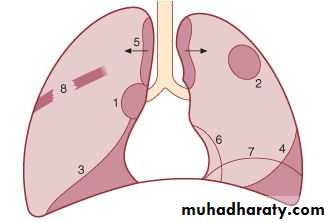
Lung cancer
Dr. Mustafa NemaConsultant chest physician
Baghdad College of Medicine
2014
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine
objectives
At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to:Define the types of lung cancer.
Describe common clinical symptoms
Relate presentation of the disease to the underlying mechanism.
List radiological abnormalities.
Outline therapeutic lines.
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of MedicineCase 1
A 55 years-old smoker man presented with cough, hemoptysis, unilateral chest pain and dyspnea for 3 months.
Later on, fever, greenish sputum, and increasing dyspnea developed.
2013LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine
He felt unwell and his appetite was decreased.
General examination showed finger clubbing.Chest examination revealed decreased chest expansion, dull percussion and bronchial breathing on auscultation on one side.
2013
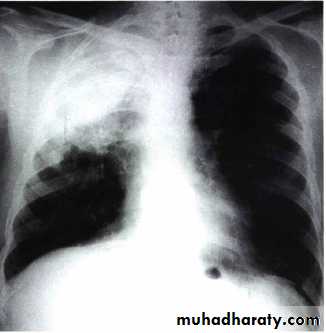
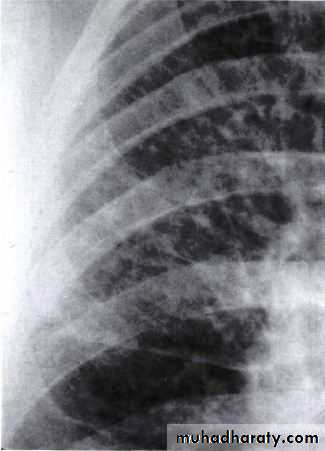
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of MedicineChest-X Ray showed an abnormal lung shadow and pneumonia-like lesion.
Antibiotic given but, pneumonia didn’t resolve completely.• How can you manage
this patient?
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine
Case 2
A 61 years-old smoker man, presented with left shoulder pain for 4 months that is poorly respond to analgesics.He also complained from weakness of left upper limb and bone pain in both wrists and feet.
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine
Later on, swelling in his face, upper chest, and both upper limbs started to develop.
Arrows:Dilated neck veins
Dilated lower chest veins
2013
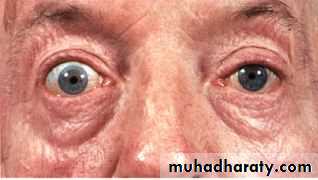
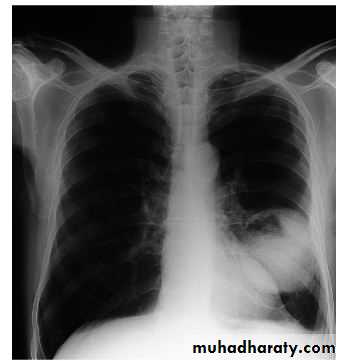
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of MedicineOn examination, the left eye and pupil looked smaller than the right, and his neck veins looked distended.
Chest X-ray showed right apical abnormal lung lesion with upper rib erosion.
How can you approach this patient problem?2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of MedicineCase 3
A non smoker 45 years-old women with history of ovarian tumor presented with mild dyspnea.• OE: Non-specific lung findings.
• CXR shows multiple nodules of different size.
What’s your primary impression?
2013LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine
Introduction
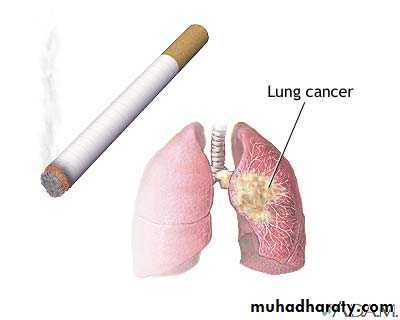
• The term lung cancer, or ’ bronchogenic carcinoma’ refers to malignancies that originate in the airways or pulmonary parenchyma.2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine
• Lung cancer is the most common cause of death from cancer worldwide, causing 1.4 million deaths per year
• The prognosis remains poor, with fewer than 30% of patients surviving at 1 year and 6–8% at 5 years.
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine
Etiological factors
Lung cancer occurs through a complex process that results from the combination of carcinogen exposure and genetic susceptibility.A number of lifestyle and environmental risk factors have been associated with the development of lung cancer.
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine
Cigarette smoking is by far the most important cause of lung cancer. It is thought to be directly responsible for at least 90% of lung carcinomas.
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine
Etiological factors
2013LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine
Smoking
Cigarette smoking responsible for at least 90% of lung carcinomas.• Compared with nonsmokers, smokers have an ,20-fold increase in lung cancer risk, depending on:
• Duration of smoking
• Number of cigarettes smoked per day.
Passive smoking increases the risk of bronchial carcinoma.
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine
Other risk factors
• Underlying acquired lung diseases (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and pulmonary fibrosis)• Environmental exposures – often with smoking- (asbestos, radon, metals, ionising radiation including previous radiotherapy and petroleum products ).
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine
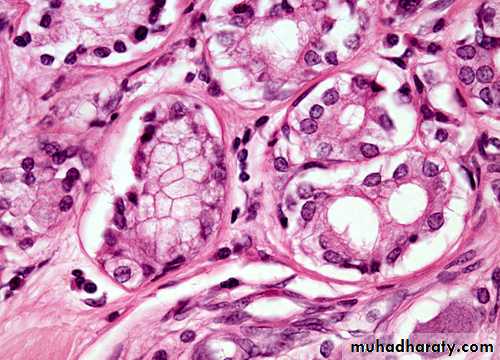
Pathology
Bronchial carcinomas arise from the bronchial epithelium or mucous glands2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine
The World Health Organization (WHO)Classification of malignant lung tumours
Pre-invasive lesions.
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC).
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC):
1) Squamous cell carcinoma
2) Adenocarcinoma
3) Large cell carcinoma.
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of MedicinePercents of lung cancers histopath. types
Cell type%
Squamous
35
Adenocarcinoma
30
Small-cell
20
Large-cell
15
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine
Recently became the most frequent one
Small-cell carcinoma
It arises from endocrine cells .
Many polypeptide hormones are secreted by these tumors
The tumor is rapidly growing ,highly malignant and spreads early so, it is almost always inoperable at presentation.
It responds to chemotherapy but the prognosis remains poor.
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of MedicineNon-small-cell carcinoma
Squamous carcinoma:Common location is central (in major bronchus).
Most present as obstructive lesions of the bronchus leading to infection.It occasionally cavitates (10%) at presentation.
Local spread is common but widespread metastases occur relatively late.
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of MedicineAdenocarcinoma :
• Common location is peripheral.
• Arises from mucous cells in the bronchial epithelium.
• Commonnly metastases to the brain and bones.
• More common in non-smokers, in women, and in the elderly.
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of MedicineHow can patient with lung cancer present to you?
The majority of patients with lung cancer haveadvanced disease at clinical presentation,
which reflects the frequent asymptomatic
course of early stage lung cancer.
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of MedicineLater on, patient may present with one or more of the following ( according to history and exam.)
• General symptoms such as anorexia, weight loss and asthenia.
• Intrathoracic tumor effect.• Metastasis
• Paraneoplastic syndrom
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine• General symptoms
Such as anorexia, weight loss and weakness, loss of appetite.2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine2. Intrathoracic effects
Bronchial obstruction• Common presentation.
• May lead to pneumonia, which is often the first clinical manifestation of a bronchial carcinoma,
• Recurrent pneumonia at the same site or pneumonia which is slow to respond to treatment, particularly in a smoker, should immediately suggest the possibility of bronchial carcinoma.
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine
Cough
• Is the most common early symptom (central airway or pleural involvement) .
Haemoptysis,
• Invasion of a vessel.
Chest pain
• Malignant invasion of the pleura, although it can occur with distal infection.
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine
Dyspnoea
• Lobar / total lung collapse or massive pleural effusion.Hoarseness
• Recurrent laryngeal nerve involvement.
Stridor
• A harsh inspiratory noise occurs when the lower trachea, carina or main bronchi are narrowed by the primary tumor or by lymph nodes.
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine• Superior vena cava syndrome
• Dilated neck veins, facial oedema occurs due to SVC obstrucion by lung tumor.Phrenic nerve paralysis
• Causes unilateral diaphragmatic palsy
• Pleural effusion
• Involvement of the pleura may produce a pleural rub or signs of pleural effusion
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of MedicineSuperior sulcus, or pancoast’s tumor ,
• Occur due to tumor present in the upper lung lobe that invades nearby structures. e.g. brachial plexus resulting in neuropathy with pain, numbness, weakness of the arm and hand muscle atrophy (Pancoast's syndrom)2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of MedicinePancoast tumor
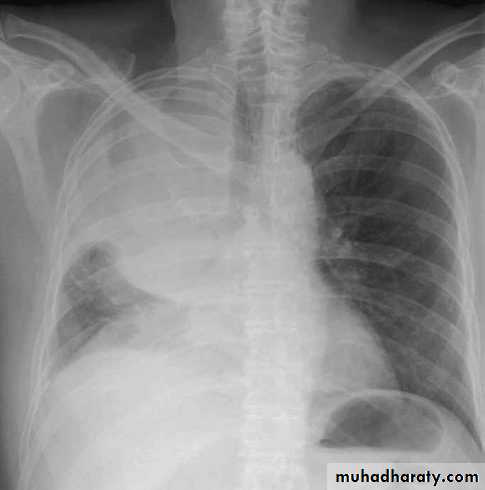
In this patient with shoulder pain, a mass (white arrows) is seen in the left lung apex on CXR (A).Pancoast's syndrom
Pain, numbness, weakness of the arm and hand muscle atrophy2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine
Note:
A smoker, elderly patient with unilateral shoulder pain may have bronchogenic carcinoma as one diagnostic possibilities.2013
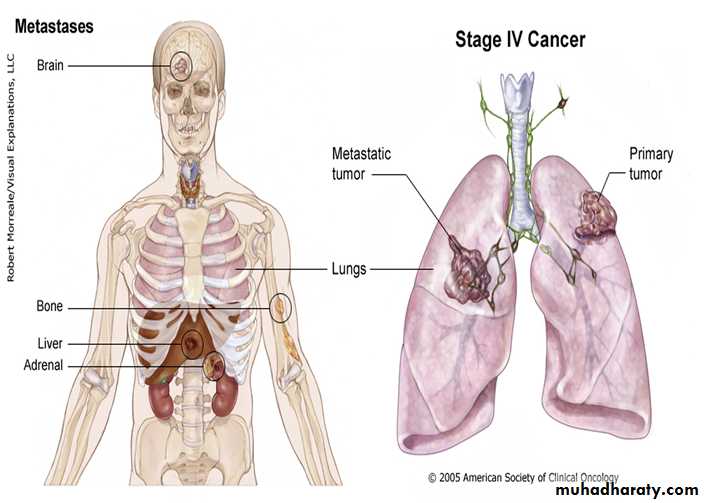
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine3) Metastasis
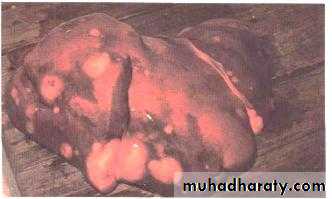
Symptoms occur due to blood-borne metastases. The most frequent sites of distant metastasis are the:• liver: (pain, jaundice, constitutional symptoms).
• adrenal glands: usualy asymptomatic.
• Bones: (pain),
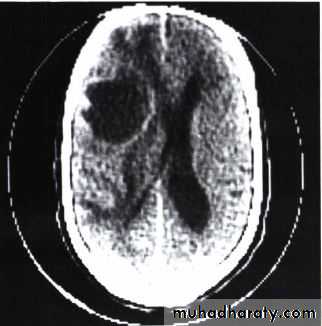
• brain: (headache, paresis, personality change, seizures)
• skin: (nodules)
Liver metastasis
Brain metastasis
2013LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine
Metastasis..
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine
Metastasis..
lymphangitis carcinomatosa• These lines represent lymphatics infiltrated by tumour.
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine4.Paraneoplastic syndrome
Non-metastatic symptoms due to paraneoplastic syndrom include:Endocrine :
Inappropriate antidiuretic hormone(ADH) secretion causing hyponatraemia
Ectopic adrenocorticotrophic
hormone (ACTH) secretion leading to Cushing’s syndrom.
small-
cell
lung ca
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine
Paraneoplastic syndrome…
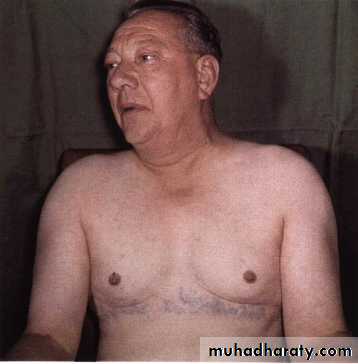
Hypercalcaemia due to secretion ofparathyroid hormone (PTH)-related
peptides.
Carcinoid syndrome.
Gynaecomastia.
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of MedicineSquamous cell ca
Neurological :
NeuropathyMyelopathy (spinal cord involvement)
Myasthenia (Lambert-Eaton syndrome)
Other :
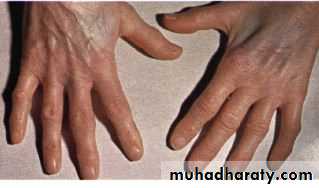
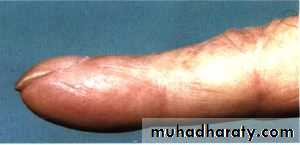
Digital clubbing (Hypertrophic pulmonary steoarthropathy HPOA)
Eosinophilia
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of MedicineClubbing
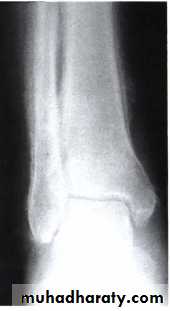
Hypertrophic pulmonary osteoarthropathy (HPO)Characterized by periostitis of the long bones, most commonly the distal tibia, fibula, radius and ulna.
This gives rise to pain and tenderness over the affected bones and often pitting oedema over the anterior aspect of the shin.
X-rays of the painful bones show subperiosteal new bone formation.
Clubbing is part of HPO.
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of MedicineWarning signs of lung ca
Change in respirationsCough that is persistent
Change in sputum
Weight loss
Chest pain
Recurring respiratory disorders such as pneumonia or bronchitis
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of MedicineDiagnosis of lung cancer
• History and examination• Investigations
• Radiology:
• CXR
• CT and MRI
• PET scan
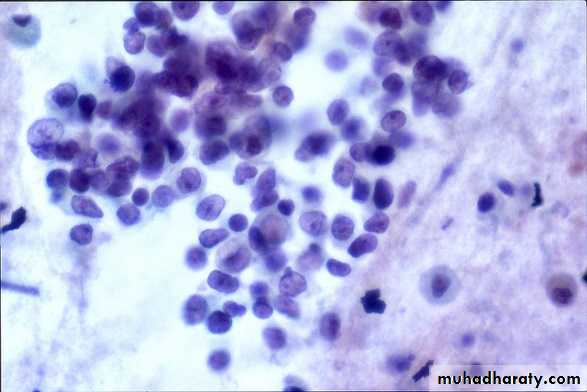
• Sputum cytology
• Bronchoscopy brush/biopsy
• Transthoracic biopsy under-
• US or CT guide
• Thoracotomy for tumor biopsy
Detecting the tumor site
Detecting the tumor type
2013LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine
Sputum
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of MedicineSquamous cell carcinoma
Radiology
• Unilateral hilar enlargement• Peripheral pulmonary opacity
• Lung, lobe or segmental collapse
• Pleural effusion
• Broadening of mediastinum,
• Enlarged cardiac shadow,
• Elevation of a hemidiaphragm
• Rib destruction
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of MedicineLarge cavitated bronchial carcinoma in left lower lobe.
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of MedicineRadiology
The most frequent finding is a mass in the lung field.Secondary manifestations seen on the CXR include lobar collapse, total lung collapse, pneumonitis because of endobronchial obstruction, elevation of the hemidiaphragm,
Elevation of the hemidiaphragm
lobar collapse & pneumonitis
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine
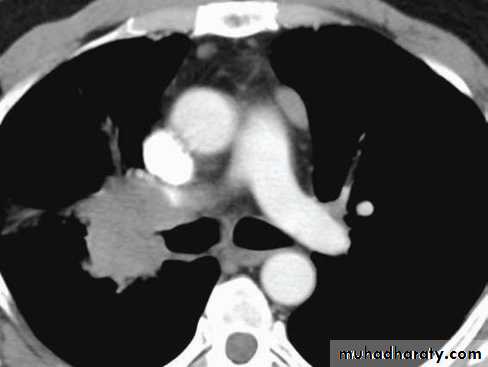
Radiology..Computerized Tomography CT- chest
Add more detailed anatomical information and detect pulmonary lymph node enlargement more clearly.
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine
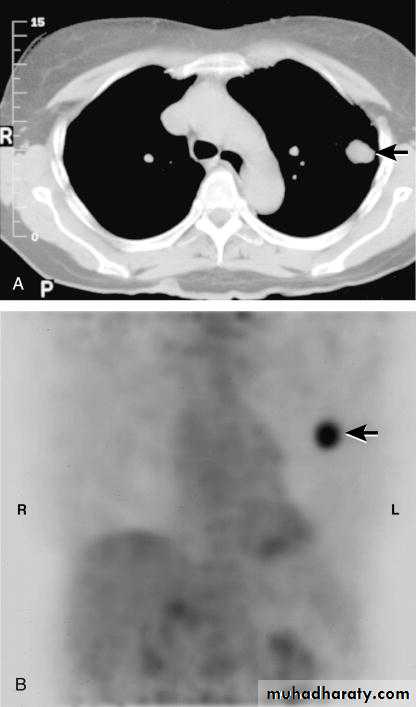
Positron Emition tomography (PET)
May shows markedly increased activity at the same area, indicative of very high metabolic activity and a high probability of malignancy.2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of MedicineBronchoscopy
Is the appropriate test for centrally located tumors, where a pathological diagnosis will be obtained in ,90% of cases, by means of forceps biopsy, bronchial brushing or washing.
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of MedicineStaging
Non-small cell lung cancer.TNM (Tumor, lymph Node, Metastasis) classification of Non-small cell lung cancer, e.g. T3N1M0.
Small cell lung cancer
Small cell lung cancer is divided into limited and extensive stage disease.
• NB: Tumor staging defines the prognosis and guides management.
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine
Treatment
SurgeryChemotherapy
Radiation
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine
Treatment of NSCLC
For medically operable patients : surgical resection ± chemotherapy.Medically inoperable patients: radiotherapy.
In advanced stage: chemotherapy plus radiotherapy.
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine
Treatment of SCLC
• Chemotherapy in combination with thoracic radiotherapy and prophylactic cranial irradiation.2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine
General treatment measures
Radiotherapy plays an important role in palliation of local problems such as superior vena cava syndrome, haemoptysis, postobstructive pneumonia, bone pain and brain metastasis.2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine
Secondary lung tumors
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine
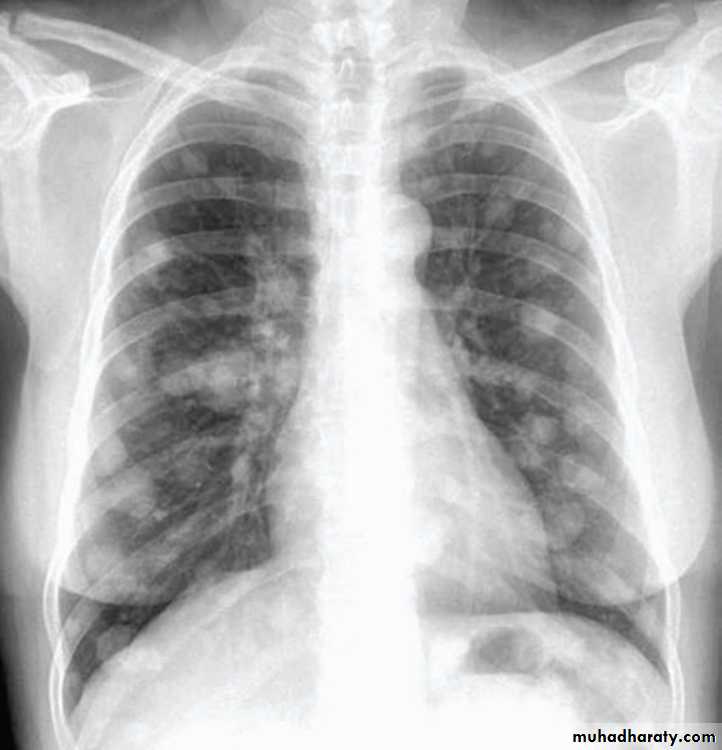
Secondary lung tumors
Metastases in the lung are very common and usually present as round shadows (1.5-3.0 cm diameter). They may be detected on chest X-ray in patients already diagnosed as having carcinoma.Typical sites for the primary tumor include the kidney, prostate, breast, bone, gastrointestinal tract, cervix and ovary.
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine
Metastases nearly always develop in the parenchyma and are often relatively asymptomatic even when the chest X-ray shows extensive pulmonary metastases
( cannon ball metastasis)
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of Medicine2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of MedicineNow can you answer the questions related to case 1 and 2 ?
Summary
Lung cancer is a tumor arising from within the lung.
It may represents the primary site or may be metastatic
Histopath. Types:
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC).
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC):
• 1) Squamous cell carcinoma:
• 2) Adenocarcinoma:
• 3) Large cell carcinoma.
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of MedicineStaged by:
TumorNode
Metastasis
Treated by:
RadiationSurgery
Chemotherapy
This is the TNM classification system
2013
LUNG CANCER - Dr. Mustafa Nema- Baghdad College of MedicineA 68 years old man, with 80 pack-year smoking history presented with dyspnea, cough, blood streaks sputum, and weight loss over the last 4 months. On examination, tempreture 36.90, looks pale, emaciated, with limited chest expansion over right lung, dull percussion and bronchial breathing sound. The most likely diagnosis is:
• Pulmonary TB
• Post pneumonic effusion• Lung cancer
• Pulmonary edema