
LUNG DISEASES DUE TO
ORGANIC&INORGANIC DUSTS
Dr.kassim.m.sultan
F.R.C.P

Definition of hypersensitivity pneumonitis(extrinsic allergic alveolitis):
Inflammatory disorder of the lung, involving alveolar walls
and terminal airways, that is induced, in a susceptible host,
by repeated inhalation of a variety of organic agents.
"farmer's lung" is the term most commonly used for HP.
Thermophilic actinomycetes species include Micropolyspora
faeni, Thermoactinomyces vulgaris.

Selected Examples of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis (HP):
farmer's lung caused by Micropolyspora faeni.
Bird fancier's, breeder's caused by exposure to avian protien
in Avian droppings or feathers.
Byssinosis in textiles&cotton industry.
Humidifier or air-conditioner lung (ventilation pneumonitis)
caused by Candida albicans, Thermophilic actinomycetes,
mycobacterium spp.
Cheese washer's lung caused by Penicillium casei from
handling Moldy cheese

Pathogenesis:
Not fully understood, and may involve T-cell mediated
immunity and granuloma formation (type IV
hypersensitivity) and/or antibody-antigen immune complex
formation (type III hypersensitivity).
It is not an atopic disease, and is not characterized by a rise
in tissue eosinophils or IgE (type I hypersensitivity).
Non-caseating granulomata are often present, and typically
are ill-defined and single associated with lympho-
plasmacytic interstitial infilterate&bronchiolitis..
Chronic HP is characterized by fibrosis

Clinical features-Acute HP:
Breathlessness, dry cough, and systemic symptoms (fever,
chills, arthralgia, myalgia, headache) occur 4-8 hours after
exposure to antigen
Examination: end inspiratory crackles on both lung fields on
auscultation.
In the absence of ongoing exposure, symptoms settle
spontaneously within 1-3 days,can be recurrent.

Clinical features-chronic HP:
Progressive exertional breathlessness, dry cough, sometimes
systemic symptoms (weight loss) over course of months-
years. May be history of acute episodes
Examination: crackles on auscultation, clubbing rare, may be
features of cor pulmonale.

Investigations:
Acute HP
CXR :bilateral Diffuse small (1-3 mm) centrilobular nodules
or infiltrates, sometimes ground-glass change,mainly in mid-
upper lobe with apical sparing.
HRCT Patchy ground-glass change and poorly defined
centrilobular nodules.
Chronic HP
CXR Typically upper- and mid-zone reticulation
HRCT Diffuse well-defined centrilobular nodules, ground-
glass change, vol.loss,honey-combing,traction
bronchiectasis.
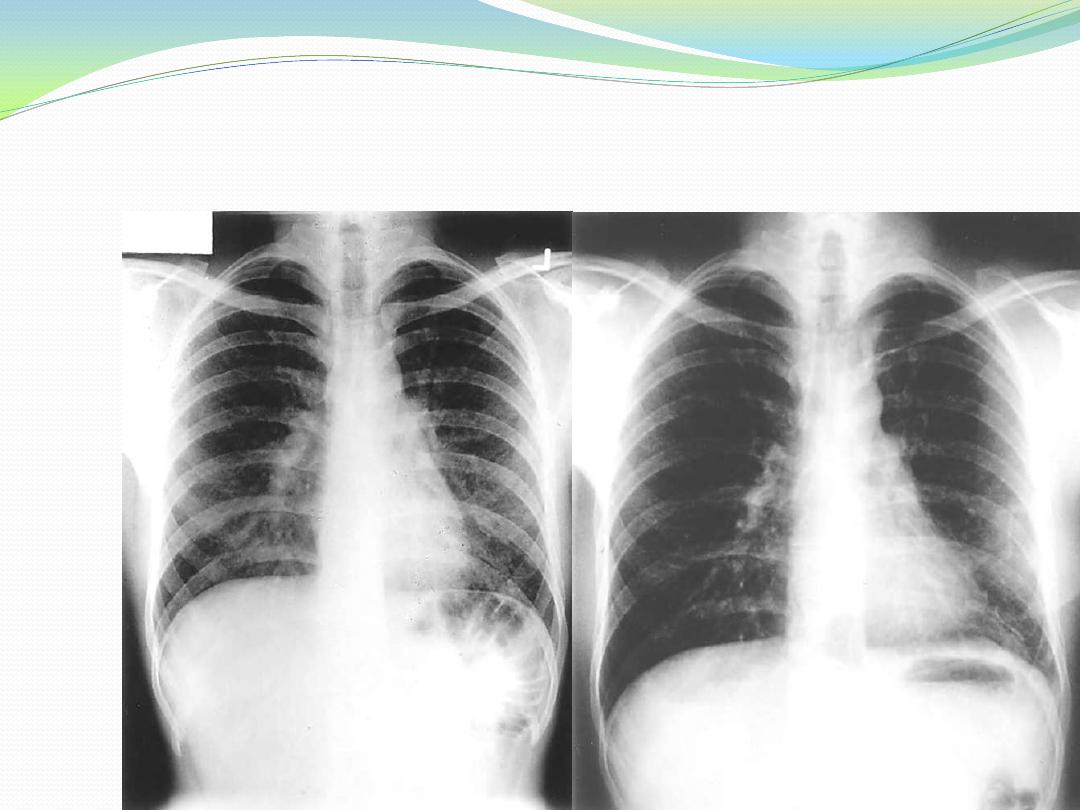
A:
Chest radiograph of a patient with pigeon breeder’s disease with fever, dyspnea, and
bibasilar rales. The patient had kept pigeons for 5 years and presented with fever, dyspnea,
and myalgias approximately 8 h after cleaning the pigeon coop. He had serum antibody to
pigeon dropping extract. Note bilateral lower lobe 2- to 3-mm nodules.
B:
Chest radiograph of the same patient 2weeks later without specific treatment. Note
clearing of the lower lobe nodules and the staples in the left chest from the open lung
biopsy.
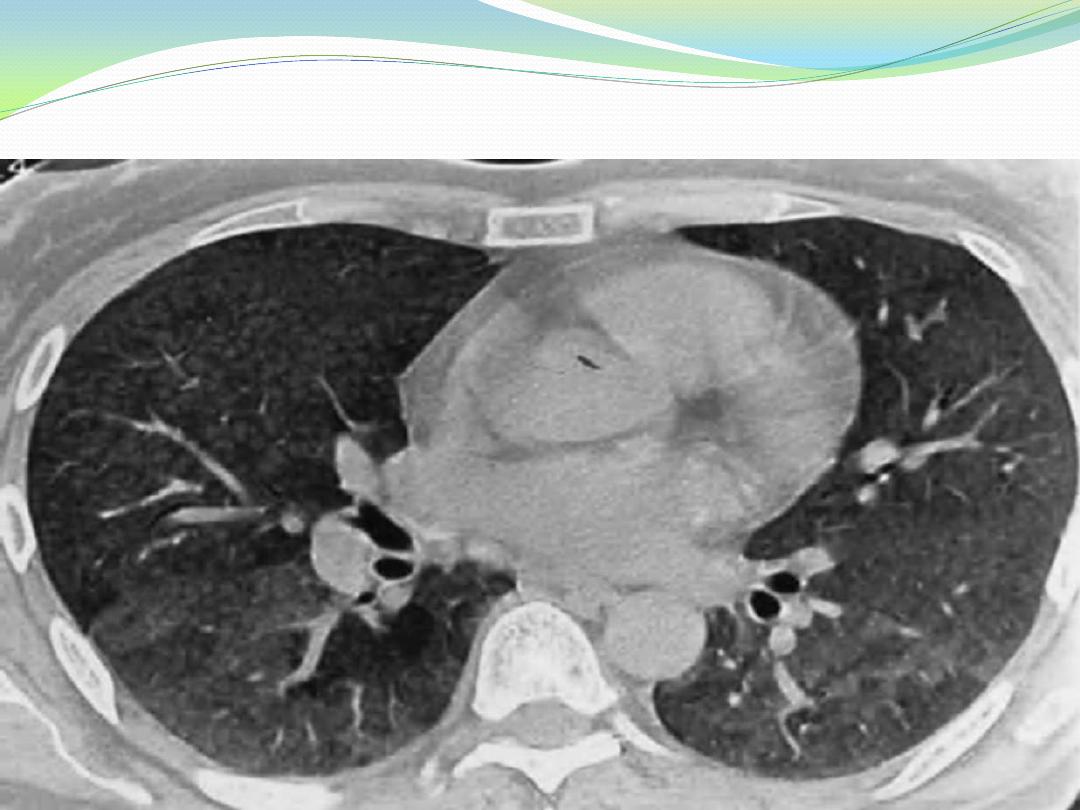
High-resolution computed tomography scan of a nonsmoking patient with exposure to
both birds ,who presented with progressive dyspnea and weight loss and had hypoxemia
and a restrictive ventilatory defect. Note the diffuse nodular radiodensities in the lower
lobes, with areas of groundglass densities posteriorly.

Investigations:
PFTs Typically restrictive pattern with reduced DLco .
Blood gasses:decrease pao2 with type I respiratory failure.
Serum antibody (IgG) precipitin results are presented either
as an ELISA or Precipitins to organic antigens are found in
90% of patients, but are also present in up to 10% of
asymptomatic farmers and 50% of pigeon breeders.
BAL :lymphocytosis (>40% of cells) is a typical finding, but
not in itself diagnostic.

Predictive factors in identification of HP:
Exposure to a known offending antigen
Positive precipitating antibodies to offending antigen
Recurrent episodes of symptoms
Inspiratory crackles on examination
Symptoms occurring 4-8 hours after exposure
Weight loss

Treatment:
Symptoms typically resolve following cessation of antigen
exposure.
Liberal O2
Prednisolone 40-60 mg daily for up to a month, and then
slowly reduce dose over several months.
Treatment of complications like respiratory failure

LUNG DISEASES DUE TO INORGANIC DUSTS

Types of mineral dust exposure:
1-Non-fibrous mineral dusts:Silicosis,Coal workers'
pneumoconiosis&Mixed mineral dusts containing quartz:
slate, kaolin, talc, non-fibrous clays
2-Fibrous mineral dusts:Asbestos,Other mineral fibres
3-Metal dusts and fumes:Iron, aluminium, beryllium, cobalt.

SOME LUNG DISEASES CAUSED BY INORGANIC GASES AND FUMES:
Irritant gases (chlorine, ammonia, phosgene, nitrogen
dioxide)may cause Acute lung injury
(ARDS)
Cadmium
Welding and electroplating cause COPD
Isocyanates (e.g. epoxy resins, paints)
Plastic, paints; manufacture of epoxy resins and adhesives
cause Bronchial asthma&Eosinophilic pneumonia

Pneumoconiosis:
Occupational lung disease result from prolonged exposure to
inorganic dust.
1-coal workers pneumoconiosis
2-silicosis
3-asbestosis
4-berylliosis

coal workers pneumoconiosis:
deposition of coal dust within the lung and its associated
inflammatory reaction.
There are two types:
1-Simple pneumoconiosis, there is nodular shadowing, with
nodules of varying size, up to 10 mm, particularly in the
upper and middle zones. it is reversible if the patient leave
his job, but if not ,it can progress to
2-Complicated pneumoconiosis, also known as progressive
massive fibrosis (PMF). one or more opacities of > 1 cm
diameter are present in the upper lobes, on the background
of simple pneumoconiosis.

Clinical features:
Simple pneumoconiosis is usually asymptomatic with no
associated clinical signs. This is a relatively benign disease.
PMF is usually associated with cough, productive of mucoid
or blackened sputum(melanoptysis), and breathlessness,
particularly on exertion, and may in time lead to the
development of cor pulmonale.
no clubbing

Caplans syndrome:
In 15 % of Miners with seropositive R.A or positive serum
rheumatoid factor can develop large well-defined nodules.
These occur on a background of simple pneumoconiosis and
in those with a relatively low coal dust exposure.

Silicosis:
Chronic nodular densely fibrosing pneumoconiosis,
caused by the prolonged inhalation of silica dioixide
particles.
Mining, quarrying, stone dressing, metal grinding,
pottery, boiler scaling, Foundry work.

4 types of Silicosis recognized:
1-acute silicosisis caused by intense exposure to fine
dusts
2-Subacute silicosis Nodules coalesce and calcify and
can progress to progressive massive fibrosis (PMF).
Associated calcified hilar lymphadenopathy (egg
shell calcification).
3-Chronic silicosis occurs with lower dust
concentrations
4-Silicotuberculosis Increased likelihood of active TB
infection

Asbestosis:
Chronic interstitial fibrosis resulting from
asbestos inhalation.
Demolition, ship breaking, manufacture of
fireproof insulating materials and brake-pads,
pipe and boiler lagging.
CXR: Bilateral symmetrical reticulonodular
pattern, primarily affecting the lower lobes, may
progress to honeycomb lung.

Thanks for your listening
