Management of acute severe asthma
Dr: MUHAMMED AL,OBAIDYCHEST PHYSCIAN
MEDICAL CITY
INTIATIONAL ASSESSMENT
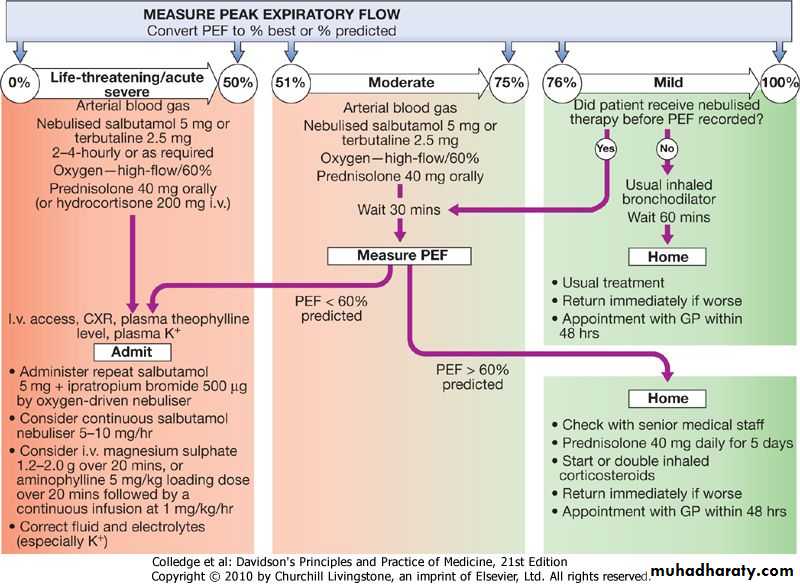
Measurement of PEF is mandatory unless the patient is too ill to cooperate.Arterial blood gas analysis is essential to determine the PaCO2, a normal or elevated level being particularly dangerous.
A chest X-ray is not immediately necessary unless pneumothorax is suspected.
Acute severe asthma
PEF 33-50% predicted (< 200 L/min)Respiratory rate ≥ 25/min
Heart rate ≥ 110/min
Inability to complete sentences in 1 breath .
Life-threatening features
PEF < 33% predicted (< 100 L/min)SpO2 < 92% or PaO2 < 8 kPa (60 mmHg) (especially if being treated with oxygen)
Normal or raised PaCO2
Silent chest
Cyanosis
Feeble respiratory effort
Bradycardia or arrhythmias
Hypotension
Exhaustion
Confusion
Coma
Near-fatal asthma
Raised PaCO2 and/or requiring mechanical ventilation with raised inflation pressures .
Treatment
Oxygen. High concentrations of oxygen (humidified if possible) should be administered to maintain the oxygen saturation above 92% in adults.High doses of inhaled bronchodilators. Short-acting β2-agonists are the agent of first choice. In hospital they are most conveniently administered via a nebuliser driven by oxygen.
TREATMENT
Systemic corticosteroids. Systemic corticosteroids reduce the inflammatory response and hasten the resolution of exacerbations. They should be administered to all patients experiencing an acute severe attack. They can usually be administered orally as prednisolone, but intravenous hydrocortisone may be given in patients who are vomiting or unable to swallow.Intravenous fluids. There are no controlled trials to support the use of intravenous fluids but many patients are dehydrated due to high insensible water loss and probably benefit from these. Potassium supplements may be necessary because repeated doses of salbutamol can lower serum potassium.
Indications for assisted ventilation in acute severe asthma
ComaRespiratory arrest
Deterioration of arterial blood gas tensions despite optimal therapy
PaO2 < 8 kPa (60 mmHg) and falling
PaCO2 > 6 kPa (45 mmHg) and rising
pH low and falling (H+ high and rising)
Exhaustion, confusion, drowsiness