LIVER DISEASES
AnatomyPhysiology
Bilirubin metabolism:• Cholic acid
• Chenodeoxycholic acid
Investigations:
BilirubinEnzymes- ALT (SGPT)
AST(SGOT)
ALP
ᴕ-gt
5’-nucleotidase
enzyme combinations
Plasma proteins Immunoglobulins
Coagulation factors
α-feto protein
copper ceruloplasmin
ferretin Fe & IBC
Serology- ANA ALKMA
ASMA SLP-PA AMA
Imaging:
• U/S• Radiography
• CT + MRI + MRCP
• Radionucleotide imaging – TC99
• ERCP
• Cholangiography
• Arteriography
• Venography
• -Portal venography
• (Portal pressure = free hepatic vein pressure- wedged hepatic vein pressure = 3-5 mmHg)
• Endoscopy
• Ascitic fluid studies
• Liver biopsy & FNA
• Laproscopy
Jaundice
• > 3 mg/dl
• 1. Hemolytic• 2. Hepatocellular
• 3. Obstructive [Cholestatic]
• - Intrahepatic- canalicular (hepatocyte)
• - Biliary Obstruction
- Extra hepatic
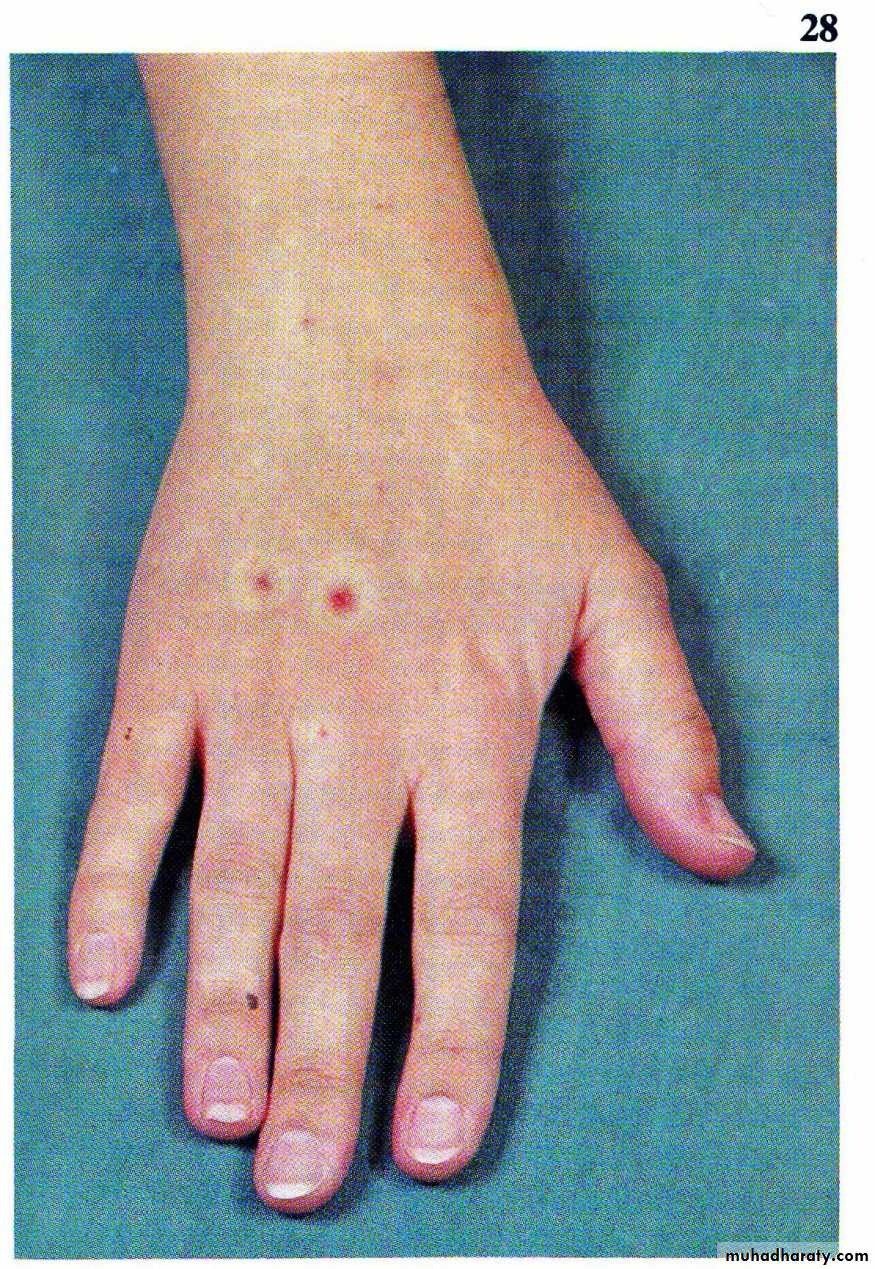
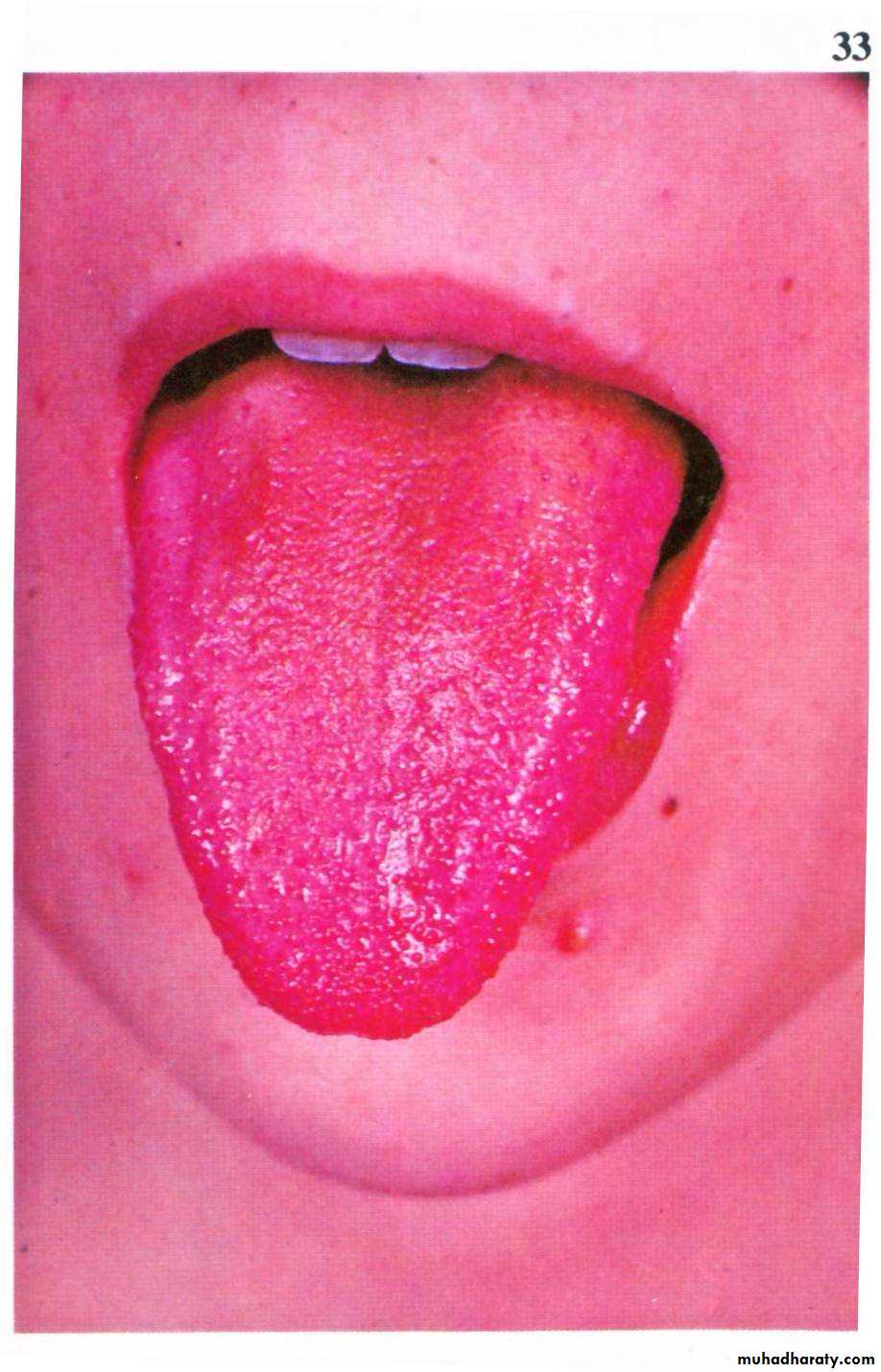
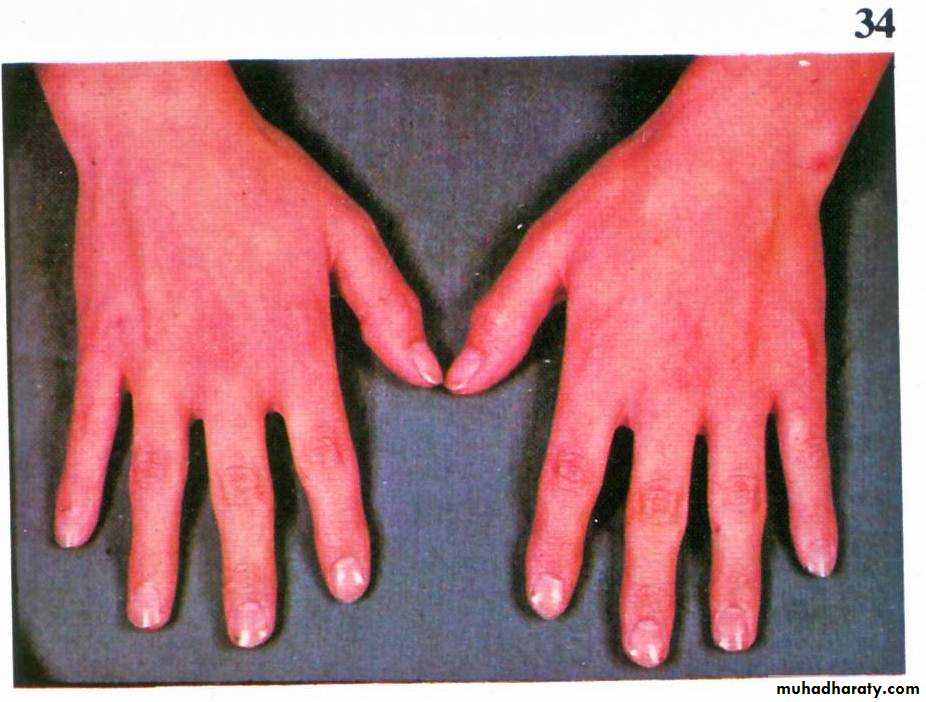
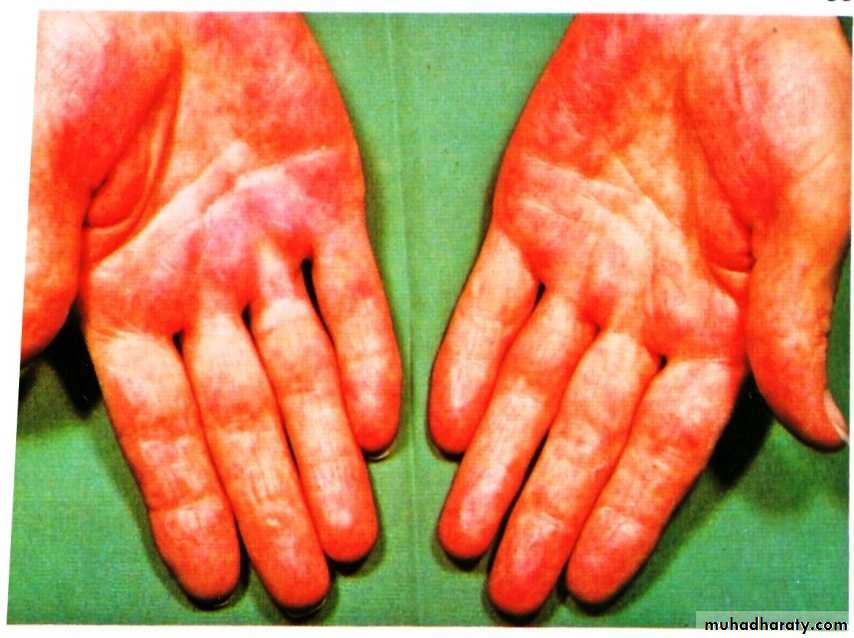
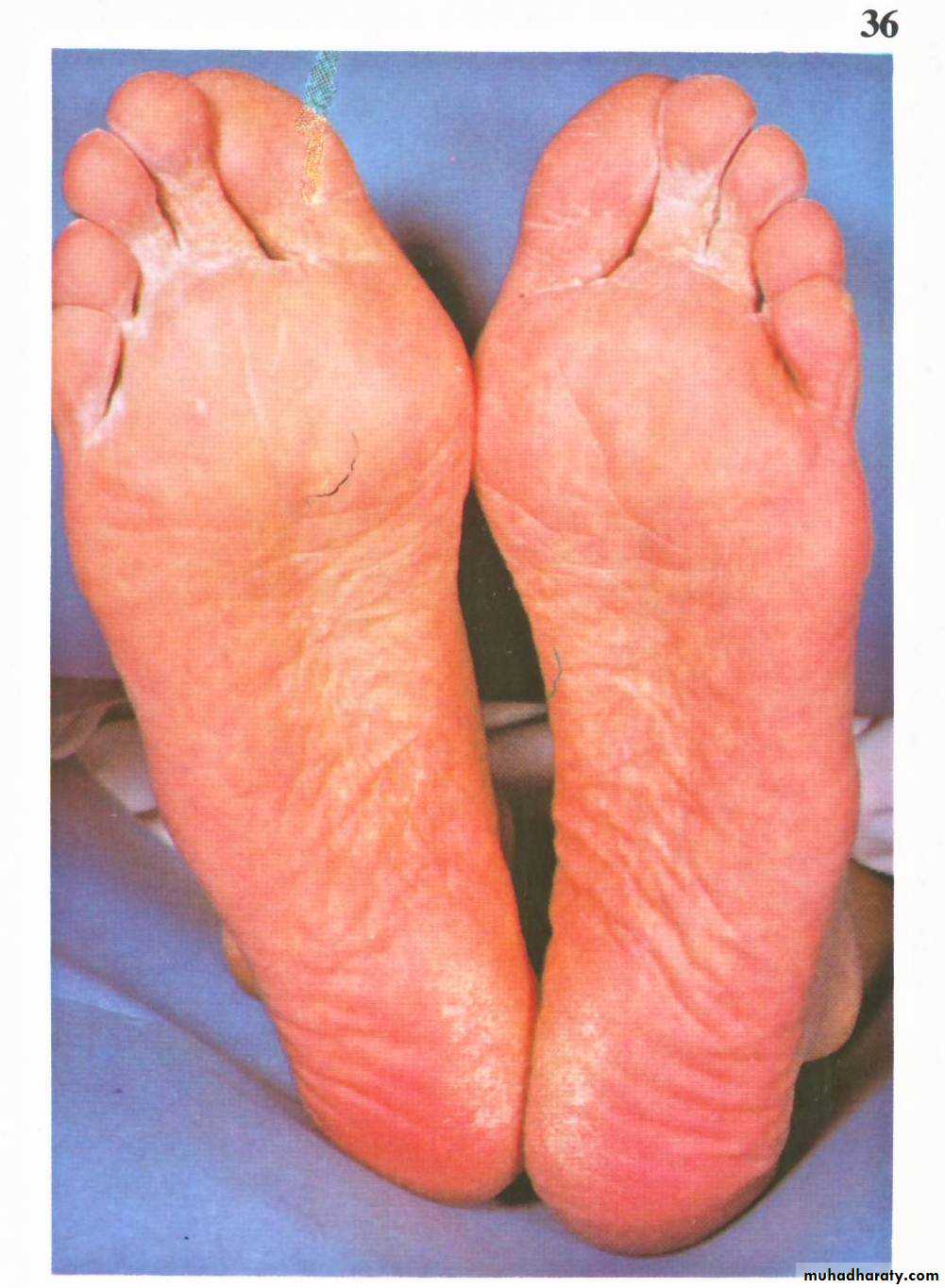
Clinical features
•
•
• Cholestasis of pregnancy
Benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis
Congenital Hperbilirubinemia
Unconjugated- Gilbert’s Syndrome (Dominant)Criggler-Najar- (I) recessive
(II) dominant
Conjugated- Dubin-Johnson (recessive)
Rotor (dominant)
Portal hypertension
Causes: (I) Pre-hepatic
- Portal vein obstructions 50% ?
- splenic vein thrombosis
- massive splenomegaly ( Banti’s Syndrome)
(II) Hepatic
- Pre sinosoidal
- Sinusoidal
• Cirrhosis
• Myoproliferative diseases
• Drugs
• Sarcoid
- Post-sinosoidal
• (III) Post-hepatic
- Budd-Chiari
- Cardiac causes
Clinical features:
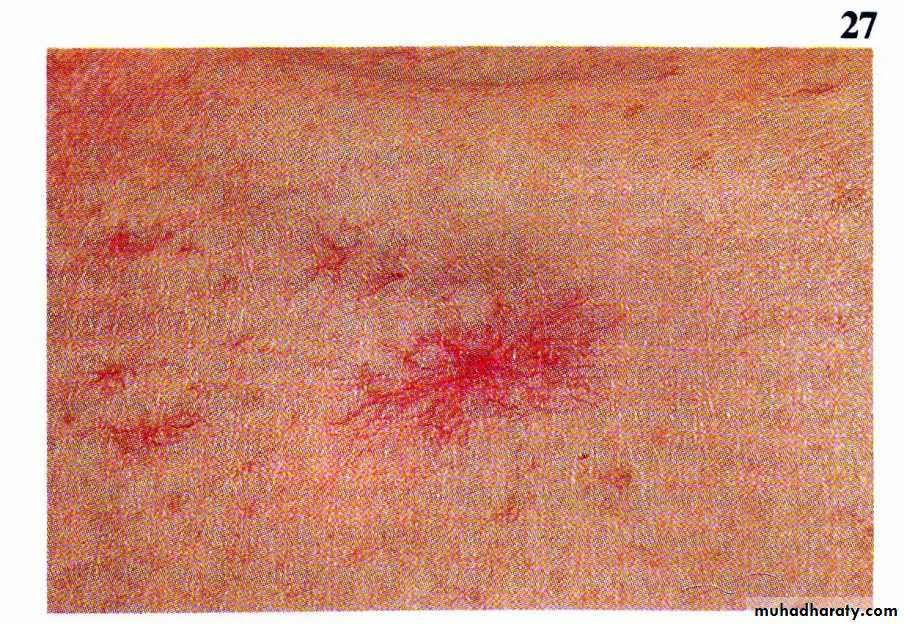
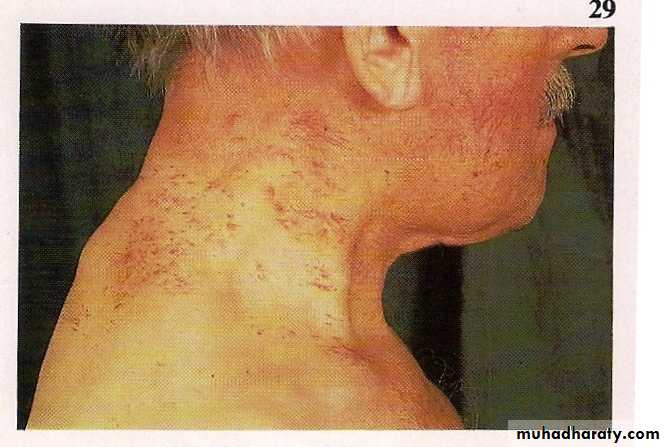
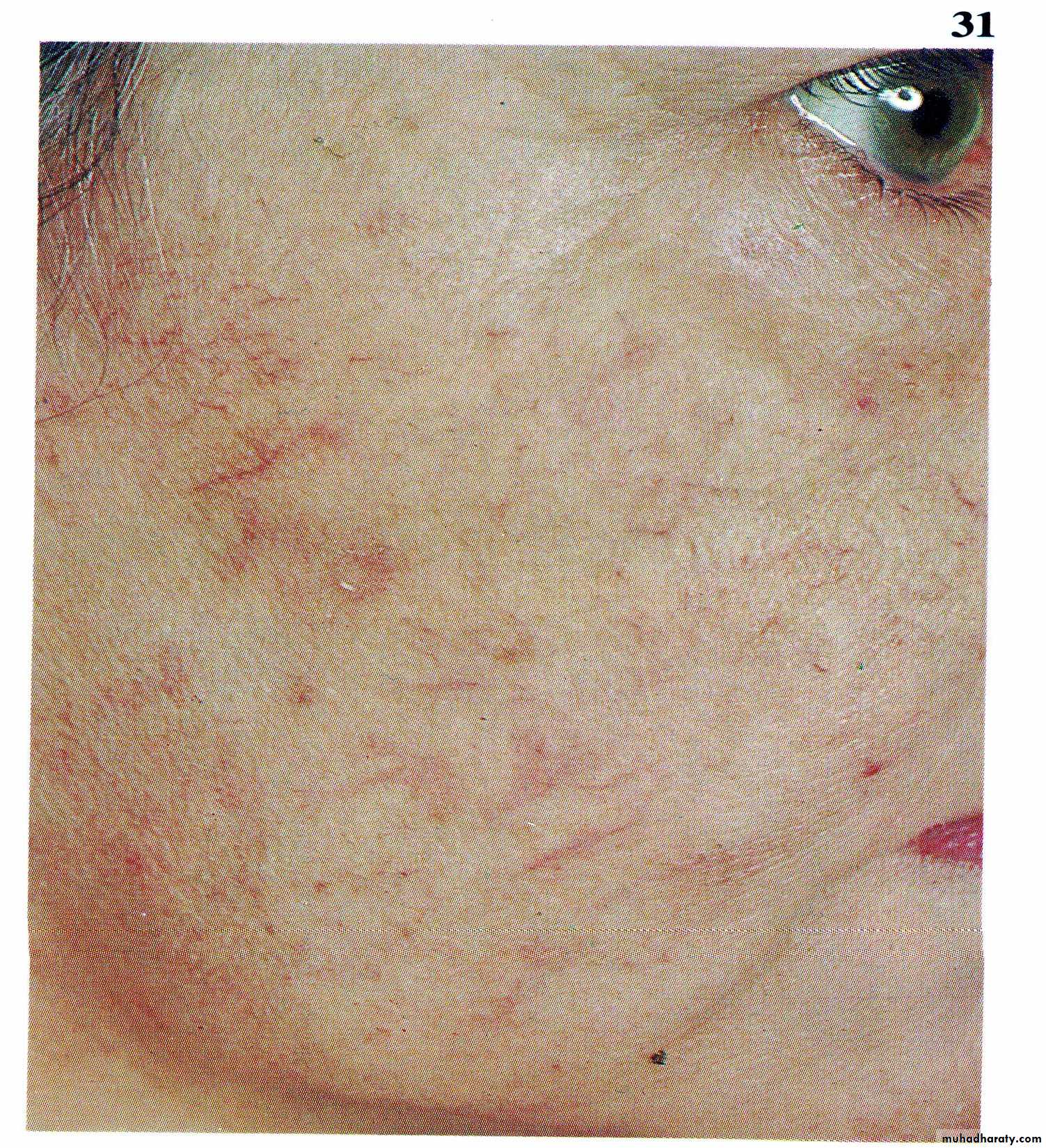
- Splenomegally- Hypersplenisim
- Collateral vessels
- Fetor hepaticus
Complications:
- Bleeding
- Hypersplenisim
Contributary factor in:
AscitesEncephalopathy
Hepato renal syndrome
Hepatopulmonary syndrome
VARICEAL BLEEDING
RecurrentRisk factors
Other sites
Management:- Supportive
- Confirm
1. reduction of portal pressure
2. Local measures
3. Prevention of recurrent bleeding
Primary prophylaxis:
Ascites
• Increased hydrostatic pressure• Decreased oncotic pressure
• Increased portal pressure
• Inflammation
• Malignancy
Causes:
Investigations:Ascites in chronic liver disease
• Poor prognostic sign• Commonly with leg edema
• 10% right pleural effusion
• Ascites in CLD doesn’t exclude other causes (HCCA or PUTH…)
• Exudative ascites – infection, malignancy, H-V obstruction.
Management:
• Decrease Na & water by restriction
• Increase urine output
• Removal of ascetic fluid if necessary
• TIPSS
Spontanous bacterial peritonitis
RecurrentHepatorenal syndrome
Hepatopulmonary syndrome
Hepatic encephalopathy• Definition
• Causes- Liver cell failure
- P-S shunting
• Features
• Precipitating factors
• Differential diagnosis
• Management
Fulminant hepatic failure
- Definition – Acute - absence of CLD
- Causes
- Pathology
- Presentation
- Investigations
- Complications
- Management
- Prognosis
Acute Hepatitis
• Pathology• Causes: - Viral - Non-viral infections
- Drug - Immune Hepatitis
- Post-viral - Metabolic- Wilson
• - α1-antitrypsin deficiency
• - Pregnancy
• -Ischemic- Shock
• - Tamponade- severe heart failures
• - Budd-Chiari syndrome
• Clinical features
• Frequently anicteric or asymptomatic
• Investigations - Management
• Complications - Prognosis
HEPATITIS A VIRUS
• Incubation 2-4 wks
• Diagnosis
• No chronic carrier• Vaccine
• Immune serum globulinHEPATITIS E VIRUS
• Incubation 4-8 wks• Water borne epidemics – fecal -oral
• High mortality in pregnant woman
HEPATITIS B VIRUS
• Incubation 4-20 wks
• Not cultured
• Only man-man
• Carrier
• Vaccine
• hyperimmune serum globilin
• HBsAg - HBe Ag
• Anti HBs Ab - Anti-HBeAb
• Anti- HBcAb IgM
• IgG
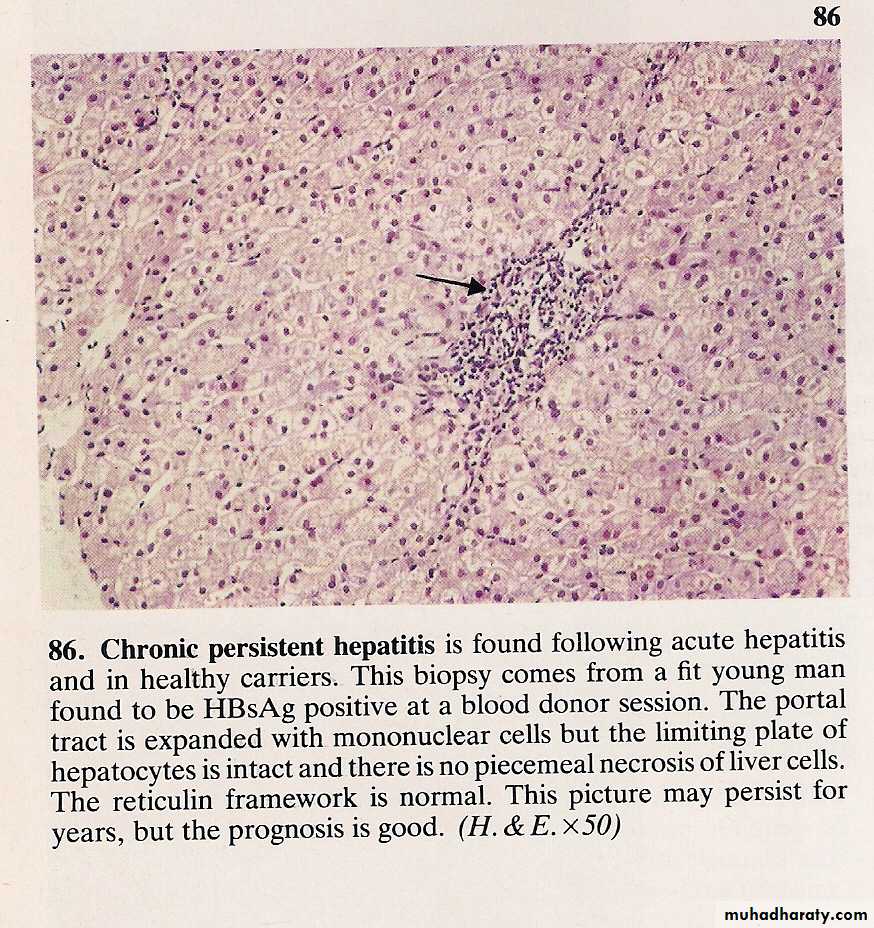
Chronic HBV infection
Activity Increased enzymes
HBsAg Anti-HBcAb
HBeAg
Anti HBeAb
Viral load (PCR)
HD virus
Incomplete RNAIncubation 6-8 wks
HC virus
• Incubate 2-26 wks• Chronic carrier > 50%
• Anti-HCV Ab ?• PCR HCV-RNA in blood
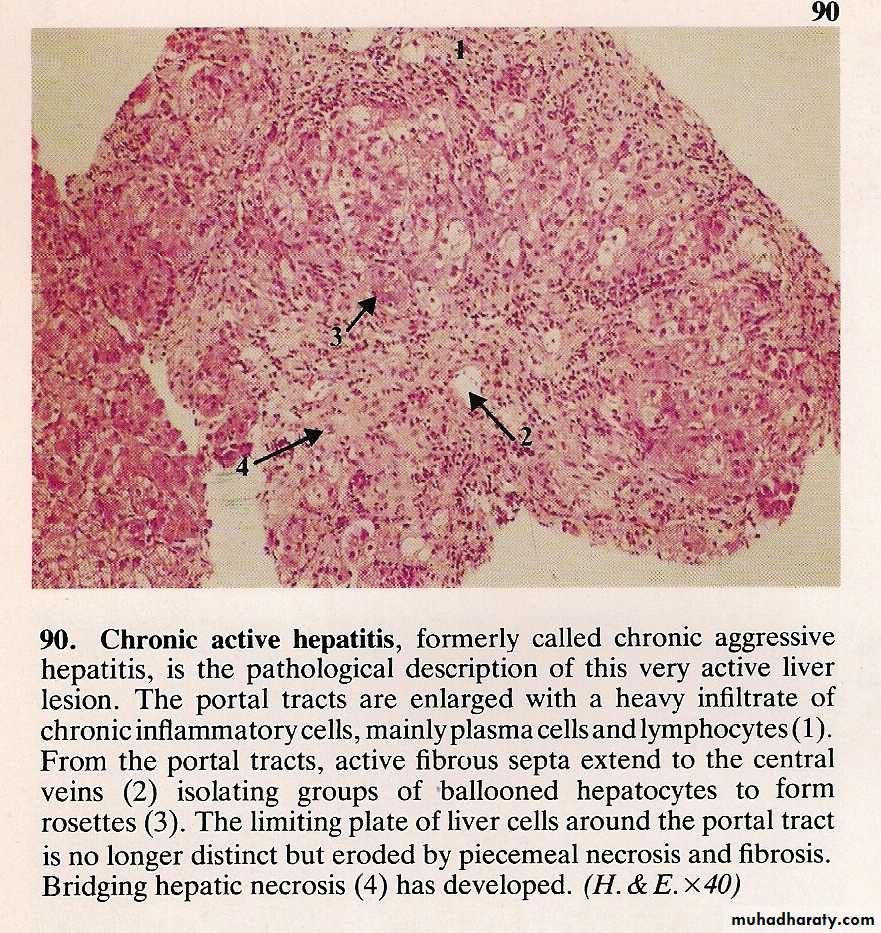
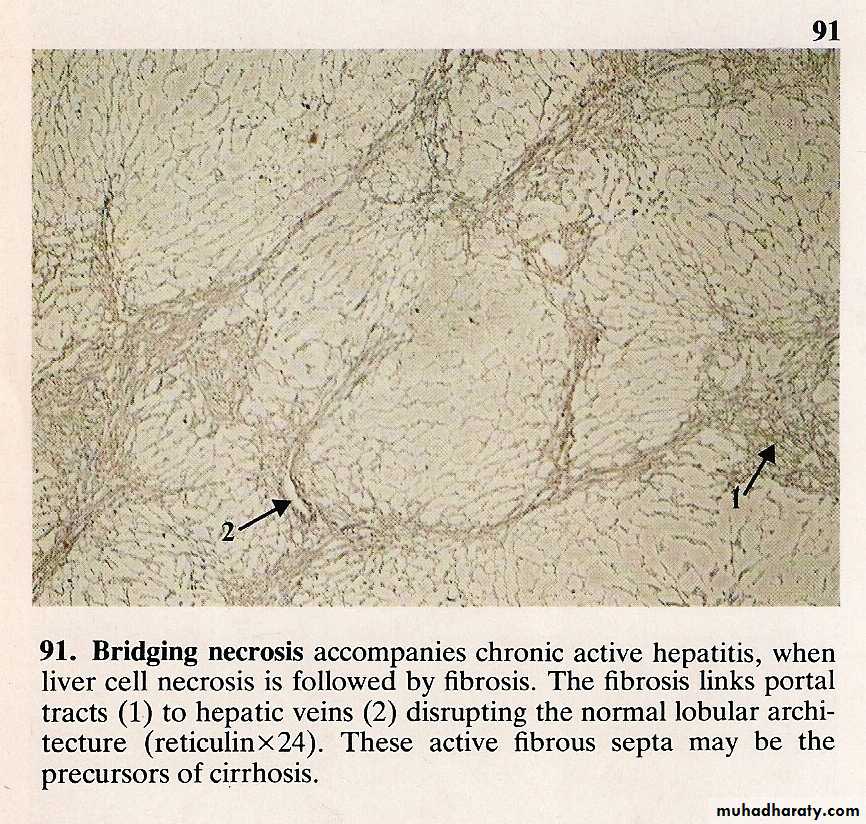
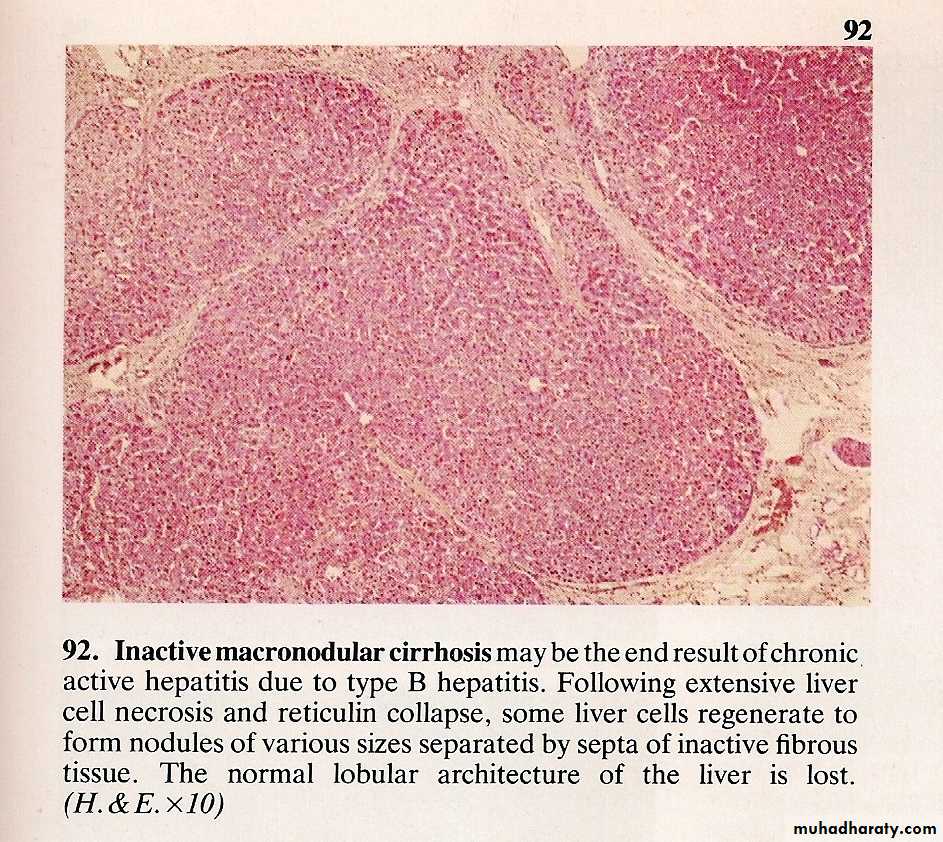
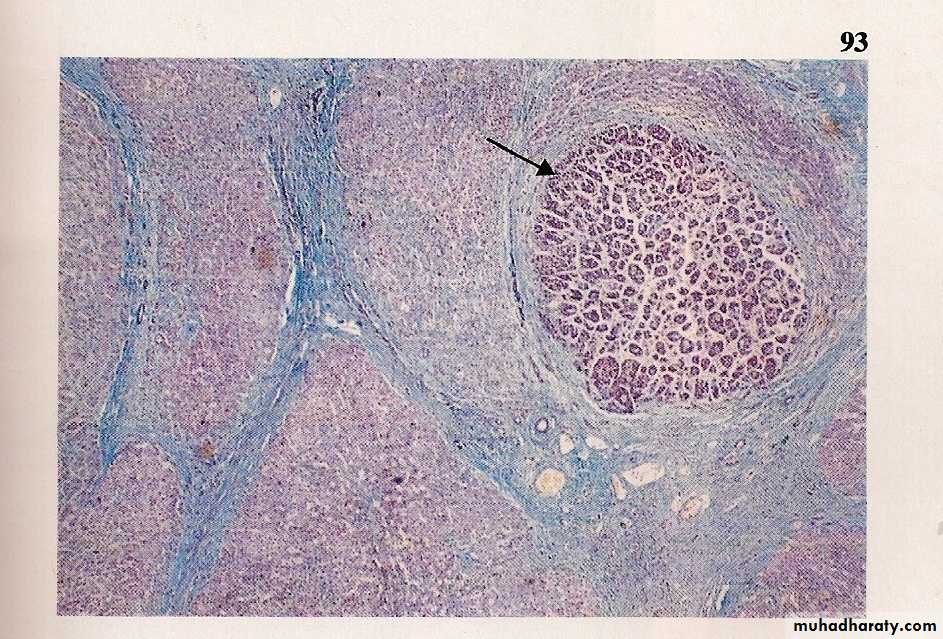
CHRONIC HEPATIC + CIRRHOSIS
• 6/12• Causes
• Viral
• Drugs and alcohol
• Metabolic
• Wilson
• Hemochromatosis
• α1 anti-trypsin deficiency
• Immune
• Nutritional (intestinal bypass)
• Biliary obstruction-
• Primary biliary cirrhosis
• Sclerosing cholangitis
• Secondary biliary cirrhosis
• Hepatic congestion-
• Budd-Chieri
• Veno-occlusive disease
• Cardiac failure
• NAFLD
• Cryptogenic
• Symptomatology
• Assessment & investigations
• Is there active liver disease ?•
• Liver functions
•
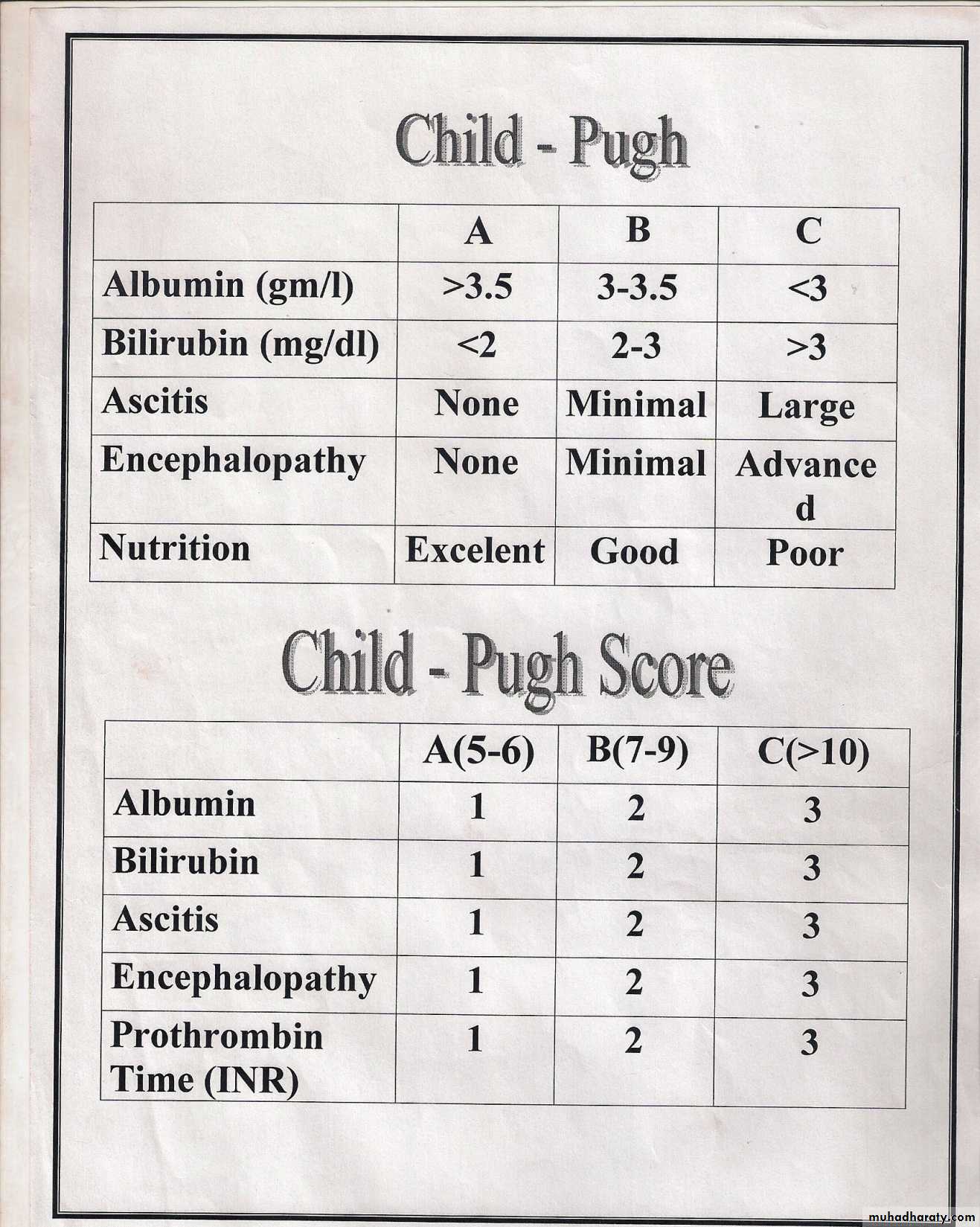
• Staging of liver disease- clinical
• Decompensated liver disease
• Bleeding• Ascites
• Encephalopathy
•
• Complications
• Infections
• Portal hypertension
• Ascites
• Hepatic encephalopathy
• Hepatorenal syndrome
• Hepatopulmonary syndrome
• Hepatoma
•
• Management
Immune hepatitis
• Presentation• Associated features
• Investigations
• ANA AMA A-LKmA•
• ASMA SLA
• Wilson disease
• ATP7B gene Ch13
• Presentation
• Investigations
• Management
Hemochromatosis
HFE gene Ch6
C282Y
Presentation
Investigation
Management
Secondary Hemochromatosis
• α1-antitrypsin deficiency
• PiM• PiS
• PiZ
•
• Primary biliary cirrhosis
• Pathology
• Presentation
• Associated auto immune disease
• Investigations
• Management
• Pruritis
• Malabsorption
• Lipids
Secondary biliary cirrhosis
Alcoholic liver disease
• Dose – Duration - Genetics – Sex
• Mechanism
• Pathology
• Fatty liver• Alcoholic hepatitis – Mallory’s hyaline
• Central hyaline sclerosis
• CAH
• Cirrhosis
• Hepatoma
• Clinical
• Asymptomatic• Gradual
• Cholestasis and abdominal pain
• Alcoholic hepatitis
• Investigations
• Establish alcohol abuse• Exclude other causes of liver disease
• Establish severity
• AST/ALT> 2/1
• Management
• Drugs and the liver
Liver metabolism conversion of fat-soluble (non-polar)
Water soluble (polar) MFO (P450) on SER
Genetics, nutritional, hepatic blood flow, plasma protein binding, combination of drugsInduction and inhibition of enzymes
Hepatotoxicity of drug:
All forms of liver diseaseAcute hepatic injury - Dose dependent – paracetamol, CCl4
- Idiosyncratic
- Cholestasis
- Fatty liver
- Chronic hepatitis
- Granulomas
- Fibrosis
- Vascular
- Tumors
- Toxins
Hepatic vein obstruction
• Anywhere from the small central hepatic veins heart
• Veno-occlusive disease
• Heart failure, tamponade
• Budd- Chiari syndrome- thrombogenic disease
• PRV
• PNH
• AT III deficiency
• Anti-phospholipid syndrome
• Protein C & S deficiency
• Vena Caval obstruction
• Webs
• Tumors
• Clinical features
• SPEED
• Management