Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Diseases of The PleuraDr.Mustafa Nema
Consultant Chest Physician
Baghdad College of Medicine
2014
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
ObjectivesAt the end of this lecture, student should be able to:
Make an ideas on common pleural diseases.
Relate the mechanism of pleural fluid formation to the underlying cause.
Learn how to differentiate between major types of pleural diseases.
Describe how can pleural diseases be presented, diagnosed and treated.
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Lecture 1
Pleural effusion
Pleurisy
Pleural malignancy
Lecture 2
PneumothoraxEmpyema
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Case scenario
Case 1: A young man presented with fever and cough. After 1 week, he developed dyspnea, right side chest pain. OE; decreased chest expansion on right side, dull percussion and decreased breath sound.What is the possible diagnosis?
How can we reach the diagnosis?
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Case 2: A 17 year’s old female came to the hospital with 1 month history of fever, night sweating, left sided chest pain and increasing dyspnea. OE; you have found signs of pleural effusion on the left side of the chest.
What is the most likely diagnosis?
How can you reach the definitive diagnosis?
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Case 3: A 67 year’s old women with known breast cancer presented with progressive dyspnea over the last month with no cough and no fever. Examination revealed signs of pleural effusion on right side.
What is your first impression on diagnosis?
How can you investigate for this effusion?
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Introduction
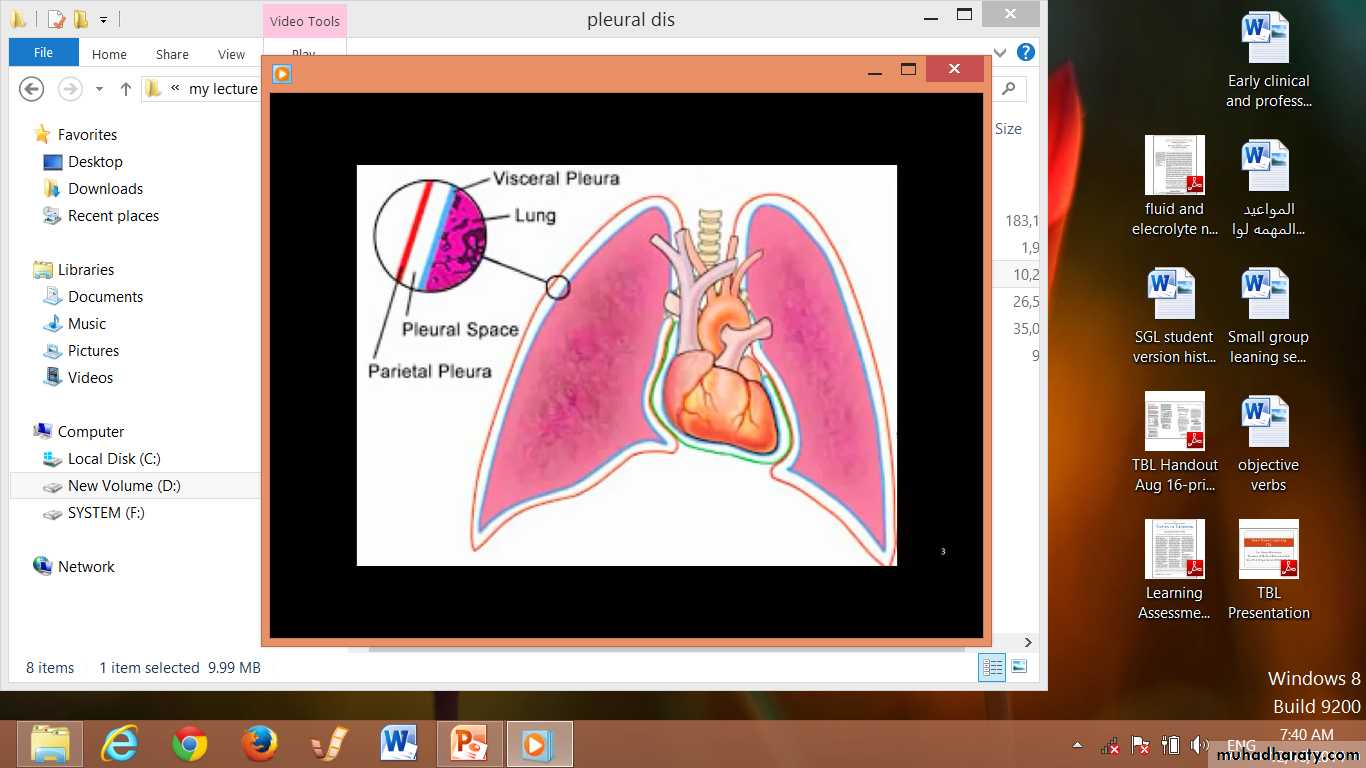
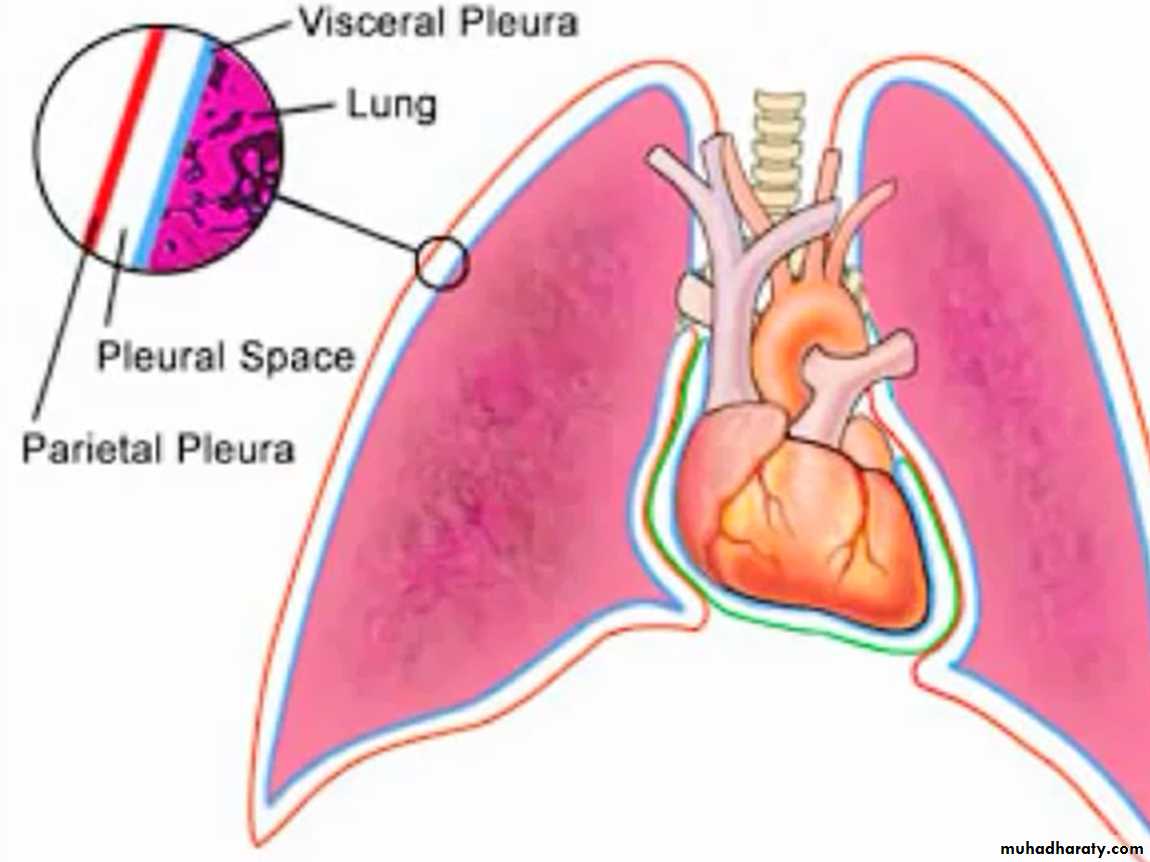
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013The PARIETAL PLEURA covers the surface of the chest wall, diaphragm, and mediastinum.
It is supplied with blood from the systemic circulation and contains sensory nerves.Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
The VISCERAL PLEURA covers the surface of the lungs, including the interlobar fissures.
Its blood supply arises from the low-pressure pulmonary circulation, and it has no sensory nerves.Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
The two layers of the pleura are separated by a pleural space, which is lubricated by to 10-20 mL of fluid, facilitates lung expansion.
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
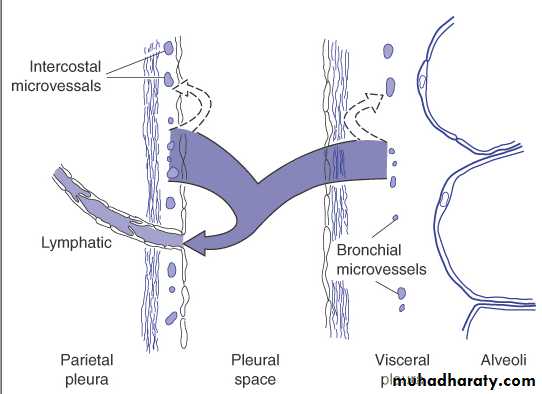
Pleural fluid
Movement of pleural fluidDiseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Normal production estimated at 15 mL/day in a 60-kg person.Pleural fluid has a low protein concentration (<2 g/dL) with a pH and glucose value similar to that of blood.
Pleural fluid is formed mainly from the parietal pleura.
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Pleural effusion
Pleural effusion result from disturbance of the physiological balance between the formation and removal of pleural fluid.
Pleural effusion is defined as accumulation of fluid in the pleural space that exceeds the physiological amounts of 10–20 mL.
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Common causes• Pneumonia (‘parapneumonic
effusion’)
• Tuberculosis
• Pulmonary infarction*
• Malignant disease
• Cardiac failure*
• Subdiaphragmatic
disorders (subphrenic
abscess, pancreatitis etc.)
* May be bilateral
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Uncommon causes
• Hypoproteinaemia*
(nephrotic syndrome, liver
failure, malnutrition)
• Connective tissue diseases*
(particularly systemic lupus
erythematosus (SLE) and
rheumatoid arthritis)
• Post-myocardial infarction
syndrome
• Acute rheumatic fever
• Meigs’ syndrome (ovarian
tumour plus pleural
effusion)
• Myxoedema*
• Uraemia*
• Asbestos-related benign
pleural effusio
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Pleural effusion
Mechanisms that lead to accumulation of pleural fluidhydrostatic force or oncotic pressure result in low-protein “transudates”. Note that the pleura itself is not involve by a disease process.
Increased outpouring by capillaries or blocking of lymphatics (or both) results in high-protein “exudates”.
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
The fluid may be transudate or exudate.The accumulation of frank pus is termed empyema , that of blood is haemothorax, and that of chyle is a chylothorax
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Pleural effusion
ExudateTransudate
Pus
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
lymph
Transudate
Blood
The nature of the fluid can only be determined by visual and laboratory inspection of an aspirated specimen.
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Transudative pleural effusion
Transudative pleural effusions occur when the “systemic factors” influencing the formation and absorption of pleural fluids are altered so that pleuralfluid accumulates.
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Causes of transudate effusion
• Congestive Heart failure: due to increased hydrostatic pressure (most common transudative cause).• Liver cirrhosis (Hepatic Hydrothorax): secondary to movement of ascitic fluid through diaphragmatic defects or lymphatic channels; the effusion is more frequent on the right.
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
3. Hypoalbuminemia : because of decreased oncotic pressure (e.g. nephrotic syndrome).
4. Urinothorax: retroperitoneal urinary leakage secondary to urinary obstruction or trauma.5. Peritoneal dialysis
6. Atelectasis
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
7. Myxedema (also can be exudative)
8. “Meigs' syndrome” is the triad of benign fibroma or other ovarian tumors with ascites and large pleural effusions. Usually on the right side. (also can be exudative)
9. Sarcoidosis (also can be exudative)
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
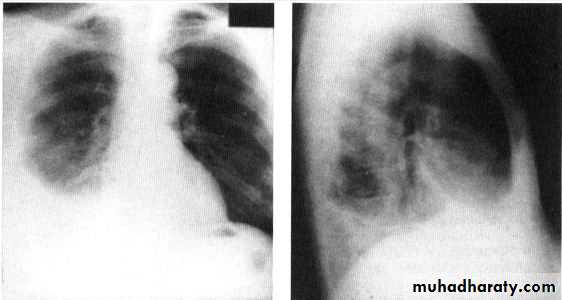
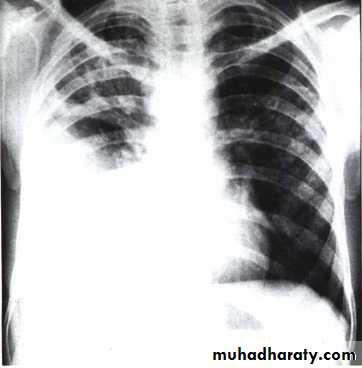
Unilateral effusionDiseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Bilateral effusion
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Exudative pleural effusionExudative pleural effusions occur when the “local pleural factors” influencing the formation and absorption of pleural fluids are altered so that pleural
fluid accumulates.
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Causes of exudate pleural effusion
A) INFECTIONSParapneumonic effusion
Associated with pneumonia or lung abscess.
Have large numbers of polymorphs.
The fluid my turned to a frank pus (empyema)
Most common exudative cause
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
• Primary TB infection.
• Subpleural focus of Mycobacterium tuberculosis ruptures into the pleural space.Presence of an ‘adenosine deaminase’ in the fluid correlate with tuberculosis.
Pleural biopsy are positive in 50 to 80% of cases (caseating granuloma on histopathology)
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Other Infective / Inflammatory Disorders
Subdiaphragmatic processes: such as an upper abdominal abscess.Pancreatitis and pancreatic pseudocysts: (more often on the left). The amylase level is higher than that in serum.
Esophageal rupture: effusion with high concentrations of salivary amylase.
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
B) NON INFECTIOUS CAUSES
Malignancy:suggested in any patient older than 60 year’s old
bronchogenic carcinoma, metastatic ca from breast, stomach, colon, thyroid ca..etc, lymphoma and pleural mesothelioma)
Rheumatoid arthritis.
Systemic lupus erythematosus.
Uremia
Asbestosis
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Drug-induced, e.g.:Nitrofurantoin
Methotrexate
Amiodarone
Bleomycin
INH
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
HEMOTHORAX
Frank blood in the pleural space is usually the result of trauma, hematologic disorders, pulmonary infarction, pleural malignancies or rupture of the aorta.
Pleural blood often does not clot.
PCV of this pleural bloodyfluid >50% of periphral blood PCV.
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
CHYLOTHORAX
Leakage of lymph (chyle) from the thoracic duct.Most commonly results from mediastinal malignancy (especially lymphoma) or thoracic surgery /trauma.
Usually milky appearance.
The best diagnostic criterion is the
presence of a triglyceride greater than
110 mg/dL in the pleural fluid.
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
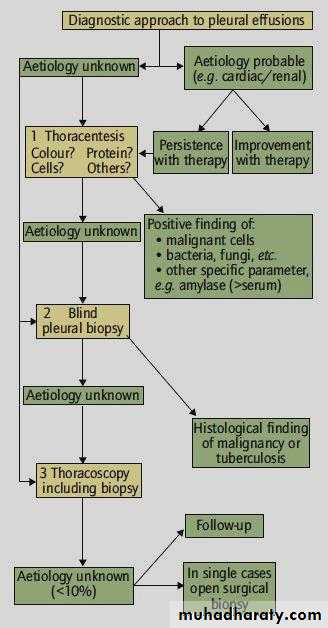
DIAGNOSING THE CAUSE AND TYPE OF EFFUSION
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
• This is based on the:Case history and clinical examination, e.g. history of TB, pneumonia or breast cancer.
Imaging techniques: CXR, US, CT, MRI
Examination of the pleural fluid, and pleural biopsy.Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
History
History of pain, dyspnea, or cough : due to pleurisy and significant amount of effusion.Symptoms (pain on inspiration and coughing) and signs of pleurisy (a pleural rub) often precede the development of an effusion.
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
On chest examination
Small effusion may be undetectable, but if 500 ml or more of fluid are present, abnormal clinical findings could be detected.What are the findings on chest exam?
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
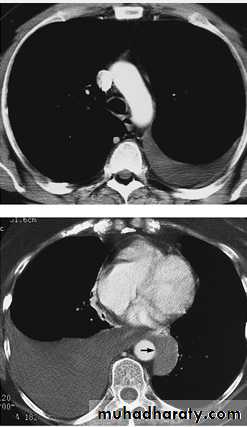
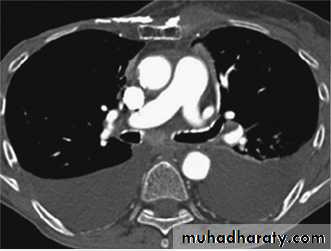
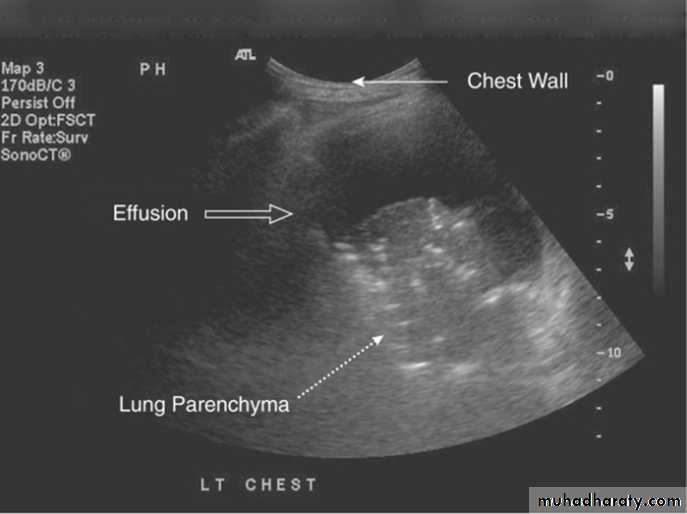
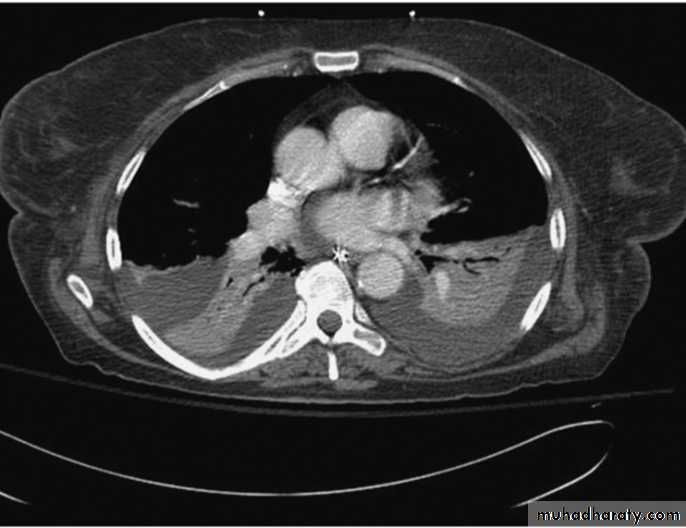
Radiology
Chest X-RayUltrasound (US) is able to demonstrate small effusions.
Computed tomography (CT).
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
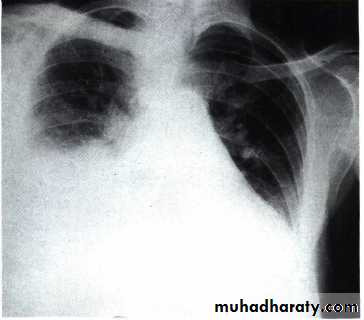
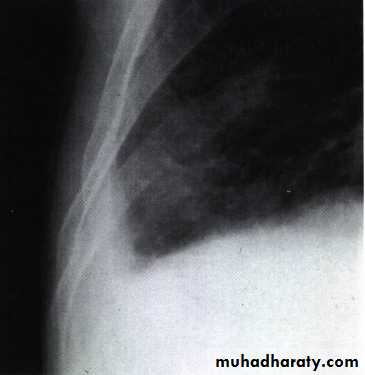
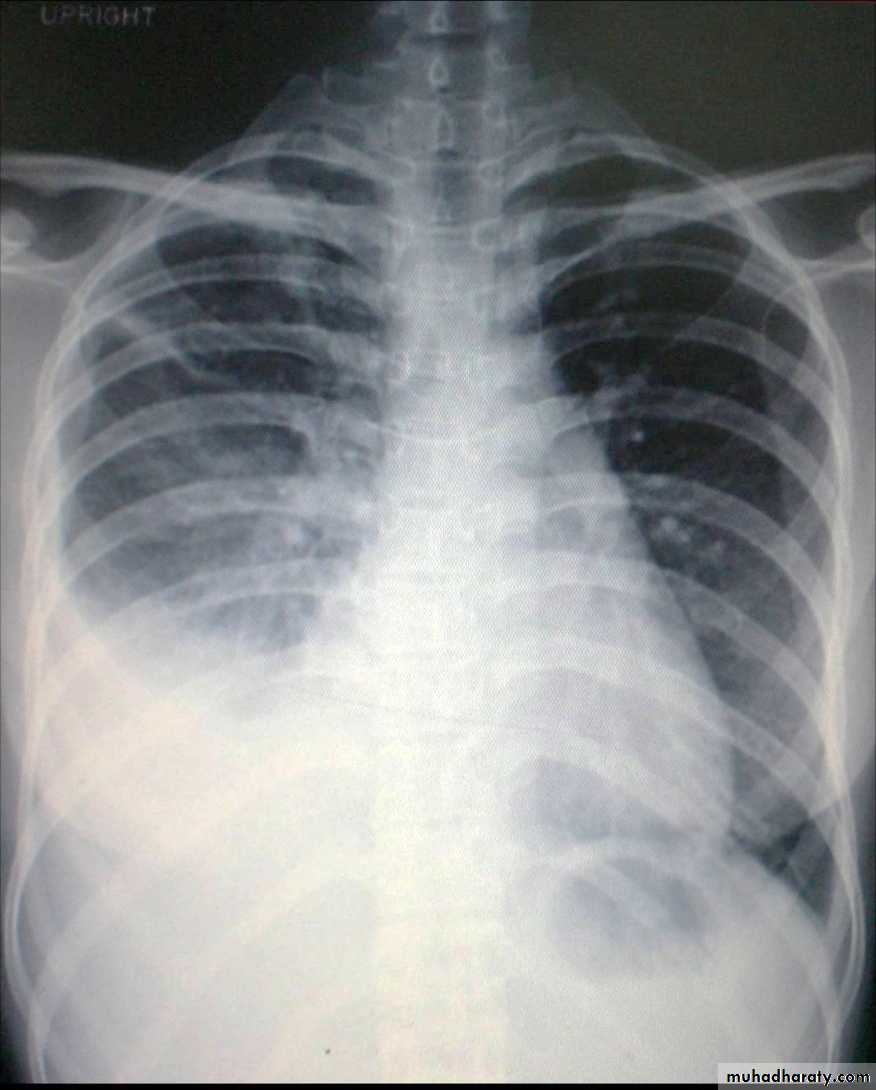
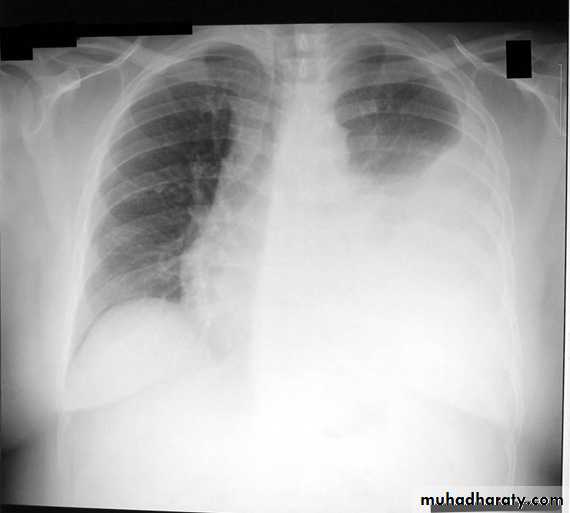
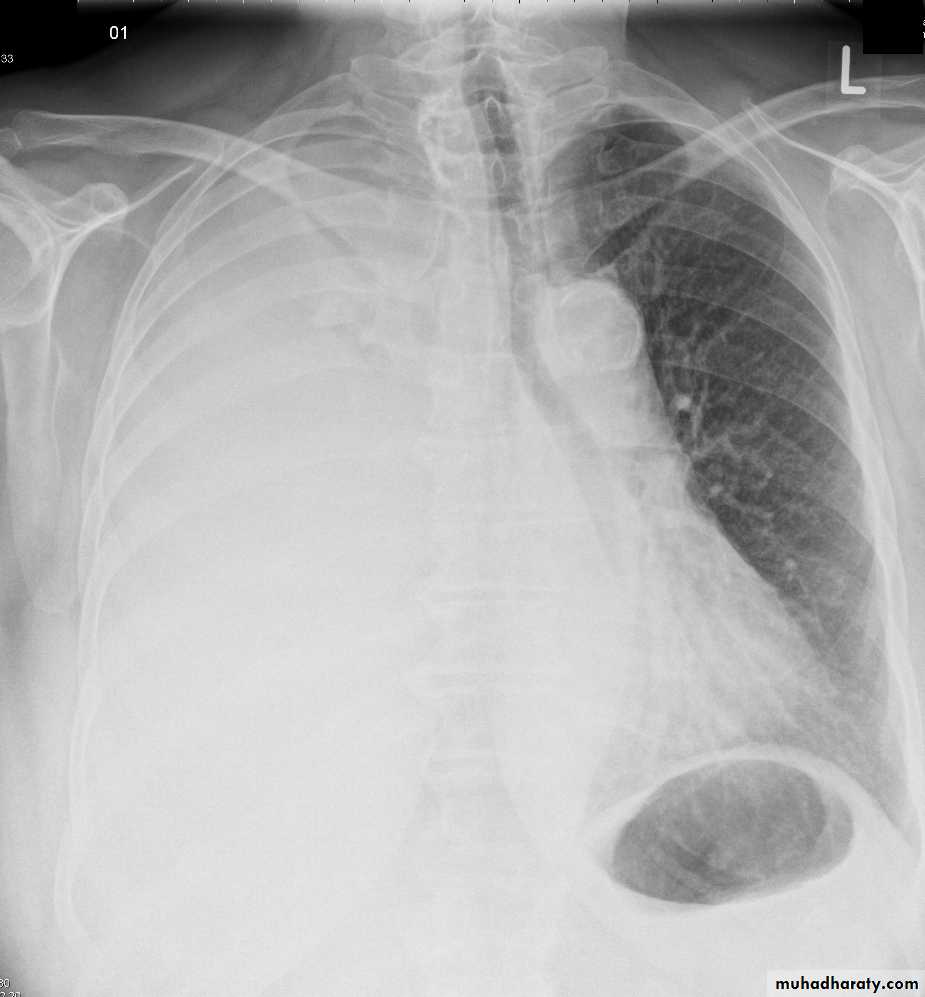
Chest X ray: The pleural fluid accumulates in the most dependent part of the thoracic cavity
The normally sharp posterior costophrenic angle is obliterated.
Upper surface is meniscus-shaped (meniscus sign).
Around 200 mL of fluid is required in order for it to be detectable
on a PA chest X-ray
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
The amount of pleural effusion may be small, large or massive.
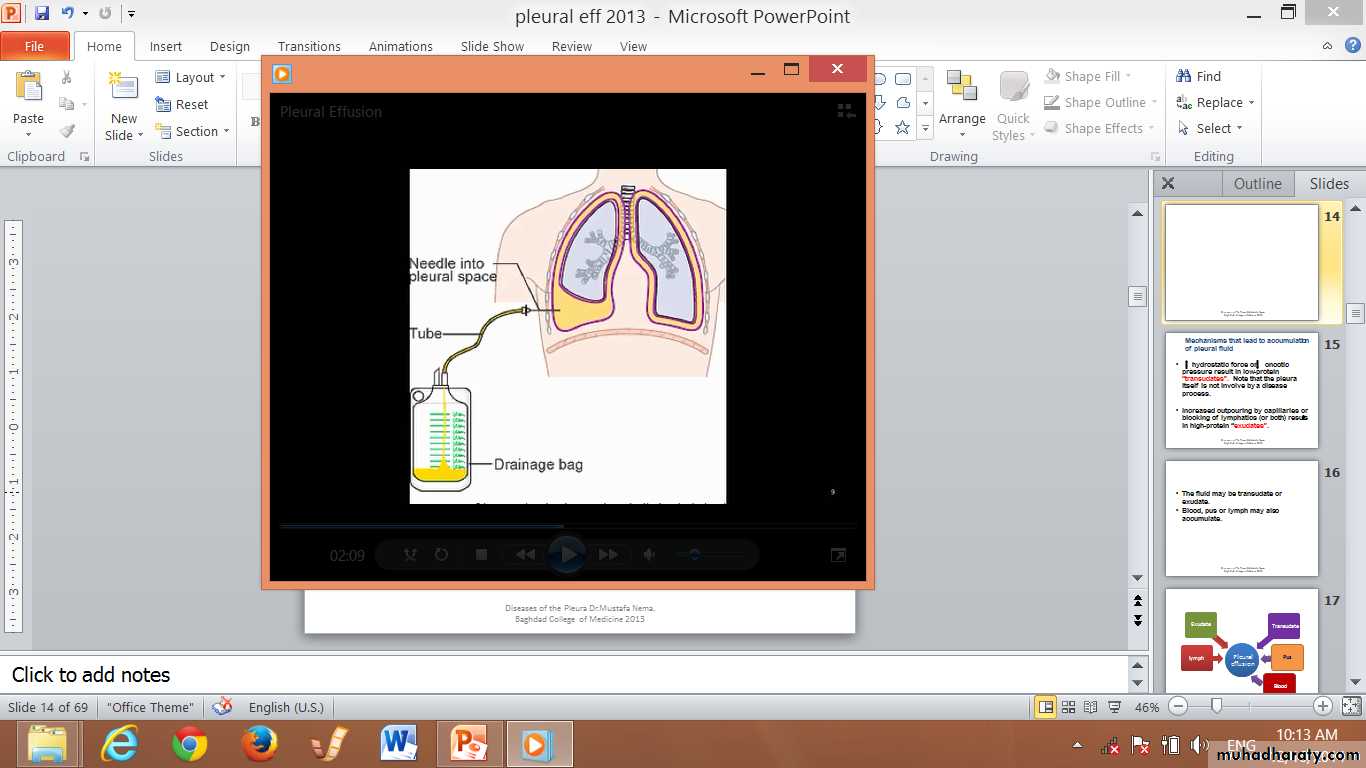
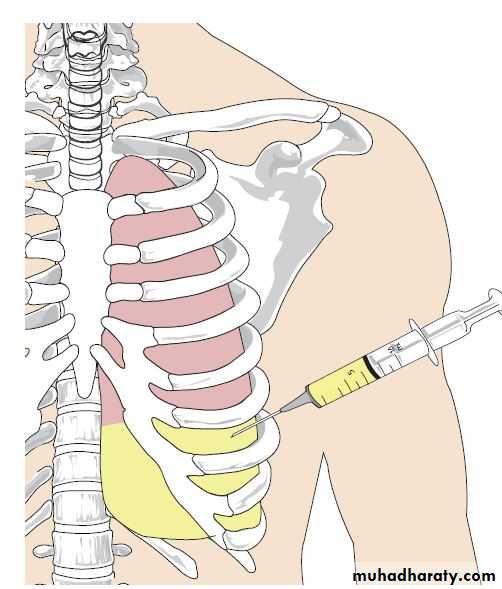
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013Thoracentesis
This mean taking a sample from the pleural effusion by a syringe.Thoracentesis is indicated in all cases of pleural effusion of unknown origin and in effusions that do not resolve after appropriate treatment.
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Thoracentesis(pleural fluid aspiration)
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
INVESTIGATIVE PARAMETERS OF PLEURAL EFFUSIONDiseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
The most important criteria are:
Appearance.Protein content.
Cellular components (cytology).
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Appearances of pleural effusion.Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Blood-stained• pulmonary infarction
or malignancy.
• High RBC count
Milky ( chylous)
• Thoracic duct obstruction
• High TG
Clear transudated
• low protein content
Light’s criteria for distinguishingpleural transudate from exudate
Exudate is likely if one or more of the following criteria are met:
• • Pleural fluid protein : serum protein ratio > 0.5
• • Pleural fluid LDH : serum LDH ratio > 0.6• • Pleural fluid LDH > two-thirds of the upper limit of normal serum LDH
(LDH = lactate dehydrogenase)
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013CORRELATION OF PLEURAL FLUID EXUDATE FINDINGS AND CAUSATIVE DISEASE
TestsDiseases
pH <7.2
Empyema, malignancy, esophageal rupture; rheumatoid, lupus, and tuberculous pleuritis
Glucose (<60 mg/dL)
Infection, rheumatoid pleurisy, tuberculous and lupus effusions, esophageal rupture
Amylase (>200 μg/dL)
Pancreatic disease, esophageal rupture, malignancy, ruptured ectopic pregnancy
Rheumatoid factor, antinuclear antibody
Collagen vascular disease
Complement (decreased)
Lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis
Red blood cells (>5000/μL)
Trauma, malignancy, pulmonary embolus
Chylous effusion (triglycerides >110 mg/dL)
Tuberculosis, violation of the thoracic duct (trauma, malignancy)
Biopsy (+)
Malignancy
Adenosine deaminase (>40 μg/L)
Tuberculosis
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Pleural fluid cells
• Cell count and Differential count e.g.:
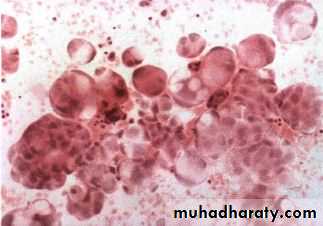
• CytologyI important for diagnosis of malignancyDiseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Malignant cells in pleural fuid aspirate ‘ Adenocarcinoma’
Pleural biopsyBiopsy procedures, such as closed needle biopsy or medical thoracoscopy/
pleuroscopy, may be necessary to confirm or
exclude malignant or tuberculous causes.
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
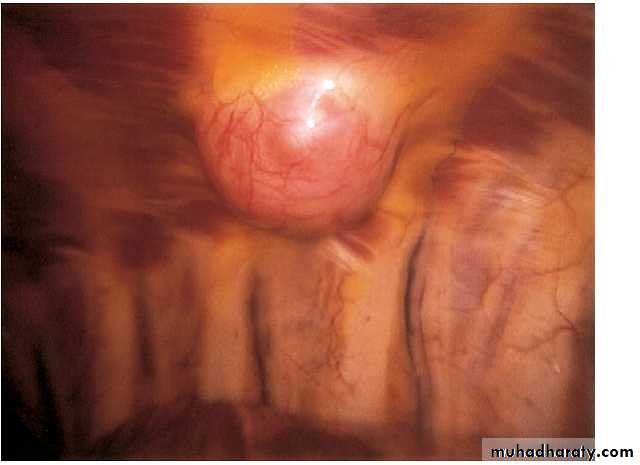
ThoracoscopyPleural mass
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
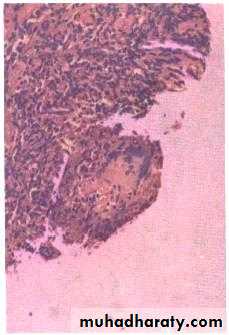
Pleural biopsy shows caseating granuloma of TBDiseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
May I be excused..My Brain is Full
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013TREATMENT OPTIONS
Drug therapy (e.g. antibiotic, anti TB )Therapeutic aspiration (using a proper gauged needle).
Therapeutic drainage ( using pleural catheter or chest tube).
Instillation of fibrenolytic agent (to prevent pleural adhesions in case of purulent disease)
Instillation of sclerosing agent (to prevent recurrent effusion e.g. in malignant effusion ).
Surgery (decortication)
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Case 1: A young man presented with fever and cough with primary diagnosis of lobar pneumonia. After 1 week, he developed dyspnea, right side chest pain. OE; decreased chest expansion on right side, dull percussion and decreased breath sound.
What is the possible diagnosis?
How can we reach the diagnosis?
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Pleural fluid analysis:Appearance: light yellow
Protein: 3.5 gm/dL. Serum protein 6gm/dL
Cell count &Cytology: high neutrophil count.
No malignant cell
Diagnosis: parapneumonic pleural effusion.
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013Case 2: A 17 year’s old female came to the hospital with 1 month history of fever, night sweating, left sided chest pain and increasing dyspnea. OE; you have found signs of pleural effusion on the left side of the chest.
What is the most likely diagnosis?
How can you reach the definitive diagnosis?
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Pleural fluid analysis:
Appearance: amber color
Protein: 3.3 gm/dL. Serum protein 6 gm/dL
Cell count/cytology: high WBC mainly lymphocytes. No malignant cells.
Pleural biopsy: caseating granuloma.
Diagnosis: TB pleura
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Case 3: A 67 year’s old women with known breast cancer presented with progressive dyspnea over the last month with no cough and no fever. Examination revealed signs of pleural effusion on right side.
What is your first impression on diagnosis?
How can you investigate for this effusion?
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Pleural fluid analysis:
Appearance: bloodyProtein: 3.6 gm/dL. Serum protein 6.5gm/dL
Cell count/cytology: malignant cells seen.
Diagnosis: malignant pleural effusion due to lung cancer metastasis
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
PleurisyPLEURISY
Pleurisy is not a diagnosis, but simply a term used to describe the result of any disease process involving the pleura and giving rise to pleuritic pain or evidence of pleural friction.Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Pleurisy is a common feature of pulmonary infection and infarction; it may also occur in malignancy.
Pleuretic chest pain is sharp localized chest pain usually in the lower chest or axillary region that aggravated by deep breath.
This pain is characteristic symptom.
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013On examination rib movement is restricted and a pleural rub may be present. This may only be heard in deep inspiration or near the pericardium (pleuro-pericardial rub).
The other clinical features depend upon the nature of the disease causing the pleurisy, e.g. bronchial breath in lobar consolidation.
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Loss of the pleural rub and diminution in the chest pain may indicate recovery or herald the development of a pleural effusion.
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
The primary cause of pleurisy must be treated.Symptomatic treatment of pleural pain , e.g. NSAIDs.
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
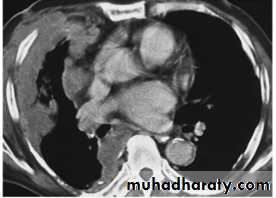
Plueral malignancyPrimary: Mesothelioma is a malignant tumour affecting the pleura (pleural mesothelioma) or, less commonly, the peritoneum (peritoneal mesothelioma) due to asbestos exposure. It has poor prognosis.
Secondary : metastasis involving the pleura with malignant effusion is more common cause than primary one.
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Malignant mesothelioma
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013Summary
Cardiac failure is the main cause of
pleural effusions.Of noncardiac causes, TB, parapneumonic effusions are commonest, followed by malignant pleural effusions.
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Small pleural effusions can be detected best by ultrasound (or CT).The most important laboratory parameter of pleural fluid is total protein, distinguishing trans- and exudates.
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Biopsy procedures may be necessary to confirm or exclude malignant or tuberculous causes.
Treatment depends upon the
underlying disease.
Diseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013
Thank youDiseases of the Pleura Dr.Mustafa Nema. Baghdad College of Medicine 2013