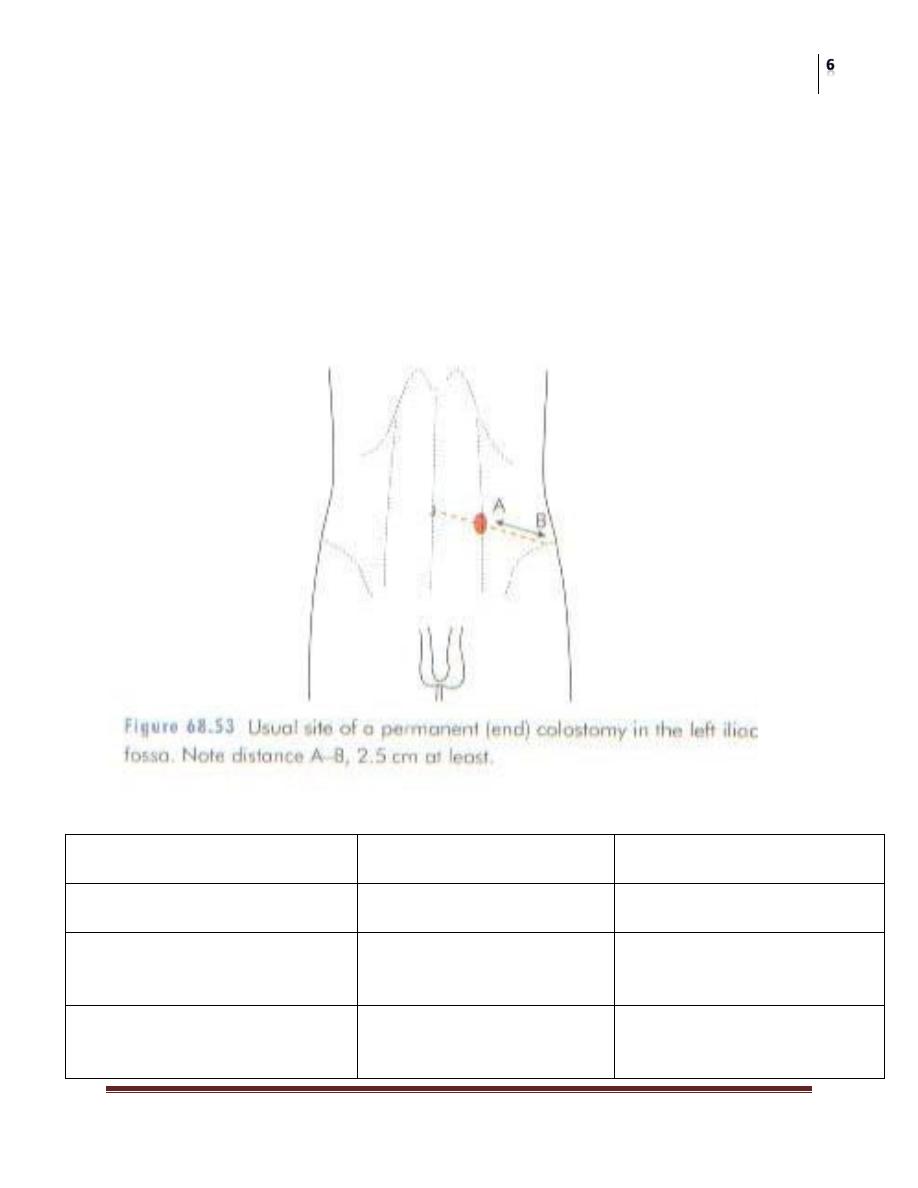
Technique of End Colostomy:
The best site is through the lateral edge of the rectus sheath 6cm above and
medial to the anterior superior iliac spine. The colon is stitched in place
immediately by sutures placed between the colonic margin and the surrounding
skin, i.e; it is usually sutured flush to the skin. The point at which the colon is
brought to the surface must be carefully selected to allow a colostomy bag to
be applied without impinging on a bony prominence. An important point after
the colostomy has been made is to close the lateral space between the
intraperitoneal segment of the colon and the peritoneum of the pelvic wall to
prevent internal herniation and strangulation of the bowel.
A sigmoid colostomy is usually brought out at the Lt. iliac fossa.
A Transverse colostomy is usually brought out in the Rt. Hypochondrium.
Complications of Colostomy construction:
1. Prolapse. (it leads to dysfunction, it is not important in temporary
colostomy which sooner or later will be closed, only in permanent cases
which will need refashioning or resiting)
2. Retraction. (due to tension and infection)
3. ParaColostomy Hernia. (Especially in end terminal colostomy).

Surgery
Intestinal Stomas
Dr. Haussam
Lec. 11
Treatment should include resiting the colostomy and the hernia defect
closed.
4. Bleeding.
5. Necrosis and gangrene of the distal end. (Due to loss of viability due to
interference with its blood supply, too much ligation of mesenteric
vessels).
6. Stenosis of the colostomy orifice. (Occurs at the mucocutaneous
junction, due to infection and cellulitis which is followed by
scarring).Treatment should include refashioning of colostomy site with
excision of skin disc.
7. PeriColostomy Abscess and Fistula. (Occurs when a misplaced suture
that fixes the colon to the deeper layers of the abdominal wall instead of
passing through the serosa, passes through the whole thickness of the
bowel). The abscess bursts and forms a fistula. Treatment should include
laying the track open and leaving it to granulate.
8. Colostomy diarrhea.
(2) Ileostomy
Definition: It is an artificial opening made between the ileum and skin of the
abdominal wall, to divert intestinal contents to the exterior, without a sphincter
to control the timing of its emptying. Effluent is usually liquid.
(1) End Ileostomy.
Indications: In cases where total proctocolectomy
is done.
1- Ulcerative colitis.
2- Crohn’s disease.
3- Familial polyposis Coli.
(2) Loop Ileostomy.
Indications: as an alternative of a loop colostomy for Defunctioning protection)
a. Low rectal anastomosis following an anterior rectal esection
procedure.
b. Ileoanal pouch procedure following Total proctocolectomy.

Surgery
Intestinal Stomas
Dr. Haussam
Lec. 11
Technique of Ileostomy:
The ileostomy opening should be 5cm lateral to the umbilicus and brought out
through the lateral edges of the rectus abdominus muscle. It is usually made in
the Rt. Iliac fossa. It should be spouted.
Complications of Ileostomy:
1- Prolapse.
2- Retraction.
3- ParaIleostomy Hernia.
4- Bleeding.
5- Necrosis and gangrene of the distal end.
6- Stenosis of the Ileotomy orifice.
7- Skin reaction around the stoma. (Excoriation, erosion, sloughing)
8- Fluid and electrolyte imbalance. (Ileostomy Flux).
(3) Caecostomy
Indication:
1- Trauma to the caecum.
2- Closed loop syndrome. (In desperately ill patients with advanced
obstruction)
Site: Rt. Iliac fossa.
Types of Bowel Stomas
1. End (terminal).
2. Loop.
3. Double Barrel. (Two ends brought to the surface seperately with a skin
bridge intervening)
4. Paul-Miculikz. (Two ends brought to the surface together where the adjacent
serosal surfaces are hitched by sutures, and adjacent mucosal surfaces are
sutured)
5. Seperation proximal faecal fistula from a distal mucous fistula.
Surgery
Intestinal Stomas
Dr. Haussam
Lec. 11
Criteria taken into consideration when positioning a stoma:
1- Away from any bony prominence.(Anterior superior iliac spine , Symphysis
pubis)
2- Away from the umbilicus.
3- Away from any previous surgical incision.
4- Visible when the patient stands.
5- Comfortable for the patient.
How to differentiate a colostomy from ileostomy?
Colostomy
Ileostomy
Site
Rt. upper abdomen
Lt. iliac fossa
Rt. iliac fossa
Discharge
Formed faeces or faeculent
fluid
Fluidy
Color of discharge
Brownish or Blackish
Brownish, Greenish -
Yellowish
Surgery
Intestinal Stomas
Dr. Haussam
Lec. 11
Odor of discharge
Very offensive (excessive
gases)
Less offensive
Stoma
Large
Constructed flush or slightly
elevated from the skin
Small
Constructed as a nipple like
projection above the skin
Reaction of the surrounding
skin
Usually normal
Erythematous, oedematous
(from enzymatic digestion)
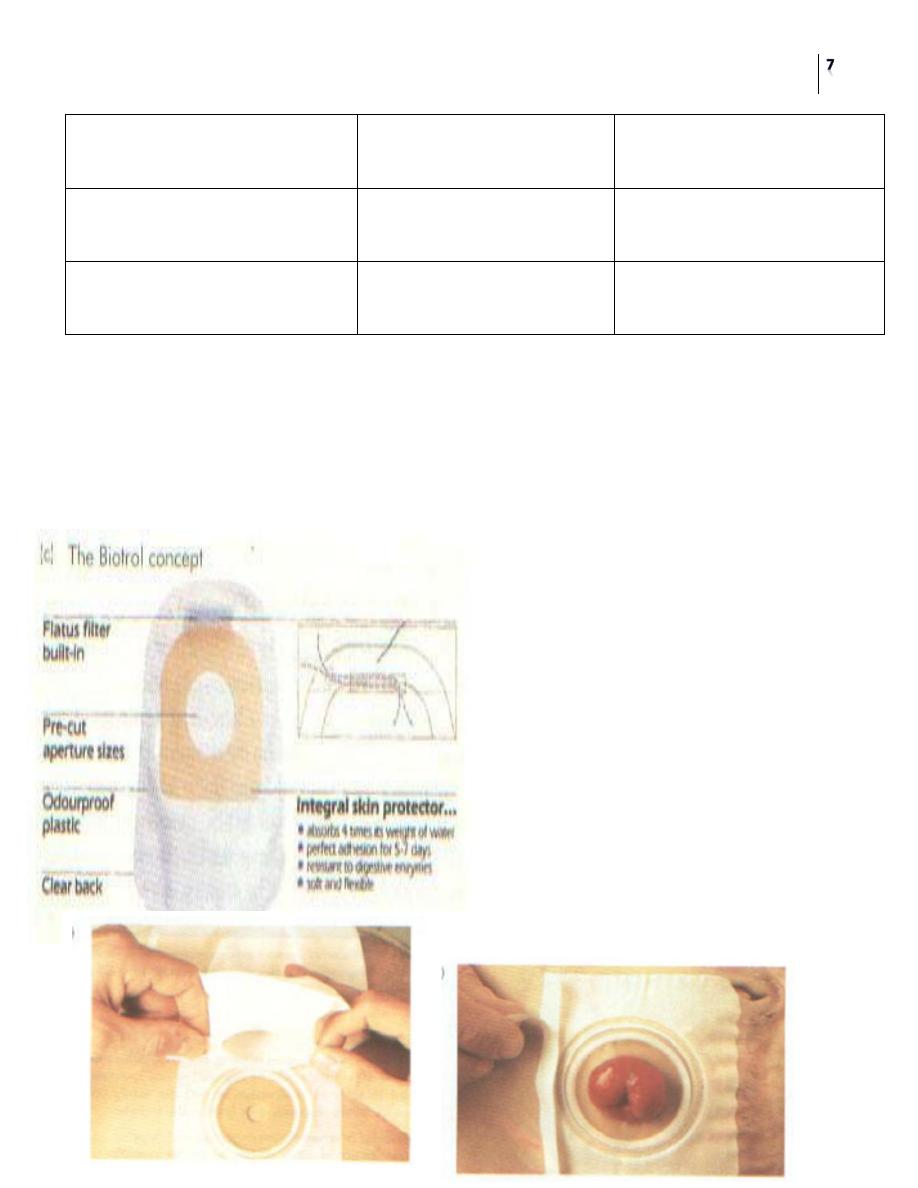
Types of stoma appliances:
1- Two piece (Bag and ring are separate). Advantage: fewer traumas to the stoma
from frequent changing.
2- One piece (Bag and ring are matted). Disadvantage: higher chance of trauma to
the stoma with granulomas and bleeding, excoriation and ulcerations around the
stoma.
Surgery
Intestinal Stomas
Dr. Haussam
Lec. 11
