ENDOCRINOLOGY
GLUCO-CORTICOID PHYSIOLOGY1.CARBOHYDRATES METABOLISM:
Hyperglycaemia (diabetogenic) due to:a.insulin-antagonisim .
b.insulin-supperssion .
2.PROTIN METABOLISM (CATABOLIC-STATE):
a.Osteoporosisb.myopathy
c.skin :
1.vascular-purpura. 2. striae (irreverssible)
d.nitrogen excretion(amino acid uria)
3.LIPID METABOLISM : fat mal distribution
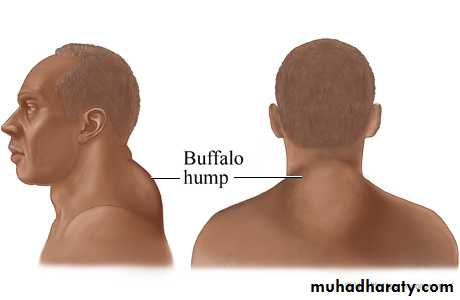
a.Truncal-obesity (lemon on stick appearance) b.buffalo-hamp c.mediastinal-widening4.ANTI-INFLAMMATORY
5.HEMATOLOGIC
6.ELECTROLYTE AND WATER BALANCE7.PSYCOLOGIC
• Mood-alieviation• deprssion
• euphorea
• acute-psychosis
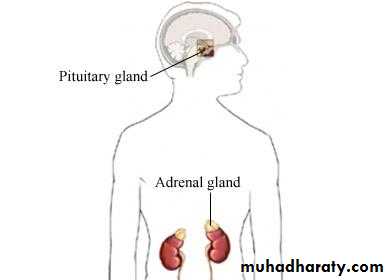
Aldosterone -physiology
Androgen physiology :-secondary sexual characteristics
-virilizing – symptoms in females
-regulated by ACTH so adrenal androgen is decreased by exogenous steroid intake
Lab-evaluation of adreno-cortical-function
A. 1. measuring plasma level of related hormone and comp.2. measuring urinary level and its metabolites.
B. Stimulation tests: used in hormone-def. Dx. 1.tests of glucocorticoid-reserve = A.C.T.H-stimulation test 2.tests of mineralocorticoid-reserve .
C . Suppression test : used in adrenal hormone test of pit-adrenal . Suppressibility 1.screening-test (over-night dexamethasone . Supp. Test ) 2.definitive test .
D. Tests of pit-adrenal reaponsiveness ; 1.insulin- induced hypoglycaemia stim.
2.metyrapone-test . 750 mg orally / 4 hr. over 24hr. 3.C.R.H injection : 1Mg bovine C.R.H / kg. BWT . Will stimulate ACTH secretion normally within 1-3 hr.
Cushing – syndrome
. DEFINITION .
. CAUSES INCLUDE :
• Adrenal-hyperplasia : a. pit. High ACTH tumor . b. non endocrine high ACTH tumors( CA . lung , CA. pancreas)
• Adrenal-neoplasia (25%) : a. adenoma. b. carcinoma(rare)
• Iatrogenic : a. long-term use of cortisol b. long term use of A.C.T.H .
Causes of Cushing's Syndrome
Prolonged or excess exposure to cortisol as a result of:Long-term use of corticosteroid hormones such as cortisone or prednisone
Tumor or abnormality of the adrenal gland, which causes the body to produce excess cortisol
Tumor or abnormality of the pituitary gland, which causes the body to produce excess cortisol (in the case of a Pituitary Adenoma , it is called Cushing's disease)
Rarely, tumors of the lungs, thyroid, kidney, pancreas, or thymus gland produce hormones that trigger the syndrome
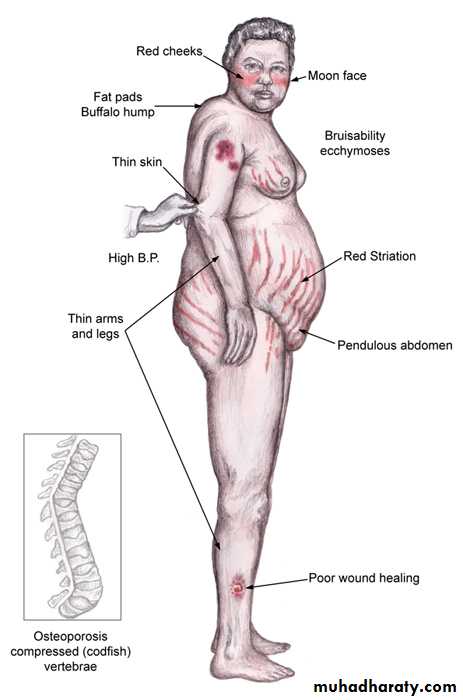
CLINICAL – FEATURES :
These logically fallow the physiological-actions of cortisol and other elevated steroidal – hormones .
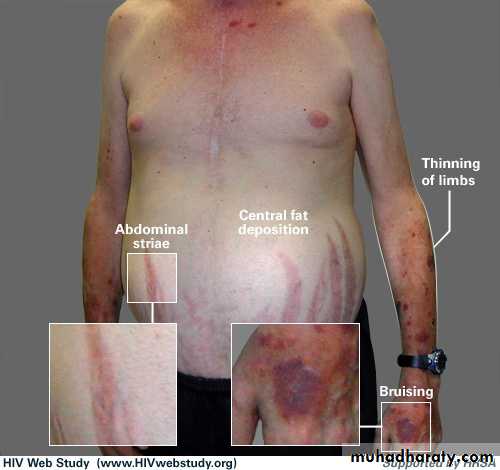
1.Protein-catabolism lead to : M. weakness (myopathy),osteoporosis , skin-bruises , cutaneous-striae ,fatiquability .
2. Impaired carbohydrate metabolism : a. hyperglycaemia b. 20% D.M.
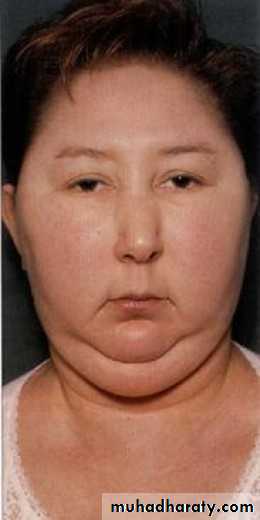
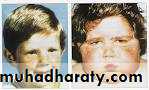
3. Lipid-metabolism : a. buffalo-hump b. truncal-obisity c. mediastinal-widening
4.Electrolyte-disorders : a.hypokalaemia b. hypernatraemia
c.metabolic-alkalosis d.hypercalcaemia
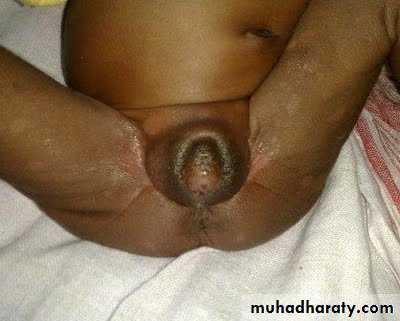
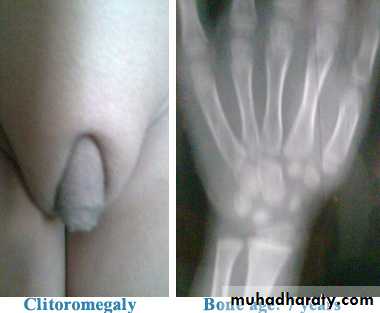
5. In women due to increase androgen (virilization) a. amenorrhoea b. oligomenorrhoea c. hirsutism d. acne-dermatitis e. clitoral- hypertrophy
Symptoms of Cushing's SyndromeAlthough symptoms may vary, common symptoms of Cushing's syndrome are:
Weight gain of the upper body and trunk
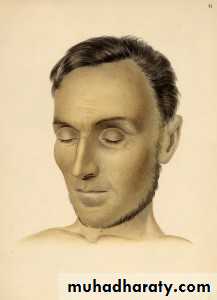
Face shaped like a moon
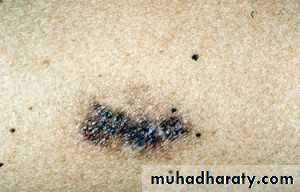
Skin changes:
Darkening of the skin
Purple stretch marks
Easy bruising
Excess hair growth or acne in women
Menstrual disorders, especially infrequent or absent periods
Diminished fertility and libido
High Blood Pressure
Water retention or swelling
High blood sugar or diabetes
Tiredness or fatigue
Personality changes or mood swings
Muscle weakness
Osteoporosis or brittle bones
Skeletal growth retardation in children
Increased thirst
Frequent urination
Psychosis
Low back pain
Diagnosis rests on
• Full-history.• C / E .
• Lab. Evaluation :
a. high-cortisol
b. Dx of the cause 1.a. screening test : over night dexameth. Supp. Test
b. definitive-test : low = = = 2.a. CT- scan for pit. Tumor
b. = = = S.R.G = (adenoma , CA )
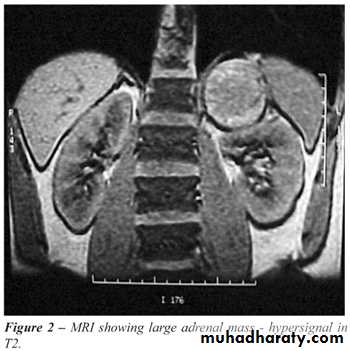
c. M.R.I for = .
Treatment :
• Adrenal-adenoma & CA by surgical removal then hormonal replacement therapy .
• Bilat. Ad. Hyperplasia second. to pit. High ACTH : -pit. Micro. Or macroadenoma (surgical excision & D.X.T ) -Bilat. Med. Adrenalectomy : 1. Metyrapone 2-3 gm / day 2. Mitotane (o , p DDD ) 2-3 gm / day 3. Ketoconazole 600 – 1200 mg / day 4. Aminoglutathimide 1gm / day All inhibit steroidogensis . -Bilat. Surg. Adrenalectomy then hormonal replace.
ALDOSTERONISM
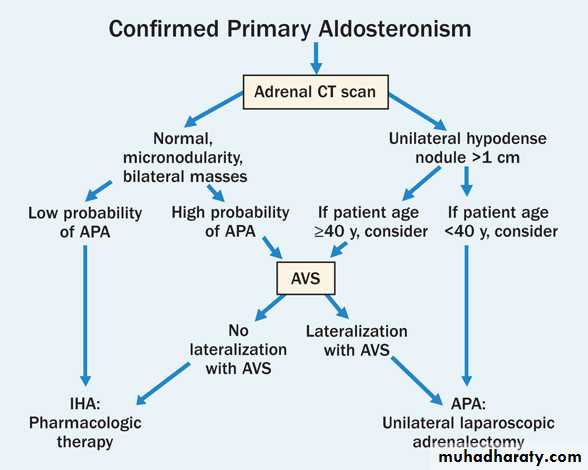
• Primary a. adrenal hyperplasia b. adrenal tumor• Secondary (extra-adrenal) : a. C.H.F. b. nephrotic-syndrome c. liver-cirrhosis Conn’s – syndrome : unilat. Ad. Adenoma 1% of hypertensive-states C/F & Dx : . Headache high B.P. . Fatique & weak. . Polyuria & polydipsia . . Hypokalaemia . No-oedema (characteristic) . . E.C.G. L.V.H. , u-wave Rx : . Operative . Conservative : a. salt decrease b. aldactone
Phaeochromocytomas
.Definition : Adrenal-tumor that produce , store , secrete & release catech. To the circulation but it may be extra-adrenal in origin . It ‘s tumor of 10% i.e .10% bilat. .10% extra-adrenal . .10% malignant . .10% familial as part of a. M.E.N. 11 b. M.E.N. 111 Diagnosis : it rests on 1. C / F . Hypertension . Unexplained hypotension & shock during surgery & stress . Paroxysms / Crises in 50% of cases that include :head ache , sweating , palpitation
apprehension , chest-pain , abd. Pain
nausea & vomiting palor / flushings
hypertension
these crises are ppt. By a. stress b. drugs . opiates . histamine . saralasin . ACTH . Aldomete . T.C.As . High B.M.R & weight-loss . .Cardiac-manifest . Includes
1. sinus tachy. Brady cardias .
2. SVT , V.P.Bs .
3. R & L B.B.B.
4. L.V strain
5. I.H.D Angina & M.I
6. Cardiomyopathy = C.H.F.
. Carbohydrate metab. = 50% I.G.T.T. , D.M ?
2. Lab. Evaluation :
. Pharmacologic-test using alpha-blocker then
beta-blocker .
. Biochemical – test .
. Anatomical diagnosis by CT scan or MRI abd.
. Clonidin-suppression-test .
Mangement : is by surgical . Pre-operative Rx. Is alpha blocker- phenoxybenzamine 10 mg / 12 hr. /2 w. Decreasing BP with Na-nitroprusside
Beta blocker- inderal 10 mg x3
Prognosis :
- M.R = 2-3%
- spontaneous-remission may occur .
- 5 year survival in 95%
- recurrence-rate is =< 10% .
ADRENAL-HYPOFUNCTION
ADDISON’S DISEASE.Definition
.Aetiology :
-Primary : 1. Anatomic-destruction of adrenal gland(acute & chronic) :
. Idiopathic (auto-immune) atrophy .
. Surgical-removal .
. Infection : T.B , Fungal , Viral (C.M.V &
H.I.V) .
. Haemorrhage .
. Invasion : CA .
11. Metabolic failure in hormone-production :
- C.A.H.
- Enzyme-inhibitors : metyrapone , O,P DDD
Ketokonazole .
- drugs : Ref. , phenytoin , opiate . ACTH-Ab.
secondary :
. Hypo-pituitatism. Pit. Supperssion :
- exogenous-steroid
- endogenous-steroid
. No mycocutaneous hyper pigmentation
. ACTH & aldosterone are normal or low
. Reversible after treatment
Diagnosis : rests on .
-Hx.
- C / E
- Lab : ACTH normal or high .
cortisol zero to low .
ACTH stimulation test .
diagnostic flow chart: S&S . Weaknes, hypotention, wt.los
+ hyper pigmentation
C / F : . GIT screening test : plasma cortisol 30-60mint.
. CVS after 250 mcg synacthin im or iv
. CNS subnormal-response : possible adrenal insufficiency
. Dermatologic . Plasma ACTH/Aldos. After 30 min.
. Haematologic . 250 mcg synacthin im or iv
. Electrolytes . ACTH low-nomal ACTH
subnormal aldoserone normal aldoserne increment
primary adrenal insufficien normal or 2nd adrenal insufficiency
TREATMENT :
a. Hormonal-replacement therapy. Cortisol 2/3 + 1/3 .
. Fludrocortisone 0.1 mg / day .
b. Supportive-therapy .
c. Advices .
In an emergency, anyone with Addison’s disease can experience symptoms of extreme weakness, a serious drop in blood pressure and mental confusion. This means they need extra steroid medication immediately, and may need an emergency injection.
As a general rule, an Addisonian should give themselves an emergency injection of 100mg hydrocortisone sodium (Efcortesol or Solu-Cortef) if they vomit more than once.
The causes of an Addisonian crisis:
Severe physical shock, e.g. a car accident
Severe infection, e.g. flu with a high temperature
Severe dehydration, e.g. stomach bug with vomiting
The symptoms of an Addisonian crisis:
Extreme weakness
Mental confusion
Extreme drowsiness, in advanced cases slipping towards a coma
Pronounced dizziness
Nausea and/or vomiting
Severe headache
Abnormal heart rate – either too fast or too slow
Abnormally low blood pressure
Feeling extremely cold
Possibly a fever
Possibly abdominal tenderness
Treatment of crisis:
1. sod.chloride iv
2. 5% glucose saline + 100mg hydrocortisone 6hrs
3. Dopamine as adjunct in extreme hypotension
4. AB when sepsis is present
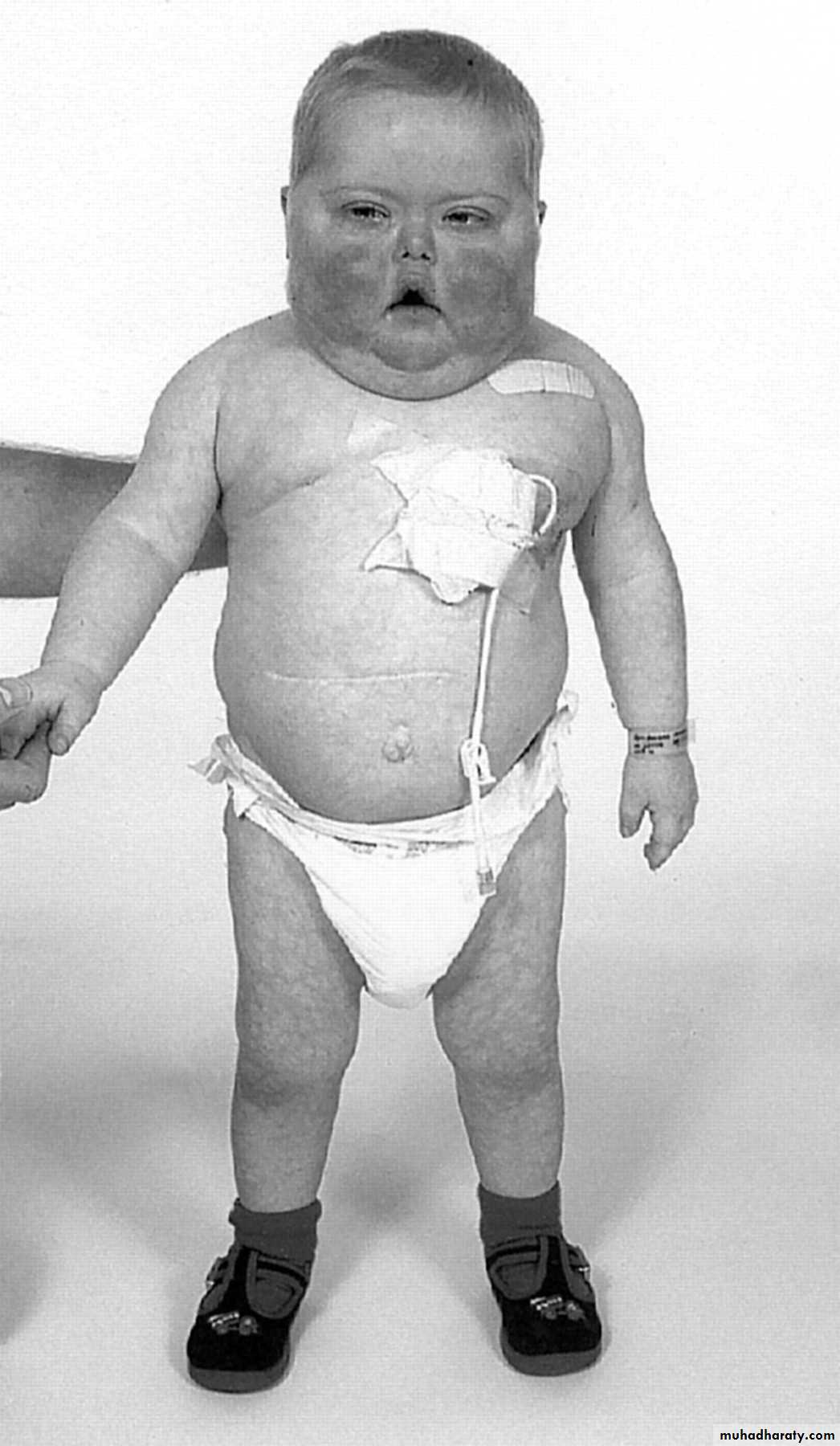
C.A.H
Though there is adrenal hyperplasia due to AR mutationThere is adrenal enzymatic deficiency causing
low cortisol and high ACTH that lead to high adrenal androgen and low LH/FSH
It is the most common adrenal disease in infancy, childhood and in female adult life.
CAH is secondary to one or combination of several defects in steroid- synthesis
C21 hydroxylaze (HLA-B of chromosome6 ) is the most common and constitute 95% of CAH increase virilisation in females at birth with ambiguous external- genitalia
In male
macrogenitalia
• Isosexual-precocity ( adolescent – life )
• Accelerated growth truncal development ( short stature )
• Bone age more than chronological age due to early epiphyseal closure
therfore 1. androgen excess
2. cortisol low
3. aldosterone low in one 3rd of cases diagnosis :
In female infant : is one of failure to thrive
pseudohermofroditism in children .
clitoral-hyper trophy
fusion of labia either partial or complete
urogenital sinus (some times )