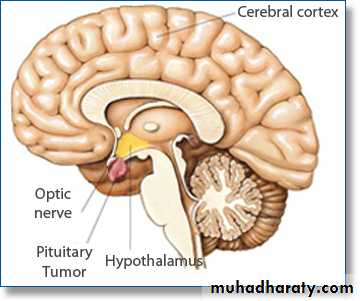
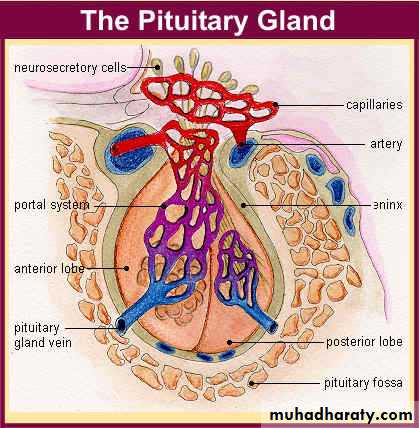
Pituitary gland
Embriologically : it develops from Rathke’s pharygshal Pouch .* It is of = 500-600 mg weight .
* = = located in the sella-tursica ventral to
diaphragma-sella .
* it comprises anatomically & functionally
distinct ant. & post lobes .
* sella-tursica is contiguous to vascular & neurologic
structures include :
. Cavernous – sinuses .
. Cranial – nerves . thus expanding
. Optic – chiasm .
* Intra sellar mass may have significant central
mass effects in addition to their endocrinologicimpacts.
* it‘s blood-supply is derived from Sup. & inf.
hypophyseal ART .
* Hypothal. Pit. Portal plexus provides the
major blood supply for ant. Pit. Allowing
reliable transmission of hypothalomic peptide
pulses without significant systemic dilution .
* post. Pit. Lobe is directly innervated by
hypothalomic neurons via pit. Stalk. Thus ADH &
oxytocin are particularly sensitive to neurologic
damage of pit. Stalk or hypothalomus .
Pituitary-gland disorder
. EXCESS : . Acromegally = after maturity .
. Gigantism . = before = .
. Hyperprolactinaemias .
. High A.D.H.
. Defiency-state : . Dwarfism .
. Kallman’s syndrome .
. Diabetes-insipedus .
Acromegally : .Causes :
A. high growth hor. Secrtion:
1. pit. Tumor 90%
a. Microadenoma . b. Macroadenoma .
2. Extra pit. Tumor < 1%
pancreatic islet cell tumor .B. High GH-releasing factor < 1%
1. central : ganglioneuromas .
2. peripheral : . B.carcinoid .
. Panc. Islet cell tumor .
. CA. lung ( small cell ) .
. Ad. Adenoma .
. Medullary thy. CA.
. Paeochromocytoma .
Clinical – Aspects :
indolent & often are not clinically Dx for 10 years or more
Which system / organ are affected ??
1. Musclo – skeletal system :. Acral – bony over growth results in :
a. frontal – bossing .
b. high hand & foot size .
c. prognathism & mandibular enlargment .
d. widened space bet. Lower incisor teeth .
e. gigantism in children .
. Soft tissue swelling results in :
* high heel pad thickness .* high glove & shoe size .
* ring tightening .
* characteristic coarse-facial-features .
* large fleshy-nose .
* hyperhiderosis & oily-skin ,
acanthosis-negricans & skin-tags .
* deep – voice .
* kyphosis .
* visceromegally : 1. cardiomegally .
2. macro-glossia .
3. hepatomegally .
4. goitre .
* arthropathy & C.T. Syndrome .
* proximal myopathy & fatique .
2. cardiovascular system :
* coronary heart dis. ( I.H.D. )
Cardiac-failure & arrhythmias .
* cardiomyopathy .
* L.V.H.
* High B.P. In 30% .
3.Upper air-way obstruction: sleep-apnoea 60%
4. Diabetes – mellitus in 25% .
Mortality : is increased three-folds & related to
. C.V.S.. C.V.A.
. Cancer .
. Respiratory failure .
Survival is reduced by 10 years if excess G.H. is not controlled .
INVESTIGATIONS : we should look for
A. cause(s)
B. confirming the Dx . C.B.C. & E.S.R.
. F.B.S. & B. urea .
. G.U.E.
. Hormonal assay (GH)
. G.H. Suppression test via
doing oral G.T.T.
. A.C.T.H. Reserve .
C. Radiologic : . Skull – X ray
. CT / MRI for sella-tursica .
. CXR .
. U/S abdomen .
D. Visual – field exam. ( perimetry )
E. Fundoscopy .
Treatment :
A. supportive .B. treatment of the cause .
C. hormonal replacement therapy .
In pituitary adenoma surgical resection is indicated .
Radiation which may result in late hypopit. By gama knife radiotherapy but you may give somatostatin – analogues ( octreotide acetate= 8aa synthetic somatostatin) prior to surgery or radiotherapy
Surgical-operative types :
trans-sphenoidal-route for large tumor µ-adenoma . & cure rate is 50% &
70% respectively .
. G.H. will be normalized within an hour .
. IGF-1 = = = = 3-4 days .
. Recurrence of acromegally several years
after operation .
. Hypopituitarism in 15%
Excess vasopressin ( SIADH )
. Causes : . Neoplasms CA :a. lung b. pancreas c. ovary
d. U.B. e. thymomas
f. B. adenomas & carcinoids
. Infection :
a. pneumonias b. lung abscess
c. PT.B d. meningitis & encephalitis
e. AIDS
. Neurologic :
a. D.S b. Gillian – barr’e
c. Hydrocephalus d. Psychosis
. Drugs :
a. vasopressin( desmopressin )b. chlorpropamide
c. vincristine , cyclophosphamide
e. tegretal .
f. Nicotine .
g. T.C.As .
h. MAO inhibitor .
. Head – injury : a. closed b. open
. Vascular : a. C.V.A .
b. cavernous-sinus thrombosis .
. Metabolic :
a. Acute intermittent porphyria
b. B. asthma & pneumothorax ,+ve press. Ventil.
. C / F : a. oligiuria & concentrated – urine .
b. high H2O / Low plasma osmolality
hyponatraemia . Headache .
. Confusion .
. Anorexia .
. N / V .
. Coma & convulsions .
. Dx : is made by exclusion via ( HX , CE & lab. Test )
. True hyponatraemia
. Urine Na - excretion
. Plasma rennin activity
. Plasma ADH assay is not of diagnostic value
Treatment :
• Treatment of the cause when possible .• Restrict total fluid intake ( in sensible loss + urine output ) .
• Give 3% saline solution for rapid
PROLACTIN Physiological concept
It is polypeptide-hormone 184 A.A secreted from the adenohypophysis . It ‘s main function is related to lactation in women & also it affects the mensis Physiological : . sleep. Pregnancy .
. Sexual .
. Lactation .
. Nipple-stimulation .
pathological : . Hypothalmic damage .
. Pit. Stalk = .. Hypothyroidisim .
. C.R.F. 90% .
Pharmacological : . Phenothiazines
. Aldomete , reserpine
. Plasil
. Morphine
. T.R.H. & T.S.H.
. Cimetidine
Hyperprolactinaemia
. Clinical-features :A. related to underlying cause .
B. related to hyperprolactinaemia perse
which commonly include galactorrhoea
&/or hypogonadism (amenorrhoea ) this
may give clue to Dx. Of pit. Adenoma or
hypothalamic-disease .
women with amenorrhoea 10-40 % have high
prolactin but 30% of women with both
amenorrhea & galactorhoea have pit. Tumor .
Amenorrhea is due to high L.H.R.H. causing decrease L.H , F.S.H.
In men 1. impotence 10% .2. infertility 5% .
Prolactinoma : micro-adenoma 90% in females .
macro-adenoma 60% in men .
INVESTIGATIONS : 1. basal serum prolactin if > 100 ng is suggestive .
2. CT scan .
3. M.R.I. for hypothalamus & pit. Gland
4. Visual-field study
5. Fundoscopy .
Growth – Hormone deficiency
In children is characterized by. Short – stature ( dwarfism ) .
. Micropenis .
. High fat .
. High propensity for hypoglycaemias .
. High pitched-voice .
Atiopathogenesis :
1. 30% hereditary
a. A.D. b. A.R. c. X-linked
2. 10% mutations .
3. Idiopathic .
4. GH RH receptors mutation
5 . GH receptor insensitivity ( laron’s synd. ) in which
GH level is N. or high .
Diagnosis :
1. Hx. & FHx.2.C / E :
a. pat. Height is > 3 SD below the mean for age.
b. Growth rate has decelerated .
c. Skull X-ray for bone–age(Gr. Plate fusion) .
d. Standarized - scale : Bayley – pinneau .
Tanner – white house .
e. Add. 6 cm. (boys) from the mid parental-
substracting 6 cm (girls) height
3. Lab. Investigations :
. MRI pit. Gland ? Mass.
. GH stimulation tests GH > 7 microgram / L
. Exercise .
. Insulin induced hypoglycaemia
. DON’T depend on random G.H assay because
of it’s pulsatile-secretion .
Conclusion
People with dwarfism live normal lives and can have families of their own. There are also people out there to educate about people with Dwarfism and a place for people with Dwarfism to go for help and to talk to people like them. One group like this is the LPA- Little People of America. The biggest thing to know is that they are not midgets and that it is not a disease but a disorder. It is also important to know that the have normal intelligences just like other people.Treatment :
• Rx – the cause .• replacement therapy by recombinant
G.H 0.05 mg / kg / D s.c
10 cm / year .
Adult GH Deficiency A.G.H.D.
It is due to hypothalamic / pit. Somatotrophe-damageClinical – features :
1. impaired quality of life :
a. low energy & drive .
b. poor concentration .
c. low self esteem .
d. social – isolation .
2. body – composition changes :
a. low lean body mass .
b. high fat deposition centrally .
c. high waist – hip ratio .
d. high body fat mass .
3. reduce exercise capacity :
a. low cardiac – function .b. low muscle – mass .
c. low max. O2 uptake .
4. cardio-vascular risk factor :
a. abnormal lipid-profile .
b. atherosclerosis .
c. omental – obesity .
d. low frinolytic activity .
5. imaging : a. pit. : Damage .
b. bone : low bone-density .
c. abd. : omental-adiposity .
6. laborotary : . Evoked GH < 3 mg / c.c
. IGF-1 low or normal
. High LDL
. Gonadotropin / TSH / ACTH reserve
deficit may be present
Treatment :
G.H replacement therapy. Contra – indications :
a. active malignancy .
b. Intra - cranial hypertension .
c. uncontrolled D.M & retinopathy .
. Side – effects ( dose – related ) :
a. headache , high B.P , tinnitus .
b. arthralgia , oedema .
c. carbal tunnel synd.
d. paresthesia .
e. high insulin – resistance .
Kallmann’s syndrome
Results from defective hypothalamic GH RH ( Gn.RH ) secretion associated with
A. anosmia .
B. color – blindness .
C. optic - atrophy .
D. nerve deafness .
E. cleft–palate/renal & neurologic abnormalities
F. crptorchidism .
Aetiopathogenesis :
A. hereditary : A.D
A.R
B. Congenital .
C / F : delayed – male puberty with clear hypogonadism ( micropenis in male & primary amenorrhea in females ) plus failure of 2nd sexual characteristics .
laboratory :
. Low Gn.RH
. Low LH / FSH
. Low sex-steroids ( testost. / estradiol )
Treatment :
. Gn RH administration .
. HCG : restores pubertal develop. & 2nd
sexual (for male ) characteristics .
in female : . Cyclic-estrogen-progestin .
. Gn . RH .
. Portable infusion pump of S.C pulstile
Gn. RH .
Diabetes insipidus
It is an endocrine illness causing systemic-symptoms due to :
A. low vasopressin secretion .
B. = = action ( high ADH
receptor resistance i.e. nephrogenic )
Polyuria ( large urine volume ) :
a. high urine-frequency . Lead to sleep dist.
b. high nocturia . Day time – somnolence
c. high enuresis .
polydipisia ( high thirst )
dehydration is uncommon unless fluid intake is
impaired.
Aetiology :
A. central D.i :1. head – injury .
2. pit. Tumor .
3. infections : a. chronic meningitis .
b. encephalitis .
c. toxoplasmosis .
4. inflammatory :
a. Wegener's granulomatosis .
b. S.L.E
c. scleroderma .
5. chemical – toxin : snake – venom .
6. vascular :
a. Sheehan's synd.
b. internal carotid aneurysm .
c. hypoxic encephalopathy .
7. pregnancy .
8. idiopathic .
9. genetic : a. A.D b. A.R c. X – linked .
Treatment :
1. A.D.H therapy :
a. I.V
b. S.C
c. nasal – inhalation
d. = drops
2. Chlorpropamide via unknown
mechanism but it is teratogenic .
B. Nephrogenic D.I :
1. Drugs : . Lithium. Demeclocycline .
. Methoxyflurane .
. Amphotericin – B .
. Aminoglycosides .
. Cisplatin .
. Rifampin .
2. metabolic : . High Ca . Low K
3. Obstructive – uropathy .
4. vascular : a. sickle cell dis.
b. Ischemia ( A.T.N )
5. infiltration – amyloidosis .
6. pregnancy .
7. idiopathic .
8. genetic : a. A.D b. A.R c. X – linked .
Evaluation :
1. high plasma osmolality .
2. low urine osmolality
< 300 mOsmal / l diluted – urine .
3. dehydration test .
Treatment :
1. thiazide with low diet Na .
2. indocid may help .