1
Skin Graft
Lec2 Prof. Saadallah M. Al-Zacko, FRCS (Ed.)
Skin graft
Definition: is a segment of epidermis and dermis that is removed from its blood
supply at donor site transferred into a recipient site.
Types:
1-Origin:
Autograft , allo-(homo)-, xeno(hetero).
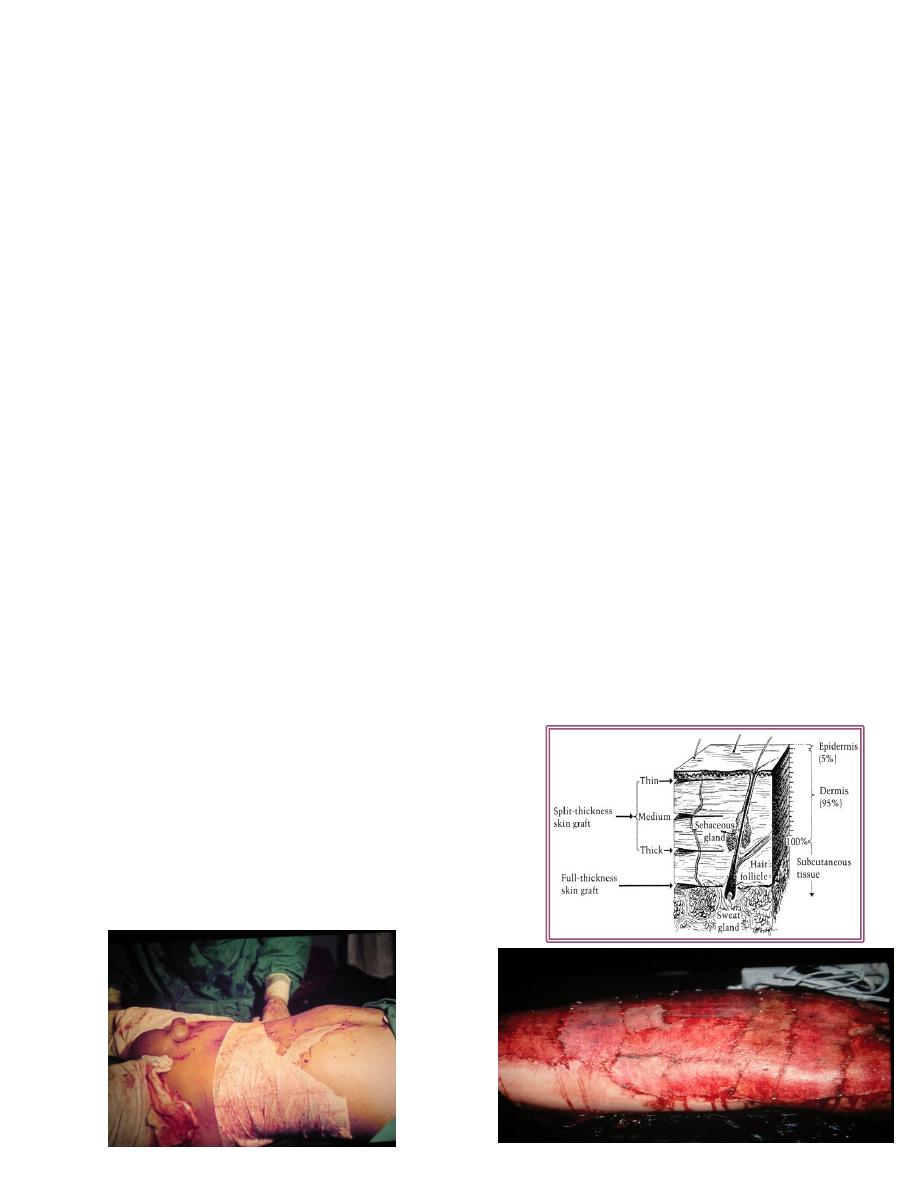
2-Thickness:
Split (Thiersh ): thin ,intermediate, thick.
Full thickness (Wolfe).
Split skin graft (SSG)
Most useful and popular.
Contains epidermis and part of dermis.
Contract more postoperatively.
Survives more.
Full thickness graft:
Epidermis and entire dermis.
Normal color, texture, hair.
Not contract, less survive.

2
Donor site:
SSG :thigh buttock, abd. wall arm.
FSG: pre-, post-auricular, supraclav, upper eyelid.
Success of skin graft:
Vascular recipient bed.
Proper contact of graft with proper tension.
No fluid beneath.
No movement.
Free from infection.
Immunological.
Indications of skin graft
Skin loss: post traumatic, post surgical, result of pathology (venous ulcer).
Mucosa loss: leukoplakia, reconstruction of vagina.
Contraindications:
Avascular recipient bed.
Infection.
3
Flaps
“ part of tissue which retains its vascular attachment to body, transplanted to
reconstruct a defect.”
The flap donor site closed by suture or SSG.
Classification
1. Content:
A. Skin.
B. Fascio-cutaneous.
C. Myo-cutaneous.
D. Muscle.
E. Osteo-myo-cutaneous.
2. Site:
A. Local : where donor area near recipient site.
Rotation.
Transposition.
Advancement.
B. Distant flap :where donor area at a distance from recipient site.
C. Free flap: by using microsurgery.
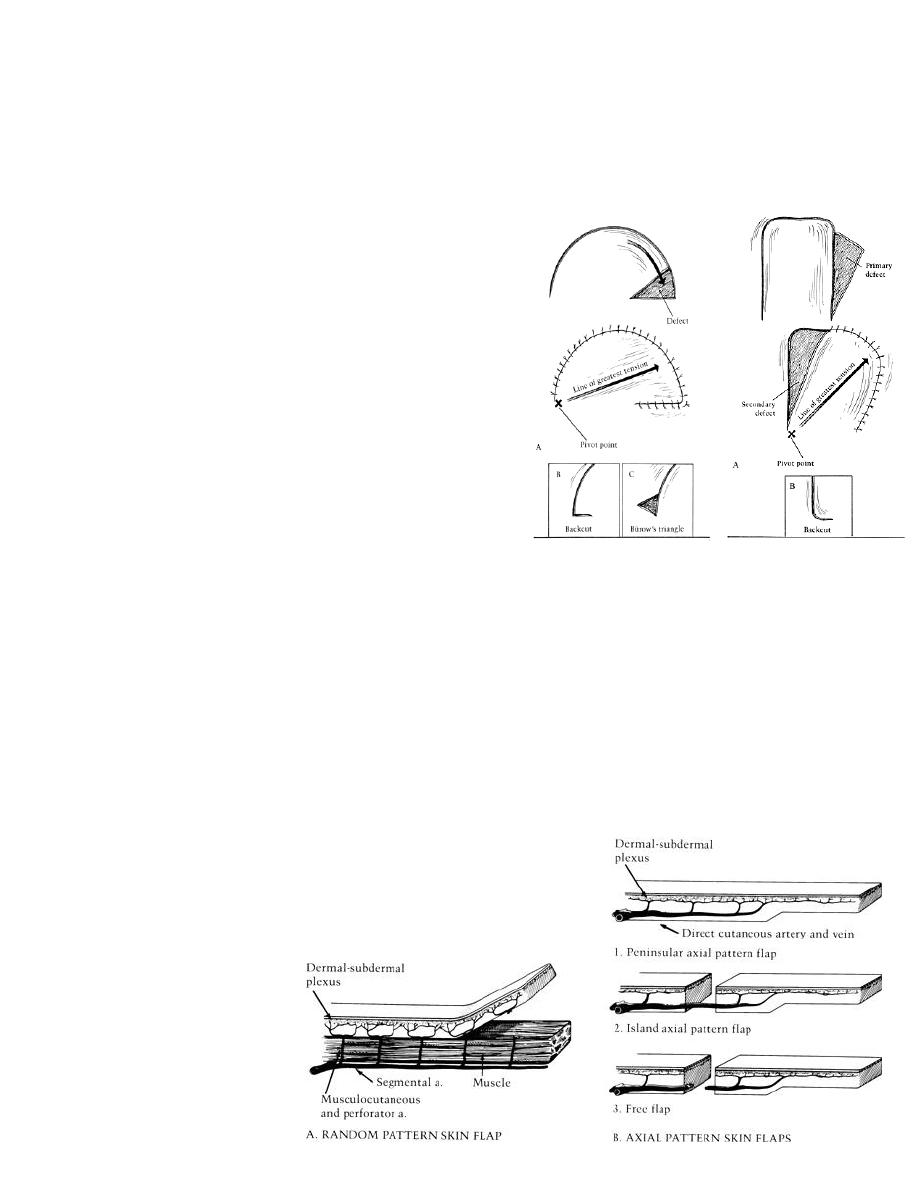
3. Vascular pattern ( skin flaps):
A. Axial pattern: longer, easier ,safer.
B. Random pattern.
Rotation
Transposition

4
Indications of flaps
1. Cover recipient bed with poor vascular supply.
2. Reconstruction full thickness eyelids, lip, nose, cheeck .
3. Padding bony prominences.
4. When operation through the wound at later date.
5. Muscle flap provides a functional unit.
6. Provide sensation.
Burns
Coagulative necrosis of tissue due to heat.
Causes:
1. Flame 45%.
2. Hot liquid (scald)30%
3. Hot object.
4. Electric.
5. Chemical.
6. Others : semi liquid, steam, UVL,XR.
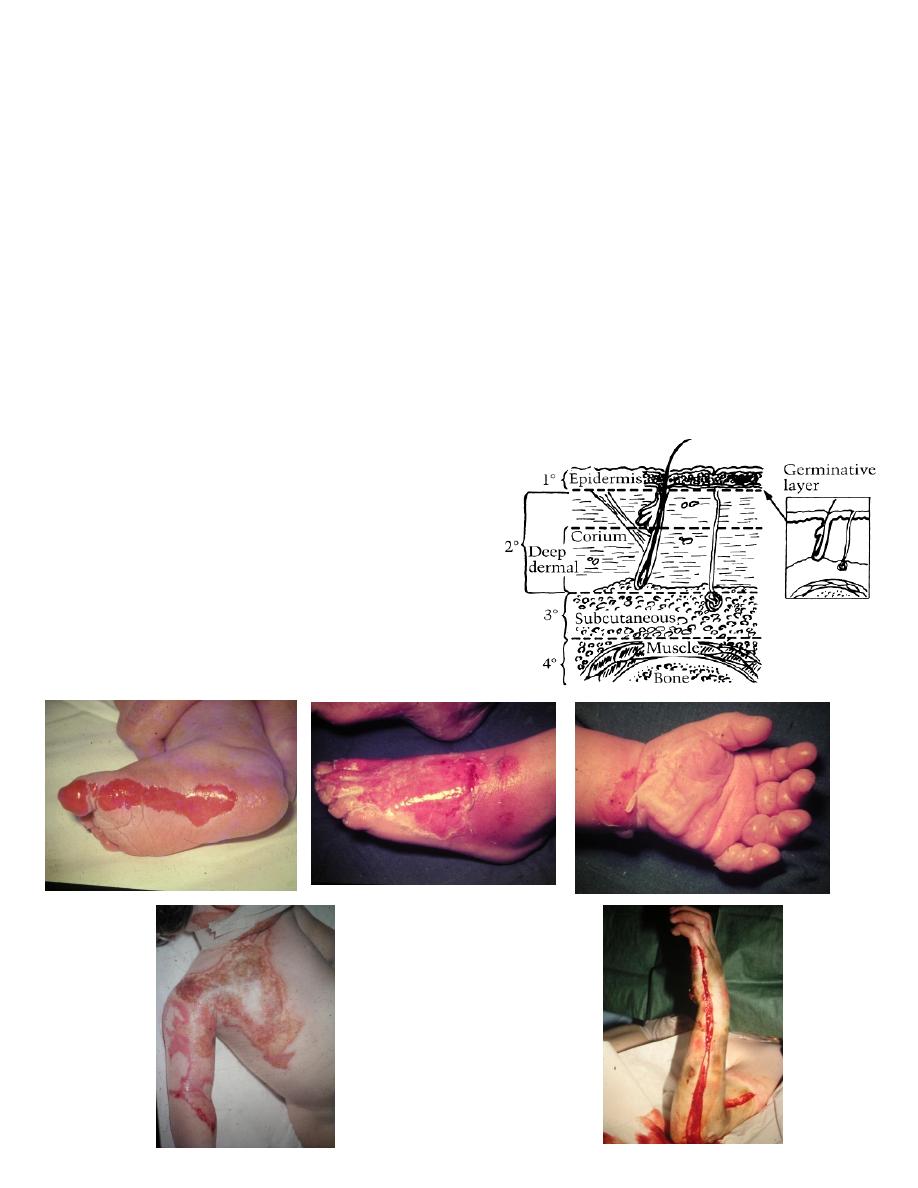
Depth of burn: 4 degrees:
1. First : epidermis.
A. Erythema, edema, scaling.
B. Analgesic, oint.
2. Second:
A. Superficial 2
nd
.
Epidermis and superf. dermis .
Blisters painful to light touch red blanch positive.
Dressing – 1w.
5
A. Deep 2
nd
( deep dermal )
Epidermis and most dermis.
Painful to pinprik, milky white blanch –ve.
Early excision + grafting.
3. Third:
1. Epidermis and whole dermis.
2. White, brown or black.
3. Painless thrombosed V.S.
4. Early excision and grafting or dressing and late graft.
4. Fourth : muscle and bone.
6
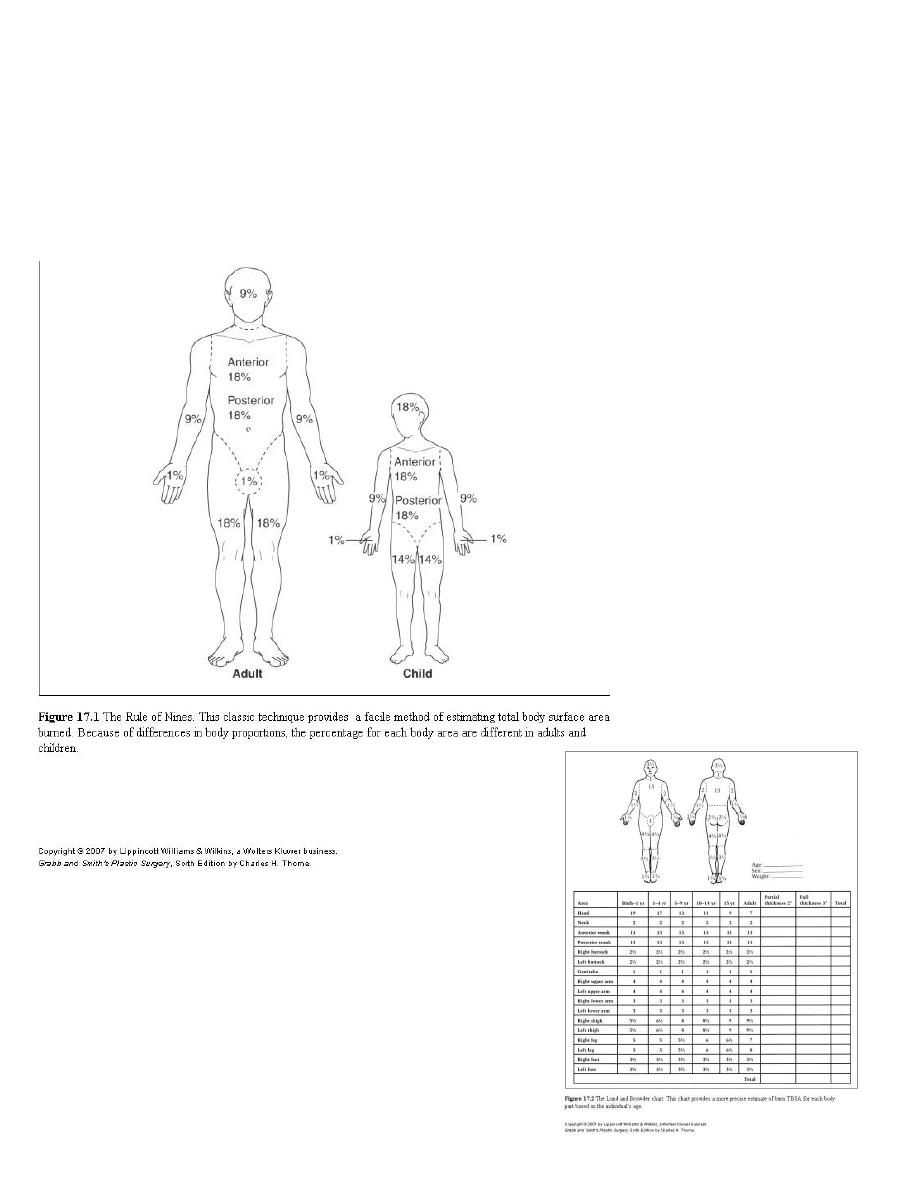
Extent :
1. Rule of nines.
2. Lund and Browder chart.
3. Palm method (1%).

7
Management of burns
1. ABC:
A. Airway clear.
B. Breathing humidified O2 , respirator.
C. Circulation cannula :
Blood sample (Hb., PCV, urea, electrolytes ).
Sedation.
IV Fluids.
2. Assessment :
A. History
B. Exam:
General
Local (depth, %).
2. Sedation: (i.v)
Morphine , pethidine, + largactil.
4. Iv :
A. Given in :
10% + in children.
15% + in adults.
B. ½ amount in 8 h,1/4 in 8h, 1/4 in 8h.
5. Investigations: Hb, PCV, bl. urea, s.elect. , blood group.
6. Urine:
A. Foly’s catheter.
B. Hourly output (0.5-1 ml/kg/h)
8
7. Tetanus toxoid 0.5 ml
or 250 mg human immunoglobulin + toxoid.
8. Antibiotic : pencilline 5 days.
9. Nothing by mouth, N.G. tube
10. Wound care:
A. Clean, ointment (Flamazine).
B. Dressing ( open, closed)
C. Operation (SSG ,flaps)
Complications
1. Shock: neurogenic, hypovolemic, septic
2. Infection: wound, resp., urinary, septicemia.
3. Renal failure.
4. Curling ulcer.
5. Deformity, scars, keloid.
6. Metabolic.
7. Psychological.
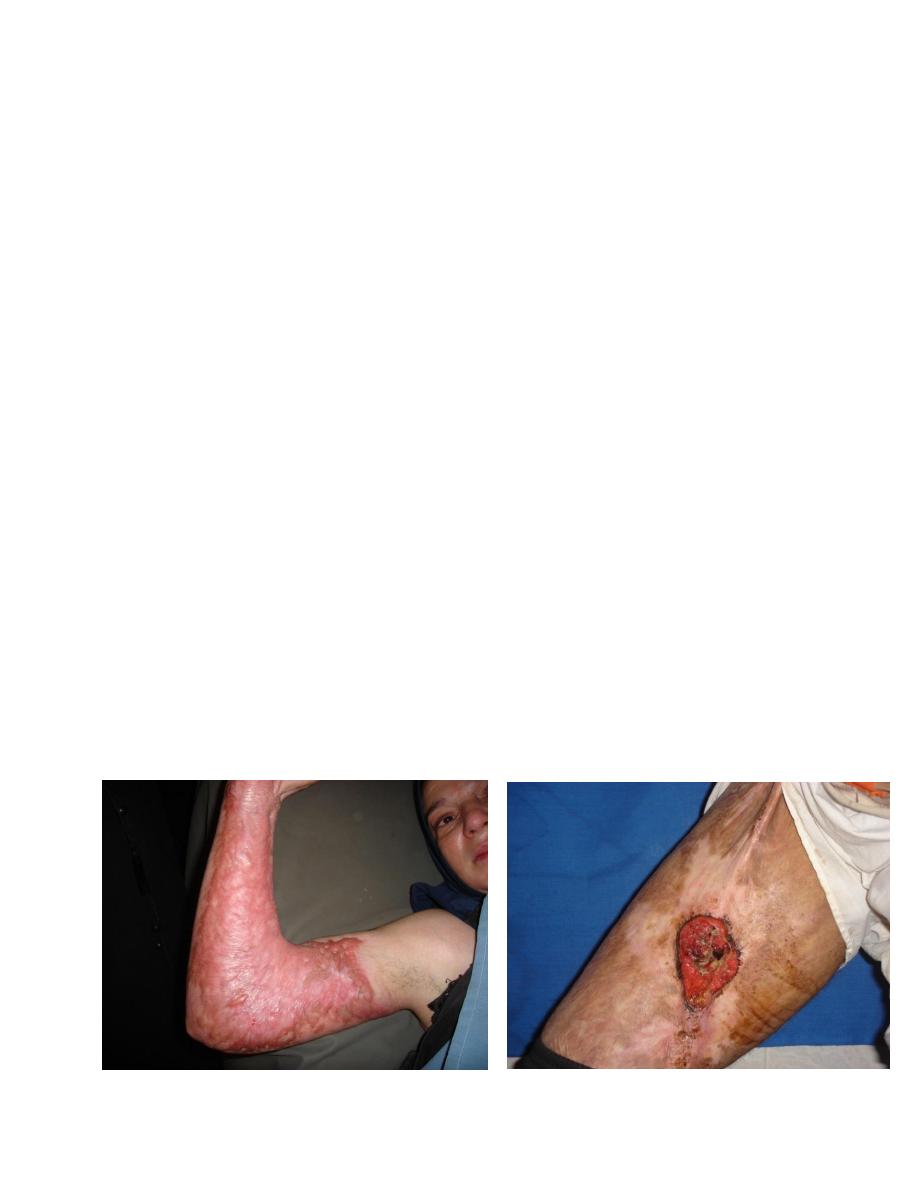
8. Marjolin (sq. cell carcinoma).
Sq.c.ca.(Marjolin ulcer)
Joint contracture



